The formation of a primary occlusion is a multi-stage process, which is characterized by a number of features that can largely affect the further development of a person’s dentition. It is during this period that the fundamental basis of the dentofacial apparatus is formed.
Primary occlusion is characterized by gradual teething, and it is sequential in nature - teeth erupt one after another. The characteristics of primary teeth differ from those of permanent teeth.
There are two stages of primary occlusion:
- emerging: the period from the appearance of the first tooth, usually between the ages of 6 months and 3 children. Characterized by active eruption and growth of baby teeth. It is at this stage that it is recommended to make the first visit to the dentist and orthodontist - at the age of 2-3 years;
- formed: characterized by the presence of all teeth and active growth of the jaws.
Development of primary occlusion
The primary occlusion is one of the most important periods in the formation of the dentofacial system. The fact is that even the slightest deviation that occurs at this time can lead to the development of serious violations in the future.
To assess the correct development of the primary occlusion, the following characteristics are used:
- timing of eruption: normally, the first milk tooth erupts at 6 months, and the last at 30 months. The norm is also a deviation of 3-5 months. Violation of eruption juices is the main sign of the presence of anomalies in the development of the dentofacial apparatus;
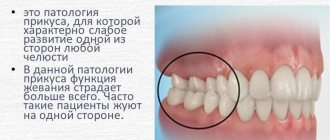
- pairing: during the period of primary occlusion, simultaneous eruption of antagonist teeth occurs on both sides of the jaw. Growth retardation of one of them for a period of no more than 1 month is the norm. A more significant violation of pairing may signal disturbances in the development of the jaw, for example, slow growth of bone tissue.
Consequences
What are the consequences of incorrect occlusion, and why is it important to correct a child’s bite in a timely manner? Proper closure of the dentition promotes high-quality chewing of food and evenly distributes muscle load (so that the temporomandibular joint does not suffer).
Correct closure depends on:
- straight posture;
- correct articulation;
- blood circulation of the brain;
- symmetrical facial features;
- gastrointestinal health.
Also, the health of the mucous membranes and soft tissues of the oral cavity depends on proper closure. With uneven chewing load, those parts of the periodontium that are most loaded suffer.
How is a milk bite different from a permanent bite?
Signs of a milk bite are:
- the length and radius of the upper tooth are usually greater than the same parameters for the lower tooth;
- the dentitions have a semicircular, symmetrical shape;
- the interdental space of the front teeth coincides on the upper and lower jaws;
- not all teeth of the same name touch each other;
- the enamel is intact and does not wear off;
- There is no overlap of the lower row of teeth with the upper ones.
As the dentofacial system develops, these signs become less pronounced and completely disappear by the period of permanent dentition.
The main difference between a temporary bite and a permanent one is the number of teeth. With a permanent bite, there are normally 32 of them, and with a milk bite there are only 20. The shape of the teeth also differs: temporary teeth have a more convex shape with a pronounced relief, while permanent teeth are smooth and flat.
What it is?
The period of formation of temporary teeth begins at the 20th week of pregnancy, when all the rudiments are formed in the fetus. The first baby teeth appear only 5 or 6 months after birth and continue to grow until about six years of age.
Concept
Temporary type occlusion represents the initial phase of the formation of permanent dentition. During this period, the foundational basis for the proper development of the dentofacial apparatus is laid.
The primary occlusion is characterized by the gradual sequential eruption of teeth, whose characteristics differ from permanent ones.
Stages
Temporary occlusion, from the moment the first tooth appears until the last one is fully formed, goes through two stages:
- Emerging .
It is counted from the appearance of the first specimen, which occurs at the age of about 6 months and continues until 3 years. During this interval, active eruption and growth of primary teeth occurs. Despite the fact that the bite is considered to be developing, with a 2-year-old child it is already recommended to visit the dentist, since after the appearance of the incisors, deviations in the development of the dentition or jaw arch can be identified and corrective treatment can be prescribed, which will quickly correct the situation. - Formed. This stage refers to the age period from 3 to 6 years. The period of formed occlusion is characterized by the presence of all temporary teeth and active growth of the jaws.
The tissues of the alveolar ridge begin to prepare for the growth of molars, the appearance of which means the development of a removable and then permanent dentition.When the temporary dentition is fully formed, its anomalies and deviations in the development of the jaw apparatus can be determined independently.
Our next review is devoted to the topic of possible complications of malocclusion.
In a separate article we will tell you how long a child should wear braces.
Here https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/okklyuzii/pravilnyiy-prikus-u-cheloveka-raznovidnosti-i-foto.html we will talk about what constitutes a correct bite of a person’s teeth.
How to prevent the development of anomalies?
Some parents mistakenly believe that deviations in the development of the jaws at the stage of primary occlusion are only temporary and do not need to be treated. This is wrong.
To prevent possible serious consequences that arise already during permanent occlusion, parents need to visit the dentist in a timely manner - the first visit should take place at the age of 2-3 years, if indicated, it is necessary to undergo an examination by an orthodontist.
