What is chronic tonsillitis
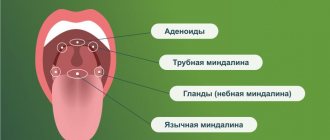
The human oropharynx has special structures called tonsils; they protect the body from pathogenic microorganisms. In childhood, these structures are subject to enormous stress, because every day the child comes into contact with new microbes that are not yet familiar to him.
When bacteria “settle” on the surface of the tonsils on the back wall of the pharynx, and the immune system cannot cope with them, inflammation develops - tonsillitis. If this inflammation persists for a long time, acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis) turns into a chronic inflammatory process.
Tonsils in chronic tonsillitis do not perform their functions, but on the contrary, they become a source of infection. This leads to infectious and autoimmune complications.
Classification
Taking into account the causes of inflammation, sore throat occurs:
- Primary or simple.
Initially develops in the tonsils. In 85% of all cases, the causative agent is streptococcal infection.
- Secondary.
It occurs as a manifestation of any other disease. Mostly occurs against the background of blood pathologies, with typhoid fever, scarlet fever, measles, diphtheria.
- Specific.
Causes a specific infection - pathogens of chlamydia, candidiasis.
Along the way, tonsillitis can be acute, and with frequently recurring inflammation it becomes chronic.
Depending on the nature of the changes in the lymphoid pharyngeal ring, several clinical forms of the disease are distinguished:
- catarrhal;
- lacunar,
- follicular,
- combined,
- herpes,
- phlegmonous,
- ulcerative-membranous,
- fibrinous.
According to the severity, tonsillitis occurs in mild, moderate or severe form. The severe form is characterized by complications, exacerbations of chronic diseases, and the addition of a secondary infection.
Symptoms of chronic tonsillitis
Tonsillitis is accompanied by local symptoms directly in the throat, and general symptoms from other organs and systems.
Chronic tonsillitis is characterized by repeated recurrence of tonsillitis.
Main symptoms:
- pain and discomfort in the throat, it hurts the child to swallow solid food;
- enlargement and tenderness of the cervical lymph nodes;
- increase in body temperature to 37-38 degrees;
- bad breath;
- signs of intoxication - fever, headache, weakness;
- abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting;
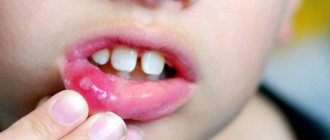
- upon examination, redness of the pharynx, tonsils are visible, possibly with a white coating (normally, the tonsils do not protrude from the palatine arches, they are not visible).
The infectious process is not limited to the throat; symptoms of tonsillitis are followed by a runny nose, hoarseness, and cough. Possible development of conjunctivitis, otitis, meningitis.
The mechanism of development of sore throat in children
The infection reaches the tissues of the lymphoid pharyngeal ring through the respiratory tract, where it adheres, multiplies and releases toxic products. At the site of introduction of the pathogen, an inflammatory focus is formed with local changes - swelling of the lymphoid tissue, accumulation of purulent masses in the lacunae.
With the accumulation of exotoxins, tissue breakdown products and microbial bodies, a toxic and allergic syndrome develops. The infection from the source of inflammation spreads through the bloodstream throughout the body, affecting internal organs and systems. With a strong immune system, early and properly selected treatment, inflammation can be stopped at any stage.
Causes of chronic tonsillitis
Tonsillitis
- infection. Among the pathogens that can cause tonsillitis are:
- bacteria (streptococci, staphylococci, diphtheria bacillus, etc.);
- ARVI (influenza viruses, parainfluenza, adenoviruses);
- herpes viruses (cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus);
- measles virus;
- yeast fungi (candida).
Provoking factors include hypothermia, consumption of cold foods, contact with sick people, stress, and poor nutrition. Candidal tonsillitis may indicate immunodeficiency.
Symptoms of a sore throat
In children, the symptoms of sore throat are much more pronounced than in adults. The baby becomes restless, cries, and refuses to eat. Often the disease becomes chronic and subsequently recurs. General signs of sore throat in a child:
- increase in body temperature above 39.0C
- intense sore throat;
- pain when swallowing;
- general weakness;
- poor appetite;
- moodiness and tearfulness (in young children).
