Increased sensitivity of teeth (hyperesthesia) is a short-term occurrence of pain under the influence of temperature, chemical or mechanical irritating factors. Usually occurs when drinking cold water, sour, sweet, salty, or touching with a toothbrush. The intensity of pain varies from mild to unbearable.
According to WHO, every second person in the world suffers from hypersensitivity. In Russia it is about the same: 45–65% of adults aged 20–55 years. More often women make complaints.
The effect of sugar on enamel
The product itself is not an aggressor and does not destroy surfaces. But when entering the oral cavity along with food, light carbohydrates create favorable conditions for the rapid growth of pathogenic microflora.
Bacteria, feeding on fructose and glucose, actively release waste products, including many aggressive acids. It is they that lead first to a decrease in the thickness of the protective layer, then to the destruction of the enamel and increased tooth sensitivity to sweets.
Medicines and alcohol
Some medications and all alcoholic drinks disrupt the water balance and cause dry mouth. The secretion of saliva decreases, it stops constantly washing the teeth, cleaning them and saturating the enamel with minerals. Dry mouth makes the gums vulnerable to injury and inflammation, which can lead to periodontal disease. Sweet alcoholic drinks are especially harmful: liqueurs, wines. Adding to the dryness when consuming them is the effect of sugar and acids. Red wine additionally stains the enamel.
Why does sensitivity increase?
Here's what the process looks like step by step:
- acids have a negative effect on the surface;
- the enamel becomes thinner and looser;
- cracks appear into which pathogenic microorganisms and food debris penetrate;
- As bacteria multiply, they move deeper into the tooth, exposing the nerve endings.
As a result of this chain, sensitivity increases and, as a result, hyperesthesia develops. Glucose itself, penetrating through microcracks, irritates the nerve roots in the pulp, causing pain. You can get rid of them only by rinsing your mouth with water, a decoction of herbs, or a special rinse as prescribed by your doctor.
Non-carious lesions
When your teeth hurt from sweets, the cause of the pain may not only be caries. Manifestations occur both with local pathology and with the following deviations from the norm:
- calcium deficiency;
- insufficient intake of vitamins B and D3.
These substances are directly involved in the absorption of glucose. And with existing hypovitaminosis, the body compensates for the lack of useful compounds by leaching calcium from bones and dental tissue, weakening them and increasing destruction. This happens due to poor nutrition, an irrational menu that lacks the necessary substances.
The tooth reacts and begins to ache from sweets, what else could this mean? Discomfort appears as a result of the following problems.
- Incorrect bite, which increases surface friction. This gradually leads to the abrasion of the enamel and its thinning.
- Dentist mistakes during whitening or professional cleaning procedures.
- Attempts to change the color of the dentition at home using either improvised materials or special means without a doctor’s prescription.
- Too frequent use of a hard brush and aggressive cleaning, incorrectly selected toothpaste.
Why does eating sweets make your teeth hurt? Common somatic diseases can also provoke this sensation. Most often it is caused by pathologies of the nervous system, endocrine organs, gastrointestinal tract, and hormonal imbalance.
Significant discomfort appears when there are foods in the daily diet that can damage enamel. This occurs when consuming citrus fruits, pineapples and other fruits, marinades and pickles, and smoked foods, which contain a large amount of acids.
Carious causes
Caries is the most common reason why teeth hurt from sweets and cold. This pathological process exposes the nerve roots located in the pulp and allows glucose and fructose to penetrate inside, causing pain.
Hyperesthesia in this case can be divided into two types.
- Primary is when discomfort occurs at the site of a lesion that has not been treated before. Pain while eating may occur even in the absence of visible damage to the surface.
- Secondary – when the pathological process spreads beyond the previously treated area. In this case, hyperesthesia is detected in the presence of a filling.
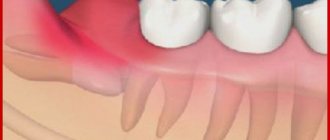
Periodontal diseases
If your gums hurt, then you should suspect the development of a disease in this group, especially if a doctor has previously removed the nerves. There are several pathologies.
- Gingivitis is an inflammatory process of the oral mucosa.
- Periodontal disease is a violation of the blood supply, as a result of which the tissues atrophy, settle and expose the neck.
- Periodontitis is a serious disease of the supporting apparatus of the jaw. Deep pockets may form where food becomes trapped.
If a tooth under a crown reacts to sweets, what does this mean and what are the reasons? In this case, problems should be looked for in soft tissues, examining the area where pain occurs. Because under restoration, as a rule, the nerve endings have already been removed by the dentist. We recommend not to delay and consult a doctor as soon as possible and take an x-ray to exclude the development of a pathological process.
Gum pathologies very often cause hyperesthesia. Any inflammation leads to it - be it ulcers on the mucous membrane or serious illnesses, the presence of pockets or receding gums.
Injuries
Toothache from sweets can cause trauma.
- One-time damage to the masticatory apparatus - due to a blow to the jaw or a fall.
- Regular injury may be a consequence of eating too hard foods (for example, nuts, crackers), or having the habit of constantly gnawing something (pencils, nails).
