How inflammation begins
All about dental health
How to maintain beautiful healthy teeth? We tell you in detail: - how to brush your teeth correctly, - how to choose a toothbrush, - how to choose other devices for cleaning your teeth, - how to choose toothpaste, - how to preserve tooth enamel, - how to care for your first teeth, - how to use calcium for dental health. , - how sugar and other foods affect dental health, - how to use chewing gum correctly, - what are the misconceptions about dental health.
Gum inflammation, or
gingivitis
, is caused by bacteria that grow in plaque.
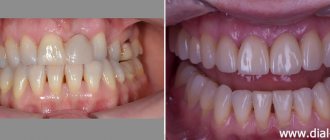
They penetrate under the gums and release enzymes and toxins. At the same time, the gums change color. It turns red if the inflammation is acute, or becomes bluish if the process has entered a chronic stage - and swells. However, the first sign of inflammation that you will notice on your own is bleeding gums
when brushing your teeth or eating solid foods.
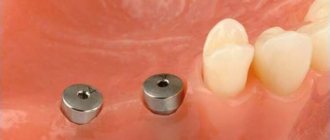
Condition of the gums at the orthopedic stage of implantation
Gingival contour formation and abutment
Before installing the prosthesis, it is necessary to install a former to create the correct gingival contour. Its fixation does not take much time (about 20 minutes) - an incision is made in the gum, the plug is unscrewed and the former is fixed under the influence of a local anesthetic. After a week or two, you can begin prosthetics.
After the former, an abutment is placed, which acts as a connecting link between the implant and the crown. It is selected individually and should protrude slightly beyond the gums.
Gum formation is an important point in dental implantation. It is he who will subsequently determine during prosthetics what the gums will look like after prosthetics in the smile area. A tight fit of the crown or prosthesis in the frontal and chewing area will prevent unwanted penetration of bacteria into the gap between the gum and the artificial tooth.
Stage of prosthetics on an installed implant
Prosthetics recreate the complete appearance of the dentition. The emphasis is placed not only on the natural appearance of artificial teeth, but also on their functionality. This is the stage of joint work between an implantologist and an orthopedist.
The crown is made individually based on pre-made impressions. Before final fixation, several fittings and adjustments are carried out. On average, this takes from 2 to 4 weeks. Fixation of the orthodontic structure depends on its type.
After installing a crown or denture, the gums should have a natural appearance. The design should not press, rub or cause discomfort. Otherwise, you need to consult a doctor.
See a doctor immediately
If your gums are bleeding, you need to see a dentist as soon as possible in order to begin treatment while the inflammation in the gums is still reversible. Without appropriate treatment, inflammation will progress and may progress to the next, more severe stage – periodontitis. This is the destruction of the bone tissue of the tooth socket and the formation of a periodontal pocket - the space between the tooth root and the gum. In this case, the tooth becomes mobile and, with significant bone destruction, falls out. By the way, periodontitis
is one of the most common causes of tooth loss.
How to avoid gum disease
- Visit your dentist
- at least twice a year.
A specialist will examine your oral cavity, teach you how to brush your teeth, select the hygiene products you need, and carry out professional removal of dental deposits - plaque and tartar. — Take regular and thorough oral care
: brush your teeth with a toothbrush and toothpaste, use dental floss and mouth rinses as recommended by your dentist.
— To prevent and treat
the early stages of gum inflammation, use toothpastes and rinses containing extracts of medicinal plants and essential vegetable oils.
Consult your dentist - he will select the most suitable products for you and tell you how to alternate them so that addiction does not occur. - Toothpastes and rinses with antiseptics
- chlorhexidine, triclosan, cetylpyridine chloride - are usually prescribed in the presence of inflammation.
The duration of the course of using these drugs is determined by the dentist. It is necessary to follow his recommendations to avoid negative effects on the normal microflora of the oral cavity and the appearance of dysbacteriosis. — Gum massage
helps improve blood circulation.
It can be done every time you brush your teeth - at the end of brushing, making light circular movements with the toothbrush with your teeth closed. — Hydromassage
of the gums can be done using irrigators - special devices that precisely deliver a stream of water or an antiseptic solution under pressure from 0.7 to 4.8 bar.
— Clean the interdental spaces very carefully
so as not to injure the gingival papillae located between the teeth. Chronic trauma from dental floss or toothpicks can cause changes in their contour and the formation of gaps between the teeth.
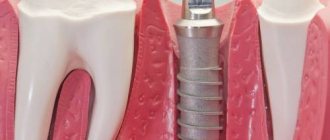
What happens to the gums during the surgical implantation stage
- Peeling of the mucoperiosteal flap. The area of gum where the implant is installed is cut and shifted to access the bone tissue.
- Preparing the bed for the implant. A narrow channel is drilled, the diameter of which does not exceed 2 mm. The bed is then gradually expanded with wider drills. To achieve maximum accuracy in parameters, a pre-prepared 3D template is used.
