Inflammation of the part of the gums adjacent to the teeth is called gingivitis. Accompanied by bleeding gums, gingivitis is often confused with periodontitis, but in the latter case the disease leads to the destruction of bone tissue. Periodontitis is the result of neglected gingivitis.
Gingivitis happens:
- catarrhal;
- hypertrophic;
- ulcerative-neurotic.
Each of these forms has its own distinctive characteristics and methods of treatment.
Gingivitis in adults: causes of the disease
The disease, which affects all categories of people (children, adults, pregnant women), occurs primarily due to weakened immunity and poor oral hygiene.
The development of the inflammatory process occurs at a low speed, so the disease is often not noticeable for a long time to an ordinary person who is far from dentistry. However, if you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, serious complications may develop, which can lead to a more painful course of the disease and lengthy treatment.
There are three stages of development of gingivitis:
- mild (the disease affects only the spaces between the teeth);
- medium (the disease affects the edge of the gum);
- heavy.
The more time passes without treatment, the further the lesion spreads, eventually covering the oral mucosa.
The causes of the disease are divided into internal and external.
External ones include:
- injuries;
- burns of the oral cavity;
- influence of radiation;
- effects of heavy metals on the human body.
The internal reasons are as follows:
- development of molars (often during their growth, soft tissues are injured, which causes bleeding);
- lack of vitamins and minerals in the diet, which leads to decreased immunity;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- various infections;
- neglected carious formations.
What oral diseases, besides caries, can lead to tooth loss?
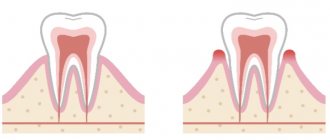
In addition to caries, periodontal diseases - gingivitis and periodontitis - can lead to serious consequences, including tooth loss. The main symptom of these oral diseases is the inflammatory process of the tissues surrounding the tooth. Usually, at the very beginning, the symptoms of the disease are not pronounced and appear only when the inflammation is already at the stage at which it is almost impossible to stop. That is why diseases of the gums and other periodontal tissues are much more likely than caries to lead to tooth loss.
Symptoms of gingivitis in adults
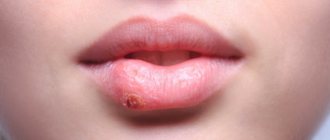
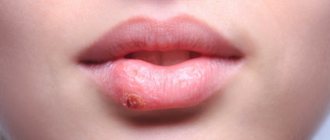
The onset of the disease is indicated by a feeling of discomfort that occurs in the oral cavity. The affected area turns red and may increase in volume. While brushing your teeth and eating solid foods, some bleeding is allowed, but there is no pain at this stage yet. Increased salivation may occur.
Gradually, the inflamed gum begins to lag behind the tooth, and food debris accumulates in the resulting gap, which leads to the formation of an unpleasant odor. If treatment is ignored, the resulting pocket may develop tooth decay.
At this stage, pain begins to appear, which intensifies while eating (especially when eating hot or cold food). Often inflammation can be accompanied by increased body temperature, a feeling of weakness, and increased irritability.
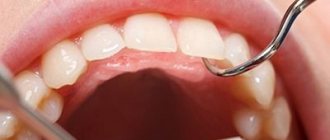
During the examination, accumulated plaque or caries is clearly visible in the area of inflammation. Blood may be released during a dental examination.
If the disease has become chronic, then the above symptoms may not be so clearly expressed, but it is impossible not to notice hypertrophied soft tissues.
Gingivitis
With gingivitis, inflammation occurs both localized (in the area of a specific tooth) and generalized (in the area of several or all teeth).
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, gingivitis can be dealt with fairly quickly. This is the mildest form of gum disease, which does not affect dental tissue and does not destroy teeth.
Gingivitis can also appear due to damage from:
- incorrectly installed fillings (if there is an overhanging edge);
- incorrectly installed dentures;
- from blows;
- burns;
- general somatic diseases.
Periodontists recommend that patients undergoing orthodontic treatment pay special attention to oral hygiene. Fixed structures make daily necessary maintenance significantly more difficult.
If the destructive influence of bacteria is not stopped, the inflammatory process will begin to spread and more obvious symptoms will appear:
- redness;
- swelling (swelling) of the gums;
- sensitivity to cold and hot;
- pain when chewing.
Gingivitis can smoothly progress into the destructive form of periodontal disease - periodontitis.
Catarrhal gingivitis: symptoms and treatment
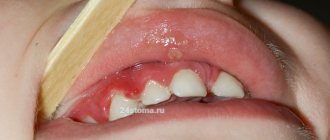
The main reason for its development lies in poor hygiene. Plaque accumulates on the surface of the teeth, including on their necks, which gradually hardens, turning into stone.
