Posted by Marbery Gedrean | Checked by: Shteba Victoria Petrovna | Last revised: April 15, 2022.
Tooth enamel is the hardest tissue in the human body. Lost enamel is not restored. You can try to restore it using home methods, such as diet and the use of special pastes. These products are known as liquid artificial enamel, but their effectiveness is limited. In some cases, professional intervention may be required.
Causes of destruction of the enamel layer of teeth
Enamel is a mineral layer about 2 mm thick that covers the crown of the teeth.
97% consists of a crystalline substance of hydroxyapatite with small inclusions of calcium, fluorine, magnesium, and carbon. Performs a protective function, protects dentin and pulp from external influences. This is the hardest tissue in the human body; 1 square millimeter of its area can support 397.6 kg. But, nevertheless, even such a durable material can begin to deteriorate due to exposure to physical or chemical factors. The most common causes of enamel destruction:
- accumulation of plaque due to poor hygiene;
- exposure to concentrated acids contained in natural juices and carbonated drinks;
- unbalanced diet, large amounts of carbohydrates in the daily diet;
- mechanical injuries to the tooth crown with the formation of cracks and chips;
- bad habits of chewing pens and pencils;
- bite defects;
- wearing braces;
- abnormal abrasion of the enamel layer;
- bruxism (uncontrolled teeth grinding);
- sudden changes in temperature (for example, hot coffee after ice cream);
- diseases accompanied by leaching of calcium from the body (diabetes mellitus and other pathologies of the endocrine system);
- hereditary factor;
- stomach diseases in which the absorption of calcium and phosphorus is impaired;
- metabolic destabilization;
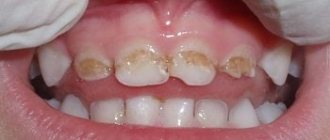
- caries;
- periodontal diseases;
- age-related tissue nutritional disorders.
Why is tooth enamel destroyed?
The destruction of tooth enamel may be a natural consequence of the patient’s age. People in the age group of fifty years and older very often complain of a decrease in the protective functions of enamel. This is a consequence of age-related changes in the body.
Enamel destruction can also be observed in pregnant women. In this case, this is a consequence of hormonal changes occurring in a woman’s body.
There are also slightly curious reasons for the destruction of the tooth surface. For example, when a person tries to crack a too-hard nut with his teeth (special tools are available for this) or demonstrate to friends how he can open glass bottles with his teeth. Such events are very dangerous because they can result not only in the destruction of the enamel, but also in the fact that the tooth can break or chip off.
How to determine when it’s time to restore enamel
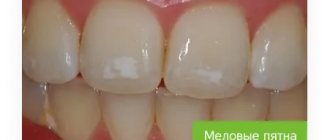
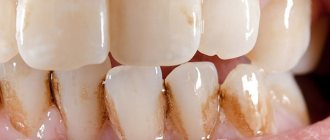
In order to preserve the integrity of the enamel layer as much as possible (or at least stop its destruction), it is very important not to miss the first signs of the pathological process. Its initial stages are characterized by demineralization of a local area of the tooth surface. It looks like a white, non-glossy spot. This clinical picture is called caries in the white spot stage. Another sign is the appearance of tooth sensitivity. Normally, a person does not feel the touch of the tongue on the teeth, there are no unpleasant sensations when chewing food. There is also no reaction when the teeth come into contact with cold, hot, sweet or sour foods. If any of the listed signs appear in the patient, this means that the enamel layer of his teeth has begun to gradually deteriorate. The following stages of enamel corrosion are visible to the naked eye. A local dark area forms on the surface of the tooth, then it begins to expand in area and go deeper into the dentin. These are signs of a serious defect. Correcting it will require more complex measures than when the first symptoms appear.
Important: a person cannot always independently see the stage of a white spot or a small black spot. Therefore, it is extremely important to visit your dentist for a checkup twice a year. Specialists from our network of clinics will be able to promptly detect an emerging defect and eliminate the damage with minimal intervention in the tooth structure (or without it at all). Our branches are equipped with modern equipment and instruments, including dental microscopes for diagnosis and treatment.
Myths about tooth enamel
Here are some common myths and misconceptions about tooth enamel.
The first myth is that enamel is destroyed very quickly. Actually this is not true. The process of enamel destruction is gradual and can last ten years. This is why proper prevention of tooth enamel destruction is so important.
The second myth is that tooth enamel is destroyed immediately on most of the teeth. This is also not true. It happens that one or more teeth suffer from enamel destruction more than the rest. This is a sign that inflammatory processes have begun inside the tooth and it is necessary to urgently contact a dental clinic.
The third myth is that enamel destruction is not a disease. In fact, damaged enamel is not only a cosmetic defect, as many people think. This is a disease, the progression of which can lead to complete destruction of all tooth tissues and subsequent loss.
The fourth myth is that enamel destruction can be diagnosed only by external signs (darkening of the tooth surface, the formation of pigment spots). This is not true. Symptoms such as an acute reaction of teeth to external irritants (cold, hot and cold food), as well as the presence of toothache (cutting or aching), indicate that your tooth enamel has been destroyed.
Restoration methods for the initial stage of destruction
Restoration of tooth enamel is the implementation of measures aimed at reconstructing the appearance of the enamel layer and restoring the protective functions it performs.
It is performed using various methods depending on the condition of the enamel. The earlier measures are taken, the better the effect. When initial symptoms appear, the following measures are effective:
- professional hardware teeth cleaning;
- remineralization – saturation of enamel with essential minerals, including fluoridation (coating teeth with a special varnish).
Note: it is impossible to restore enamel at home. The patient can only help the doctor. To do this, he must review his diet, carefully carry out hygienic dental care, eradicate bad habits, and begin treating systemic diseases (if any).
