Caries is the most common disease worldwide. Every person sooner or later experiences dental caries. The disease has several stages of development and at the initial stages of the pathological process it appears as a white spot. Treatment of caries in the stain stage can be treated therapeutically, that is, without preparing the tooth. There are several methods to stop the destruction of enamel and eliminate the lesion. In order to carry out treatment in a timely, painless and quick manner, it is necessary to undergo a preventive examination by a specialist every 6 months.
Causes of caries in the spot stage
There are quite a lot of theories about the occurrence of caries and the factors that cause the pathological process. Nowadays, experts adhere to the modern theory of origin. Under unfavorable conditions in the oral cavity, an acid-base imbalance occurs on the surface of the teeth. Dental deposits in the form of plaque and stone contain pathological microorganisms and food debris. Microbes process simple carbohydrates and release acids that damage the enamel structure.
At the spot stage, the enamel loses trace elements in the subsurface layer and the lesion looks like a white spot. In the absence of treatment and good hygiene, further tissue destruction occurs and a cavity forms in the tooth. In a chronic course, pigmentation of the spot may occur, then a defect appears in the form of a brown spot.
Factors that contribute to the occurrence of caries:
- Poor or insufficient hygienic care of the oral cavity. The accumulation of plaque on the dental surface is a favorable environment for the growth and development of pathological microorganisms. The infection causes various diseases of the oral cavity, negatively affects the body, and can cause exacerbation of chronic pathologies or decreased immunity. Dentists recommend regularly and thoroughly cleaning your teeth and tongue from plaque.
- Genetic predisposition. Some hereditary factors contribute to the development of the carious process: malocclusion, thickness and composition of saliva, thickness of enamel, etc.
- Disturbances in the process of formation of tooth germs. If during pregnancy there was insufficient intake of vitamins and minerals into the body of the mother and baby, then there is a risk of disruption of the normal process of formation of dental tissues. As a result, after teething, the baby’s teeth have a weak structure and are quickly susceptible to carious lesions.
- Diseases of the body. Some pathologies of the body can disrupt the composition and thickness of saliva. Oral fluid not only mechanically washes the teeth, but also participates in the process of enamel mineralization and neutralizes the effect of acids. In people with viscous saliva, the cariogenic situation in the oral cavity is often unfavorable; multiple dental lesions occur.
- Diseases of the salivary glands. Pathologies are accompanied by disturbances in the production, composition and functions of oral fluid and can, in combination with other factors, cause caries.
- Poor nutrition. An elementary lack of vitamins, minerals, and microelements in the diet can be the cause of pathology.
Superficial caries
Over time, a small spot on the enamel will increase in diameter, then the pathology will spread deeper into the tooth tissue, resulting in the formation of a carious cavity. There is a deepening at the level of the enamel, without damaging deeper tissues. This stage is no longer reversible and requires traditional treatment using a drill and subsequent restoration with a composite material (restoration).
Treatment of superficial caries
| Examination in a chair and carrying out diagnostic procedures (X-ray to assess the volume of the carious cavity); |
| Anesthesia, pain relief for the working field. For painless removal of carious tissues; |
| Selecting the color of the filling; |
| Installation of rubber dam: complete isolation of the tooth from saliva. Saliva is the richest environment in microbes and can cause poor adhesion of the filling and the development of recurrent caries; |
| Removing carious tissue with a drill: drilling, which in most cases causes fear in the patient, in this case will not last at all, because superficial caries usually affects small areas of enamel. Formation of a cavity for filling; |
| Drug treatment; |
| Drying the surface; |
| Restoring the natural shape of a tooth by filling. Installation of a light-curing filling; |
| Grinding and polishing the filling. Grinding and polishing the filling is not only mandatory, but an important step: the surface must be smooth, because a rough surface is a favorable environment for the accumulation of bacteria. Anatomically, the filling, completely replicating the tooth, should not cause any discomfort. |
Symptoms
The initial stage of the disease is characterized by mild symptoms. The patient is not bothered by pain. The lesion rarely causes discomfort, soreness or unpleasant sensations when eating too spicy, salty, sour, or sweet foods. In the acute course of the pathological process, the formation of a chalky spot occurs at the initial stage; in the chronic case, a brown, dark spot occurs.
Caries in the spot stage often causes an aesthetic defect, especially if the lesion is located on the front teeth. A white spot can be localized in any part of the tooth, but is most often observed in the cervical area. Caries in the stain stage can be located under dental plaque, so it is detected during professional hygiene and preventive examination.
