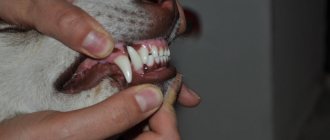
What is a deep bite?
People strived for a perfect smile back in ancient times, evidence of this is found in mummies from Ancient Egypt, which had ropes obtained from animal intestines entwined around their teeth.
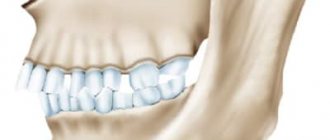
They played the role of modern dental wires for braces. Now it is much easier to correct a deep bite. To achieve faster and more effective results, you need to start treatment from childhood. A deep bite is an anomaly that manifests itself in the form of overlap of the lower dentition with the upper one. The defect can be diagnosed when there is an overlap of more than 1/3 of the height of the crowns. The “lucky” one with a deep bite experiences discomfort while chewing food, speech impediments, and injuries to the gums and palate.
Causes of deep bite
Such an unpleasant phenomenon as a problem bite can appear both in childhood and in older age. In dentistry, there are several reasons that can lead to the development of pathology:
- birth defects associated with facial deformation;
- genetic inheritance of the specific structure of the dental system;
- improper dental prosthetics;
- delay in prosthetics.
Also, the causes of a deep, incorrectly formed bite can be constant finger sucking and lip biting. Even a pacifier can lead to the development of occlusion. The pathology does not go away on its own, but fortunately orthodontics is now very well developed, making it possible to effectively eliminate the manifestations of deep bite.
Classification of deep bite
According to the nature of origin, a deep bite can be:
- Primary – develops for reasons of irregular structure in the facial skeleton and dentition. The anomaly is most often represented by a deep blocking bite, which is manifested by limitation of jaw movements other than closing and opening. This pathological occlusion comes in two forms: dentoalveolar and skeletal deep bite.
- Secondary. The main reason for the formation of such a bite is due to previous diseases of the dental system. This could be periodontal disease, tooth loss, etc.
There is also a classification of deep bite according to the type of interaction of the lateral dentition:
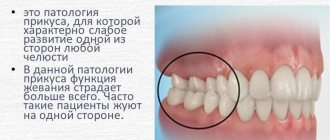
- Distal - with this form of bite, the upper row of teeth overlaps the lower row by the length of the crown. The pathology is characterized by an underdeveloped lower jaw, a slightly sloping chin, a shortened face, and exposure of the crowns to the neck when smiling.
- Neutral - with such a bite, there are no pronounced defects in the skeletal structure of the face, its lower part is slightly shortened, and the chin is of a normal shape.
The stages of development of deep bite are divided into initial, progressive and traumatic.
Types of mesial occlusion
By form:
- Dentoalveolar form. Malocclusion as a result of incorrect position of the teeth.
- Gnathic or skeletal form is an abnormal bite formed by a pathology of jaw development.
A more complex form of malocclusion, sometimes requiring surgical intervention. Often, clinical cases of mesial malocclusion combine both forms - incorrectly positioned teeth and abnormal jaw sizes.
For reasons of occurrence:
- Congenital abnormal jaw sizes: macrognathia of the lower jaw - a large or elongated lower jaw; micrognathia of the upper jaw - underdeveloped, small upper jaw.
- Prognathia of the lower jaw is a forced position when individual teeth interfere with the normal closure of the jaws and jaw growth. This type of bite occurs in children on their baby teeth due to fangs that cling to the lower teeth and prevent the lower jaw from taking a normal position.
- Retrogression of the upper jaw is the posterior position of the upper jaw relative to the proportions of the face. Unlike micrognathia, in this case the jaw is of normal size, but incorrectly positioned.
- Abnormal tooth sizes: macrodentia - large teeth on the lower jaw, microdentia - small teeth on the upper jaw.
Deep bite in children
The cause of deep occlusion can be birth trauma, a long period of sucking a pacifier or finger, late loss of baby teeth, calcium deficiency, or trauma to the dental system. In 15% of schoolchildren, a distal deep bite is diagnosed - the upper jaw is strongly pushed forward. It can develop against the background of impaired nasal breathing, adenoids, enlarged tonsils, frequent colds, and rickets. Also, improper formation of the bite can be caused by the removal of teeth at an early age, or the habit of propping up the chin.
Why does a bite defect form?
The formation of occlusion is influenced by genetic predisposition, intrauterine development and factors that can occur after childbirth.
