Tonsillitis is an inflammation of areas of lymphoid tissue (tonsils) located on the back wall of the pharynx. They protect the body from the penetration of potentially dangerous viruses or bacteria, but in some cases they themselves can become infected. In many acute cases, the disease is viral in nature, so tonsillitis can be treated without the use of antibiotics. The chronic form of the disease is associated with the long-term existence of bacteria in the tonsil tissue. It requires complex therapy, and in some cases, surgical intervention. Tonsillitis most often affects children, but it can develop in people of any age.
Symptoms of tonsillitis
Signs of tonsillitis depend on its form and course. In the simple form, only local symptoms are observed. The toxic-allergic variant is accompanied by damage not only to the tonsils, but also to internal organs. Treatment of this form of chronic tonsillitis should begin as early as possible.
Possible symptoms of tonsillitis:
- sore throat, discomfort when swallowing, in young children food refusal is possible;
- signs of intoxication - fever, headache, weakness;
- redness, swelling of the tonsils, the appearance of white plaque or purulent plugs on them;
- hoarseness, cough, bad breath;
- abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting;
- enlargement and tenderness of the cervical lymph nodes;
- runny nose, red eyes, ear pain.
When the first symptoms of tonsillitis appear, you should consult a doctor, as this disease can become chronic or cause complications in the internal organs.
Treatment methods for chronic tonsillitis
It is very important to defeat chronic tonsillitis: otherwise, there remains a constant source of infection and intoxication of the entire body, not to mention the threat of severe autoimmune complications.
Home methods can reduce the severity of symptoms, but achieving a complete cure is difficult. Tonsillitis is a disease that is too complex in its nature and course. Therefore, if you suspect chronic tonsillitis, you should consult a doctor.
First of all, a comprehensive examination should be carried out to determine the pathogen and the stage of development of the disease.
Before treating tonsillitis, it is necessary to eliminate other sources of infection - cure carious teeth, inflammatory processes in the nose and paranasal sinuses. If your child often suffers from sore throats, then it is very likely that one of the family members is a carrier of the infection. In this case, it makes sense to get the whole family examined.
With complaints corresponding to the symptoms of chronic tonsillitis, you can contact a general practitioner (family doctor or therapist) or a specialized specialist - an otolaryngologist (ENT).
Children's appointments are conducted by qualified pediatricians and ENT doctors.
The Family Doctor clinics have the necessary equipment and a staff of qualified specialists to conduct examinations, establish diagnoses and perform all procedures in accordance with the prescribed course of treatment, and, if surgical treatment is required, to perform operations.
In the treatment of chronic tonsillitis the following are used:
Washing the lacunae of the tonsils
The course of treatment for chronic tonsillitis, as a rule, involves washing the lacunae of the tonsils using vacuum drainage. During rinsing, various anti-inflammatory drugs are used that penetrate deep into the tissue, destroying microorganisms that multiply in the tonsils.
Physiotherapy
In parallel with washing the tonsils, physiotherapeutic procedures (treatment with short-wave ultraviolet radiation, magnetic laser therapy, phonophoresis) can be prescribed.
More information about the treatment method
Antibacterial therapy
If chronic tonsillitis is caused by a bacterial infection, it is treated with antibiotics.
More information about the treatment method
Surgery
If the inflammatory process has gone far enough, surgical treatment methods are used. At JSC “Family Doctor” you can use the modern method of laser tonsillotomy. Laser tonsillotomy is a high-energy treatment of the palatine tonsils, in which only the affected part of the tonsils is removed. The tonsils themselves are preserved, if possible, which is very important for the immune system. In the most severe cases, the tonsils are completely removed.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
Causes
Tonsillitis is an infectious disease. It can be caused by various types of viruses:
- adenovirus, enterovirus, influenza and parainfluenza viruses;
- Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus infection;
- pathogens of measles, herpes simplex and others.
Bacterial tonsillitis is most often caused by streptococci. It can also be caused by staphylococci, gonococci, corynebacterium diphtheria, anaerobic flora, and spirochetes. Candida sore throat sometimes occurs in young children.
