Many of our patients (as well as patients, for example, of chiropractors or neurologists) do not even realize how interconnected the problems they are being treated with are. For example, the jaw joint hurts, the head hurts, shooting in the ear, clicking in the jaw, pulling at the base of the skull... it would seem that these are different symptoms, but the reason may be the same for everyone: TMJ dysfunction
.
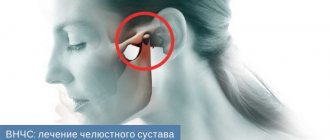
Functions of the TMJ
TMJ
or
temporomandibular joint
is a joint located above the ear that connects the temporal bone to the lower jaw and the lower jaw to the skull. The muscles that are attached to this joint are actively involved in speaking, facial expressions, chewing, and swallowing. Together, muscles, ligaments, cartilage and joints make up the apparatus, thanks to which we can generally open and close our mouth, move our jaw back and forth and left and right, and the load on this apparatus is significant - comparable to the load, for example, on the knee joint.
The temporomandibular joint is the only paired and symmetrically moving joint in the human body, and problems with its functioning lead to numerous unpleasant diseases. TMJ dysfunction—limited work and mobility of the jaw joint—occurs when the joint on the right and left sides of the skull does not move synchronously or evenly. For example, to open the mouth, the patient must first move the lower jaw from side to side, “until it clicks.” Or when you open your mouth, you feel pain in your jaw or temples.
This disease has many names: arthritis (arthrosis) of the TMJ, myofacial syndrome, myoarthropathy of the TMJ, chronic dislocation of the lower jaw, Costen's syndrome (named after the American doctor who first identified this disease). This pathology is difficult to diagnose and treat, and at the same time it can cause a wide variety of pain - from headaches to neck pain.
Statistical fact: from 30% to 70% of dental patients suffer from functional pathology of the temporomandibular joint. And these are not always older people, as one might expect. On the contrary, people of all ages, including children, suffer from TMJ pain and related pain.
TMJ dysfunction was first described by otolaryngologist (ENT doctor) Kosten in 1934. Kosten studied pain and noise in the ears and burning in the nose, which intensified during or after eating, and was the first to think of linking them with malfunction of the temporomandibular joint. Subsequently, his colleagues and other doctors who examined this problem expanded and supplemented the list of symptoms. Now this list is quite extensive, and often not all symptoms can be associated specifically with TMJ problems.
TMJ dysfunction - causes and consequences.
Orthodontist-dentist Nikolaeva Nadezhda Nikolaevna
The temporomandibular joint ( TMJ ) is a paired joint formed by the head of the mandible, the mandibular fossa and the articular tubercle of the temporal bone. The heads of the mandible meet at an obtuse angle at the anterior edge of the foramen magnum. The TMJ ensures the movement of the lower jaw and represents a complex activity of the body in the form of chewing, swallowing, talking, yawning. The muscles of mastication ensure precise movement of the joint in an error-free manner, unless there is dysfunction ( TMJ )
. According to WHO, about 40% of the population aged 20-50 years suffer from TMJ . But not every person seeks help from a gnathologist or osteopath with complaints about the joint, preferring to visit other doctors with headaches, fatigue, attacks of fear, pressure... Dysfunction manifests itself in the form of a neurological clinic: headache, dizziness, clicking and crunching joint, muscle tension, spasms in the head, neck, throat. Otology clinic: noise, ringing, ear congestion, hearing loss. But there are other, hidden and long-term consequences of TMJ dysfunction:
- Cervical lordosis. Poor posture, when the neck is excessively straightened or, on the contrary, the head protrudes noticeably relative to the person’s body.
- Curvature in the sacroiliac joint (pelvic bones) as a result, a change in the length of the limbs.
With pain and dizziness, it would seem clear: head, ear, joint. Everything is close, everything interacts. But what effect does TMJ on the entire musculoskeletal system, especially on the length of the limbs?