The mechanism of development of hyperesthesia
With frequent consumption of sugar, the acidity in the oral cavity changes - from alkaline it becomes slightly acidic. A pH shift leads to the destruction of the surface layer of enamel; it is destroyed faster under mechanical stress; a network of small cracks is formed on the teeth, through which food molecules and microorganisms penetrate into the thickness of the dentin.
The mechanism of changes in acidity due to excessive consumption of glucose is associated with the activation of pathogenic bacteria - it is they who secrete acids that destroy the surface during their vital activity.
The thinner the enamel becomes, the more your teeth ache from sweets. As the pathology worsens, negative manifestations begin to arise from eating any food, react to hot, cool temperatures, and even to the air when talking.
Sweets
The main “enemies” of teeth are chewing candies and caramel. Pieces of toffee or other chewing candies can get stuck in the spaces between teeth, contacting the enamel for a long time, causing accelerated growth of bacteria. Caramel changes the composition of saliva if it is absorbed; it can cause tooth decay, chips, cracks if it is chewed.
Dried fruits are considered harmful sweets. They contain a lot of sugar, stick to teeth, and get stuck in the spaces between teeth.
The exception is dark chocolate, which is considered beneficial for teeth due to the content of polyphenols and flavonoids. They have antibacterial properties and slow down plaque formation.
Symptoms of sensitivity
At the beginning, hyperesthesia manifests itself as unpleasant sensations upon contact with food and drinks (too warm or cold). Minor discomfort rarely lasts long - it usually goes away on its own after 25-30 seconds, and immediately subsides when rinsed with water.
With severe damage to the enamel, teeth hurt quite a lot from sweets. There may be a feeling of aching, pulsation, or shooting. In some cases, it can be difficult to independently determine which unit is damaged (if there are no visible pathologies). This occurs due to large-scale thinning of the enamel - painful symptoms can spread to neighboring areas, even affecting healthy tissue.
Discomfort tends to occur in waves, weakening over time, creating a feeling of false recovery. But in the absence of adequate treatment, the pain always returns.
Roasted seeds and nuts
Fresh nuts and seeds can even be healthy, but when heated, most of the valuable substances are destroyed. Instead of vitamins, fatty acids, amino acids, harmful substances are formed. Particles of seeds and nuts can get stuck in the spaces between teeth, under the edge of the gums. If a person often gnaws on seeds, he injures and wears out the enamel on his teeth. Crunching hard nuts cannot be called useful either. If you cannot do without such snacks, it is better to cook them yourself, frying them so that they remain raw inside.
Types of hyperesthesia
Depending on the clinic, hypersensitivity can be classified into degrees:
- I – pain during sudden changes in temperature, when eating too hot or cold food;
- II – characterized by the appearance of a teeth reaction to sweet, salty or sour foods, as well as after minor temperature fluctuations;
- Stage III of hyperesthesia is manifested by severe pain, which occurs with any irritant - even with the movement of air during a conversation and touching the affected areas.
Increased sensitivity can be local - appear strictly at one point, or be widespread and affect individual areas of the jaw. In the latter case, the entire dentition is exposed to the disease.
Non-systemic reasons
- Exposure to food acids. They are rich in citrus fruits, cabbage of various varieties, radishes, sweet carbonated waters;
- Non-carious lesions of hard dental tissues. Enamel wears off quickly, especially if not properly cared for;
- Development of caries. It provokes erosion of dental tissues or wedge-shaped effects (V-shaped flaw);
- Mechanical tooth destruction. Occurs during strong impacts, bleaching, grinding for subsequent installation of crowns;
- Inflammation of soft dental tissues (pulpitis). The reason is the penetration of infections, mainly bacterial.
Diagnosis of hyperesthesia
If your teeth hurt from sweets, what should you do? It is imperative to conduct a high-quality examination, including in order to exclude serious diseases: pulpitis and periodontitis. This can only be done by a professional - therefore, you should not self-medicate, and if pathological symptoms occur, consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Dentists adhere to a certain algorithm.
- A visual inspection is carried out, during which significant enamel defects and chips may be detected.
- EDI (electroodontodiagnosis) is a research method that monitors the reaction to a directed electric current. Pathology should be suspected if the final value exceeds 2-6 microamps. But this technique only works on living pulp, and is considered not always reliable and already outdated.
- The cold test is a more common test used by dentists. During the study, the surface is exposed to cold or heat, in which the nerve endings react to the stimulus. The dentist evaluates the speed and severity of the reaction. The Freeze test is the most accessible, fastest, convenient and reliable method for determining the disease.
Treatment of hyperesthesia
When your teeth hurt after eating sweets, what should you do? The main thing is not to delay going to a specialist. You should not self-medicate, as this can aggravate the situation and lead to the development of complications.
The maximum that can be done before visiting a doctor to reduce pain is to take an anesthetic tablet and rinse your mouth with a rinse marked “for sensitive enamel”, a soda solution or sage decoction.
General treatment strategy
Only a doctor can determine which direction you should follow.
If you are asking the question: “Why do my teeth hurt when I eat sweets?”, then there are several approaches to restore the integrity of the enamel in the presence of microcracks.
- Remineralization.