Dental caries is...
Dental caries (lat. caries dentis) is a complex, slow-moving pathological process that occurs in the hard tissues of the tooth (dentin with a cavity, covered on the outside with enamel and cement). Dentin (lat. dentinum) is the hard tissue of the tooth, making up its bulk in the area of the crown, neck and root. The coronal part is covered with enamel, the root part of the dentin is covered with cement. Dentin in its structure is a crystallized material that contains 70% inorganic substances, 20% organic substances and 10% water.
Types of caries
Dental caries can be single or multiple depending on the number of teeth affected. There are different types of disease depending on the location of the lesion: cervical, approximal, fissure, contact. Depending on the course, the disease can be acute or chronic.
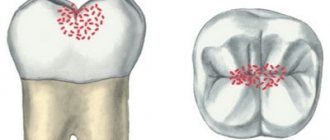
White spot
Caries at the white spot stage is an acute pathological process of tissue destruction, which is characterized by primary damage to the enamel. It is characterized by the progressive loss of minerals by the tissue, the formation of a chalky spot. Upon examination, the enamel appears white, dull, and is easily destroyed by various irritants.
The lesion can have different sizes, round or oval shape. If left untreated, the disease enters a chronic stage or progresses and becomes acute initial caries. In this case, the enamel is destroyed and a defect is formed in the form of a cavity (hole). It is very important to identify the disease in a timely manner and eliminate it, since at the stain stage the enamel can be restored naturally without filling.
Dark spot stage
Initial caries in a chronic course looks like a brown or dark (black) spot. With prolonged flow, pigments and dyes enter the subsurface layer of enamel, which stain the tissue. It is also possible to spread infection, microbial decay products into porous enamel. This contributes to the progression of the disease and complicates treatment.
Average caries
The upper layers of dentin are subject to carious lesions.
Dentin is a hard tissue that makes up the main part of the tooth, but its structure is still softer than that of enamel. Despite the fact that enamel is considered the hardest fabric, it is quite fragile and can crack.
Through these microcracks, bacteria penetrate into the dentin, where, on more fertile soil, they multiply much faster, which leads to the formation of a carious cavity.
In this case, on the surface of the tooth, upon visual inspection, the diameter of the lesion is small. But even a small dark point in depth can extend to the pulp (neurovascular bundle).
This stage is not the easiest, but with timely contact with a specialist and proper treatment, you can keep the tooth alive without removing the nerve.
There are two manifestations of average caries:
Chronic
It can last a long time and not show itself in any way.
Layers of dental tissue are gradually affected. Pathology can develop over several years. This is fraught with transition to a more advanced form, deep caries, and even threatens tooth depulpation and canal filling.
Spicy
Rapidly developing stage.
Perhaps an acute reaction to various irritants, which quickly passes after their removal. This form is characterized by an abundance of softened dentin on the walls and bottom of the tooth cavity with sharp and fragile edges.
Diagnostics
Diagnostics is an important stage of the examination, with the help of which the doctor will accurately diagnose and determine the treatment method for caries in the spot stage. The dentist conducts a clinical examination, probing, thermal diagnostics and various diagnostic tests.
When probing, a rough enamel surface is determined. Thermal tests are negative, that is, pain does not occur when exposed to cold or hot water. In some cases, radiography is performed to rule out periodontal disease.
Samples are necessary to differentiate caries in the spot stage from hypoplasia, fluorosis and other non-carious defects. Before using dyes, the tooth is cleaned and any dental deposits are removed. The enamel is dried and a special preparation is applied (methylene blue or red, tropeolin, carmine). The stage of caries development and the boundaries of its distribution are determined by the degree of staining of the defect. Non-carious defects are not stained with dyes, so the doctor excludes them.
Causes
Caries in the spot stage occurs for various reasons. Among them are:
- Inadequate diet
. Frequent, uncontrolled consumption of carbohydrates, fermented foods, and sugars provides an ideal environment for the growth of bacteria. - Lack of fluoride
. Practice shows that saturating water with fluoride reduces the number of infections. - Lack of vitamins
. Vitamins are involved in many chemical processes, including the mineralization of enamel. - Decreased immunity
. The body does not have enough resources to neutralize pathogens. - Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
. Belching and increased acidity disrupt the acid balance in the oral cavity. There is too much acid, it begins to destroy the enamel. - Insufficient oral care
. This is why tooth decay is so common in children and adolescents. They don’t have the patience to brush their teeth for 2 minutes, and kids don’t yet have the skills to do it correctly.