The development of the disease also involves factors that reduce the overall resistance of the body - hypothermia, malnutrition, prolonged emotional stress and others.
Treatment for tonsillitis depends on its causes. To determine the causative agent, timely consultation with a doctor is necessary.
Causes and complications
Tonsillitis occurs for many reasons, the main of which are bacteria and viruses that tend to infect the tonsils: Epstein-Barr virus, group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus, less often - pneumococcus, Staphylococcus aureus, herpes virus, etc. or mixed microflora. Factors contributing to the development of the disease:
- hypothermia due to a depressed immune system;
- avitaminosis;
- tonsil injury;
- chronic inflammation of the sinuses and oral cavity: sinusitis, caries, gingivitis, periodontitis;
- violation of nasal breathing;
- allergies.
Tonsillitis occurs in acute (angina) and chronic forms. The chronic form of the disease, in the absence of adequate treatment, can lead to serious complications from various systems and organs - joints, heart, blood vessels, kidneys, etc. This occurs due to an autoimmune reaction, which can be triggered by bacterial residues in the tonsils after acute tonsillitis that is not treated at home. The remaining bacteria support the inflammatory process, which becomes chronic. At the stage of decompensation of the disease, there is a threat of serious complications:
- paratonsillitis and paratonsillar abscess;
- systemic damage to blood vessels and connective tissues with the formation of rheumatic arthritis, etc.;
- glomerulonephritis;
- inflammatory processes in the myocardium, endocardium, which form heart defects;
- eye diseases with blurred vision;
- exacerbation of chronic pneumonia and other chronic diseases;
- complications on the liver and biliary system;
- hormonal imbalance;
- thyroid diseases.
Do not self-medicate to prevent the disease from becoming chronic and causing complications that are difficult to treat. Contact the ENT doctors of the Yauza Clinical Hospital if symptoms of acute tonsillitis appear.
Classification of tonsillitis
The disease can be acute or chronic. In the first case, signs of infection disappear within 7 to 10 days. In a chronic course, pathogens remain in the tissues of the tonsils, causing periodic exacerbations. Treatment of chronic tonsillitis is a complex task that only experienced otolaryngologists can handle.
Chronic tonsillitis has 2 forms - simple and toxic-allergic. In the latter case, there are 2 degrees of severity of pathological changes.
The simple form is characterized by only local symptoms. With the toxic-allergic variant, the following pathological processes occur:
- microbial toxins that enter the blood cause sensitization (altered reactivity) of the body;
- they act directly on the tissues of internal organs;
- toxins also lead to the development of allergic and autoimmune reactions.
To treat tonsillitis in this case, a complex effect on the entire body is necessary.
Conservative therapy
Depending on the diagnostic results, the doctor draws up an individual treatment plan. Acute tonsillitis is treated by a therapist on an outpatient basis using conservative methods, using antibacterial drugs in the form of tablets, rinsing, washing, and irrigation of tonsil lacunae.
Therapy of chronic tonsillitis is the responsibility of an otolaryngologist, who acts together with an immunologist.
A good result in the treatment of the disease is achieved by affecting the tonsils themselves. The hospital's otolaryngologists conduct courses of medical manipulations, during which:
- caseous plugs are removed;
- The folds of the tonsils (lacunae), which hide foci of infection, are cleaned.
During the treatment process - washing, lubricating and irrigating the tonsils with medicinal solutions, inflammation is stopped, the compensatory stage of the disease is prolonged, which makes it possible to delay or avoid tonsillectomy. Additionally, complex treatment at home is prescribed.