The TMJ is the structure of one complex - the DENTAL GNOSTIC system. The dental system is a complex of interactions between the structures and functions of the head and neck. Includes components of the bones of the skull, lower jaw, hyoid bone, clavicle and sternum, muscles and ligaments, joints, vascular, lymphatic and nervous systems, as well as soft tissues of the head and teeth. In addition, it has a connection with the sacrum and coccyx through the dura mater. Everything in the system is interconnected and depends on the normal functioning of all its parts.*
Main functions of the dental system:
- Providing basic body functions: chewing, swallowing, biting, speaking, breathing.
- Participation in maintaining statics: gait mechanism, cervical, vertebral and muscle balance, pelvic balance, equilibrium.
- Effect on cranial (cranial) function - especially the temporal bone.
- Influence on the functions of the nervous, endocrine, lymphatic systems.
Let's look at the basic functions of the body: chewing, swallowing, speaking, breathing. These basic body functions are performed through the movement of the lower jaw. The movement of the lower jaw is ensured by the movement of the head of the lower jaw in the articular fossa of the TMJ , with the help of the temporal, masticatory, pterygoid, hypoglossal and other muscles. The line of closure of the teeth - the occlusal plane, or simply the bite, should normally be parallel to the planes of the entire musculoskeletal system. The main planes of which pass through the pupils, the line of closure of the teeth, the second and third cervical vertebrae, shoulder blades, iliac crests, knees and ankles. The parallelism of the lines indicates the health of the musculoskeletal system and the dental system. A change in any of the planes leads to changes in the other planes. Therefore, a violation of the occlusal plane relative to others can cause pain and negative changes in completely unexpected parts of the body.
Violations of occlusion as a result of tooth wear, congenital malocclusion, and more often, inadequate dental treatment or prosthetics, inept use of braces, illegal removal of healthy teeth, lead to response disorders in the cervical spine and spasm of the muscles of the back of the neck. Prolonged spasm causes structural changes in the muscle, shortening it and causing it to lose its ability to contract and relax. Muscle spasm leads to spasm of the chewing and facial muscles. Thus, for the body, muscle spasm on one side is a pathological process that leads to spasm in another area. For example, the temporal muscle is involved in supporting statics; the masticatory muscles are its synergist. These muscles contain a large number of proprioceptors (sensory fibers). A constant flow of nerve impulses from proprioceptors is involved in the regulation of the vertical position of the body. Violation of occlusion (bite) leads to unbalanced movement of the lower jaw and maxillofacial muscles, incl. masticatory and temporal muscles. A change in the flow of nerve impulses, due to dysfunction of the TMJ , causes curvature of the spine in the cervical region and sacroiliac joint, which leads to twisting of the pelvis and changes in the length of the limbs.
An imbalance in the TMJ sends a negative stimulus to the nervous system 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. Any malocclusion changes the direction of force in the skull. For example, premature contact on the lateral teeth causes uncoordinated muscle movement and distortion of nerve impulse transmission to the brain. Uncoordinated muscle movements often cause tension in the fascia of the neck. The nodes of the sympathetic trunk of the autonomic nervous system lie anterior to the prevertebral fascia of the neck. Thus, dysfunction of the TMJ , causing tension in the fascia of the neck, can irritate cervical sympathetic communications, provoking a reflex spasm of the vessels of the head. Spasm of the blood vessels in the head causes a disturbance in the blood supply to the cerebellum, which is manifested by a lack of coordination, dizziness - as a result of anxiety. TMJ dysfunction causes torsion (torsio; Latin “rotation, twisting”) of the temporal bone, in which the labyrinth with the vestibular apparatus is located. Changes in the vestibular system lead to imbalance and dizziness. Nasal congestion may also be associated with TMJ . Due to the shortening of the fascia of the neck muscles, there is a violation of lymphatic drainage and the outflow of venous blood from the head. This may manifest itself in the form of tissue edema in the area of the nasal passages, since this area is rich in blood vessels. Diseases of the temporomandibular joint have the following causes :
- Malocclusion (occlusion) is a closure of the teeth, which disrupts the shape and function of the dental system. This manifests itself in the form of deformation of the occlusal surface of the teeth with blockade of the movement of the lower jaw. Which can lead to pathological wear of teeth, functional overload of the TMJ and chewing muscles. The most common TMJ problem is a decrease in bite height. This is due to several factors: impaired teething, bruxism, premature loss of milk or permanent teeth, congenital absence of a group of teeth, microdontia (small teeth), pathological abrasion of enamel, violation of the vertical size of teeth due to the work of the dentist. Changes in the position of the TMJ due to illiterate orthodontic treatment, illegal or forced removal, tooth decay.