If left untreated, symptoms of cardiovascular disease may occur: tachycardia, hypotension, chest pain.
The clinical picture of the disease depends on the form of acute tonsillitis. In medicine, it is customary to distinguish catarrhal, follicular, lacunar, fungal, herpetic and ulcerative-necrotic tonsillitis.
Manifestations of catarrhal tonsillitis
The mildest and most common form of the disease is catarrhal. Catarrhal tonsillitis is characterized by superficial damage to the tonsils: their swelling and redness. This form rarely exists as an independent disease, being one of the manifestations of other pathologies of the upper respiratory tract. General symptoms are not very acute - there is an increase in temperature to subfebrile levels (37.1-38C), sore throat and moderate pain in the throat, painful swallowing.
Manifestations of follicular tonsillitis
Follicular (purulent) tonsillitis manifests itself with high body temperature (over 38C), severe sore throat, inability to swallow normally, and increased salivation. Small whitish or yellowish pustules, 1-2 mm in diameter, form on the tonsils. There is an increase in lymph nodes in the neck and back of the head; when palpating the lymph nodes, the child feels pain.
Manifestations of lacunar tonsillitis
The symptoms of lacunar tonsillitis are similar to those of the follicular form. However, in this case the clinical picture is more pronounced. Purulent discharge does not occur on the follicles of the palatine tonsils, but on their ducts (lacunae).
Manifestations of fungal sore throat
With the fungal form of the disease, the child experiences enlargement and slight redness of the tonsils and low-grade body temperature. The main symptom that distinguishes this form is the presence of a bright white cheesy coating on the tonsils, which can be easily removed from the palatal tissues.
Manifestations of herpetic sore throat
The main difference between the herpetic form of the disease is the formation of rashes in the form of many small blisters on the tonsils. Inside each bubble is a colorless liquid. In some cases, small ulcers occur with herpetic sore throat.
Manifestations of ulcerative necrotic tonsillitis
This form of acute tonsillitis is one of the most severe. In a child, areas of necrotic (dead) tissue appear on the palatine tonsils. After the dead tissue is separated, deep ulcers form on the tonsils.
Complications due to improper self-medication and lack of treatment for tonsillitis
There are a simple form of tonsillitis - accompanied only by local symptoms, and a toxic-allergic (complicated) - manifestations of intoxication and dysfunction of all organs and systems come to the fore.
Toxic-allergic manifestations are characteristic of chronic tonsillitis of streptococcal origin. With this form, antibodies to streptococci are formed in the blood, which are also capable of attacking the body’s own tissues. The most vulnerable to such autoimmune aggression are the kidneys, heart and joints. Therefore, chronic tonsillitis leads to the following complications:
- glomerulonephritis and subsequently renal failure;
- endocarditis, myocarditis, pericarditis;
- rheumatism, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus.
Therefore, any tonsillitis should be examined and adequately treated. It is necessary to monitor the child’s condition for 3-4 weeks after recovery. If alarming symptoms appear in the heart (chest pain, rapid heartbeat, high temperature), joints (pain with movement, stiffness), kidneys (swelling, lower back pain), seek medical help.
Complications
In the early period, complications arise caused by the spread of the inflammatory process to nearby organs and tissues. These are otitis media, lymphadenitis (inflammation of the lymph nodes), peritonsillar abscess (formation of a purulent cavity in the peritoneal tissue), laryngitis, laryngeal edema.
With frequently recurring episodes of tonsillitis and improper prescription of antibiotics, the disease passes from an acute form to a chronic one. In this case, the tonsils do not perform a protective function, but turn into a reservoir that contains pathogenic microorganisms and toxic products of their vital activity. An infection from the tonsils spreads through the bloodstream throughout the body, affecting internal organs and systems.
The most common complications of tonsillitis in the long term:
- meningitis;
- glomerulonephritis - inflammation in the kidneys;
- recurrent pneumonia;
- sepsis;
- renal and liver failure;
- infectious-toxic shock;
- hemorrhagic stroke;
- peritonitis - inflammation of the abdominal cavity.
