6851
Increasingly, people turn to dental clinics with problems regarding the appearance of their teeth. Patients are concerned not only about changes in the shade of the enamel, but also about its deformation.
The main cause of such manifestations is considered to be dysplasia of enamel and dental tissues, which not only reduces the aesthetics of a smile, but can also lead to complete tooth destruction.
What it is?
Enamel dysplasia is a group of diseases of non-carious origin, characterized by abnormal development of dental tissue.
This pathology is congenital, developing during the intrauterine development of the fetus, or is provoked by genetic factors.
Abnormal tissue development begins during the formation of primordia. Symptoms of the disease are not age specific . They can appear both during the period of first teething and in adulthood.
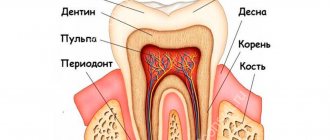
Dysplasia can affect the entire dentition, but is most often localized in its anterior section. Violation of integrity with the same intensity is observed in all segments of the tooth: cement, dentin, enamel.
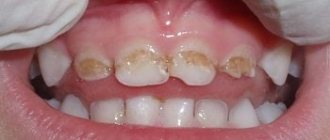
Photo: tooth enamel dysplasia in a child
How does it manifest?
This pathology has certain signs that allow it to be differentiated from other diseases affecting the enamel:
- change in the color of the enamel, which takes on a gray tint;
- thinning of the enamel, which results in increased tooth sensitivity;
- partial or complete absence of the enamel layer ;
- uncharacteristic shape of the cutting part, which includes many notches and chips;
- heterogeneity and surface deformation. Most often, longitudinal grooves and cracks are found on the enamel during visual inspection, and ribbing is detected during instrumental examination;
- the appearance of irregularly shaped white spots , which darken as the disease progresses. They first turn yellow and then turn brown;
- symmetrical arrangement of spots on the teeth of the same name in one jaw;
- surface uniformity in the spot area , here the enamel is dense and smooth, but over time it becomes dotted or grooved;
- the affected area is not stained with caries markers ;
- in the area of the pathological spot, tissue loss , leading to their gradual destruction;
- Pain syndrome may due to exposure to local irritating factors. Once the source is eliminated, the pain disappears.
Due to the disruption of dentin formation, the teeth take on an irregular shape: cone-shaped, barrel-shaped, pear-shaped.
Who is at risk?
Among the provoking factors are:
- late toxicosis or pathologies that caused a pronounced disturbance of metabolic processes during pregnancy;
- endocrine diseases (affecting metabolism) during the active growth of a child in the first years of his life;
- delayed reaction to taking certain medications;
- inappropriate living conditions;
- wrong approach to feeding a child.
What are the dangers for pregnant women?
During pregnancy, a woman's body experiences maximum stress. Decayed teeth, which are direct sources of infection, worsen the hard work of all systems not only of the mother, but also of the child.
Constant pain causes emotional stress and the release of certain hormones that affect the development of the psyche in children. Rotten crowns can lead to abnormal organ development, micronutrient deficiencies and poor fetal weight gain .
The main danger is that the products of decay of dental tissue stimulate the production of cytokines - substances that provoke contractions of the muscle tissue of the uterus and dilation of the cervical canal. This can cause destruction of the amniotic sac and premature birth.
That is why doctors insist on timely dental treatment. It is possible to eliminate pathologies that appear during pregnancy only during the second trimester.
But if an active or large-scale rotting process is detected, treatment can be carried out at an earlier date. Nowadays, for pain relief, pregnant women use such doses of effective drugs that cannot harm the fetus in any way.
Classification
When diagnosing pathology, the dentist relies on a certain classification, which distinguishes several types, depending on the area and nature of the localization.
There are:
- Root. The enamel surface is not damaged, but has a slight deviation in color.
Dentinal canals are present in small quantities, obliterated into the tooth cavity and have a crescent shape.The roots of the affected teeth are shortened and narrowed, which leads to their premature loss. The surface of the root part is dysplastic.
- Coronal .
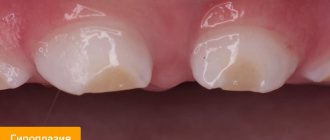
It is characterized by a change in the color of the enamel, which gradually acquires a yellow tint. In the area of the coronal part, pathological abrasion of the enamel is observed, which begins to expose dentin. Most often, pathological areas are located in the central part of the tooth or closer to its cutting surface. - Odontodysplasia .
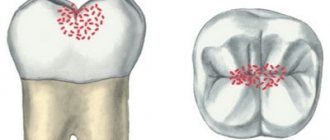
It is characterized by severe thinning of both enamel and dentin. Pathology can equally affect both temporary and permanent teeth. Most often, teeth are irregularly shaped and smaller in size. In some cases, denticles are found in the cavity.