Acute form
Sore throat, or acute tonsillitis, begins suddenly with an increase in temperature and the appearance of signs of intoxication. It has several clinical forms:
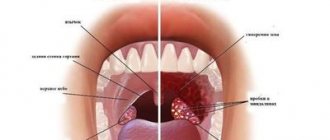
- catarrhal: redness and swelling of the tonsils, arches, soft palate;
- follicular: round or fuzzy white-yellow dots appear on the surface of the tonsils, caused by inflammation of the lymphoid follicles;
- lacunar: a light coating appears in the recesses of the tonsils, which covers their surface in the form of islands;
- fibrinous: purulent plaque lines the entire surface of the tonsils, an unpleasant odor appears from the patient’s mouth;
- phlegmonous: the formation of purulent foci (abscesses) inside the tonsil, which causes a sharp pain in the throat, the inability to move the head, and deterioration of the general condition.
The development of severe forms of the disease is usually associated with untimely or improper treatment of tonsillitis.
Prerequisites for the development of tonsillitis
The palatine tonsils, nasopharyngeal tonsil, lingual and tubal tonsils form a protective ring (lymphoepithelial ring of Pirogov) - a powerful barrier to the air and food entering the body. The tonsils do a great job - they recognize dangerous viruses and bacteria in the air and food and trigger an immune reaction.
When examining the tonsil on its surface, you can see depressions and openings with narrow, winding and deep passages (the so-called tonsil lacunae).
| 1 - crypt (lacuna); 2 - lymphoid follicles; 3 - connective tissue capsule; 4 - mouth of the lacuna (crypt). | |
The existence of deep lacunae creates the prerequisites for the development of chronic inflammation of the tonsils. Remains of food, dead immune cells, etc. settle in the gaps, which are an excellent breeding ground for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
Chronic form of tonsillitis
Chronic tonsillitis is characterized by repeated recurrence of tonsillitis. A long-lasting focus of infection forms in the palatine tonsils. This leads to a deterioration in the general condition:
- the patient experiences a constant or periodic increase in body temperature;
- the patient complains of fatigue, decreased mental and physical performance, sweating;
- Headaches, sleep and appetite disturbances are noted.
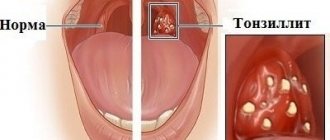
In the simple form of the disease, there is redness, enlargement of the tonsils and palatine arches, their fusion, and enlargement of the lymph nodes.
The toxic-allergic form is accompanied by damage to internal organs. In grade I, changes in the general condition, heart, joints, enlarged lymph nodes, and laboratory abnormalities are not constant. II degree of severity is accompanied by the following disorders:
- pain in the heart area, rapid heartbeat, heart rhythm disturbances, changes in the ECG;
- joint pain, which occurs not only during an exacerbation, but also during remission;
- prolonged increase in body temperature to subfebrile levels;
- changes in the functioning of the liver, kidneys and other organs, manifested by corresponding symptoms and changes in laboratory data.
Chronic tonsillitis is part of the pathogenesis of many other diseases - rheumatism, polyarthritis, glomerulonephritis, sepsis, pathology of connective tissue, endocrine, nervous, and digestive systems.
Surgery
If no conservative treatment methods lead to a lasting therapeutic effect, the doctor recommends surgical treatment: tonsillotomy or tonsillectomy.
The hospital practices both of these types of tonsil removal:
- tonsillotomy - partial removal of the tonsils in children aged 3-12 years while preserving the protective functions of the lymphoid tissue that make up the tonsils;
- Tonsillectomy - complete removal of the tonsils, is used when the tonsils are pathologically changed and are a source of chronic infection, or when complications arise from the organs, blood vessels, and joints of the body.
At the Yauza Clinical Hospital, all types of operations to remove tonsils are performed under anesthesia. In the process of tonsillectomy, a bipolar coagulator is used, which minimizes trauma to surrounding tissues and allows almost completely to avoid blood loss due to coagulation of the vessels feeding the tissue.
The Clinical Hospital on Yauza uses modern technology for tonsillectomy with suturing of the wound surface. The innovative tonsillectomy technique allows:
- minimize the risk of bleeding in the postoperative period;
- significantly speed up the postoperative healing period;
- reduce the rehabilitation period: hospital stay - up to a day; restoration of working capacity - after 7-10 days.