Specifying the factors, the following causes of malocclusion can be identified:
- Mother's diseases. A child may inherit an anomaly due to the fact that his mother is sick with viral diseases, metabolic disorders, endocrine diseases and anemia.
- The course of pregnancy with pathology.
- Improper intrauterine development of the fetus.
- Bad habits such as prolonged thumb and pacifier sucking.
- Defects (acquired, congenital) of the musculoskeletal system.
- Impaired functions of sucking, speech, swallowing and breathing.
- Diseases of the digestive system.
- Diseases of the ear, nose and throat.
- Osteomyelitis of the jaw.
- Caries of lateral teeth.
- Too early loss of primary first molars or lateral teeth.
- Teething with delays.
- Jaw injuries.
- Change of primary permanent teeth with a time delay.
- Congenital anomalies (disorders of the facial skeleton).
Considering the frequency of occurrence of deep bite, we can say that it accounts for approximately 20% of all tooth curvatures.
There are secondary reasons for the appearance of a deep bite: incorrect posture, mouth breathing, frequent lip biting, muscle tone greater than normal, infantile swallowing.
Symptoms of deep bite
Externally, improper closure of teeth is manifested by shortening of the lower third of the face, the formation of a pronounced supramental fold, and turning of the lower lip outward. Among the oral signs:
- overlap of the lower frontal dentition with the upper one by the size of the crown;
- inflammatory process of the mucous membranes of the mouth;
- rapid erosion of tooth enamel, which leads to the development of caries;
- excessive overhang of the upper jaw over the lower jaw;
- decrease in the depth of the vestibule of the oral cavity.
Also, with malocclusion, secondary symptoms appear that develop against the background of the primary ones: problems with diction, breathing, deformation of the cranial vault, pain while chewing food.
Characteristic signs
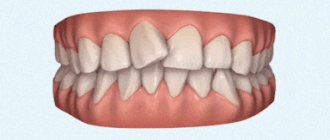
An anomaly is considered to be an occlusion in which the teeth in the front part of the jaw are >1/3 covered by the opposing teeth. Pathology has several forms:
- Declining - a progressive violation of the closure of teeth, in which the incisors of one jaw, not having support on the tubercles located on the inside of the crown of the opposite jaw, are shifted to the edge of the gum.
- Traumatic - when closing, the cutting edges of the lower jaw incisors violate the integrity of the soft tissues of the oral cavity.
- Deep frontal, or incisive, is the absence of contact between the incisors of both jaws and the contact of the cutting edge of the crowns of the incisors with the soft tissues of the opposite jaw.
- Disocclusion is a separation of the dentition, in which compression of the jaws leads to an uneven fit of the cutting edges and the formation of gaps - slides.
With a pathological bite the following are observed:
- shortening of the lower part of the face;
- distal position of the lips relative to the aesthetic Ricketts plane;
- deep nasolabial folds;
- retrusive position of the lower lip;
- pronounced supramental groove.
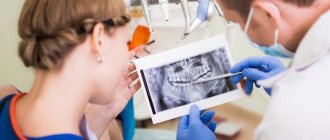
Diagnosis of deep bite
Occlusion can be determined by external signs, but not all forms of improper closure of teeth are pronounced, so additional diagnostics are required. The specialist examines the patient’s medical history and conducts a visual examination of the oral cavity. The following activities can be carried out:
- taking an impression with alginate mass, followed by making diagnostic models and measuring them;
- photo of the face in profile and front;
- X-ray examinations;
- measurement of dental arches, apical base;
- performing an occludogram.
When making a diagnosis, data obtained from the results of electromyography, orthopantomography and teleradiography play an important role.
How to determine mesial bite?
- By the face. Mesial occlusion can be determined by the structure of the face even without looking at the smile. The profile is concave - the middle third of the face falls back slightly, especially relative to the lower third. The chin protrudes forward and looks massive and disproportionate to the face and upper jaw. At the same time, the lower lip looks thicker, and the upper lip sinks. The facial expression seems angry.
- By posture. The temporomandibular joint is directly connected to the spine, so its malposition (as a result of malocclusion) affects the posture and balance of the entire body. Those with complex forms of mesial occlusion are characterized by a slight deviation of the body backwards. If you draw a straight line through the entire body in profile, the head will be tilted slightly back, and the pelvic bones will be pushed forward.
