The structure of the formations, their size and type of contents vary, depending on the location and duration of the onset of the pathological process. They are true (inside lined with epithelial cells) and false (without lining). Based on the type of appearance, neoplasms are divided into:
- retention (usually formed due to a disruption in the process of outflow of secretions in tissues and organs, occurring in the mammary glands, uterus, cervix, ovary, etc.);
- ramolitic (usually found in the ovaries, brain and spinal cord, can form in areas of tissue necrosis, for example after a stroke);
- parasitic (appears in different organs, is the shell of the parasite);
- traumatic (due to bruises);
- dysontogenetic (usually congenital, include different tissues of the embryo);
- tumor (formed due to metabolic disorders, have cavities filled with physiological fluids).
Cysts in women and men: symptoms and treatment
In the initial stages of development, cystic elements do not have symptoms. When they grow and suppurate, they manifest themselves differently, depending on the etiology, location, composition of the contents and size. For example, when the ovary is damaged, women complain of a feeling of heaviness and compression of the lower abdomen, pain during menstruation, cycle disruption, etc. With kidney pathology, the lower back hurts and aches, it is difficult to empty the bladder, and jumps in blood pressure are noted.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic methods depend on the location of cystic formations. Most often this is an ultrasound, but MRI, CT, and radiography can also be prescribed. Laboratory tests are also carried out - blood and urine.
Surgery
The intervention tactics are determined by the doctor based on the location, size of the cystic formation and the patient’s complaints. The classic technique is scalpel excision of the tumor along with adjacent tissues. Today, such an operation is performed mainly laparoscopically using an endoscope. Laparoscopy of a cyst is less traumatic, the patient’s recovery lasts one day. You can also choose the method of aspiration (suction) of the contents with further cauterization of the capsule with a laser, liquid nitrogen, radio wave or a special drug for sclerosis of the walls. The removed lesion must be sent for histological examination.
Is surgery necessary?
When making such a diagnosis, many patients wonder whether the cyst needs to be removed. Some tumors, if they are small and do not bother the person, can remain under observation. Others, such as cervical cysts, can have consequences: bacteria accumulate in them, which sooner or later will lead to inflammation or suppuration. The need for removal should be discussed with your doctor.
Unconventional methods of combating cystic formations
If you are diagnosed with a tumor-like formation, do not worry - this is not a death sentence. As a rule, this deviation is amenable to conservative treatment methods, without the use of surgical manipulations. If medications do not produce results and the cysts do not stop growing, you should think about unconventional ways to combat the disease. Below are recipes that suppress the growth of tumor-like formations.
The main types of cystic formations
Ovarian
This is a fluid-filled bladder that causes the ovary to enlarge, leading to pain and sometimes infertility. The main reason for its appearance is hormonal imbalance. The disease often occurs without symptoms; when the formation is large, the cycle is disrupted, pain is felt in the lower abdomen, a false urge to urinate occurs, and bleeding occurs outside of menstruation. Methods of surgical treatment: oophorectomy (complete removal of the ovary), laparoscopic cystectomy (excision of the cyst), adenxectomy (surgery to remove the uterine appendages). In most cases, the choice is not classical surgery, but gentle endoscopic removal of the cyst while preserving the patient’s reproductive function.
Read more about ovarian cyst removal
Coccygeal
Most often occurs in men aged 15-30 years. It is an opening in the area of the gluteal fold, approximately 10 cm from the anus. Externally it looks like a fistula. It can be congenital or acquired - due to too much hair in this area. It manifests itself as pain when walking, sitting, redness of the tailbone, a feeling of discomfort and the presence of a foreign body in the area where it is located. At a later stage, pus is released from the hole.
Read more about the treatment of coccygeal cyst
Bartholin gland
Appears due to blockage of the gland duct due to infection or chronic inflammation. The formation has a capsule and is filled with secretion, which gradually gels. If it is large, it interferes with walking and sitting, makes intimate intimacy inaccessible, and can become infected and lead to an abscess. Usually reaches 2 cm, but there are formations up to 9 cm. The main causes are chronic bartholinitis, candidiasis, bacterial vaginosis, decreased local immunity.
