Periodontist
Fisenko
Marina Nikolaevna
47 years of experience
Dental surgeon of the highest category. Member of the International Federation of Dental Anesthesiology Societies IFDAS
Make an appointment
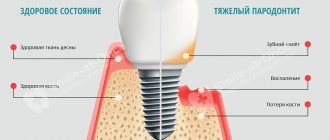
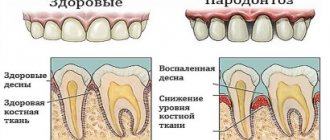
The complex of tissues surrounding the tooth and holding it in the alveolus is called periodontium. Accordingly, inflammation of these tissues in medicine is periodontitis. As this dental disease progresses, it destroys the ligaments of the tooth and the bone tissue of the jaw. Subsequently, the teeth begin to loosen and fall out, which can lead to abscesses and fistulas.
Causes
More often, periodontitis is diagnosed in middle age - 30-40 years, but today the disease is increasingly appearing in younger people, including those who have irregularly shaped teeth or bite. Pathology develops for several reasons. The main one is considered to be infection of the gums through:
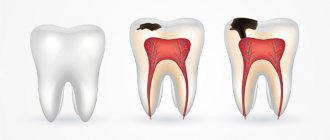
- dental tissues - as a result of caries or dental plaque, which leads to the formation of tartar;
- dental pockets - against the background of gingivitis (inflammation of the gums).
Gingivitis is considered an early stage of periodontitis, since inflammation gradually spreads from the dental pockets to other tissues. The source of infection may not be in the oral cavity. Sometimes periodontitis develops against the background of other internal inflammatory diseases. The following factors can contribute to the development of periodontitis:
- smoking;
- chewing tobacco;
- hereditary predisposition;
- long-term use of antidepressants, anti-inflammatory drugs;
- treatment with immunosuppressants or calcium channel blockers (cause gingival hyperplasia);
- injury to the gums due to physical impact
- unprofessional dental treatment;
- improper prosthetics;
- insufficient oral hygiene;
- diabetes;
- changes in hormonal levels during menopause, pregnancy, lactation;
- vitamin B or C deficiency.
The development of periodontitis is also promoted by constant eating too soft food. It impairs the process of self-cleaning of teeth. Another cause of periodontitis may be the habit of chewing on only one side, since this disrupts the uniform distribution of load on the teeth.
Features of the chronic course of the disease
The impetus for the development of chronic periodontitis can be gingivitis or other diseases of the oral cavity. Insufficient hygiene and neglect of treatment when the first signs of periodontal inflammation are detected are the most common causes of the development of the chronic form. It has two stages:
- An exacerbation in which constant throbbing pain, bleeding, and pus discharge are observed in the gums; abscesses form, pathological tooth mobility increases, body temperature rises, and the submandibular lymph nodes become inflamed. This often occurs against the background of acute respiratory viral infections, pneumonia, stress and other factors.
- Remission, which occurs after treatment. During this period, the main symptoms of the disease are absent and the patient does not experience severe discomfort.
Symptoms and signs
Periodontal inflammation is rarely accompanied by pain. More often the disease manifests itself in the form of swelling and redness of the gums. They may experience bleeding, and sometimes a local increase in temperature is observed. At an early stage, it is difficult to recognize the disease. Most patients go to the doctor with complaints of bleeding gums while brushing their teeth or eating.
If the disease is not treated, the gums subsequently begin to separate from the teeth, causing them to become longer. Significant gaps appear between the teeth. They fall out at a later stage of the disease. Other characteristic symptoms of periodontitis:
- bad breath;
- purulent discharge on the gums;
- chronic toothache;
- plaque on teeth;
- viscous saliva;
- increased gum sensitivity;
- yellow plaque on the root part of the enamel;
- sensation of pulsation in the gums.
These symptoms also affect the general condition of a person. Sometimes general weakness and headache appear, and the temperature rises.
Periodontitis. Causes and prevention.
Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease of the tissues that support the tooth. These include bone, gums, mucous membrane and adhesive layer. Thus, during the development of periodontitis, the supporting apparatus of the tooth is destroyed. It is for this reason that most people lose their native units ahead of time.
It is quite difficult to cure periodontitis.