The cost of tonsillectomy is calculated for each patient separately and depends on the diagnostic examination, surgical method, and length of hospital stay.
At the Clinical Hospital on Yauza you are guaranteed:
- strict adherence to the treatment protocol;
- examination in a laboratory equipped with the latest advances in medical science;
- conservative treatment and tonsillectomy using the most effective technologies and using innovative equipment;
- stay in a comfortable room;
- constant supervision of experienced practitioners.
For any manifestations of tonsillitis, contact the Clinical Hospital on Yauza through the website by filling out the online appointment form.
You can see prices for services
Complications of tonsillitis
Tonsillitis, both acute and chronic, can cause local and general complications.
The first group includes damage to the tissues of the pharynx: paratonsillar abscess, parapharyngitis, laryngitis. Local complications also include acute otitis media and cervical lymphadenitis.
Common complications associated with damage to internal organs:
- diseases of the joints and connective tissue: rheumatism, rheumatoid arthritis, infectious polyarthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus;
- damage to the heart and mediastinum: myocarditis with the development of dilated cardiomyopathy and heart failure, mediastinitis;
- inflammation of the lungs, kidneys, appendix, sepsis and others.
To avoid the development of such complications, if there are symptoms of tonsillitis, it is necessary to carry out its full treatment.
Why is tonsillitis dangerous?
Chronic tonsillitis is very dangerous: if you do not consult a specialist in a timely manner and self-medicate, complications may develop, among which the most dangerous are diseases of the heart and blood vessels, and rheumatic joint damage.
Tonsillitis in adults often leads to damage to the kidneys ( tonsillorenal syndrome ) and heart ( tonsillocardiac syndrome ). This is due to the fact that infectious and toxic factors that damage internal organs enter the body from the palatine tonsils. Streptococcus, for example, secretes a toxin, the effects of which can cause myocardial dystrophy and heart disease or rheumatism . In addition, purulent contents entering the gastrointestinal tract from the lacunae of the tonsils can provoke dysbacteriosis.
Diagnostics
Recognition of acute or chronic forms of the disease is based on the following diagnostic data:
- enlargement and possible soreness of the submandibular and cervical lymph nodes;
- swelling, redness of the tonsils and arches, their inflammatory infiltration;
- discharge of purulent contents when pressing with a spatula on the surface of the tonsils.
To diagnose lesions of other organs, laboratory tests, ECG, radiography of the paranasal sinuses and other studies are used.
Causes, main risk factors
Up to 30 different colonies of pathogenic microbes can be sown on the surface of the tonsils of patients suffering from chronic tonsillitis. But in crypts and lacunae staphylo- or streptococcus is usually determined. A key role in the pathogenesis of chronic tonsillitis is played by beta-hemolytic strains of streptococcus (type A). Other flora - gram-negative coccal, fungal, viral - have an impact on local immunity, they support inflammation.
There are a number of factors contributing to the occurrence of the disease:
- hypothermia;
- decreased immunity;
- microtrauma of the tonsils;
- foci of inflammation in the mouth and in the head area (caries, sinusitis, adenoids, etc.);
- smoking;
- poor nutrition;
- allergy.
Viruses and bacteria that cause tonsillitis can come from the external environment.
Types of treatment for tonsillitis
Treatment of acute tonsillitis is carried out taking into account its cause. For bacterial sore throat, antibiotics are prescribed. Anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, painkillers, and gargling with antiseptic solutions are used.
Treatment of chronic tonsillitis includes external therapy, tonsil lavage, physiotherapy, and surgery.
Treating tonsillitis at home
During the period of remission of the disease, the following means can be used to mechanically remove pathogens and increase the body’s reactivity:
- applying a mixture of aloe juice (1 part) and honey (3 parts) to the tonsils;
- gargling with infusions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, yarrow, St. John's wort, linden blossom, garlic, eucalyptus);
- using propolis in the form of pieces or ingesting a solution of propolis in warm milk.