Another 3 types are distinguished by the nature of enamel lesions:
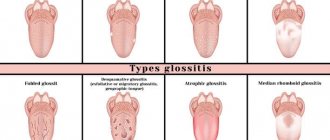
- Spotted .
It is expressed in the appearance of white round spots on any surface of the front and lateral incisors. The spots have clear boundaries and a shiny surface. Over time, it becomes rough. The thickness of the tissues of the affected area does not differ from the thickness of healthy enamel. In most cases, the spots do not change throughout life. - Erosive .
It is distinguished by cup-shaped or oval-shaped depressions formed as a result of damage to the enamel. The recesses are characterized by their overall width and depth. The bottom of the affected area is covered with thinned enamel, through which dentin is visible. Further development of the pathology leads to complete loss of enamel in the area of thinning. - Sulcata .
With this form of the disease, grooves are formed on the vestibular surfaces of the teeth. The groove is located parallel to the cutting part of the teeth. In the area of the furrow, the enamel is thinned or completely absent.
For those who should choose Pilot metal braces, read in a separate publication.
In this article we will talk about the causes of tooth enamel hypoplasia in children.
Here https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/okklyuzii/perekrestnyiy-prikus.html we will discuss whether braces are effective for crossbite.
Grooved shape
In this case, one or more grooves are formed on the vestibular (front) surface parallel to the cutting edge of the incisors. The depth of damage may vary. As a rule, teeth of the same name are affected symmetrically. As in the case of the erosive form, the anomaly can be seen on the radiograph even before the incisors erupt (horizontal lesions).
Here are some more types of hypoplasia:
- Linear - manifests itself in the form of numerous wavy stripes on the vestibular surface.
- Aplastic is a severe disorder characterized by severe damage to the enamel. Occurs in the case of amelogenesis imperfecta.
- X-ray examination does not reveal the disease.
- Mixed - most often we are talking about a combination of erosive and spotted forms.
Causes
three main factors that cause enamel dysplasia :
- Diseases of a hereditary nature .
Most often, they lead to darkening of the enamel and its thinning. Basically, pathology begins to appear in children already on their baby teeth. As a result of the pathological process, it becomes thinner over the entire surface, leading to dentin exposure. In hereditary diseases, tooth enamel is yellow immediately after eruption. - General diseases, occurring in an acute form, leading to disruption of the metabolic processes of mineral components.
As a rule, due to such reasons, dysplasia can be focal in nature and affect single specimens.This pathology is most often complicated by carious processes, which are characterized by rapid progression.
- Pathologies of the skeletal system , leading to disruption of the process of tooth formation due to a lack of bone-forming elements. Such diseases include rickets, periosteal dystrophy, marble disease.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of Stanton-Capdepont syndrome is based on anamnestic data, clinical examination and the results of additional research methods. During a physical examination, the dentist reveals gray, opalescent or brown pigmentation of the teeth. The shape of the teeth is correct.
The size of crowns in Stanton-Capdepont syndrome is within normal limits. The enamel is thin and fragile, quickly chips after eruption, exposing the dentin layer. Due to dentin staining, teeth become dark brown. As a result of increased abrasion, sharp edges are formed that injure the oral mucosa.
In Stanton-Capdepont syndrome, the pulp chambers are visible. X-rays reveal a decrease in the height of the roots, a narrowing of the tooth cavity, and obliteration of the root canals. Also, in patients with Stanton-Capdepont syndrome, periapical foci of bone tissue destruction are often detected radiographically.
Stanton-Capdepont syndrome is differentiated from other genetically determined malformations of hard dental tissues: amelogenesis imperfecta, types 1 and 3 of dentinogenesis imperfecta, dentin dysplasia. The examination is carried out by a dentist-therapist. To identify hereditary factors of the disease, genetic consultation is indicated.
Consequences
Almost all types of dysplasia are characterized by complications and serious consequences.
If left untreated, dysplasia leads to at least an aesthetic defect . In more complex cases, dentin is exposed and infections occur.
Such teeth are most often affected by caries, which quickly reaches the pulp chamber, provoking purulent inflammation. In this case, not only hard tissues, but also adjacent soft tissues can be damaged.
Teeth affected by dysplasia are fragile and susceptible to easy chipping, which disrupts their integrity and shape.
In most cases, without appropriate therapy, the pathology leads to complete destruction of the tooth or its severe loosening, which is an indication for removal.
Possible complications
In the early stages, the disease manifests itself in the form of small cosmetic defects without causing serious discomfort. If the spots are clearly visible, this indicates more intense destruction of the enamel. In the second case, treatment must be carried out as quickly as possible, since ignoring the problem can cause serious consequences, such as:
- Increased wear of incisors.
- Tissue destruction.
- Deformation and loss of damaged teeth.
- Development of malocclusions.