Despite this, the process cannot be left to chance. Modern dentistry has enough innovative technologies in its arsenal to combat pathology. Causes
The etiology of periodontitis requires serious consideration by specialists. The method of treatment will depend on this. After all, the causes of periodontitis are quite diverse:
- The predominance of pathogenic bacteria in the microflora of the oral cavity. This happens due to poor hygiene.
- Diseases of internal organs (atherosclerosis, diseases of the digestive system, etc.).
- Pathologies in the development of the dentofacial apparatus (bad bite, position of units in a row).
- Errors in the work of a dentist (defects in fillings, crowns, bridges).
- Presence of predisposition.
The pathogenesis of periodontitis is such that any of the listed factors, together with a weakening of immune functions, leads to an inflammatory process.
Symptoms
Signs of periodontitis may change at different stages of its development. The first symptoms are expressed in the form of bleeding gums while brushing teeth and the addition of an unpleasant persistent bad breath.
Upon closer examination, the following symptoms can be detected:
- tartar and soft deposits above and below the gum;
- swelling of soft tissues;
- pale color of the gums due to impaired blood supply in them;
- unpleasant sensations (pain, burning, itching).
Symptoms of periodontitis in the initial stage are similar to those of gingivitis. However, in the deep layers the mechanism of pathological changes has already been launched. The formation of gum pockets filled with serous contents indicates that a person has developed dental periodontitis. If the disease is not treated, destruction of bone tissue leads to loss of stabilization of units in the row.
Kinds
The classification of periodontitis allows you to divide the disease based on the characteristics of its course. The disease comes in acute and chronic forms. These phases alternate, replacing one another:
- The acute form is characterized by a sudden onset. The most common type of periodontitis is localized periodontitis, which involves the tissue around one or more units. The generalized form, which affects almost the entire gum, is diagnosed less frequently.
- The chronic form occurs in most cases. The stages of periodontitis alternate between exacerbations and stages of remission. Most often, the disease results from gingivitis, covering the deep layers and spreading along the jaw row. Therefore, localized periodontitis in chronic form is extremely rare.
It is worth noting that if you consult a doctor in a timely manner during the acute course of the disease, in most cases you can achieve recovery.
There is also such a thing as purulent periodontitis. The disease is characterized by the release of exudate from the gum pocket. During therapy, doctors use all possible remedies for periodontitis: cleaning deposits, antiseptics, antibacterial tablets, ointments, hardware and surgical treatment.
Classification by severity
If the disease is not treated, the pathological process progresses. Periodontology has 3 stages of the disease. They differ in symptoms and treatment methods.
Mild periodontitis is diagnosed if:
- Only the gum papillae are affected;
- pocket depth no more than 4 mm;
- a small part of the bone tissue underwent resorption.
Moderate periodontitis:
- depth of gum pockets – 6 mm;
- the inflammatory process also extends to the edge of the gum;
- Symptoms include a strong odor, increased bleeding and cyanosis of the tissues.
Severe periodontitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- the alveolar part of the gum is inflamed;
- pockets reach 8 mm;
- Severe periodontitis is characterized by noticeable tooth mobility;
- The symptoms are accompanied by a noticeable pain syndrome, which often prevents cleaning with a brush and paste.
Depending on the location, the disease can interfere with proper chewing of food.
Diagnostics
Before starting gum treatment for periodontitis, an examination is carried out. An important step is measuring the depth of the pockets. The size of the gap formed between the gum and tooth is taken into account.
To determine periodontitis and the severity of inflammation, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- visual examination and questioning of the patient;
- clinical examination allows you to identify the type of pathological bacteria;
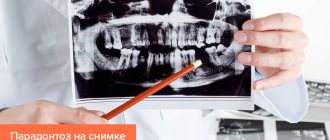
- instrumental sounding;
- X-ray examination.
Periodontitis in children is diagnosed much less frequently than in adult patients. The examination stages are carried out according to the same scheme.
Treatment
Treatment methods for periodontitis in modern clinics are quite varied. The choice of method to solve the problem depends on the clinical picture and individual characteristics of the patient. Mild gum periodontitis can be completely cured. In severe cases, doctors strive to achieve stable remission. Let's consider treatment methods:
- The medicinal method involves the use of antiseptics (Chlorophyllipt, Chlorhexidine, Rotocan). Antibacterial drugs fight pathogenic microflora (Levomethicin, Summed, Erythromycin). Be sure to prescribe a course of immunomodulators and vitamins.