Where and how to remove a Bartholin gland cyst
Eye
A hollow formation filled with non-inflammatory fluid - products of the activity of the cornea or conjunctiva. May originate from the cornea, iris, conjunctiva and other eye membranes. Causes: inflammation and trauma, congenital anomalies. The disease is manifested by pain, a feeling of fullness, blurred vision, and the presence of translucent dots in the field of vision.
Maxillary sinus
A cavity containing fluid and having a membrane attached to the wall (usually the lower) of the maxillary sinus. A cystic formation can be true (its walls consist of mucous membrane) or pseudocyst (the mucous membrane is split and fluid accumulates in it). It manifests itself as headache, difficulty breathing through the nose, a feeling of fullness and heaviness in the eye and cheek area, mucus discharge from the nose and its flow down the wall of the pharynx, discharge of yellow transparent fluid from the nose, frequent sinusitis with suppuration. It is formed due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the nose, blockage of the excretory duct of the glands of the maxillary sinus, inflammation of the teeth, spreading to the roots.
Read more about the treatment of abscesses and cysts of the ENT organs
Mammary gland
A cavity bounded by a capsule of connective tissue and filled with fluid is formed in the ducts and can be single or multiple. It is formed due to an increase in the duct of the mammary gland, the accumulation of secretions in it. The lesion may be round, oval, or irregular in shape. The disease is asymptomatic for a long time; over time, pain and burning appear in the mammary gland, and may be accompanied by suppuration and inflammation. One of the varieties is a fatty cystic formation that occurs when the sebaceous gland of the skin is blocked and filled with secretions. The main provoking factors are mastitis, thyroid disease, inflammation of the genital organs, and ovarian dysfunction.
Learn more about symptoms and treatments
Uterus and cervix
These are dilated and clogged glands, inside of which secretions (mucus) accumulate. The disease occurs against the background of endocervitis, cervitis. Provoking factors: abortion, childbirth, infections, menopause, hormonal imbalance, use of an intrauterine device, infections. Nabothian cystic formations are localized in the vaginal area of the uterus and are not removed until they reach a certain size. Retention occurs due to an excessive amount of secretion in the gland duct. The disease is often asymptomatic; its indirect signs are frequent inflammation.
Read more about surgical treatment of uterine and cervical cysts
Brain
A cystic formation is an accumulation of fluid in the substance or membranes of the brain. When large in size, it entails intracranial hypertension and puts pressure on the surrounding brain structures. Can form at any age. Depending on the location, cerebral (intracerebral) and arachnoid formations are distinguished. The first are found in the internal structures of the brain, in areas of necrosis. The second ones are in the meninges. Provoking factors: inflammatory diseases, trauma, including birth, cerebrovascular accident, parasites, complications after surgery. They manifest themselves as nausea, a feeling of pressure on the eyes, decreased performance, sleep disturbances, pulsation or noise in the head, and visual impairment.
Thyroid gland
Small formations (up to 5 mm) may not have pronounced symptoms. If the thyroid cyst has dense inclusions and a complicated structure, then special studies (for example, ultrasound), tests and biopsy are needed, because such a condition may be a sign of malignant degeneration.
Read more about surgical treatment of thyroid cysts
Larynx
Cysts of the larynx can be located in any part of the larynx. They do not grow into the mucous membrane, but grow towards the lumen of the larynx and thereby narrow it. The cause of retention cysts is blockage of the excretory ducts of the laryngeal glands. There are cysts of the vocal cords that arise due to constant irritation.
More information about surgical treatment of laryngeal cyst (laryngocele)
You can find out the prices for cyst removal endoscopically or by another method, as well as the cost of preoperative diagnostics on our website or by calling honey. +7 (812) 435 55 55.