In addition to neglect of hygiene, catarrhal gingivitis can be caused by a lack of vitamin C in the body, hormonal imbalances and blood diseases. This form of the disease is the most common, occurring very often in women carrying a child.
The disease can be distinguished by the following symptoms:
- swelling of the gum edge, its redness or cyanosis;
- bleeding and pain during cleaning;
- plaque visible to the naked eye.
Catarrhal gingivitis can be:
- acute - this condition is characterized by the rapid development of symptoms;
- chronic, when the symptoms are mild, exacerbating only during periods of weakened immunity (for example, during a cold).
Catarrhal gingivitis: treatment in adults
Since the cause of gingivitis is plaque, the first step is to eliminate it. You can get rid of it by using a regular brush, but if the plaque has managed to mineralize and turn into stone, then you will have to spend time visiting the dentist.
Plaque mineralizes within less than 16 hours from the moment it forms: this is how tartar appears.
So, the main stages of treatment:
- Removing plaque and tartar. Ultrasonic cleaning has proven itself to be the best, after which it is imperative to undergo the procedure of polishing the teeth and treating the gums with gel. Typically, the total session duration is one hour. As practice shows, even after completing this stage of the treatment process, the patient feels much better.
- Anti-inflammatory therapy. Since catarrhal gingivitis affects only the surface of the gums, treatment can be carried out at home. It takes 10 days, then you will need to visit the doctor again for a follow-up examination. In most cases, anti-inflammatory gels are prescribed, which should be applied to the gums, rinses with Chlorhexidine, and a special toothpaste.
Description of anti-inflammatory therapy
For gingivitis treatment to be effective, it is recommended to treat the gums twice a day. Of the wide variety of gels, it is worth using “Cholisal Gel”, and using Chlorhexidine 0.05% as a rinse solution. The widely advertised Metrogyl Denta gel is slightly less effective.
The procedure is as follows: after waking up, routinely brushing your teeth (it is better to buy a Soft brush during treatment) and breakfast, you should thoroughly rinse your mouth with Chlorhexidine, then dry the surface of the gums with gauze and rub it with your finger. The gel should be applied both from the outside of the teeth and from the tongue. After treating your gums with gel, you should not drink or eat for at least half an hour. Some components of the product can cause salivation: saliva can be swallowed without fear, since it does not contain anything harmful to health.
It is necessary to clearly understand that curing gingivitis and then returning to your previous lifestyle means dooming yourself to the recurrence of symptoms in the near future. To prevent this from happening, prevention is important, which consists of properly brushing your teeth after every meal. Minimizing the risk of relapse is also influenced by the absence of caries, so carious cavities must be healed.
Drugs for the treatment of gingivitis
Treatment for gingivitis may involve the use of medications in different forms. Mouth rinses based on antiseptics allow you to solve two problems at once: mechanically remove food debris and bacterial plaque, and also deliver active ingredients to inflamed tissues. Dentists recommend using ready-made pharmaceutical products; in each specific case, a specialist will prescribe a medicinal solution to quickly alleviate the condition. Ready-made formulations are more convenient to use, and the concentration of active components in them is known, this distinguishes them from traditional methods.
The most popular are rinses based on the following antiseptics:
- chlorhexidine;
- furacillin;
- chlorophyllipt;
- Metronidazole.
Calendula, chamomile, yarrow, oak bark, and St. John's wort have antiseptic properties. Doctors do not recommend preparing alcohol infusions; it is better to choose decoctions. The recipes call for using one teaspoon of dry raw materials per glass of boiling water. It is important to cool the broth to a comfortable temperature. Take into account possible allergic reactions, give preference to those herbs to which there was no previous intolerance. It is necessary to discuss with your doctor the possibility of using traditional methods.
Effective drugs for the treatment of gingivitis are ointments and gels. Multicomponent local products for applications not only help relieve inflammation, but also have an analgesic, decongestant, and antipruritic effect. The active components of such drugs can be lidocaine, antibacterial, antifungal substances, and antiseptics. The doctor will select a gel or ointment taking into account the shape and type of gingivitis. Thus, for ulcerative inflammation, it may be advisable to use regenerating agents, and acute catarrhal gingivitis will require the use of a powerful anesthetic gel.
For hypertrophic gingivitis, surgery may be required - a simple gingivectomy. This operation involves excision of excess tissue and application of a bandage, and is performed under local anesthesia.
Necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis: symptoms and treatment in adults
The cause of the disease, as in the previous case, is non-compliance with hygiene, which has taken a critical form.