- Ultrasound procedures using the Vector device are combined with medication. The medicine, together with radiation, destroys microbes and stimulates tissue regeneration.
- Surgery is recommended in difficult cases. The doctor performs curettage or flap surgery. Splinting is used to stabilize loose units. At this point, anesthesia is administered. After the operation, the doctor prescribes antibacterial drugs.
- Laser treatment is considered the most advanced method. The result is achieved due to a good cleansing and antibacterial effect.
Treatment of periodontitis in children is carried out practically as in adults:
- professional cleaning of deposits accumulated in the child;
- eliminating the cause of periodontitis;
- teaching children proper oral hygiene;
- prescription of rinses with anti-plaque effect;
- antiseptic rinsing solutions (Chlorhexidine, Givalex, Etonium);
- anti-inflammatory drugs (Traumwell, calendula tincture, Rotokan, Stomatofit).
If necessary, the doctor prescribes antibiotics, determines the dosage and duration of therapy.
Possible complications
Neglect of treating an inflammatory disease can provoke the development of other ailments. Let's consider possible complications:
- Periodontal abscess.
- Early tooth loss.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Endocrine disorders.
- Respiratory diseases.
- Various pathological processes during pregnancy.
Preventing the development of the inflammatory process in the oral cavity and its progression will preserve the health of the entire body.
Preventive measures
Following simple rules significantly reduces the risk of illness. Prevention of periodontitis consists of proper oral care and timely treatment of any dental diseases:
- Regular teeth cleaning.
- Correctly selected products
- personal hygiene.
- Healthy lifestyle.
- Balanced diet.
- Strengthening the immune system.
An important role in preventing all dental problems is played by the habit of going to the dentist once every six months for a preventive examination. You should have your teeth professionally cleaned of plaque at least twice a year. These simple rules will preserve the aesthetics of your smile for many years. After all, healthy gums that frame the teeth are no less important in this matter.
Oral hygiene in persons with periodontal diseases
The general principles of oral hygiene are the same as at a young age. But in case of periodontal diseases, it is necessary to pay much more attention to the individual selection of hygiene products and more carefully follow all stages and rules of oral care
Preventative manual toothbrush.
Preference is given to bristles of medium hardness (medium), but if there is a slight reaction of the teeth to cold/hot, sour/, sweet or other external irritants, you should use a “Soft” type brush. If there are wedge-shaped defects of significant depth, pathological abrasion of teeth, exposure of the necks and roots of teeth against the background of periodontal diseases and characterized by a pronounced pain reaction to external stimuli, it is necessary to use a “Sensitive” type brush. But in any case, it should have rounded and polished bristle tips, a multi-level brush field consisting of a power protrusion and an active recess, micro-textured bristles and an indication of the degree of wear. These are the main parameters that can significantly increase the cleaning efficiency of a toothbrush and transfer it from hygienic to preventive.
Therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste.
For periodontal diseases, it is recommended to use special-purpose toothpastes that have anti-inflammatory and astringent properties (due to extracts and/or oils of herbs and/or plants) and pronounced antimicrobial properties. First of all, preference is given to “herbal” pastes. With increased bleeding of the gums, pastes with pronounced astringent and hemostatic properties are needed. If the teeth have slight hypersensitivity, then you can limit yourself to a paste of the “Sensitive” type; if it is significant, you can use a paste with pronounced desensitivity properties, belonging to the “Oral - B Sensitive original” type.
Therapeutic and prophylactic mouth rinses.
It is advisable to use mouth rinses from the same brand and series as preventive toothpastes. For periodontal diseases, rinses are recommended that reduce the formation of dental plaque and have antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects.
Dental floss (floss).
With periodontal disease, over time, gaps appear between previously tightly standing teeth, and the gums do not adhere tightly to the surface of the tooth root (a periodontal pocket appears). All this makes it difficult to maintain oral hygiene using conventional means. Superfloss (ultrafloss) is an integral component of a hygiene kit for people with periodontal diseases. Due to the rigid guide, superfloss is inserted into the spaces between the teeth or periodontal pockets, and the loosened part most effectively collects and then removes plaque from the lateral surfaces of the teeth and underlying gums.
Special purpose toothbrushes.