- Stress (overexertion, strong clenching of teeth).
- Jaw trauma (fractures of facial bones and jaw).
- Endocrine, metabolic disorders, infectious diseases.
- Excessive physical activity.
- Bad habits (biting nails, holding the phone incorrectly, etc.)
Symptoms of temporomandibular joint diseases:
- Headache, spasms in the facial muscles and jaw area.
- Clicking, crunching, grinding when the jaw moves.
- Pain, congestion and ringing in the ears.
- Enlarged submandibular lymph nodes.
- Dizziness.
TMJ diseases on human health is far from being studied, in contrast to the methods of diagnosis, treatment and restoration of TMJ by a doctor. In most cases, a transparent corrective aligner is enough to save yourself from many present and future health problems.
Symptoms of TMJ dysfunction
- Pain in the jaw, increasing when opening the mouth, chewing, speaking, yawning;
Clicking in the joint of the lower jaw, the jaw “jams”, it does not open, does not close, or has begun to close differently;- Pain in the temples, in the eye area, visual impairment, photophobia (sensitivity to light);
- Pain, ringing and noise in the ears, in the ear area, feeling of pressure in the ears;
- Frequent headaches, dizziness, migraines;
- Sleep disorders, insomnia, anxiety, depression;
- Pain in the neck, in the lower part of the skull;
- Tooth pain from sweets, hot, cold.
This diversity in symptoms, which often makes it difficult for doctors to diagnose, is explained by the fact that the joint is connected to many important organs and parts of the body (eyes, ears, neck, head) and errors in its functioning can affect everything at once, or they can only affect something one. It is usually possible to determine that the problem is in the temporomandibular joint only in a complex manner.
In most cases, TMJ dysfunction is manifested by pain in the face, joints of the jaw, neck, shoulders, ears, crunching and clicking. Complaints of dizziness, difficulty chewing food, speech and hearing disorders, difficulty opening the mouth, “jamming” of the jaw, or even the appearance of swelling and fever are also common.
What else do you need to know?
As mentioned above, it is impossible to independently identify the cause of unpleasant sensations when opening your mouth. Even when the patient consults a doctor, additional examination is required. The specialist usually prescribes an X-ray of the jaw, computed tomography, and MRI. Do not forget that each specific ailment requires a special approach to treatment. The general condition of the patient, the nature of the disease, and its stage are taken into account. Usually the pathology disappears when the cause that provoked it is eliminated. So:
- Injuries. A fixing bandage is applied and analgesics are prescribed. Cold compresses are recommended for patients; they will help relieve swelling and pain.
- Dental diseases are quite common. Caries, cysts, and other ailments require immediate treatment. After eliminating the problems, the pain usually goes away. Patients are also prescribed antibiotics.
- Neuralgia. This category includes a number of dangerous ailments. For their treatment, vitamins, antiviral drugs, and special physical training are recommended (exercises will help strengthen the jaw and relieve discomfort when it opens).
- ENT diseases. With otitis media, sinusitis and other ailments, patients often complain of pain that occurs when opening the mouth. For treatment, antipyretics, antibiotics, physiotherapeutic procedures, and drugs to strengthen the immune system are prescribed.