Due to the increase in plaque volume, gum necrosis develops. This often occurs against the background of decreased immunity or exacerbation of chronic diseases.
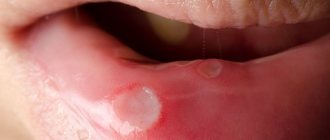
The first sign of ulcerative necrotic gingivitis is areas of ulceration on the gums and an increase in temperature to 39 degrees. Headaches and smell of rotting breath are possible.
This form of the disease should be treated by a dentist, and on an emergency basis. Dental plaque is removed along with the gray-greenish plaque, strong antibiotics are prescribed, then, when the inflammation subsides, gels are prescribed to accelerate the healing and restoration of the mucous membrane.
Types of gingivitis
Gingivitis can be acute or chronic. In the first case, noticeable symptoms occur. Chronic forms are characterized by mild symptoms, pain is absent or minimal. Periodic slight bleeding of the gums during brushing and halitosis may occur. It is important to understand that sluggish gingivitis is characterized by periodic exacerbations.
Inflammation of the gums is classified not only by its form, but also by the nature of its course.
Catarrhal gingivitis
Catarrhal gingivitis is characterized by redness of the gum area. Itching and bleeding due to mechanical action and mild pain may occur. This is the most common and easiest to treat type of inflammation. Quite often it acts as the initial stage of development of other forms.
Ulcerative gingivitis
Necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis is characterized by the formation of open ulcers, death of areas of gum tissue, and strong bad breath. One of the typical symptoms is the appearance of a grayish coating. The disease is more difficult to treat; in the absence of timely assistance, purulent foci and severe necrosis may appear.
Hypertrophic and atrophic gingivitis
Ulcerative-necrotic gingivitis is followed by hypertrophic gingivitis - excessive growth of tissues occurs that cover the crowns of the teeth. There is keratinization of areas of the gums.
The atrophic form of the disease, on the contrary, is characterized by a decrease in the level of the gums and exposure of the necks of the teeth. This condition is dangerous due to the loss of healthy teeth.
Desquamative gingivitis
This type of inflammation is characterized by abundant desquamation of the gum epithelium. Distinctive features are pronounced redness and noticeable peeling areas of the surface of the mucous membranes.
Hypertrophic gingivitis: symptoms, treatment methods
It is characterized by fibrous growth or an increase in the volume of the gums due to swelling. Occurs due to disturbances in the endocrine system, hormonal imbalances and malocclusion.
Treatment will depend on the form of the disease:
- the edematous form involves the use of sclerotherapy, that is, when a special solution consisting of glucose, calcium chloride and magnesium sulfate is injected into the gingival papillae. The procedure is carried out with anesthesia; at least 3 injections are required into each papilla with a break of 2 days.
- in the fibrotic form, deposits are removed and factors traumatic to the gums are eliminated, then anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed, including applying bandages with heparin ointment and other medications.
Gingivitis: Common Treatments in Adults
Regardless of the type of disease, there are general treatment methods:
- To diagnose the disease, the degree of contamination of the surface of the teeth is assessed. To determine the amount of plaque, special tinting compounds are used - the affected areas change color, which allows the doctor to accurately determine the extent of the problem;
- the patient is selected with the most suitable toothpaste and brush, and is also told about the need to adjust their diet (for example, if a person avoids solid food, this can lead to the accumulation of pathogenic microflora in the spaces between the teeth);
- Professional teeth cleaning is carried out using modern methods (usually ultrasound and further polishing of the cervical area are used);
- the affected tissues are treated with medications, and surgical intervention is used if necessary;
- When chronic diseases are detected, the patient is sent to specialists for further treatment.
Disease Prevention
The truth that our parents teach us from early childhood does not lose relevance in adulthood. If your gums are inflamed, and brushing your teeth begins to bring noticeable discomfort and pain, this is just a signal to visit the dentist. You still need to brush your teeth twice a day.
| First of all, you need to start by consulting a specialist. |
| Brush your teeth correctly, choose the right brush and toothpaste. |
During the consultation, the periodontist will not only select individually for your clinical case the necessary additional hygiene products (dental floss, rinses, brushes, irrigators) that inhibit the growth of bacteria. But it will also show you how to use them correctly, without injuring your gums.
| Proper nutrition |
One of the causes of gum disease is an unbalanced diet, lack of essential microelements and solid foods. Therefore, review your menu and include in it foods that contain the necessary substances, and also more often pay attention to solid foods - apples, carrots. Do not overuse starchy, sweet, spicy foods, as well as overly hot foods and drinks.
After cleaning, pay attention to the color and smell of the thread. Blood or a bad odor is a clear sign that there is an active infection in the gum pockets around the tooth.