Mono-beam toothbrushes are used to clean the cervical (near-gingival) areas of teeth, as well as the distal (far) surfaces of distant teeth or periodontal pockets. If periodontal pockets and interdental spaces are not sufficiently cleaned with a monotuft toothbrush, it is recommended to select a brush-brush, which come in various sizes and are more convenient for use in periodontal pockets.
Oral deodorants.
Oral deodorants can be used during the day if mouth rinses are not possible.
Oral irrigators.
Oral irrigators are compact devices that can be used to wash away food debris and plaque from hard-to-reach areas, such as periodontal pockets, with a stream of water or antiseptic. They are very effective for washing away food debris in the “jet” mode and massaging the gums in the “shower” mode. Jet - before starting hygiene procedures; shower at the end.
Stages
During the course of the disease, there are three main stages, which differ in the nature and severity of symptoms. These are the next stages.
- First. Periodontal pockets are still shallow - up to 3 mm. Periodically, after brushing, bleeding gums are noted. It is not accompanied by pain or loosening of teeth.
- Second. The depth of the pockets increases to 5 mm, due to which the neck of the tooth is partially exposed. Hypersensitivity also occurs when eating hot or cold foods.
- Third. This stage, with a non-aggressive course of the disease, develops approximately 4-5 years after the onset of inflammation. In severe cases, the dental pockets deepen up to 6 mm. Food debris accumulates in them, which leads to suppuration. This causes the teeth to become very loose.
Classification and forms of periodontitis
Before starting treatment for periodontitis, the dentist conducts a diagnosis, the purpose of which is to determine the form and stage of the pathology. Based on the study of the characteristics of the course of the disease, the following types of periodontitis are distinguished:
Acute stage of periodontitis: this stage is characterized by the rapid development of foci of infection, which in a short period of time can lead to serious complications. The gums begin to bleed heavily, and acute painful sensations appear when pressing on areas of inflammation, brushing teeth, or eating hard foods.
Within a very short time (several days), periodontitis can lead to the rapid formation of significant abscesses and the subsequent formation of fistulas.
Chronic form of periodontitis: when periodontitis is chronic, the pathology usually does not manifest itself with such pronounced symptoms as in acute cases. The patient may not experience any discomfort or experience minor discomfort, but this fact does not mean that the inflammatory process does not occur and does not develop.
Degree of tooth mobility
With periodontitis, teeth gradually become loose. Depending on their mobility, there are 4 degrees of the disease:
- 1st degree, when the tooth moves no more than 1 mm to the adjacent tooth, in the bucco-lingual and vestibulo-oral directions;
- 2 degree, in which mobility is observed in the same directions as in the first degree, but only by more than 1 mm;
- 3rd degree. Teeth become mobile in any direction, including vertical;
- 4th degree. Mobility is observed in all directions, and the tooth can even rotate around its axis.
Forecast and preventive measures
If treatment is started in the early stages of the pathology, this leads to remission and the possibility of its extension. In restoration measures and in the process of preserving tissue functions, compliance with recommendations related to the implementation of preventive measures plays an important role. If the disease is advanced, the prognosis is unfavorable. This may be due not only to the loss of almost all teeth, but also to the fact that severe systemic complications will begin to develop, especially in the cardiovascular system.
The preventive complex involves compliance with a number of care and hygiene measures:
- timely brushing of teeth;
- a competent choice of cleaning products and tools - toothpastes, powders, brushes, threads;
- regular implementation of professional hygiene;
- timely treatment of emerging diseases;
- removal of deposits from the teeth;
- carrying out treatment of concomitant pathologies.
With these simple measures you can prevent illness and feel great.
Thus, generalized periodontitis is a serious disease that tends to constantly develop and progress. In this regard, it is necessary to diagnose it in a timely manner and take therapeutic measures. This approach will prevent complications and keep all teeth normal, eliminating unpleasant symptoms and improving the patient’s well-being.