Concave profile with mesial bite
Poor posture with mesial occlusion - By smile and teeth. The clinical situation in which the lower incisors are in front of the upper ones is called reverse incisal overlap. This is the most characteristic intraoral sign of progeny. It is also characterized by: gaps between the teeth, dystopia (improper position) of the teeth, tilting of the lower teeth into the oral cavity.
Consequences of deep bite
Elimination of deep occlusion is necessary not only to achieve an aesthetic result, but also to treat phenomena that bring a lot of discomfort in everyday life. Teeth that do not fit properly can cause the development of speech defects, facial asymmetry, and various aesthetic deviations. Besides:
- a large load on the front teeth provokes increased sensitivity and rapid abrasion of the enamel, which leads to caries;
- Loose teeth and frequent inflammatory processes in the gums appear against the background of their constant injury.
The pathology also leads to a decrease in the height of the bite, headaches, tooth wear and subsequent loss of tone of the masticatory muscles.
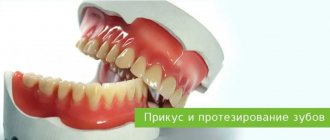
Treatment of deep bite
For deep bites in adults, braces are usually used. A very interesting fact is that for the manufacture of certain types of braces, nickel-titanium is used - a material created by NASA for use in space. Clear aligners can also be used, which are more aesthetically pleasing. In addition, they are convenient, as they can be removed when eating or brushing your teeth. It takes at least 12-14 months to correct improper closure. The effectiveness of treatment and its duration depend on the degree of pathology and the correct choice of orthodontic design. To achieve a good result, it is important for the patient to comply with the rules established by the treating dentist. Treatment of deep bite in children is simpler, since the dentition is not yet fully formed; the course of occlusion can be influenced by the following methods:
- the child needs to be accustomed to solid food in order to create optimal stress on the teeth;
- it is important to cure dental caries;
- during the change of baby teeth, plates or other orthodontic structures (Frenkel, Bruckle, trainers) are installed on molars;
- At the age of 12 years, vestibular and lingual braces can be installed.
The iOrtho network of clinics selects the most effective treatment method taking into account the specific situation. We provide high-quality services and a modern treatment method using Invisalign aligners. Book your consultation now to enjoy a beautiful smile in just a few months.
Treatment errors
When turning to inexperienced specialists, you may be faced with the selection of the wrong treatment method. If there is a mistake in choosing devices such as occlusal pads, crowns, mouthguards for children, their large molars and incisors may become separated. This leads to rapid erasure of the cusps on the antagonist teeth located in the lateral row. In the anterior part, on the contrary, there is a sharp separation of the teeth and their protrusion forward, worsening the incisal overlap.
Deep bites in adults and teenagers can only be completely corrected if there is enough space underneath. Once the jaw has formed, some teeth will need to be removed to gain sufficient space. You also need to take into account the fact that when removing tooth protrusion in the anterior part of the dentition, the incisal overlap increases.
The effectiveness of treatment using the Herbst apparatus
Deep overbites are often corrected using the Herbstat appliance, a permanent orthodontic appliance. To correct the occlusion, it must be worn for at least 3-12 months. Its main task is to restrain the growth of the upper jaw, correct the lower jaw, and rebuild the functioning of the muscles of the dental system. The choice of this treatment method allows you to accurately predict the result and achieve it in a short time. The device does not interfere with eating or talking.
Price
The tables show approximate prices in Moscow for the correction of underbite in children.
| Name of service | Price in rubles |
| Correction of occlusion anomalies with aligners | from 180000 |
| Orthodontic plate with bite pad | from 11000 |
| Correction using the Frenkel apparatus | from 70000 |
| Correction of the defect using surgical methods | from 200000 |
| Treatment using a trainer | from 11000 |
| Braces | from 63000 |
Timely correction of malocclusion in children is a significant undertaking. In adults, this feature is practically not corrected. It is important to treat this condition because it is not only an aesthetic anomaly. The patient develops dangerous conditions that threaten life.
Forecast and prevention of deep bite
The prognosis of a deep pathological bite when choosing the right treatment method is always positive. It is possible to correct incorrect teeth closure even in adulthood, but in order for the result to be of better quality, treatment must begin in the first stages of its development. Prevention is also important, it is necessary to control the loss of baby teeth and the correct growth of molars, monitor the position of the child’s head during sleep, protect him from bad oral habits, in particular prolonged sucking of a pacifier and thumb, it is important to promptly treat ENT diseases and other pathologies that can cause the development of a deep bite.