Drug treatment of tonsillitis
Conservative therapy is prescribed for acute tonsillitis (angina), exacerbation of a chronic process. Antibacterial drugs and symptomatic agents are prescribed.
During the period of remission, courses of washing the tonsils lasting 10 days are indicated 2-3 times a year. Such treatment is carried out using the “Tonsillor” or “Utes” devices. The lacunae are washed with solutions of antiseptics and immunostimulants - interferon, levamisole, lysozyme and others. After washing, the surface of the tonsils is treated with Lugol's solution or collargol.
A course of irradiation with a helium-neon laser or low-intensity incoherent red light, ultraviolet irradiation, ultrasound therapy, UHF and other physiotherapeutic techniques are used.
Such treatment cannot completely relieve the patient of tonsillitis. It only helps to reduce the frequency of exacerbations and reduce the risk of complications of the disease. If conservative methods are ineffective within 1–2 years, surgical intervention is indicated.
Causes of chronic tonsillitis
In fact, inflammation occurs constantly in the tonsils - this is their function. But sometimes the protective resources of the tonsils are unable to cope with the infection, and then the inflammation, which gets out of control, turns into a serious disease - tonsillitis.
The acute form of tonsillitis is tonsillitis. Untreated tonsillitis often develops into chronic tonsillitis. Conversely, exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis leads to an outbreak of tonsillitis. If a person gets tonsillitis every year or several times a year, then he most likely has chronic tonsillitis.
Sometimes chronic tonsillitis can develop even if a person has not had a sore throat. This is possible if there is a source of infection that can affect the tonsils for quite a long time, for example, untreated caries or chronic sinusitis.
How to treat acute tonsillitis
Treatment of acute tonsillitis or tonsillitis depends on the pathogen and the severity of the disease.
1. If we are talking about bacterial infection, then it is necessary to prescribe antibacterial drugs of different groups.
Only a doctor can prescribe an effective antibiotic!
Antibiotics are not effective against viral tonsillitis.
2. Symptomatic treatment:
Includes taking antipyretics, painkillers, as well as the use of local anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial drugs in the form of solutions, lozenges, tablets.
3. A gentle diet. Namely, the exclusion of spicy, fried, and sour foods will help reduce irritation to the inflamed tissues of the throat.
4. If treatment is ineffective or complications occur, hospitalization is indicated. In the hospital, the patient will be under the close attention of doctors, blood tests will be monitored, and hormonal and anti-inflammatory drugs may be administered. It is possible to use systemic antibiotics in the form of tablets or intravenously or intramuscularly.
If necessary, surgical intervention is performed.
Regardless of the severity of the disease, pathogen and form, treatment must be comprehensive, that is, have an antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. Uncontrolled treatment with folk remedies can only do harm.
Anatomy of the throat
In the pharynx, on the sides and along the back wall, as well as on the border of the oral and nasal cavities, there are accumulations of lymphoid tissue - the so-called lymphoid-pharyngeal ring. It performs a protective function, and each of the tonsils of this ring is an important organ of our immunity.
The largest accumulations of lymphoid tissue are called tonsils (they are also called tonsils ) and there are several of them: two palatine, two tubal, one pharyngeal (aka adenoid) and one lingual.
Inflammation of the palatine tonsils (in everyday life they are called tonsils) is called acute tonsillitis or tonsillitis .
Diagnosis of the disease
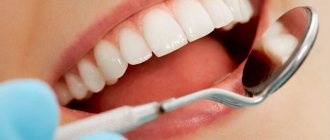
The first stage of a diagnostic examination is examination of the patient. The condition of the pharynx is assessed using special lighting, as a result of which the doctor notes enlarged lymph nodes, pronounced redness of the tonsils, yellowish purulent plaque and other signs characteristic of tonsillitis.
The next step, which is very important for prescribing competent treatment for tonsillitis, is taking tests. To determine the causative agent of the disease, a smear is taken from the surface of the tonsils and the posterior wall of the nasopharynx. This analysis is sent to the laboratory, where the material will be further examined. The presence of a certain group of microorganisms allows us to understand what specifically provoked damage to the tonsils and led to tonsillitis.
