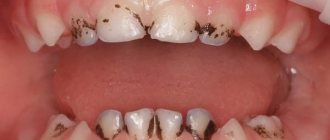
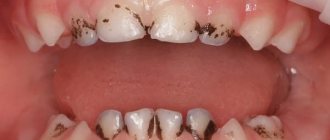
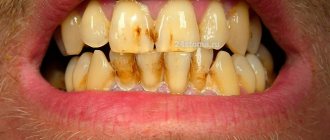
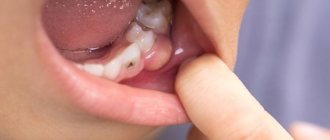
What is Priestley's plaque
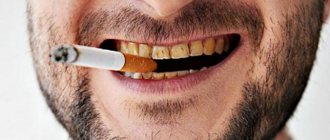
Plaque on baby teeth of a yellowish, black or brown color appears in a child when bacteria actively multiply in the oral cavity. Priestley's plaque is often seen at an early age, but can also occur in older children. When deposits appear, teeth lose their attractiveness, which can negatively affect the child’s psychological state. If symptoms of this unpleasant phenomenon develop, you should immediately contact your dentist to eliminate Priestley’s plaque in children.
Stages of plaque formation
Plaque on the teeth of children does not form immediately, but sequentially, going through several stages:
- Pellicle formation. This is an organic film of minimal thickness, the basis of which is the glycoprotein components that make up human saliva. This film is characterized by the absence of microorganisms in it.
- Precipitation of bacteria. Over time, the number of microorganisms consistently increases due to the appearance of new films, which in turn causes an increase in the thickness of deposits formed on the surface of the teeth.
- Actions of anaerobic agents. In air conditions, bacteria are active, resulting in the release of acid. This, in turn, affects tooth enamel, washing away minerals from it.
- Formation of an anaerobic environment. At this stage, the density of deposits increases to a state in which it is not possible to remove them with saliva or rinsing the mouth. The enamel is actively losing minerals.
The rate of formation of deposits on teeth is largely individual. It depends on the composition of saliva, the intensity of epithelium changes, a person’s tendency to inflammation, and so on.
Causes of black plaque in children
The main causes of black plaque on teeth are:
- Priestley plaque is the main cause of deposits. Growing up, the child gets rid of this problem, since plaque almost never settles on permanent teeth. This phenomenon does not harm health and is characterized as a purely aesthetic defect.
- Tooth decay is a serious disease that can lead to tooth loss. The carious process is accompanied by yellowing and subsequently blackening of the tooth enamel. When the first symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a dentist.
- Dysbacteriosis is a disease that leads to the appearance of dental plaque due to disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system. The causes of the disease are poor diet, long-term use of medications, chronic diseases affecting the liver or intestines.
- Oversaturation of the body with iron. Prescribing iron-containing medications to children leads to the formation of both black plaque and deposits that are dark purple or brown in color.
In addition, teeth can darken due to a lack of calcium in the body caused by some disease. In general, the exact cause will be revealed during an examination by a dentist.
Types of plaque
- White.
By the end of the day, all children have a small amount of harmless white residue. Abundant formation indicates vitamin deficiency, reduced immunity or insufficient hygiene. This type of plaque can be removed from a child’s teeth if you brush your teeth thoroughly every day. The presence of hard fruits and vegetables in the diet, such as apples and carrots, promotes mechanical cleaning. If no action is taken, the layer will harden, mineralize and turn into tartar.
- Yellow.
Indicates insufficient hygiene and poor nutrition. In children under two years of age, it can occur, for example, due to the consumption of sweet liquids from a bottle. It may also indicate the initial stage of caries. By choosing the right toothpaste and brush, as well as brushing your teeth more thoroughly, this problem can be solved.
- From light gray to green.
Gray - possible with abundant release of chlorophyll, sometimes acquires a greenish tint. Green - provoked by a fungus - chromogenic bacteria. Damages the pellicle, the natural protective film on the teeth. Only a dentist can help remove such plaque.
- Brown.
Indicates a fungal infection of the oral cavity and a disorder in the gastrointestinal tract. The result is darkening of the enamel. Iron supplements can also stain teeth brown. How to remove such plaque from a child’s teeth? Sometimes it goes away on its own after you stop taking iron-containing foods or medications. If the deposits have hardened, you will need professional teeth cleaning - ultrasound or chemical whitening. It is also necessary to adjust the child’s nutrition.
- Black.
Black plaque is the first harbinger of caries. Especially if it has a point character. In such cases, it is better not to postpone a visit to the dentist.
What does ignoring the problem lead to?
Failure to promptly contact a dentist when plaque appears on baby teeth leads to the following negative consequences:
- development of the inflammatory process;
- bleeding gums, which occurs if the child eats or brushes his teeth;
- the likelihood of developing diseases such as caries, stomatitis and periodontal disease increases;
- milk teeth with a black coating are very unaesthetic, which is fraught with the development of complexes in the child;
- deposits may be accompanied by bad breath.
A child has black teeth - what to do?
It is dangerous to ignore this symptom, since the pathology that caused it will develop further. In addition, plaque is a favorable environment for the active proliferation of bacteria, therefore increasing the risk of developing caries.
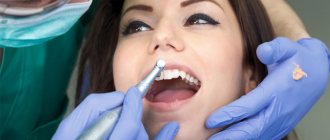
Diagnostics can take place in several stages. First, the dentist will examine the child's teeth for caries. If caries is excluded, examination using laser equipment and radiography are prescribed. You may need to consult with doctors of other specialties. In cases where no pathology is detected, plaque is simply removed during an ultrasound procedure.
