Distal bite: what is it and how does it happen?
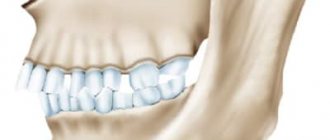
This is an anomaly in which the lower jaw “retracts” to the rear position, and the upper jaw protrudes forward.
The defect may be mild and almost invisible. Or it turns out to be too obvious.
Braces correct distal occlusion, but you need to seek help from a professional who has many successfully treated clinical cases.
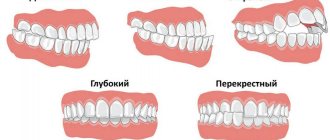
This violation is divided into types:
- Horizontal. The incisors of the upper jaw are inclined, raised towards the lip. The lower antagonists rest against the sky.
- Vertical. The upper incisors are inclined inward, often touching the gums near the lower ones.
The chin visually appears small. Doctors name several signs
, which indicate the severity of the pathology:
- There is a minor problem when the sixth upper and lower teeth are in contact.
- If closure is not observed, the unit ends up between the fifth and sixth antagonists, then urgent intervention is necessary and a long treatment process will be required.
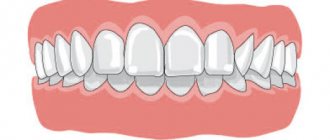
The distal bite can be corrected and after wearing braces the profile becomes symmetrical and proportional.
Kinds
Malocclusion can be either congenital or acquired. Abnormal closure of teeth can be:
- Open – individual groups of teeth do not close together;
- Deep – the upper teeth overlap the lower teeth by half the crown;
- Distal - either strong development or non-development of the lower or jaw;
- Crossed - one jaw develops differently from the other;
- Mesial - the lower jaw moves forward;
- Dystopian - teeth are not in the right place.
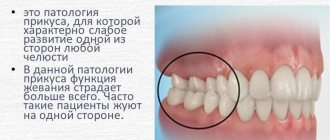
The most common type of dental correction in adults is deep bite correction. Indeed, with this defect, in addition to the above points, the work of the masticatory muscles is disrupted; while eating, you can hear crunching and clicking in the jaw joints.
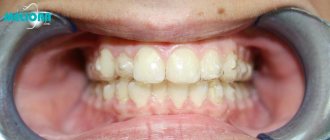
Signs of distal bite
Distal occlusion requires mandatory intervention from a specialist; treatment with braces is indicated; aligners can be used (especially when the diagnosis is made in childhood).
Signs of distal occlusion:
- The child spontaneously bites his lower lip
:
- The profile is slightly beveled. To define it, the term “avian” is used.
- The lips are thin and fall inside the oral cavity
. If you visually draw a line from the tip of the nose to the middle of the chin, then the lips will not appear on it:
- The lower third of the face is disproportionately small. A crease appears on the chin due to the jaw moving back.
It is possible to correct distal bite without braces when treatment is carried out in childhood. Aligners are approved for installation in children with baby teeth. They are installed in older preschool age, when the child can consciously follow the dentist’s recommendations.
In my practice, there are already more than 300 successful cases of bite correction using aligners. This is a promising method. Invisalign and FlexLiner aligners have proven themselves to be excellent in the treatment of distal occlusion. Star Smile aligners also correct this dental pathology quite well, although they require more careful attention from the attending physician. Whether correction of distal bite with aligners is right for you or your child can only be said with confidence during a consultation.
Treatment tactics
Initially, the dentist conducts a thorough examination of the patient’s oral cavity and determines the degree of mobility of the units. If necessary, additional diagnostics are prescribed.
If pathology is detected, the orthodontic system is removed and therapeutic measures are carried out. Depending on the type of disease, antibiotic therapy, filling, professional teeth cleaning, or splinting may be required.
Orthodontic treatment is continued after the disease that caused the loosening of the elements has been eliminated.
Structure mobility
Some patients are faced with the problem of loosening elements of the brace system: displacement or unsticking of clasps, deformation of the power arc, slipping of the ring. A similar phenomenon occurs due to neglect of the rules of operation of the orthodontic device.
If defects are detected in the structure of the device, the patient should make an appointment with the attending orthodontist. Before the visit, loose elements are secured with orthodontic wax.
The dentist will inspect and assess the condition of the system and offer a solution to the problem.
After removing the device
At the end of the orthodontic correction, the patient experiences discomfort and a feeling of unsteadiness of the elements for some time. Without the influence of the locks, the elements of the row tend to return to their usual position.
Ligaments and adjacent tissues are flexible and, if not fixed, teeth can shift again. Wearing retainers allows you to consolidate the correction effect. The duration of use of the devices depends on the patient’s age, the degree of pathology and the duration of orthodontic treatment. Removable or non-removable devices reliably hold elements and ligaments in the correct position, preventing their displacement and bite deformation. The minimum retention period is one year. Some patients have to use devices throughout their lives.