Types of Ovarian Cysts and Treatments
There are functional and organic ovarian cysts. The former can be treated with medication, the latter can only be removed surgically.
Functional cysts:
- Follicular cyst
. This is a benign, single-chamber neoplasm filled with fluid, which can reach from 2 to 10 cm in diameter. - Luteal cyst (corpus luteum cyst)
. Similar to a follicular cyst in appearance and size.
Reasons for development:
hormonal disorders, serious stress, excessive physical activity, inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs
Danger:
cyst rupture, cyst pedicle torsion
Type of treatment:
observation for 3 menstrual cycles, conservative treatment with dydrogesterone drugs and oral contraceptives. Functional cysts completely disappear within 2–3 months if the gynecologist’s recommendations are followed. If the cysts do not shrink within 60 to 90 days, they are removed surgically.
Organic cysts:
Endometrioid cyst.
A single-chamber neoplasm filled with menstrual blood. The size can reach from 5 to 20 cm. They often grow on both sides and increase from one menstruation to the next.
Reasons for development:
ovarian endometriosis
Danger:
development of infertility, adhesions in the pelvic organs, risk of malignancy
Dermoid cyst.
A neoplasm up to 15 cm in size, filled with mucus, fat and other tissues.
Reasons for development:
disruptions in the regulation of embryonic cells
Danger:
inflammation of the cyst, which can result in peritonitis
Paraovarian cyst.
A single-chamber tumor with thin walls of a large size - 13–30 cm. It grows not in the ovary, but next to it from the ligaments between the ovaries and the uterus.
Reasons for development:
malfunction of the thyroid gland, severe overheating, frequent abortions, frequent inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs, incorrect use of hormonal drugs
Danger:
suppuration and rupture of the cyst capsule
Mucinous cyst.
Single- or multi-chambered formation, the contents of which are thick mucus. It can reach very large sizes - from 20 cm or more.
Reasons for development:
chronic inflammation of the ovaries, ovarian dysfunction, genetic predisposition, serious hormonal imbalances during menopause
Danger:
torsion of the cyst stalk and, as a consequence, tissue necrosis
Cystadenoma (serous cystadenoma, true cyst).
Benign 1-, 2- or 3-chamber formation with a diameter of up to 15 cm, filled with yellow liquid.
Reasons for development
: STDs, pathological changes in hormonal levels, heredity, early puberty
Danger
: ovarian rupture, disruption of nearby organs, relapses, malignancy
Organic cysts cannot be cured with hormonal drugs; they are removed endoscopically or laparoscopically. And the faster the operation is performed, the less damage the cyst will cause to the woman’s health. Very often they are the cause of infertility in women.
What is an ovarian cyst?
As a rule, the term “ovarian cyst” refers to a formation in the ovary that has a capsule and contents.
The fluid in the cyst can be very varied: very watery, or dense, viscous. Tumors of various origins and structures develop in the ovaries; in this regard, the ovaries occupy one of the first places among other human organs.
Figure 1. Diagram of an ovarian cyst
Leading specialists in the treatment of uterine cysts in the Southern Federal District
Ermolaeva Elvira Kadirovna is a well-known and recognized specialist in the North Caucasus in the treatment of cervical cysts, nabothian cysts. She is a gynecologist, ultrasound doctor, physiotherapist-resortologist. Elvira Kadirovna is approached by women who want to improve the aesthetics of the genital organs, reduce the size of the vagina and refresh intimate relationships from all regions of Russia and foreign countries.
Ermolaev Oleg Yurievich Candidate of Medical Sciences, operating gynecologist with 25 years of successful experience in treating cervical cysts. Able to see relationships that elude others.
Shchepkin Petr Sergeevich Gynecologist, specialist in the treatment of cervical cysts, nabothian cysts. Experienced ultrasound doctor.