There are many other reasons, such as the thickness of saliva, impaired tissue formation, and structural features of the teeth, which also affect the incidence of caries. However, the main ones remain those listed above.
How is caries treated in the spot stage?
Treatment of caries at the white spot stage is carried out using several methods:
- Remineralizing therapy. The most popular and effective treatment method, which is carried out at the stage of only the white spot. It involves saturating the affected tissues with microelements and minerals through the application of medicinal substances. Procedures are carried out daily or every other day, the course consists of 10-15 procedures.
- Fluoridation. Treatment consists of saturating the enamel with fluorides, as well as other microelements. Fluorapatites are more durable than hydroxyapatites, thus strengthening the enamel.
- Silvering. The method involves impregnation of carious lesions with a special preparation. During the procedure, silver ions are released, which settle in the enamel and stop the destructive carious process. Currently, the method is used extremely rarely, since it is not able to eliminate caries and stains the teeth in a dark color.
- The Icon technique is the most modern technology that has many advantages. It consists of layer-by-layer application of several drugs to the white spot. The products eliminate the porous layer, remove germs and seal the enamel. In this way, the cavity is filled without the use of boron. The treatment is very effective, painless and simple.
- Grinding. If other methods are ineffective, sanding the stain, usually brown, is used. The dentist, using a special bur or brush, carefully removes the affected tissue, followed by a course of fluoridation and remineralization.
- Classic filling. If treatment with other methods is impossible, filling is used. To do this, the doctor uses a small bur to remove the destroyed tissue, and then restores the tooth with filling materials.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures. Physiotherapy procedures are used as complex therapy: electrophoresis and phonophoresis of calcium gluconate, phosphorus, sodium fluoride and other trace elements.
How is the treatment carried out?
Dental treatment consists of the following stages:
- Examination of the oral cavity, diseased tooth and collection of the patient’s medical history;
- Diagnostics, accurate diagnosis - clinical tests, x-ray diagnostics;
- Choosing the most appropriate treatment method;
- Professional teeth cleaning;
- Prescription of a course of applications, grinding or filling, depending on the method of treatment;
- Strengthening enamel and preventing hyperesthesia;
- Recommendations and advice to the patient after the procedure.
Remotherapy in the treatment of initial caries
Caries begins with demineralization of the enamel, the source of which is a white spot on the enamel. Remotherapy helps restore a healthy balance of minerals in tooth enamel. Remineralization is performed in two ways - application or using a mouthguard. In the first case, a special concentrated composition is simply applied to the teeth to restore mineral balance. In the second, the drug is fixed on the teeth using a sealed mouth guard made from an impression of the patient’s jaw. For remineralizing therapy, solutions of calcium gluconate, gels based on calcium phosphate and a number of other drugs are used.
The enamel remineralization method is effective at the early stage of the carious process. This procedure strengthens tooth enamel, normalizes its mineral composition, reduces sensitivity, and prevents further spread of caries.
Treatment at home
Some procedures to eliminate the disease can be performed at home. To do this, you need to visit a specialist who will carry out professional hygiene and prescribe procedures. Treatment of enamel caries in the stain stage can be carried out using professional means: toothpastes, gels, applications. Very popular and quite effective are remineralizing gels (TOOTH MOUSSE, ROCS Medical Mineral and others), medicated toothpastes with a high content of fluoride and calcium (ROCS Medical, Elmex, Biorepair).
The products are used for cleaning teeth, and also in the form of applications - applied to the required surface for 5-10 minutes daily for 1-2 weeks. The active components of the products penetrate into the lesion, promote its remineralization - restoration of the structure with mineral substances.
Self-treatment of caries without consulting a specialist is most often ineffective; the carious process does not stop and affects the underlying tissues. The therapy procedure is quite serious and requires precise, correct implementation of the dentist’s prescriptions.
The use of traditional medicine, unfortunately, will not help eliminate carious defects. There are no herbs or remedies that can stop the disease. Some traditional medicine recipes have an antiseptic, anti-inflammatory effect, and therefore can only improve the general health of the oral cavity.
Fissure sealing for the treatment and prevention of caries
Fissures are natural depressions, pits and grooves on the surface of chewing teeth. They are especially vulnerable to tooth decay for two reasons. They often accumulate food debris, which means that cariogenic bacteria actively multiply. Plus, the enamel in the fissure area is thinner and contains less minerals.