Restoration methods for serious enamel defects
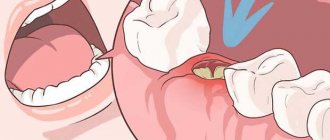
In cases where the enamel layer has undergone significant destruction, a set of measures consisting of two stages is indicated, the first of which is dental treatment of the damaged tooth. Only then will the dentist begin the actual restoration. This could be the application of artificial enamel, composite restoration or dentures. The methods listed above help stop decay, restore the appearance, and protect the inner layers of the tooth.
Relatively small defects can be eliminated by applying artificial enamel or composite reconstruction (the doctor uses special materials to recreate the shape of the tooth). More serious problems of the enamel layer are solved by installing microprostheses (veneers or lumineers). These are the thinnest pads that the orthopedist fixes to the vestibular surface. If the dental element is destroyed to a significant extent, then the doctor forms a stump and installs a crown on it.
Note: the choice of restoration option for the enamel layer is made by the dentist after diagnostics and identification of the extent of the damage.
Causes and consequences of damage to tooth enamel
- Bacterial fermentation of sugars produces various organic acids and lowers the pH in the mouth. This negatively affects the enamel.
- Enamel is damaged not only by acids of bacterial origin. This is a tissue that undergoes physiological, slow abrasion throughout a person’s life. The enamel is subjected to especially strong stress if a person has an incorrect bite or bruxism.
- There are often cases of defects in the enamel due to partial dissolution by acids from food, the working environment or the body. What does it mean? People who consume large amounts of fruits and fruit juices, sports drinks, and energy drinks are most susceptible to this process. People working in industry (due to acids generated in the work environment) and people swimming in swimming pools (due to the effects of chlorine added to the water). The defect also appears in people with recurrent vomiting and gastrointestinal reflux (due to stomach acid affecting the teeth).
Prevention measures
- Careful hygiene at home - at least twice a day, every day
- Clinic visits for professional cleaning – once or twice a year
- Eating foods high in vitamins and minerals
- Reducing intake of high carbohydrate foods
- Avoiding carbonated sugary drinks
- Timely treatment of dental and periodontal diseases
The network of dental clinics “Smile” offers services for restoring tooth enamel. Contacting our specialists has a number of undeniable advantages:
- treatment by highly qualified doctors;
- compliance with treatment protocols that meet international standards;
- family and savings discounts;
- transparent pricing;
- Convenient work schedule: daily until 21:00 (Sunday until 16:00).
You can make an appointment at any of the branches of our clinic in Moscow, located within walking distance from metro stations:
- Art. Alekseevskaya (VDNKh district, etc. Mira), address: st. 3rd Mytishchiskaya house 3, building 2;
- Art. Shelepikha, address: Shelepikhinskaya embankment, address: building 34, building 1.
The high qualifications of our specialists and modern equipment allow us to solve the problem of restoring enamel at any stage of destruction. We guarantee the effectiveness of treatment and the safety of the methods used. Your health is in good hands!
Thin enamel
Enamel is highly durable and can withstand even high loads. Its main task is to protect the tooth from the effects of chemical agents, temperature changes, and pathogens that lead to the development of pathological processes in the oral cavity. Therefore, the thinning of tooth enamel creates the preconditions for dental diseases, the most common of which is caries.
Causes
The main causes of thin enamel are:
- abuse of sweets
: the presence of foods high in sugar in the daily diet increases acidity in the oral cavity, thereby creating favorable conditions for the contamination of the mucous membrane with pathogenic and opportunistic bacteria, the activity of which causes thinning of the enamel; - improper brushing of teeth
: the use of too hard brushes and pastes with aggressive whitening components gradually leads to the removal of mineral substances from the enamel, that is, its demineralization begins, as a result of which it becomes porous and loses its strength; - bruxism
: as a result of teeth grinding, which often occurs unconsciously and mainly at night, when the patient cannot control the activity of the masticatory muscles, the enamel wears down; - malocclusion
: the load placed on crooked teeth during chewing is not physiological, so increased tissue abrasion may occur in certain areas.
Bad habits play an important role, for example, biting nails, pencils, pens and other objects, as well as frequent drinking of alcoholic beverages and smoking, which change the composition of saliva and cause thinning of the enamel.
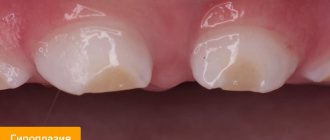
Clinical picture
Thin enamel has a characteristic clinical picture. Symptoms appear as the layer wears off:
- Initially, slight pain may occur when brushing your teeth, which is short-term and goes away on its own after completing hygiene procedures;
- then the teeth begin to react to chemical and thermal irritants, increased sensitivity appears when in contact with hot and hungry food and drinks;
- further thinning and destruction of the enamel is indicated by cracks and grooves located on the vestibular surface of the teeth, with a tendency to deepen.
If the described signs appear, it is recommended to seek help from a dentist to prevent further tooth decay and prevent oral diseases.
Treatment
After examining and sanitizing the oral cavity, the specialist prescribes treatment taking into account the cause of thin enamel:
- often, to protect the tooth, it is enough to carry out remineralization (therapy involves the application of special remineralizing gels, which contain minerals and trace elements necessary to restore tooth enamel);
- in case of severe thinning, treatment is prescribed using special filling materials, and the installation of veneers and crowns is also recommended to restore the integrity of the teeth.
If thin enamel is a consequence of pathological abrasion, therapy is aimed at eliminating the causes of its development. After which, depending on the clinical picture, the orthopedic doctor carries out treatment using microprostheses, bridges and other structures. If dental anomalies are detected, the help of an orthodontist is required, who will help correct the bite and restore the proper functioning of the temporomandibular joint.