The roots of the teeth are exposed - what to do and how to treat them
Laser gingivectomy in the area of one tooth
Open and closed curettage of periodontal pockets
Catarrhal and hypertrophic gingivitis symptoms and treatment in adults
Splinting teeth for periodontitis with fiberglass and tape
Treatment of generalized moderate and severe periodontitis
Diagnostics
The first stage of diagnosis is an external examination of the oral cavity. The specialist performs probing (periodontal test) - a procedure that will determine the depth of the formed dental pocket. This is necessary to establish the severity of periodontitis. Additionally, the following studies are prescribed:
- benzidine test. Allows you to identify pus in periodontal pockets without performing a microscopic examination. To do this, turunda soaked in a solution consisting of benzidine, acetic acid and polyethylene glycol is inserted into the pocket. If there is no pus, then the color of the turunda does not change, but if it is present, it becomes blue, green or bluish-green;
- Schiller-Pisarev test. It is aimed at identifying glycogen in the gums, a substance whose amount increases sharply during inflammation. The gums are lubricated with a modified Lugol's solution, after which the color is assessed. It changes from light brown to dark brown;
- radiography. In the image, the specialist determines how much the bone tissue is affected by the pathological process;
- swab from a dental pocket. The study is carried out to determine the causative agent of the disease that caused the inflammatory process;
- panoramic tomography. This procedure allows you to get a complete view of the affected jaw. The study is often carried out if generalized periodontitis is suspected.
Stages of development of periodontitis. Localization of infection in periodontitis
Localized form of periodontitis: The onset of this type of periodontitis is usually caused by minor trauma to the mucosa. The localized form, in the absence of dental care, can progress to the next stage of the disease.
Generalized form of periodontitis: inflammation in the generalized form of the disease, inflammation develops along the entire length of the alveolar ridge. Experts in the field of periodontology argue that this form can quickly develop and become more complicated due to weakened immunity, for example, with a cold, hypothermia, infection with another infection, or self-medication with antibiotics.
Forms of periodontitis
According to the severity of periodontitis, there are: mild form, moderate form, severe form. At the beginning of the pathological process, slight bleeding, slight pain, and the formation of small periodontal pockets are observed. In the moderate form of the disease, large gaps appear in the periodontal pockets, and the teeth become mobile and loose. With the development of severe periodontitis, deformation of the interdental septa, decay of collagen fibers and root tissues are observed. Periodontal pockets become large, they contain purulent contents, and teeth fall out.
Treatment methods
The treatment regimen and effectiveness depend on the severity of the pathological process. First, measures are taken to improve the condition of the gums themselves. For this purpose, local therapy is carried out, which includes:
- curettage or ultrasonic teeth cleaning. The procedure is necessary to remove tartar - supra- and subgingival. Ultrasound can also polish tooth enamel, which helps prevent future tartar formation;
- use of local antibacterial drugs. They come in a variety of gels that help suppress the development of bacteria in periodontal pockets. Examples of such drugs: Apident Active, Metrogyl Dent, Adepta;
- the use of anesthetic gels, such as Kamistad, Mundizal. They help get rid of sore gums;
- rinsing the mouth and washing periodontal pockets with antiseptic solutions such as Chlorhexidine and Miramistin;
- the use of special toothpastes with anti-inflammatory properties. They complement the main treatment prescribed by the doctor. Experts often recommend pastes such as Parodontax, Splat Active, Elmex Sensitive, Asepta.
Local anti-inflammatory therapy lasts for at least 10 days. Treatment is carried out twice a day: morning and evening. In parallel with the removal of tartar, caries is treated and non-viable teeth are removed. Even at the stage of drawing up a treatment plan, a decision may be made about the need for prosthetics. In this case, doctors prepare for this process, including tooth removal.
Sanitation of periodontal pockets can also be carried out using laser treatment. The laser is directed deep into the gums, which allows you to destroy pathogenic microorganisms, prevent bleeding and sterilize the oral cavity. This technique also stimulates recovery processes.
The general strengthening treatment regimen also includes various types of physiotherapy:
- balneotherapy,
- phototherapy,
- peloidotherapy,
- gum massage,
- UHF therapy,
- darsonvalization,
- electrophoresis,
- diathermocoagulation.
Surgical intervention
When the depth of the periodontal pocket exceeds 5 mm, doctors decide on surgical treatment. In this case, a flap operation is performed - gingivectomy. It is carried out according to the following scheme:
- The gum is dissected, after which the gum flap in the area of the periodontal pocket is turned away.
- Next, the tooth root is cleaned and destroyed tissues and microorganisms are removed from the pocket.
- Then the tissues are washed with an antiseptic, after which the gum flap is returned to its place and sutures are applied.