- Screwing in the titanium rod. A special tool is used for this. After the part is tightly fixed, it is closed on top with a plug that prevents gum tissue from growing into the internal hole of the implant.
- Stitching. All previously detached areas are returned to their place.
What it should normally look like during the healing process
The sutured gum looks inflamed for the first few days. Pain, swelling, bleeding, and hematoma may occur within a week. If symptoms do not go away after 5-7 days, you should contact an implantologist.
The duration of osseointegration of the artificial root with the jaw structures varies from two to six months. On the lower jaw it is completed faster than on the upper jaw. Stitches are removed on days 7-10.
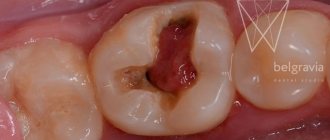
Possible complications
Bleeding, swelling, and pain are considered normal in the first days. If symptoms persist or increase, you should urgently visit a doctor.
- Hyperplasia. Rapid tissue growth in the surgical area. The pathology is eliminated by removing part of the mucosa.
- Fistulas, suppuration. The first sign of these unpleasant phenomena is white spots on the gums and plaque. Through them, the purulent contents come out. The inflammatory process can occur due to:
- violations of sterility during surgery;
- unqualified actions of a doctor;
- infectious foci in the vicinity of the operated area;
- injuries to the walls of the nasal sinuses;
- incorrectly selected prosthesis;
- neglect of the rules of oral hygiene.
- inflammatory processes;
- doctor's error;
- trauma to the implant area;
- deficiency of bone tissue volume;
- smoking;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases, emergence of new ones;
- development of an allergic reaction to the pin material.
Strict adherence to the implantation technique by the specialist and adherence to his recommendations by the patient minimize the risk of complications.
First aid for gum disease
At home, if it is not possible to immediately seek dental care, you can use the following recommendations:
- Solcoseryl dental paste will help cope with the symptoms of inflammation. When the product is applied to the operated area, pain is reduced and gum tissue is regenerated.
- Follow a diet. Spicy, hard, hot and cold foods fall into the restricted area. Food should have a liquid consistency to prevent chewing. Ideally, the food temperature should be as close as possible to body temperature.
You need to sleep on a high pillow so that your head is located higher relative to the level of your feet. This will ensure blood flow away from the inflamed area, which will reduce swelling.
Treatment of complications
Implantation is a complex procedure, and patients are often prescribed antibiotic therapy immediately after surgery. It is aimed at preventing the development of infectious processes. In addition, antiseptic wound-healing drugs are used.
Chlorhexidine 0.05%. An antiseptic with disinfecting properties is used for oral baths in the first days after installation of implants. The liquid is held on the side of the installed implant for 2-3 minutes and then spat out. Use the solution 4 times a day. For one bath, 15 ml of product is enough. 5 days after implantation, when the wound has healed, more active rinses can be used.
Betadine 10 % To relieve inflammation, dilute 3 drops of antiseptic liquid in 100 g of water. Oral baths are taken 4-6 times a day. The product stops the development of the infectious process, creates a protective shell, and restores damaged tissue.
Amoxiclav . The drug contains amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. Together, the substances inhibit bacteria and prevent their enzymatic action. Inflammation is relieved and healing of the gum surface damaged during implantation is accelerated.
Dexalgin . Anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drug with analgesic effect. The action lasts from 3 to 6 hours. The drug reduces swelling, normalizes temperature, and relieves pain.
Eat right
— Eat less foods rich in fast carbohydrates. These include flour products, sweets, and many fast food products. They contribute to increased plaque
and serve as a breeding ground for pathogenic bacteria that destroy teeth and gums.
- Include solid foods
- raw vegetables, hard fruits - that require intensive chewing, which leads to an increase in saliva flow and natural cleansing of the oral cavity.
It is advisable to eat hard vegetables and fruits after eating sweet, sticky and soft foods. — Include a sufficient amount of protein
for normal renewal of the mucous membrane of the mouth and gums.
— Avoid developing hypovitaminosis. After all, pathological changes in the gums most often develop with a deficiency of vitamins
A, C and D.
What happens if gum recession is not treated?
- root caries (the root, unlike the crown of the tooth, is not covered with enamel - a dense “pearl” shell, and therefore is more vulnerable). Normally, the root is covered by the gum and is not exposed to the aggressive environment of the oral cavity (acids, humidity, microorganisms, enzymes). With gum recession, the exposed root is susceptible to destruction.
- abrasion of root tissues (again, due to the lack of enamel, tooth root tissues are not resistant to abrasion).
- increased sensitivity of teeth.
- the transition of a recession to a class that is not subject to complete closure.
- more plaque (the surface of the root is rougher than the surface of the tooth crown, which means that plaque is retained more when the roots are exposed).
Large gum recession, caries of the exposed tooth root, an abundance of soft plaque on the root surface.