Pain in the jaw joint: causes
- Defects in the dentition - lack of teeth, overestimation of fillings;
Pathological abrasion of teeth;- Broken bite
;
- Overload of the masticatory muscles (for example, if you chew on only one side for a long time);
- Inaccurate prosthetics, errors in orthodontic treatment;
- Other anomalies of the oral cavity and jaw structure;
- Bruxism, involuntary grinding of teeth.
- Birth trauma, trauma to the skull and jaw;
- Osteochondrosis and scoliosis of the spine;
- Severe constant stress
;
- An infection in the joint cavity that provokes inflammation of the TMJ.
Symptoms of TMJ arthritis
Depending on the cause of the disease and the nature of the inflammation, arthritis manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- sharp pain when moving the jaw. Increases in opening/closing of the mouth, strongly radiates to the temple, back of the head, tongue;
- when you try to open your mouth wider, the jaw moves to the side;
- inability to close teeth tightly;
- hearing loss, dizziness;
- crunching when moving the jaw.
If at least 2 signs are detected, we recommend that you do not wait for the consequences, but contact the dentist. Correct diagnosis ensures the necessary treatment and recovery in a short time. In the later stages, the dentist will not help. And treatment will cost much more.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
Diagnostics and x-ray of the temporomandibular joint
Diagnosis of TMJ when it is dysfunctional is difficult due to the variety of clinical complaints. This leads to the fact that the patient can undergo examination by different specialists for a long time, wasting time. A full examination is carried out by dentists
(primarily an orthopedist or orthodontist) and neurologists.
Diagnosis with the naked eye is difficult, and TMJ problems can only be directly noticed if the malocclusion is clearly visible. Most often, dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint is associated precisely with disorders of bite and jaw closure.
The most reliable and effective way is to conduct x-ray diagnostics and orthopantomogram
jaws. In some cases, an MRI may also be done.
Prevention
Based on what was written above, we can conclude that painful sensations when opening the mouth do not just arise. They are a manifestation of dangerous illnesses. To prevent this phenomenon from occurring, it is necessary to spend as much time as possible in the fresh air, exercise your jaw, and strengthen the immune system. It is also recommended to respond in a timely manner to disruptions in the body, even minor ones, and undergo preventive examinations from specialized specialists. As mentioned above, a crooked bite can cause pain when opening the mouth. Therefore, this pathology must be eliminated at an early age. The price of veneers is quite affordable, and their installation does not take much time and is carried out by experienced specialists in a dental office.
Treatment of the temporomandibular joint
Complex treatment of TMJ is possible only in dentistry, and is possible thanks to:
- surgery on the lower jaw;
- orthodontic treatment
(prescribing special trainers that will be worn at night and reduce pain by adjusting the load on the joint - the same trainers are recommended for bruxism) and bite correction with braces;
- orthopedic treatment
and
implantation
(insert a suitable prosthesis to restore the correct closure of the jaws).
Treatment is always prescribed individually, based on the results of an examination by an orthodontist, and is most often carried out comprehensively. It is dangerous to neglect TMJ diseases: this can lead to arthrosis, in which connective tissue grows in the joint cavity, which, in turn, threatens complete immobilization of the joint (ankylosis).
Severe pain and joint spasms can be relieved with compresses and painkillers; Stresses that provoke tension in the joint can be relieved with sedatives, but all these are half measures that do not treat the root cause of the pain.
Self-help methods for diseases of the temporomandibular joint:
The following self-help methods may provide temporary pain relief:
- Moist Heat: Compressing with a hot pack or bottle wrapped in a warm, damp towel can improve chewing function and reduce pain. Be careful to avoid burns when using high temperature.
- Ice: Ice packs can reduce inflammation, numb pain, and promote healing. Do not place the ice pack directly on your skin. When using, wrap the bag with a clean cloth. Do not use the ice pack for more than 10-15 minutes.