- Physiotherapy.
- Application of fluoride varnish.
All of these methods are applicable when there is no significant defect. If there is caries, then it is subject to high-quality treatment. If there are problems with the gums, an appropriate therapeutic strategy is selected.
Remineralization
If the surface layer of enamel is partially destroyed, it is recommended to use special gels that contain a complex of minerals (fluorine and calcium).
If your teeth and gums hurt from sweets, but there is no caries, this is the best option to eliminate the problem. With regular application of remineralizing agents to damaged elements, microcracks are eliminated and sensitivity to external irritants is reduced.
Fluoridation
The procedure is carried out in two ways:
- Simple. It can be carried out when the enamel is slightly damaged. The bottom line is that a remineralizing mass is applied to the damaged parts and protective caps are put on top. The mixture is kept for 15 minutes, after which the oral cavity is treated. For more effective treatment, you need to undergo several such procedures.
- Complex fluoridation begins with professional cleaning, after which a special composition is applied intermittently.
What can you do at home?
What to do at home when your teeth react to sweets and hurt from chocolate?
- If you experience severe discomfort, you can take a tablet of any painkiller before going to the doctor.
- Use special gels and pastes, rinses that reduce hypersensitivity.
- Traditional methods are usually ineffective, but can temporarily relieve discomfort. These include rinsing the mouth with a decoction of oak bark, sage, and applying tea tree oil to problem areas.
It should be remembered that self-medication is not recommended. This may be a necessary measure while waiting for an appointment with a doctor. It is advisable to carry out all independent manipulations after consultation with a specialist.
Experts' opinion
The clinical effectiveness of Asepta products has been repeatedly proven by scientific research. For example, as part of a clinical study of the line of products conducted by Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor A.I. Grudyanov, the high effectiveness of the Asepta mouth rinse for moderate periodontitis was established.
Research conducted at the Kazan State Academy also determined that the use of preparations from the Asepta line (gels, balms, toothpastes, rinses) makes the treatment of chronic catarrhal gingivitis and other inflammations, mild and moderate chronic periodontitis, hyperesthesia of hard dental tissues more effective , which together significantly reduces the duration of treatment and increases the duration of remission in this category of patients.
Sources:
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic agents of the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (A.I. Grudyanov, I.Yu. Aleksandrovskaya, V.Yu. Korzunina) A.I. GRUDYANOV, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department I.Yu. ALEXANDROVSKAYA, Ph.D. V.Yu. KORZUNINA, asp. Department of Periodontology, Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow
- The use of drugs from the Asepta line in the complex treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (N.V. Berezina E.N. Silantyeva S.M. Krivonos, Kazan State Medical Academy. Kazan.) N.V. BEREZINA, E.N. SILANTIEVA, S.M. KRIVONOS Kazan State Medical Academy
- Report on the determination/confirmation of the preventive properties of personal oral hygiene products “ASEPTA PLUS” Remineralization doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pkFytNfE0NM
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xRPTq5y9YRQ
Sensitivity Prevention
To prevent the occurrence of hyperesthesia, it is important to pay due attention to regular hygiene procedures. After finishing meals, rinse your mouth thoroughly.
If your tooth hurts after eating something sweet, you need to undergo systematic preventive examinations at the dentist. If necessary, have it professionally cleaned - this will help avoid the formation of plaque and get rid of the stone.
Clean your teeth with the right toothpaste, containing the entire set of microelements. Choose brushes of medium hardness that do not injure your gums. Carefully remove food debris from between teeth using floss. Use a waterpik regularly.
Selection of paste for prevention
For hyperesthesia, it is important to choose the appropriate care designed for sensitive enamel. Such products are distinguished not only by more delicate cleansing, but also contain components that promote remineralization and reduce gum inflammation.
What parameters to pay attention to when choosing.
- When your teeth become clogged with sweets, choose products to cleanse your mouth that contain ingredients designed to reduce sensitivity - fluoride, strontium, zinc salts, hydroxyapatite, potassium chloride or nitrate, calcium carbonate and arginine.
- The product should have an abrasiveness no higher than 25-35 RDA (for example, for bleaching options this figure can reach 100-120).
Let's sum it up
Only a qualified doctor will be able to determine the tactics and scope of therapy, so you should not self-medicate. Timely medical intervention will help resolve problems and prevent the development of complications.
If your teeth hurt from sweets or react to heat or cold, then it is important to identify and eliminate the cause as quickly as possible. This may be a banal thinning of the enamel or lesions that require serious therapy. Visit the website dentika.ru and find out everything about modern dental care first-hand.
Caffeine
Drinks containing caffeine (any type of coffee, cola, energy drinks) provoke dehydration and slow down the absorption of vitamins and minerals (including calcium). They stain teeth, change the color of enamel, making it darker. Therefore, dentists at the Dentospas clinic do not recommend drinking coffee in large quantities.
Caffeine also has beneficial properties: it contains fluoride and has an antibacterial effect, but coffee drinks do more harm to teeth than good. You can replace coffee with chicory. For those who are used to drinking a lot of green tea, it is better to switch to herbal teas.
You have questions?
We will call you back within 30 seconds
+7