A blood test is also taken for examination. Indicators that confirm the presence of the disease will exceed the normal level:
- The ESR indicator reaches 18–20 mm/h.
- The number of immature neutrophils increases.
- The level of neutrophils in the blood reaches 7-9x109/l.
- The presence of metamyelocytes and myelocytes is detected.
A test to determine sensitivity to antibiotics allows the doctor to select the most effective treatment in the future. During treatment, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics, each of which is capable of suppressing the proliferation of a certain group of pathogenic microorganisms.
Prevention of tonsillitis
There are individual preventive measures aimed primarily at strengthening the immune system.
A healthy lifestyle and the absence of bad habits such as smoking and drinking alcohol play a key role. Don’t forget about hardening the body, doing physical exercise, regularly spending time in the fresh air, and consuming enough vitamins with food.
In the modern world, special attention is paid to the use of various biologically active additives (BAS) to improve health, including for the prevention of colds and strengthening the immune system.
The composition of such supplements is very diverse and rich, including various vitamins, minerals, nutrients, and substances of plant origin.
They come in the form of tablets, lozenges, dragees, drops, etc. But you shouldn’t count on “magic”; such supplements will not cure all diseases, but they will really help direct the body to work in the right direction and improve the effect of the main treatment. It is also important to choose the right biological supplement, focusing on the body’s needs and its problem. For example, lozenges can help strengthen the immune system.
Tantum® Propolis 13
Propolis is a valuable substance that has been used for medicinal purposes since the times of Hippocrates, Discorides, Avicenna and others, and is used in modern medicine to this day.
Plants from which bees collect and carry resinous substances have bactericidal, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulating, and antiviral properties.14 Find out more
Not being a medicine, Tantum® Propolis can support the patient’s immunity during seasonal ARVI and influenza, reduce pain, irritation and itching in the throat, and also replenish the lack of vitamins in the patient’s body.
In preventing complications, it is very important to consult a doctor on time, follow the prescribed treatment regimen and recommendations, and avoid self-medication.
Preventive actions
Before carrying out preventive measures, it is necessary to identify the factors that provoke the occurrence of tonsillitis. The greatest number of cases of the disease is observed in the autumn-winter periods. Living in unfavorable environmental conditions and frequent stays in crowded places also leads to an increased risk of developing the disease.
To reduce the likelihood of infection, it is recommended to take responsibility for your personal health. During periods of outbreaks of tonsillitis, it is advisable to take vitamin complexes aimed at strengthening the body's defenses. It is important to avoid hypothermia, which can cause sore throat and tonsillitis in particular.
When visiting public places, if possible, you should minimize contact with people infected with tonsillitis or wear a special mask. Daily walks in the fresh air and hardening will help improve immunity and also allow the body to resist tonsillitis.
We care about your health
Tonsillitis is one of the most common diseases. Infections of a viral or bacterial nature enter the respiratory tract (often one of them is joined by another), causing an inflammatory process. A surge in tonsillitis is most often observed in the spring and winter, when many people have a weakened immune system. Also, this disease can develop against the background of existing foci of infections in the body, for example, with dental caries, periodontal disease, sinusitis and others.
Tonsillitis is transmitted mainly by airborne droplets, pathogens: staphylococci, streptococci, fungi, bacilli.
Tonsillitis can have both acute (called sore throat) and chronic forms. Acute tonsillitis most often occurs as a result of an exacerbation of the chronic form, when a person with reduced immunity could, for example, become hypothermic.
Symptoms of tonsillitis
Compared to chronic tonsillitis, acute tonsillitis occurs in a more severe form: the body temperature can rise to 40 degrees, the patient feels a very strong pain in the throat, and it is difficult for him to swallow. The tonsils are swollen and enlarged, with the presence of purulent plugs. Patients feel headache, weakness, and their lymph nodes are enlarged.