- Diet - Soft Foods: Soft or mixed foods allow the jaw to rest temporarily. Remember to avoid hard, crunchy, and chewy* foods. Do not stretch your mouth when trying to bite off large pieces or the whole fruit.
- Over-the-counter analgesics: Over-the-counter (over-the-counter) analgesics are useful for temporarily reducing pain. Together with your doctor, carefully read the instructions for each medication before using it.
- Lower jaw exercises: Slow, gentle exercises of the lower jaw can help increase jaw mobility. Your doctor or physical therapist can evaluate your condition and suggest appropriate exercises based on your individual needs.
- Relaxation techniques (relaxation techniques): Relaxation can help combat the pain that accompanies TMJ dysfunction. Deep, slow breathing increases relaxation and reduces pain sensitivity.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and hold LEFT Ctrl and press Enter.
You can send no more than 5 messages in 30 minutes!
Liked? Tell your friends!
Diagnostics
Diagnosing TMJ disorders first involves taking a medical history, followed by a physical examination. The doctor applies light pressure on the side of the face where there is discomfort, on the masticatory muscle fibers. At the same time, the patient closes and opens his mouth. Popping or clicking sounds and jaw thrusting are analyzed. If indicated, an MRI may be prescribed. The procedure will show whether there are internal problems with the joint. If osteoarthritis is suspected, x-rays and CT scans can confirm the diagnosis.
Pain in the jaw joint when chewing and opening the mouth often occurs with infectious arthritis. Diagnosis is made by inserting a needle into the joint itself to collect fluid. This research method is called aspiration. The liquid is analyzed for the presence of pathogenic bacteria. Hypermobility and ankylosis are determined by the width of the mouth opening. Sometimes the patient is referred for polysomnography to determine sleep disorders. An orthopantomogram of the jaw plays an important role in the research process.
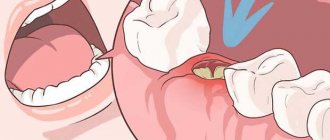
Why does wisdom tooth hurt?
Wisdom teeth almost always grow crooked. Problems with teething are dictated by the following anatomical features:
- “Eights” appear later than all other teeth. As a rule, the jaw bones are fully formed, the dentition is stable, and the “newbie” simply does not have enough space;
- The third molars do not have milk “predecessors”, and the rudiments of wisdom teeth developed for too long and not in very favorable conditions. Because of this, they erupt chaotically, damaging the adjacent tooth or causing inflammation of the gums.
When talking about the causes of pain associated with one or more molars, it is worth distinguishing between some concepts. Toothache can occur against the background of abnormal eruption, due to deformations of soft tissues of neighboring teeth. This clinical picture is typical only for “eights”; other teeth are cut much more smoothly.
Causes
However, the cause of toothache may also lie in fairly classic causes associated with common dental pathologies: caries, periodontal disease or periodontitis. If you systematize all the reasons that cause tooth pain, you will get the following list:
- The wisdom tooth rests too much on the tissues of the oral cavity, squeezing and injuring them;
- The tooth is rotated around its axis. The greater the angle of rotation, the more tense the dental nerve is, which provokes pain;
- Carious cavities have formed on the surface of the wisdom teeth; if they reach the dental tissues, the pain will intensify;
- Tartar deposits have formed, which rub the gums and cause inflammation;
- Due to the fact that the rapid growth of the “eight” and crooked eruption damaged the root system of the neighboring molar, it is this neighboring tooth that hurts;
- If the wisdom tooth, due to its incorrect position, begins to pinch the jaw nerve, pain occurs in the lower jaw. In this case, neuritis manifests itself in this way;
- A follicular cyst has formed at the neck of the tooth. It often occurs against the background of permanent damage to the gum tissue and the tooth itself.
It is worth noting the fact that a follicular cyst near wisdom teeth is often accompanied by all sorts of complications. For example, an abscess may occur that can even deform the jaw in a neglected state. The periodontal tissues may also become inflamed and pericoronitis may develop.