The duration of the operation can be from 1 to 3 hours, it is performed under local anesthesia. During the process, the doctor can also straighten the bone tissue if inflammation has already spread to it. Depending on the nature of tissue damage, other operations may be performed:
- Gingivoplasty is a soft tissue transplantation. It is carried out when they are completely atrophied, when the tooth is completely exposed and visually becomes longer. To cover the defects, tissues from the palate are used. This helps stop the deepening of the periodontal pocket.
- Osteoplasty. It is carried out in case of destruction of bone tissue by inflammation, which can no longer hold the tooth in its place. During the operation, a graft made of bone tissue or synthetic material is used.
Another surgical method for treating periodontitis is splinting mobile teeth. This procedure allows you to keep them in place and save them from spontaneous removal. Splinting today is carried out in different ways:
- A horizontal bar and fiberglass tape are placed over several teeth. Then everything is filled with a light composite, as a result of which the dentition is connected.
- On the teeth, the upper part of which is previously ground down, crowns are put on, welded together.
- A clasp prosthesis is placed on the jaw, which allows you to evenly distribute the load on both the teeth and gums, and when installed on the upper row, on the upper palate.
Indications
Vitamins A and C are especially important for patients with periodontitis. It is necessary to include more fruits, vegetables and herbs in the diet. At an early stage, when the teeth are not yet loosened, you can eat the fruits in solid form. This will ensure the necessary load on the dental system. It is necessary to chew on both sides, and not just one, so that all areas of the teeth work actively. It is useful to include the following products in the menu:
- seafood;
- apples;
- Bell pepper;
- avocado;
- dill, parsley;
- black currant berries;
- carrot;
- peanut;
- citrus.
The diet must include dairy products, which are a source of calcium. The patient needs to consume more milk, sour cream, cottage cheese, and different types of cheese. Vitamin A, which promotes epithelial regeneration, is found in pork and beef liver, pumpkin, apricots, broccoli and spinach. Zinc, which is present in lentils, peas, and seafood, is useful for bone tissue. If you have periodontal disease, it is better to drink green tea or natural juices.
What to do to avoid complications
To avoid complications, it is necessary to recognize the disease in the early stages and take measures for adequate treatment. All this will allow you to achieve stable and long-term remission and preserve the functions of your teeth and gums. In order for the dental system to be healthy, it is necessary not only to observe the rules of personal hygiene, carrying out regular care procedures, but also to periodically visit a specialist who will perform professional cleaning in order to remove minor dental deposits.
General symptoms of the disease
In the initial stages, the patient suffers from severe bleeding gums. They become loose and swollen. The patient feels itching, throbbing, severe burning, pain when he chews food. An unpleasant odor begins to emanate from the mouth. Dental pockets at this stage are shallow, they are located mainly in the interdental spaces. At the initial stages, the teeth are motionless and not displaced anywhere. The patient's general condition is normal.
The clinical picture of the developing disease is somewhat different. In addition to the above symptoms, the patient may experience:
- displacement of teeth and their loosening;
- high sensitivity of teeth to external irritants (temperature fluctuations);
- problems chewing food;
- disturbance of general well-being (typical of severe forms of pathology), accompanied by weakness, malaise, and increased body temperature;
- an increase in the size of regional lymph nodes, which in addition become painful;
- during a dental examination, the doctor observes signs of diffuse gingivitis;
- Plaque and deposits accumulate abundantly on the teeth;
- tooth loss, fistula, abscesses (signs are characteristic of advanced stages of the disease).
In the case of a chronic form of the disease, the gums have a pale pink tint. There are no dental deposits, manifestations of pus or blood. There is a possibility of exposure of the roots of the teeth. X-ray does not show signs of bone resorption.
Advantages of treatment at JSC "Medicine"
By contacting JSC “Medicine” (clinic of Academician Roitberg), you can be sure that the examination will be carried out as completely as possible and exclusively using high-precision equipment. From the first contact to receiving test results, no more than a day passes. Also, each patient of the clinic is provided with:
- an accompanying person to move around the clinic;
- personal physician-supervisor who will monitor the progress of diagnostics and treatment processes;
- written recommendations regarding treatment and all necessary information regarding prescribed medications.
At the clinic of JSC "Medicine" you will not waste your personal time in line. Our medical center provides services at an international level of quality, and if controversial issues arise, the administration is always ready to consider any requests.