It is also necessary to prevent the development of harmful orthodontic habits in a child: prohibit gnawing and sucking objects, intentionally swallowing incorrectly, breathing through the mouth with normal nasal breathing.
Causes of pathology
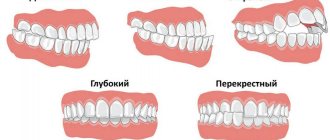
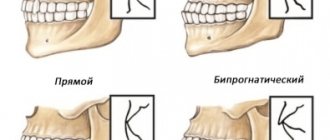
The most common occlusion defects are open or cross bite. Also common defects include a large distance between units, a sagittal gap. The reasons for the development of anomalies can be various factors. But more often, defects originate at the stage of intrauterine development of the baby. A genetic predisposition cannot be ruled out.
Pathologies in the development of the dental system can appear as a result of bad habits: prolonged pacifier sucking, thumb sucking in sleep.
Sometimes the shape of the pacifier and improper grip of the nipple by the lips of the newborn are directly related to the incorrect formation of occlusion. Timely diagnosis of the cause will allow you to find optimal methods for correcting the defect.
Possible reasons for the formation of a pathological bite:
- maxillofacial injuries;
- absence of a large number of molars;
- musculoskeletal disease;
- presence of bad habits;
- foreign objects in the baby's mouth;
- breathing through the mouth;
- infantile type of swallowing.
Malocclusion is also directly affected by untimely eruption of permanent molars.
First year: attention to congenital characteristics
Immediately after birth, the baby is examined by a neonatologist. This is necessary to detect possible developmental abnormalities, for example, defects of the palate, which occur approximately once in 2,500 children. Most birth defects need to be corrected surgically at an early age to avoid problems with health, nutrition and speech development.
At one month, the child should be shown to the dentist - by this time you may notice a shortening of the frenulum of the tongue. If the tongue is pulled too far towards the lower jaw, it will negatively affect the development of the bite.
A short frenulum is also a cause of difficulties with breastfeeding
Trimming the frenulum of the tongue is a very simple and quick procedure that is performed right at the appointment and does not cause any discomfort to the child.
Complications
If anomalies are not corrected, then not only the baby’s appearance suffers. The consequences of impaired occlusion are numerous somatic pathologies.
What does the anomaly affect:
- diseases of the digestive tract develop;
- widespread caries;
- formation of dental plaque;
- inflammatory processes in the oral cavity;
- poor posture;
- respiratory disorders;
- disruption of the process of chewing food;
- previous tooth loss.
The baby develops articulation disorders, and the pronunciation of sounds suffers.
Pediatric doctor vs. Adult doctor
I would also like to dispel the incorrect belief that a child can also be treated by an adult doctor. So, there is a clear distinction between doctors for children and adults. These are different departments at universities. Other approaches, and as for dentistry, other materials for filling and dental treatment. These materials are simply not available in adult dentistry. And materials for adults can harm a child’s body. As I mentioned above, there is a difference in the structure of a child’s and an adult’s tooth, this must be known and taken into account. A child is physically smaller than an adult - accordingly, the tools, at least turbine tips, should be somewhat smaller than usual. A pediatrician must have not only an appropriate certificate, but also extensive experience in communicating with young patients. A child is often afraid of the strict environment of an adult medical facility, while modern dental clinics aimed not only at adults are equipped with screens with cartoons, pleasant design, and most importantly, gentle, patient doctors.
Correction methods
Early identification of the problem and timely correction is the path to successful correction of occlusion. The correction technique is selected individually.
Correction methods:
- special gymnastics;
- removable plates;
- aligners, aligners;
- braces;
- trainers;
- surgical correction.
With the help of special gymnastics, minor occlusion defects can be leveled. The child also breaks the habit of bad habits that led to improper closure: thumb sucking, addiction to a pacifier.
Removable plates are installed for children under 14 years of age. These are special orthodontic devices made of polymer materials that are attached to the teeth using hooks. The purpose of the plate is to form the jaw. If a child has a naturally narrow jaw, the plate stimulates its growth. If the jaw is wide, the plate prevents it from expanding even more.
Aligners are custom orthodontic appliances made from an impression of the patient's jaw. Modern aligners can also be worn by adult patients; they are a successful alternative to braces. If mouth guards are prescribed to children, parents should constantly monitor them. Children do not realize the importance of the issue and may secretly remove the aligners.
Braces are prescribed only to children over 14 years of age, as well as adults. This is an effective way to correct occlusion, but is quite inconvenient. Caring for your mouth while wearing braces is difficult. The method also causes pain at the initial stage of addiction.
Trainers correct occlusion and also correct other defects of the dental system. First, the patient wears soft silicone trainers, then puts on a more rigid structure.
Surgical intervention is prescribed for severe anomalies when hardware methods do not produce results. This happens in rare cases.