About the doctors of the Clinic in detail...
| INTERNATIONAL RECOGNITION of the reputation and achievements of the Women's Health Resort Clinic in the development and implementation of effective and safe treatment methods and the quality of medical services provided is the AWARDING of the Women's Health Resort Clinic in Pyatigorsk with the SIQS International QUALITY CERTIFICATE in the field of medicine and healthcare. International Socratic Committee, Oxford, UK and Swiss Institute for Quality Standards, Zurich, SWITZERLAND. |
The resort clinic for women's health operates both for paid services and in the voluntary health insurance system.
We work seven days a week and on holidays:
Monday - Friday from 8.00 to 20.00, Saturday, Sunday, holidays from 8.00 to 17.00.
Treatment of cervical cysts by appointment by multi-channel phone 8 (800) 500-52-74 (toll-free within Russia), or +7, or [email protected]
| ONLINE information about the treatment of uterine cysts can be found at: [email protected] REGISTER ONLINE for treatment of cervical cysts here. SIGN UP online for uterine cyst removal here. Buy coursework by phone +7 (928) 022-05-32 or here. |
Make an appointment with a gynecologist
The spa clinic for women's health facilitates the accommodation and accommodation of women, women with children and couples during examination and treatment.
Read more about the living conditions and transfer from Mineralnye Vody airport and Pyatigorsk railway station in the article “Accommodation”.
If you need to book accommodation, please coordinate your arrival date no later than 7 days in advance.
We are at your FULL DISPOSAL if you have any doubts or wishes.
What studies are carried out for ovarian tumors
- Bimanual examination remains relevant even with the most modern equipment, as it allows one to obtain important information.
- Speculum examination provides access to the cervix for examination, allows you to take aspirate and examine the endometrium.
- Washing and puncture of the abdominal cavity for cytological examination.
- Ultrasound using vaginal and abdominal sensors.
- Nuclear MRI and computed tomography allow for precise layer-by-layer studies to identify the presence of metastases in the lymph nodes.
- Ultrasound and mammography - examination of the mammary glands.
- Study of the condition of the endometrium.
- Examination of the intestine for the presence of a tumor (irrigoscopy, rectromanoscopy).
- Examination of the gastrointestinal tract, since the appearance of a metastatic tumor in the pancreas, intestines, and stomach is possible.
- Tumor markers. Increase in tumor marker CA-125 - more than 35 units. indicates an increased risk of developing an oncological process. But this statement is not always true, since there are cases where a significant excess of the tumor marker norm in endometrial ovarian cysts and endometriosis is not related to oncology.
- Carrying out laparoscopy
Symptoms
When a leg bone cyst forms and begins to grow, there are no symptoms. They appear when the formation reaches a sufficiently large size. In children, an absolutely asymptomatic course is sometimes observed, and the neoplasm spontaneously disappears with the end of the formation of the skeleton.
But the cyst can also be characterized by aggressive growth, in which case clinical manifestations arise, the localization of which depends on the location of the cavity. Cysts of the foot bones are characterized by the following manifestations:
· pain that tends to occur and intensify when walking, running, jumping and other activities;
· dense swelling in the area of the heel, ankle joint, metatarsus, which can be felt;
· transient lameness;
· discomfort when wearing tight shoes and high heels.
A cyst of the talus of the ankle joint can provoke pain and other symptoms in the heel and bones of the middle third of the foot, since it is closely related to them.
Often the first sign of bone cyst formation is a pathological fracture. This is accompanied by swelling of the foot, heel, and severe limitation of mobility, including due to pain when applying a load, which occurs while maintaining a normal range of motion in the ankle joint.
A fracture of the talus, which forms the ankle, is especially dangerous, due to its specific structure. This bone has an intensive blood supply, and at the time of a pathological fracture, its acute disruption occurs. This is fraught with the development of avascular necrosis and even disability.
Uncomplicated fractures of the metatarsal bones resulting from the formation of a cyst usually heal without consequences. In this case, closure of the cystic cavity is observed. This is especially true for children.