Depending on the type of sore throat, which can be lacunar, herpetic, catarrhal, follicular, etc., ulcers, follicles, and a film called plaque form on the palatine tonsils.
With chronic tonsillitis, the temperature can rise to 38. The patient has a light coating on the palatine tonsils, and the tonsils themselves look enlarged and reddened. A person feels weakness, muscle pain, and aching joints.
Chronic tonsillitis is characterized by stages of remission and exacerbation. During the period of remission, the focus of infection is passive, and the person is not bothered by unpleasant symptoms. But as soon as one becomes hypothermic (especially with reduced immunity), he immediately begins to feel an unpleasant sore throat, pain when swallowing, cough, fatigue, poor general health and lack of appetite. The patient's lymph nodes may become inflamed.
Chronic tonsillitis is a long-term inflammation of the pharynx and palate. Its simple form has only a local symptom: sore throat. But if the picture is complemented by persistent lymphadenitis of the neck, changes in the functioning of the heart and high temperature, then this is already a toxic-allergic form.
Chronic tonsillitis has several stages: compensated, when the source of infection is not active, and decompensated, when exacerbation occurs due to repeated sore throats, inflammation of the ear and nose.
Tonsillitis (tonsillitis) - what inflammation looks like (photo of the disease)
Photograph of the throat with purulent sore throat
Photo - throat with follicular sore throat
Catarrhal sore throat - photo
Photo - lacunar tonsillitis
Possible complications of tonsillitis
Like many other diseases, tonsillitis is dangerous due to its complications . These include, first of all, rheumatism. After suffering from a sore throat, a person may feel severe aching in the joints and an increase in temperature.
In second place, as a rule, are cardiovascular diseases. Interruptions in heart function, shortness of breath, tachycardia are sure signs that a sore throat has caused complications.
Another unpleasant symptom after tonsillitis is swelling and tenderness of the lymph nodes, which have become infected from the tonsils. This is lymphadenitis.
The infection can also spread from the tonsils to the surrounding tissues of the upper respiratory tract, leading to pain when swallowing. And this disease is a complication of tonsillitis and is called paratonsillitis.
It should be noted that more than a hundred diseases are known that arise as a result of complications after acute tonsillitis. These include a variety of kidney, eye, skin and thyroid diseases.
Diagnosis of tonsillitis
It begins, of course, with an examination by a doctor, who determines whether the tonsils and adjacent tissues are swollen and red, and whether the ear and cervical lymph nodes are inflamed. The patient is sent for a general blood test.
Before prescribing treatment to the patient, the ENT doctor determines the nature of the inflammatory process: in what form does tonsillitis occur - chronic or acute, the type of inflammation (purulent, catarrhal), is the sore throat primary or secondary, what is the causative agent (this is determined in the laboratory - a culture is done from the throat ).
Treatment of tonsillitis - specifics of therapy
In the treatment of tonsillitis, both conservative methods and surgical intervention can be used. Treatment methods depend on the specifics of the disease.
For chronic tonsillitis, if necessary, antibiotics are prescribed in tablets, and for sore throat they are often administered intramuscularly. Local treatment is also carried out: purulent plaque on the tonsils is removed, the lacunae are washed with antibacterial solutions, physiotherapy and a course of vitamins with immunomodulators are prescribed.
In case of acute tonsillitis, it is recommended to irrigate the oral cavity with antiseptic solutions, rinse, treat the tonsils with iodine-containing preparations (if there are no allergic reactions to iodine), inhalations, and resorption of antibacterial tablets are useful. You should also drink a lot (weak teas, fruit drinks, juices, rosehip decoctions, etc.), take antipyretic and painkillers.
Acute tonsillitis is not recommended to be treated with antibiotics, because they reduce local immunity. But if the form of the disease is more severe, then the patient requires mandatory bed rest and antibiotic therapy. However, the prescription of antibiotics should be preceded by an analysis of the results of culture in the pharynx area, which will identify the causative agent of the infection. It is recommended to include in the course of treatment drugs that enhance immunity, as well as general strengthening and anti-inflammatory drugs. Physiotherapy will also be useful.
