HIV is an infection that stands for human immunodeficiency virus. This is a virus that affects the immune system, and the cells that protect the body from infections die. The human body stops fighting external infections, bacteria and viruses. The virus lives exclusively inside the human body. The human immunodeficiency virus dies only at high temperatures above 56 degrees. That is, sterilization of instruments completely kills the infection.
What is HIV infection and AIDS
HIV infection is a disease caused by one of the representatives of the group of retroviruses, causing the gradual development of immunodeficiency.
A characteristic feature of the disease is slowly progressive damage to the immune system, AIDS - human immunodeficiency syndrome, up to the development of the terminal (fatal) stage. The human immunodeficiency virus was first isolated in 1983. Since then, the disease has claimed about 32 million lives [2]. According to WHO, HIV is a major global public health problem. This virus is widespread, so many dental specialists may encounter its manifestations when examining the oral cavity of patients carrying HIV. For example, according to 2022 data, over 1 million people live in Russia with only a laboratory-diagnosed diagnosis [3].
The disease is characterized by extensive damage to the immune system. At the same time, the body’s defense against infections and certain types of cancer is significantly weakened, which manifests itself in autoimmune reactions, immune pathologies and metabolic disorders that lead to damage to blood vessels and connective tissue.
ROOTT dental implants are the best choice for patients with HIV
ROOTT implant structures are made of biocompatible titanium with an antimicrobial surface. When the package is opened, titanium reacts with oxygen and a hydroxyapatite film is formed on the surface of the implant. Hydroxyapatite is an element that makes up bone tissue. This increases the chance that the jawbone will not reject the titanium root. The polished surface prevents the accumulation of bacterial plaque in the cervical area, which minimizes the risk of peri-implantitis.
Transmission of infection and its development
The source of infection is a person in whose body the immunodeficiency virus is present. The virus is transmitted through biological fluids (blood, semen, vaginal secretions, breast milk). There are several routes of transmission: sexual, from mother to child and parenteral (during medical interventions, for example, during operations, blood transfusions, organ transplants and others).
In the early stages, HIV infection is asymptomatic or similar to other diseases. Later, due to weakened immunity, it is joined by multiple secondary infections, which the body of healthy people can usually resist. These are sore throat, pneumonia, candidiasis, herpes virus infection, stomatitis and other diseases that often accompany HIV. Cardiovascular, neurological, endocrine and osteoarticular pathologies gradually develop.
The final stage of infection is acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). If left untreated, the syndrome develops on average within 2–15 years. AIDS is characterized by multiple severe infections and cancers that affect all organ systems. These are, for example, lymphomas, Kaposi's sarcoma, tuberculosis, meningitis and other diseases.
It is currently impossible to cure HIV infection. However, so-called antiretroviral therapy makes it possible to curb the development of the disease, significantly improving the quality and increasing the life expectancy of patients.
Manifestations of HIV in the oral cavity
In the initial stages of the disease, its manifestations are very diverse due to the symptoms of multiple infections. Among the first signs of the development of HIV are lesions in the oral cavity. The suppression of immunity that accompanies the development of infection contributes to the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms, as well as weakening the control of tumor growth. This leads to the development of various forms of candidiasis, hairy leukoplakia, periodontal diseases and some neoplasms (Kaposi's sarcoma and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma).
Oral candidiasis in HIV . This disease is one of the first and very common signs, which occurs in 75% of patients with late stages of HIV infection and AIDS [4]. Patients may complain of dry mouth , burning sensation, and a feeling of tightness on the mucous membrane of the lips. Diphtheria (pseudomembranous) candidiasis can affect any area of the oral mucosa. Moreover, if in healthy people it occurs in an acute form, then with HIV infection it can persist for months. The disease manifests itself in the form of a white or yellowish coating, under which red or bleeding spots are hidden.
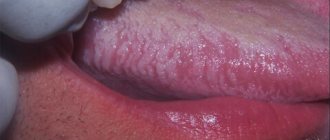
Hairy leukoplakia is associated with the Epstein-Barr virus. This disease develops on the lateral surfaces, back and root of the tongue. It appears in the form of growths resembling hairs. On the mucous membrane of the cheeks, the lesion takes on a flat shape. Experts believe that hairy leukoplakia is an important sign of immunodeficiency and serves as confirmation that the patient may develop AIDS.
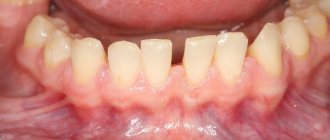
Gingivitis and periodontitis are another group of diseases that often occur in patients with HIV infection. Despite the fact that these pathologies also develop in healthy people, with concomitant HIV infection they often acquire an intense and atypical course.
For example, gingivitis in such patients develops even if the rules of oral hygiene are observed, occurs with relapses, and there may be no positive dynamics in response to treatment.
Periodontitis can also develop rapidly. It is characterized by rapid loss of bone tissue, the formation of pockets between the gum and tooth, and loosening of teeth. The effectiveness of traditional treatment methods is also reduced.
Kaposi's sarcoma develops mainly in the later stages of HIV infection. Therefore, its symptoms are characteristic signs of AIDS in the oral cavity. With the spread of antiretroviral therapy, the number of cases of this pathology has decreased.