Remedies
Several types of methods are used to treat dysplasia. Some of them are corrective in nature, others are aimed at solving the problem by general strengthening of dental tissue .
Treatment methods are selected depending on the extent of the lesion and the intensity of the symptoms.
You will learn about the features of treatment of dentin dysplasia from our next review.
In the next article we will talk about the pros and cons of Clarity Sl self-ligating braces.
At this address https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/zubov/formyi/konicheskie-i-shilovidnye.html you will find information about the sequence of treatment for spiky teeth.
Therapeutic
This group includes treatments aimed at visually correcting the appearance of enamel .
The following methods are used for this:
- Composite restoration. It is used for small foci of dysplasia. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia with preparation of damaged areas.
After preparing the cavities and the surface of the tooth, it is treated with an adhesive agent and a light-curing composite is applied. Most often, Consize and Evicrol are used for this.These materials allow you to accurately convey the appearance and structure of healthy enamel. They are highly durable and do not stain over time.
- Veneers. For extensive lesions, it is recommended to install veneers. They are thin ceramic plates that accurately replicate the relief of the vestibular and incisal parts of the teeth.
Before fixing the veneers, a small grinding is carried out, which is necessary to visually reduce the volume. The overlays are installed using special glue or conventional composite.In appearance, they are no different from the surface of real teeth and protect thinned enamel from the aggressive effects of external factors.
- Prosthetics with crowns .
Used in cases of volumetric destruction. Either single crowns or bridges are used, which are made from individual casts.
For one of the methods for eliminating enamel damage, watch the video:
General strengthening
General restorative treatment is indicated for minor manifestations of dysplasia in the spot stage, characterized by gradual modification.
Therapy consists of remineralization and includes the use of the following drugs :
- klamin _ Used orally, 1 tablet per day for a month. The drug must be taken 20 minutes before meals.
- calcium glycerophosphate . Just like the previous remedy, it is indicated for use for 1 month. The product should be taken no more than 1.5 g per day;
- multivitamin complex, for example, Kvadevit or Complivit. Take no more than 2 tablets per day;
Also prescribed:
- electrophoresis with a solution of calcium glycerophosphate . Conduct at least 10 sessions 3 times a year;
- enamel treatment with sodium fluoride.
Preventive measures
Treating rotten teeth is not always a simple process. This often requires a long period of time. To avoid this, it is necessary to carry out the usual prevention, which consists of the following:
- Pay a lot of attention to oral hygiene. Teach your child to use special cleansers from early childhood. Don't forget that brushing your teeth twice a day is just the minimum requirement;
- Visiting the dentist should be carried out regularly, even in the absence of dental pathologies. Visits must be made at least once every six months;
- eat a balanced diet rich in nutrients;
- give up habits that are harmful to your body and an unhealthy lifestyle.
When the first spot of decay appears, contact your dentist. Only he will help you stop this process and qualitatively treat your teeth, which, with proper care, will last you a lifetime.
When are teeth actually rotten, and when are people mistaken and their problem is completely different? Watch the video:
Sources
- https://tvoyzubnoy.ru/bolezni-i-ih-lechenie/bolezni-zubov/displaziya-zubnoj-emali-u-detej.html
- https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/zubov/strukturyi-tverdyih-tkaney/displazija-emali.html
- https://zubovv.ru/lechenie/zubyi/karies/gnilyie-foto-etiologiya-terapiya.html
- https://spacream.ru/stomatologiya/prichiny-vozniknoveniya-displazii-emali-molochnyh-i-postoyannyh-zubov-u-detej-foto-i-lechenie
- https://www.adent.ru/displazija-zubov
- https://spas-dent.ru/zuby/plohie-zuby-u-detej-foto.html
- https://denta-da.ru/displaziya-zubnoy-emali-detey-prichiny/
Treatment of hypoplasia
There are several ways to treat this disease. In the initial stages, as a rule, conservative therapy is sufficient, the purpose of which is to eliminate metabolic problems. The method involves the use of vitamins and medicines containing minerals such as calcium, phosphorus and fluorine.
If we are talking about systemic hypoplasia with severe damage to the enamel coating, mineralization will not be enough. In this case, the doctors at the Nutcracker pediatric dentistry also use the whitening method. The essence of the technology is etching and grinding the enamel with a boron, as well as subsequent polishing. Whitening allows you to highly effectively eliminate dark spots and other defects on the outside of your teeth.
Prevention of fluorosis
The only possible way to prevent and prevent further development of fluorosis is to stop drinking water with a high fluoride content; in case of severe air pollution, move to another area. Fortunately, in Russia, only 2-3% of the population lives in areas where fluorosis is endemic (that is, in areas where the fluoride content in water can cause the development of fluorosis in children and adolescents). In the Leningrad region this is the Volkhov district.
make an appointment with a pediatric dentist online or by phone: +7(812)3310000