If a person suffers from tonsillitis more than twice a year, has complications from this disease, and conservative treatment does not bring the expected results, then removal of the tonsils may be recommended. There are many modern methods of performing this operation (infrared laser, ultrasound, biopolar, radiofrequency ablation and others), but many consider the cold plasma coblation method to be the most effective and gentle. However, it should be remembered that the tonsils are the first protective barrier that stops and disarms pathogenic bacteria . But in many cases (especially after frequent colds), the tonsils stop performing their functions and themselves become a source of infection, causing serious complications. In this case, it is better to remove them.
Treatment of tonsillitis (tonsillitis) at the Medkvadrat ENT center in Moscow, Kurkino and Khimki.
Reviews
Andrey
For most of my life I was tormented by constant exacerbations of chronic tonsillitis. Every spring and autumn I consistently lost two weeks for treatment. Surgery to remove tonsils has bothered me since childhood. My wife almost forcibly brought me to the clinic. I didn’t even imagine that new techniques can eliminate the problem absolutely painlessly. I have been living without constant exacerbations for a year now, and I am very grateful to the hospital specialists for this.
Natalia
Not long ago I had to bring my child to have his tonsils removed. From my own experience I remember how unpleasant and painful this procedure is. I was more worried than my son. However, the clinic doctors were able to find an approach to the child and calm him down. The operation was performed without pain or blood. Now I know for sure that your clinic employs super specialists and kind, sympathetic people.
Answers to popular questions about tonsillitis
What antibiotics are prescribed for tonsillitis?
In the treatment of acute tonsillitis, there are several groups of antibiotics:
- aminopenicillins;
- amoxicillin;
- amoxicillin with clavulanic acid;
- II-III generation cephalosporins;
- macrolides - azithromycin, clarithromycin;
Only a doctor can prescribe antibiotics. Uncontrolled self-use of antibiotics is prohibited, as this is associated with the development of bacterial resistance to the antibiotic, which leads to the ineffectiveness of a certain drug against the bacterium in the future. Antibiotic treatment is not indicated for viral tonsillitis !
Is it possible to get vaccinations for tonsillitis?
You should definitely consult your doctor. Vaccination can be done for chronic tonsillitis, but ONLY IN THE ABSENCE OF EXCERNSATION.
Which doctor treats tonsillitis?
In modern medicine, acute tonsillitis or tonsillitis can be treated by an otolaryngologist (ENT), an infectious disease specialist, and a therapist.
Is it possible to do inhalations for tonsillitis?
The use of inhalation for acute tonsillitis is permissible only after consulting a doctor! This procedure is not suitable for all forms of angina. Indications and contraindications depend on the form of acute tonsillitis and the causative agent, so differential diagnosis plays a key role. Only a doctor can prescribe a medicine for inhalation and its correct dosage. Your doctor will also help you choose the right type of nebulizer.
Is it possible to eat ice cream if you have tonsillitis?
Eating ice cream for a sore throat is not recommended. There are many private opinions that cold ice cream will reduce a sore throat, but this is not entirely true. Cold does have a local anesthetic effect by affecting nerve endings, but only for a short time, it does not have any benefit or positive effect. Outside of an exacerbation, you can eat melted ice cream.
What tests are prescribed for tonsillitis?
- pharyngeal smear - from the tonsils, arches, posterior pharyngeal wall to determine the pathogen and antibiotic resistance, including for diphtheria;
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- ESR;
Can tonsillitis occur on only one side?
Basically, tonsillitis always occurs with bilateral damage to the tonsils, but there are exceptions. Tonsillitis can occur not only as an independent disease, but also be a manifestation of some other disease. For example, with tularemia or primary syphilis, tonsillitis appears on one side.
How long does it take to treat tonsillitis?
On average, treatment can take 7 days. For example, antibacterial therapy is prescribed for 5-10 days. It all depends on the antibiotic group and the presence of complications.