Inflammatory processes of the tissue covering the wisdom tooth
Inflammation of the hood is a common phenomenon. If a wisdom tooth erupts through several crown cusps at once, phenomena may occur when the chewing surface of the crown is partially covered by tissue. The part of the gum and mucous membrane that overhangs the molar and is called the hood. He is constantly susceptible to injury and prone to inflammation.
Under the surface of the hood, particularly favorable conditions arise for the accumulation of various biological “garbage” and the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. Often even the slightest damage causes irritation. The gums around the “eight” may not hurt much, so they don’t always turn to people with such a problem.
However, if the inflammatory process is severe, the tissues not only swell, but are also irritated. The patient complains of painful swallowing, sometimes it is difficult even to simply open his mouth. There may be pus and severe hyperemia on the gum near the wisdom tooth. Only a doctor can save you from such an obsessive and severe dental inflammation by excision of the hood.
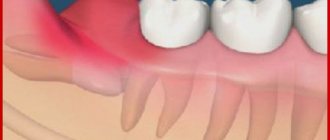
Lack of space during teething
If there is not enough space for the wisdom tooth in the dentition, neighboring tissues are injured during eruption. The pain is total. It hurts not only the place where the molar erupts, but also the neighboring teeth. Swelling, hyperemia, and severe pain that are permanent may also be observed. It is difficult for the patient to open his mouth, especially if the “eights” grow in the direction opposite to the jaw. Such teeth must be removed. This is due to the fact that a crooked tooth can damage the entire dentition, up to its noticeable curvature.
Caries
If a wisdom tooth is affected by caries, the first symptom indicating the disease will be pathological increased sensitivity of the teeth. They will react painfully to any irritants - sour, spicy, salty foods, sweets, cold irritants.
Situations often occur when the curvature of a wisdom tooth injures the neighboring tooth, which causes caries in it. The most dangerous situation is when the “eight” damages the root of the neighboring “seven”. Caries develops just below the gum, and the doctor is not always able to visually identify the carious lesion. At the same time, a severely advanced form of “root” caries is difficult to treat and the tooth can almost never be saved.
Pulpitis
In acute pulpitis that affects the wisdom tooth, patients complain of acute pain that occurs in attacks. The disease and its main manifestations are characterized by a spontaneous nature. Unpleasant sensations can occur spontaneously and last up to 15 - 30 minutes. At night the pain intensifies.
In the chronic form of wisdom tooth pulpitis, the pain is not so pronounced. Unpleasant, aching sensations occur against the background of exposure to cold or heat. If the irritant is removed, the pain continues for some time.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is characterized by aching pain that constantly worries the patient. At the same time, the diseased tooth will react to any irritant with acute pulsating, shooting pain. Slight mobility of the affected tooth is also noted, and swelling and soreness of the gums are often observed.
It is interesting that with chronic periodontitis the pain is almost not disturbing. Very minor unpleasant sensations can only appear when the “figure eight” is tapped on the patient’s tissues.
Possible causes of pain
Most often, the joints of the jaw hurt because the muscle fibers are strained and anatomical changes occur in the joint unit. The situation is aggravated by psychological reasons, sleep disorders, and emotional stress. In addition, provoking factors include:
- Bruxism, that is, grinding of crowns;
- Osteopenic disorders of the body;
- Genetic bone pathologies;
- The jaw joint near the ear hurts when an infection develops, the patient has suffered a neck or head injury;
- Muscle pain, internal disorders, tension;
- Ankylosis, arthritis, excessive mobility;
- Lack of chewing organs, unprofessional orthodontic treatment;
- Active conversation load;
- Pain in the jaw joint and radiates to the ear in patients with the habit of biting nails or placing the smartphone close to the hearing organ;
- Problems of the central nervous system, scoliosis and osteochondrosis of the spine;
- Pathologies of the endocrine system;
In addition, dysfunction occurs with asynchronous movements of the joints on both sides.