The development of Kaposi's sarcoma is associated with infection of the patient with one of the types of herpes virus. Most often the skin is affected, then the mucous membrane of the mouth. At the same time, dark red or burgundy spots appear on the gums and hard palate.
Vacuum of knowledge
However, this issue is regulated by written rules. Thus, the Decree of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated May 18, 2010 N 58 (as amended on June 10, 2016) “On approval of SanPiN 2.1.3.2630-10 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for organizations engaged in medical activities”” indicates that dental handpieces must be sterilized after each patient.
This is also evidenced by modern instructions on the correct and safe processing of dental handpieces. The Kemerovo correspondent for AIDS.CENTER conducted a small experiment: she specifically walked through the city’s dental offices to check how these documents work. It turned out that there was no way. When a woman sat down in a chair and asked uncomfortable questions, the answer, as a rule, in most places was the already familiar “We treated it,” which in practice often meant: they wiped the top twice with a cotton swab containing chloramine.
However, there is no need to panic. Professor of the Department of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology of the Moscow State Medical University named after A. I. Evdokimov Irina Shestakova answers a question on our site that it is quite difficult to really assess the likelihood of such an infection. And the risk is not as great as it might seem at first glance.
Symptoms of HIV infection in the oral cavity and diagnosis
Manifestations and lesions of the oral cavity due to HIV infection and AIDS are diverse and nonspecific, so it is often difficult for a dentist to diagnose them. In addition, in the early stages of the disease it can be asymptomatic or disguised as other infections. However, during the examination, the dentist should pay attention to atypical lesions or formations in the mouth, which may indirectly indicate HIV: ulcers, tumors, spots, erosions and others.
The diagnosis of HIV infection is established by an infectious disease doctor through a comprehensive assessment of epidemiological data, the results of a clinical examination and laboratory tests
“HIV infection in adults. Clinical recommendations" Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation
At the same time, during a preventive examination, the dentist can pay attention to possible signs of HIV. It can be:
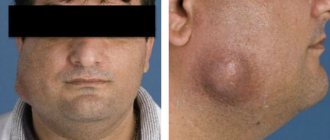
- enlargement of lymph nodes of different groups;
- rapid weight loss of the patient;
- protracted purulent-inflammatory diseases;
- atypical manifestations of candidiasis, gingivitis and other oral diseases [4]
When are dental implants installed?
Tooth loss can result from a variety of circumstances, including illness or neglect, accidents, or bad habits. The situation in which a person loses teeth is always associated with discomfort. Sometimes even more important than aesthetics is a purely functional issue.
Dental implants are installed:
- when a tooth is lost as a result of carious changes or trauma
- in people with undeveloped dental buds
- when some or all teeth are missing
Specifics of treatment of dental diseases
The success of treating oral lesions and dental diseases associated with HIV depends on making a timely and correct diagnosis. Therapeutic methods are more effective against the background of highly active antiretroviral therapy.
As a rule, specialists select medications with minimal side effects, and surgical interventions, for example, a tooth extraction , are carried out under the control of blood clotting. In this case, treatment should be as atraumatic as possible.
In addition, strict oral hygiene is recommended for HIV-infected people.
It is important for doctors to remember about prevention when examining the oral cavity of patients infected with HIV. The main danger is contact with the patient’s infected blood on the skin, mucous membranes of the eyes, mouth, and nose. When examining and manipulating the oral cavity of patients with HIV and AIDS, specialists are recommended to use double latex gloves, a protective screen, wear protective clothing made of non-woven material and observe other precautions.
List of sources
1. HIV infection in adults. Clinical recommendations. National Association of Specialists in the Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment of HIV Infection // Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. 2022. // URL: https://rushiv.ru/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/kr79.pdf (access date: 06/13/2020).
2. HIV/AIDS // WHO Information Bulletin. July 25, 2022 // URL: https://www.who.int/ru/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hiv-aids (access date: 06/13/2020).
3. Help. HIV infection in the Russian Federation as of April 30, 2020 // Federal Scientific and Methodological Center for the Prevention and Control of AIDS of the Central Research Institute of Epidemiology of Rospotrebnadzor. // URL: https://www.hivrussia.info/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/VICH-infektsiya-v-Rossijskoj-Federatsii-na-30.04.2020-g..pdf (date of access: 13.06. 2020).
4. Polyanskaya L.N. Features of manifestations of HIV infection in the oral cavity // Modern dentistry. 2022. No. 1 (66). // URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/osobennosti-proyavleniy-vich-infektsii-v-polosti-rta (date of access: 06.13.2020).
5. Petrov A. A. Providing dental care to HIV-infected patients // Bulletin of SMUS74. 2016. No. 4 (15). // URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/okazanie-stomatologicheskoy-pomoschi-vich-infitsirovannym-bolnym (date of access: 06/07/2020).
Where to place implants
The ROOTT clinic in Moscow is one of the few dental centers in Russia that specializes in one-stage implantation with immediate loading. Our implantologists have been working with the basal protocol for many years. The presence of HIV or AIDS in a patient is not a valid reason for refusing dental implantation. Our specialists will carefully study your medical history and offer the best option for restoring your dentition. Thanks to the ability to combine protocols in one system, treating patients with a complicated medical history is not a problem for us.