Tooth mobility during and after orthodontic treatment is a fairly common complaint. If this phenomenon is accompanied by pain, inflammation and swelling of the gums and other pathological symptoms, you should contact your dentist.
Reasons for the appearance of distal bite, why it is dangerous
The causes of the defect may be genetic disorders, especially in cases where relatives had a similar diagnosis.
Sometimes the occurrence of pathology is facilitated by a lack of nutrients, microelements, as well as bad habits.
– sucking toys, pacifiers.
Often, instead of a pacifier, the child uses a finger to suck
- which undoubtedly contributes to the development of distal occlusion:
The structure of the dental apparatus is disrupted in the presence of untreated diseases of the nasopharynx - breathing through the mouth provokes weakening of muscles, ligaments and jaws shift.
Correction of distal bite with braces is necessary. If you ignore pathology, you will have to overcome many problems.
Problems arising from distal occlusion:
- Diction is broken.
- There is no adequate chewing of food, not all foods are convenient to eat. Gastrointestinal ailments or somatic diseases develop.
- It is difficult to get dentures in the future.
- Uneven load often leads to loosening of units and destructive changes in tissues.
The dentist will make an initial conclusion during the first examination and order imaging to clarify the diagnosis.
Principle of operation
Immediately after braces are installed, they begin to put pressure on the teeth, gradually causing them to move. During this, the ligaments that are located around the unit are strained. As a result, the human body tries to compensate for the lack of tissue in the place where the fibers have been greatly stretched, and vice versa.
Where the fibers are strongly compressed, the tissues begin to gradually dissolve, freeing up space for the movement of adjacent teeth. The main advantage of using braces is that the results obtained, if all the specialist’s recommendations are followed, remain with the person for life.
The teeth begin to shift not because the brackets are attached to them, but due to the pressure of the metal power arc that connects them together. To maximize the effect of treatment, the arch should be changed periodically. This is due to the fact that over time the force of its pressure weakens. Also, at one of the regular preventive examinations, a specialist may come to the conclusion that it is necessary to install a more rigid arch.
Treatment: distal bite before and after braces
From 11-13 years of age (early adolescence), distal bite is corrected with braces, treatment gives good results. Within a year and a half, the pathology disappears. Adults will need more time. The structure is a metal arc fixed on overlays glued to the enamel. The wire has a “memory effect” - gradually the lower jaw develops and takes on a physiologically justified position.
But a child with baby teeth is not given braces. How to correct a distal bite without braces? In this case, aligners come to the rescue - mouth guards made of transparent synthetic, absolutely harmless to the body. The child can easily take them off and put them on, they quickly get used to them. Visually, custom-made mouth guards are almost invisible. The growth of the lower jaw is stimulated. Intervention from 7-8 years is considered optimal. The tissues are flexible, and the child already understands the importance and necessity of treatment. Plates are also effective in childhood, but as aligners develop, they are placed a little less frequently.
To consolidate the effect, after removing braces, retainers are installed or mouth guards are used. After the braces are removed and the distal bite is corrected, you can forget about the imbalances that were observed before the intervention. And pay attention to what changes have occurred after treatment: the face becomes symmetrical, facial expressions become varied. The lips are already expressive and take on clear outlines. The person becomes uninhibited.
Don't ignore the problem. Come to me for an appointment, and we will choose the appropriate method for correcting your distal bite, taking into account your characteristics.
Braces design
At first glance, braces look quite simple, but in fact the design is a complex mechanism. All its components are involved in the gradual movement of units of the dentition. In this case, the teeth can move in any direction, as well as around their axis, without changing the original inclination of the root. Braces act as delicately as possible, preventing injury to soft tissues and the tongue. As a result, a person becomes the owner of not only a beautiful smile, but also a healthy body as a whole.
Many patients are surprised how they manage to dislodge a tooth, because it sits tightly in hard, bone tissue. In fact, the connection between the tooth and the jaw joint is not very strong. The tooth is held in its socket by the surrounding fibers, which constantly stretch and compress. Under pressure, the tooth can only move as far as the fibers allow. In this case, on one side the tissues will gradually shrink, and on the other they will begin to stretch. New bone tissue will begin to form in the freed space.
The designs themselves consist of many elements: locks, ligatures, arcs. The staples are attached to the surface of the enamel using a special dental glue, the excess of which is removed after installation. The arc is inserted into special holes in the locks (grooves) and held in place with ligatures (small rubber bands). Also very popular are non-ligature models, in which the arch is secured with clip-on locks.