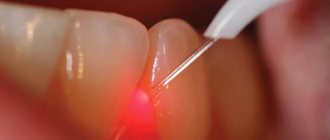
What complications does a dental cyst lead to?
Untimely treatment or removal will lead to the following complications:
- Periostitis.
- Swelling.
- Abscess.
- Phlegmon.
- Temperature increase.
Usually the cyst does not make itself felt in any way, so complications may appear unexpectedly. To exclude serious consequences, you need to be examined by a dentist at least once every six months. The appearance of a capsule with pus can occur against the background of deep caries or severe inflammation of the gums, so do not delay a visit to a specialist.
The lack of results with conservative treatment leads to the fact that the cyst has to be removed along with the tooth.
What do normal ovaries look like during ultrasound examination?
Normally, during an ultrasound examination, both ovaries are almost the same size:
- length – 30-41 mm;
- width – 20-31 mm;
- thickness – 14-22 mm;
- volume - about 12 cubic ml.
Due to the maturing follicles, the surface of the organ looks bumpy. Since the ovary is well supplied with blood, its tissues contain many blood vessels.
Typically, at least 12 cells mature in two ovaries. Among them stands out a dominant follicle measuring 10-22 mm, from which an egg will be released in the middle of the cycle. If ovulation has already passed, the corpus luteum is visible inside the ovary, secreting hormones necessary for implantation and development of the embryo. If conception does not occur, the corpus luteum dissolves.
Diagnostics
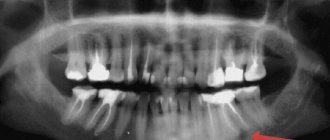
The main method for diagnosing bone cysts is x-ray. The images are taken in 2 projections, and the detected changes correspond to benign tumor-like formations. Cystic cavities are visualized as round-shaped neoplasms less than 5-6 cm in size and delimited from healthy tissue. The cortical layer is thinned, and there is no periosteal reaction. Aneurysmal cysts usually have the appearance of “soap bubbles,” while solitary cysts are always single-chamber.
It is important to differentiate a cyst from other tumors and diseases of the bones of the feet, since the effectiveness of treatment directly depends on this. Therefore, ultrasound, CT and MRI may be additionally prescribed.
Symptoms
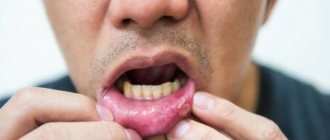
Most epithelial cysts are small in size, so they do not particularly bother patients. Some epithelial cysts can often be recognized with a simple examination. When located superficially, such a cyst presents:
- rounded formation;
- clearly demarcated;
- ranging in size from a millimeter to several centimeters;
- movable;
- dense elastic consistency;
- painless;
- without changes to the skin above it.
If the cyst is located in the area of the floor of the oral cavity, the patient sometimes has noticeable swelling in the sublingual or submental areas.
Redness of the skin or mucous membrane over the cyst indicates a complication - inflammation or the formation of an abscess. Thus, a coccygeal cyst often manifests itself only when it is inflamed by the appearance of pain in the coccyx or sacrum, anal itching, and pus discharge.
Is treatment necessary?
The doctor decides what to do with the identified cyst. It depends on its size, contents, patient complaints:
- Small formations, if they do not bother you, there is no rapid growth and no risk of degeneration into oncology, just observe.
- If the formation is large, causes pain, impairs the functioning of the organ in which it is located, grows quickly, festers or has signs of malignancy, it is removed. After surgery, the tissue is sent to a histology laboratory for examination.
Classic surgery is an open intervention with removal of the cyst using a scalpel. If possible, preference is given to gentle options - using endoscopic techniques, small incisions, and a short rehabilitation period.
The formation is removed using instruments inserted through incisions in the skin, or aspirated with a vacuum device. To avoid relapse, in the latter case it is necessary to cauterize the walls of the cyst. This can be done with a laser, injecting a sclerosant, treating the capsule with radio waves or cold (cryotherapy with liquid nitrogen).