The course of sore throat is often aggravated by rheumatism. This is an inflammatory disease of connective tissue, which primarily affects the organs of the cardiovascular system and the musculoskeletal system.
Recommendations for the prevention of tonsillitis
To prevent the development of chronic tonsillitis, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- avoid hypothermia of the child;
- protect him from communicating with sick people;
- monitor the child’s nutritional status;
- promptly show the child to a pediatrician or pediatric ENT doctor when the first symptoms of a sore throat appear;
- Visit the dentist with him in a timely manner to remove carious teeth, which are a source of bacterial growth in the mouth.
Treatment of sore throat in children
Mild and moderate forms of tonsillitis are treated on an outpatient basis. If the disease is severe, therapy is ineffective, or a purulent complication is suspected, the patient is hospitalized in the infectious diseases department. During a sore throat, the child is isolated for 3-4 days, bed rest, plenty of fluids, and gentle nutrition are prescribed.
When a bacterial infection is isolated, antibacterial drugs are taken taking into account the resistance of the pathogen - macrolides, penicillins, cephalosporins. The course of treatment is 5–15 days. For viral sore throat, antiviral drugs are indicated.
To alleviate the severity of symptoms and prevent the development of a secondary bacterial infection, local treatment is carried out:
- gargling with antiseptics and herbal decoctions;
- dry heat and warming compresses on regional nodes (unacceptable for fever, body temperature above 37°C);
- irrigation of the pharynx, treatment of the back wall of the pharynx and tonsils with antimicrobial drugs;
- resorption of lollipops, tablets with antiseptic action;
- vitamin therapy;
- aromatherapy with essential oils;
- inhalation.
Taking into account the specifics of the disease and its clinical manifestations, the therapist prescribes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antipyretics, immunomodulators, and antihistamines. In the subacute period, physiotherapy is included - ultraphonophoresis, laser radiation, UV therapy, UHF therapy.
For frequently recurring tonsillitis, the issue of complete removal of the tonsils along with adjacent tissues using a laser, radiofrequency electrode, or ultrasonic scalpel is resolved. If complications develop in the form of a peritonsillar abscess, it is opened.
Diagnosis and treatment of tonsillitis
Diagnosis of chronic tonsillitis is made based on symptoms and examination data. To assess the general condition of the child, additional examination methods may be prescribed:
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- chest x-ray;
- electrocardiography.
With chronic tonsillitis, a child may show signs of damage to other organs. Therefore, if necessary, a pediatric otolaryngologist can refer him for examination to specialized specialists (nephrologist, cardiologist, ophthalmologist, etc.).
Chronic tonsillitis involves drug treatment: gargling, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory drugs and physiotherapy.
If conservative treatment is ineffective, the child is indicated for a tonsillectomy (surgical removal of the tonsils).
Chronic tonsillitis is a focal infection that must be removed from the body as quickly as possible to preserve the child’s health.
Diagnostics
Children with suspected acute tonsillitis need to consult a therapist or pediatric otolaryngologist. At the stage of primary diagnosis, the doctor studies and analyzes complaints, conducts a visual examination of the mucous membrane of the throat, and palpates regional lymph nodes.
Characteristic signs of tonsillitis are detected when examining the pharynx - swollen, red tonsils and arches, infiltration, white plaque, and sometimes pus with an unpleasant odor. Plaque on the tonsils is easily removed with a spatula and does not leave bleeding marks.
To identify the pathogen and determine its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs, sputum culture is performed for flora. All children are prescribed a clinical blood test to determine the activity of the inflammatory process.
Reference!
An alternative to the bacteriological method is a rapid test.
The analysis is characterized by a reliable level of sensitivity and high speed of execution, which makes it possible to make a diagnosis in 15–20 minutes and begin treatment immediately. If necessary, additional instrumental studies are prescribed: ultrasound of the kidneys, radiography of the paranasal sinuses, electrocardiography of the heart. Differential diagnosis is carried out with acute respiratory infections, acute pharyngitis, and pharyngeal diphtheria.