One of the most effective ways to prevent so-called fissure caries at an early stage is to seal the natural grooves. They are sealed using a special sealant containing fluoride and calcium. Minerals nourish the enamel, and food debris no longer accumulates in the recesses.
It is especially important to seal fissures in children and those patients whose natural grooves are too large and difficult to clean during daily care.
As part of complex therapy, other methods of treating initial caries can be used. In particular, ozone or laser therapy. The doctor decides which method will be safer and more effective for a particular person.
The main task of the patient is to visit the dentist regularly in order not to miss the moment of the onset of the carious process and to stop it at an early stage.
To prevent caries, it is necessary to monitor your diet, brush your teeth twice a day in compliance with all rules, and, if necessary and only as prescribed by your dentist, take fluoride or calcium-containing medications. Also preventing caries are measures to strengthen general immunity and giving up bad habits.
Prevention of caries
The main method of preventing the disease is maintaining regular and high-quality hygienic care for the oral cavity. You should brush your teeth 2-3 times a day using selected and suitable hygiene products. Experts also recommend:
- Clean the interdental spaces daily with floss (dental floss);
- After each meal, rinse the mouth; if impossible, use chewing gum;
- If you have dentures or orthodontic structures, use an irrigator;
- Adhere to a proper healthy diet that will fully cover the daily dose of vitamins and minerals;
- Carry out professional cleaning and preventive examination 2 times a year;
- Treat chronic diseases of the body;
- Increase immunity.
We can conclude that treatment of caries in the spot stage is relatively simple, affordable and absolutely painless. It is important to diagnose and eliminate the pathological process in time, and for this it is necessary to examine the dentition yourself and visit the dentist every 6 months for preventive purposes.
Deep caries
At this stage, the tooth is already beginning to react and send us SOS signals - sharp aching pain. True, they are also temporary and, unfortunately, patients can endure these moments or help themselves with painkillers, thereby delaying the trip to the doctor. This has never ended in anything positive. Medium caries that is not treated in time slowly and quite difficultly turns into deep caries. The rate of damage varies from compensated to decompensated, which in turn is more dangerous, because in a short period of time it can cover even two teeth.
It is important to prevent infection from entering the pulp chamber and to prevent complications - pulpitis and periodontitis.
There are two manifestations of deep caries:
Chronic
It proceeds quite slowly and may even be asymptomatic. It has a visually large area of damage, but often with less spread in depth.
Spicy
Rapid productive development, accompanied by pain and reaction to various irritants, sweet, hot or cold foods.
It may have a small visual affected area, but it goes deep and expands extensively downwards. This form usually develops into pulpitis and periodontitis.
Treatment of deep caries
The technique will be based on the depth of damage to the hard tissues of the tooth and assessment of the condition of the pulp.
If the pulp is not damaged (deep dentin caries):
Treatment is carried out as for superficial caries, but if the doctor needs to observe the tooth, a temporary filling is installed and the next visit is scheduled.
If the pulp is affected:
In this case, it will not be possible to do without removing the inflamed nerve.
The tooth becomes “lifeless”. Depulpation (removal of the nerve) of the tooth and thorough cleaning of its canals is carried out.
Our doctors strongly do not recommend completing treatment with a filling; the pulpless tooth is covered with a ceramic onlay or crown in order to prolong the life of the tooth as much as possible.
After treatment in both cases, the tooth may bother you for a couple of days. If there is discomfort in the tooth (not to mention prolonged pain), after treatment, seek a re-examination by a dental therapist; you may simply need a restoration correction according to your bite.
Stages of remineralizing therapy:
- Professional oral hygiene. I remove biofilm and tartar, grind and polish the enamel. After professional cleaning, less bacteria accumulate on a smooth surface, the risk of caries and gum inflammation is reduced, and your smile becomes beautiful.
- I treat the affected teeth with products containing active fluoride and calcium, choosing the drug depending on the depletion of the enamel.
- I give recommendations on the use of specialized toothpastes and fluoride-containing products.
- To assess the effectiveness of treatment and the quality of hygiene, I schedule an appointment after 2-3 months.
The good news is that early caries can be easily treated, and most importantly, without a drill. Without treatment, a cavity forms and the deep layers of dentin become infected. If you ignore this stage, pulpitis, periodontitis, and granuloma develop, which can lead to tooth loss. The more extensive the destruction of hard tissues, the more difficult and expensive the treatment; in extreme cases, the need for prosthetics and implantation arises.