Treatment depends on the cause of the black plaque. If a child is diagnosed with intestinal problems, he is prescribed medications that restore the balance of microflora and his diet is adjusted. If there is a lack of calcium and iron in the body, an appropriate diet is prescribed, including foods containing essential microelements. If caries develops, remineralization or filling is performed. It all depends on the stage of the carious lesion.
Preventing the reappearance of black plaque on teeth
Prevention of plaque formation includes:
- Regular dental and oral care. For babies, their gums are cleaned using cotton pads and special silicone tips. When the baby turns two years old, he needs to be taught to properly brush his teeth with a brush and toothpaste, as well as to regularly rinse after meals.
- Balanced diet. Your child's diet should include fewer sugar-laden foods and more natural fruits and a variety of vegetables.
- Timely limitation of the use of pacifiers and bottles. Long-term use of these items leads to the appearance of malocclusion, the development of a certain dependence, and the formation of so-called “bottle caries.” If a child can do without a pacifier and bottle, they should be disposed of.
In addition, you should constantly monitor the state of the child’s immune system and support it with the help of vitamins, which have a beneficial effect on the health of the teeth and the whole body. If you follow these simple recommendations, your child will always delight his parents with his beautiful and healthy smile.
Reasons why tartar forms
Local factors play a major role in the formation of tartar. For starters, this is poor oral hygiene in childhood. In addition, the cause of tartar is an insufficient intake of solid foods. Also, tartar in large quantities occurs as a result of the lack of pyrophosphate in saliva - a substance that retards the development of dental plaque and the lack of protein in it, which tends to slow down the growth of crystals. Tartar on children's teeth is not always obvious. Calcium phosphate crystals can bind tightly to the surface of the enamel, making it often difficult for the dentist to determine where the stone begins and the enamel ends.
Prevention
All pathologies require preventive manipulations that are aimed directly at removing plaque and strengthening the affected tooth enamel.
Preventive procedures.
- Professional teeth cleaning.
- Remineralization of enamel.
- Fluoridation of teeth.
The dentist consults with parents and the child to teach proper oral hygiene. The specialist also gives recommendations on the choice of dental care products. For general strengthening of the body and dental tissues in particular, a vitamin-mineral complex is prescribed.
All parents want their children to smile more often and have beautiful and healthy teeth. But sometimes a situation arises when the teeth are healthy, but they are covered with a dark and sometimes black plaque that cannot be cleaned off at home.
What are the reasons for the appearance of Priestley's plaque? And how to deal with it?
Let's start by answering the question: “What is a raid?”
Dental plaque is the accumulation in certain areas of the dentition of waste products of bacteria living in the oral cavity and the remains of consumed food. This layer is usually an inconspicuous white or yellowish color and is not of concern.
But sometimes the plaque stands out clearly against the background of the enamel. In children, plaque may be:
- yellow , which indicates poor oral hygiene and poor nutrition;
- light gray - the main cause of such plaque is hypoplasia of tooth enamel;
- greenish - observed in children aged 2 to 4 years, it is formed due to damage to the dental pellicle;
- brown - may appear due to the secretion of iron in saliva;
- black - this plaque is called “Priestley’s plaque”, the main reason for the appearance of this plaque is a change in the composition of the microflora of the oral cavity and gastrointestinal tract, as a result of which the number of pigment-forming bacteria increases, the waste products of which color the plaque black.
The main reasons for the “Priestley raid”:
— dysbacteriosis;
— taking vitamins and microelements containing iron and copper;
- climate change.
Sometimes the causes of black plaque can be a lack of calcium. This reason can only be determined through laboratory tests. Only after this can the doctor prescribe a course of treatment. You also shouldn’t forget about heredity. If the parents had the same black plaque in their childhood, then there is a chance that the baby will inherit this trait. Fortunately, such heredity is extremely rare.
The problem occurs quite often, especially over the age of two years, but sometimes blackening of teeth is observed even in one-year-old babies. First, the teeth acquire a yellowish color and then darken. The rate of formation of black plaque varies, sometimes it forms overnight, and the intensity of spread varies from staining one tooth to covering all teeth with dark plaque.
It is impossible to get rid of the “Priestley plaque” at home. Plaque can only be removed with professional hygienic cleaning in a dental office. This procedure is painless and is a great chance to introduce your child to the dentist. Such a visit will not leave negative impressions on the child. But it is important to remember that plaque may appear again, as it is a symptom of disorders in the gastrointestinal tract and the presence of other chronic diseases. Therefore, it is very important to conduct a comprehensive examination. Treatment of “Priestley’s plaque” should be carried out together with a pediatrician and gastroentorologist.
Prevention:
— It is recommended to start brushing your teeth as soon as they appear. For this purpose, there are special rubber brushes that are placed on an adult’s finger and the oral cavity is cleaned with gentle massaging movements. The teething baby takes part in the procedure with pleasure. After a year, you can clean with a children's toothpaste suitable for the baby's age.
— You cannot lick a baby’s pacifier, bottle, or spoon before these items are used by the baby.
— The first visit to the dentist should be made at 9 months, the next scheduled examination is carried out at 1 year.
— If there are no complaints, it is advisable to visit the dentist 2 times a year.
Regular visits to the dentist adapt the child to the office, professional equipment, build confidence in the doctor and reduce or completely eliminate fear and stress before visiting the doctor. Prevention will help keep your baby’s teeth healthy and beautiful!
Author of the article:
Lyutichenko Olesya Sergeevna
dentist at the Bobrenok Children's Dental Clinic.
What are the types of tartar?
Dentists distinguish two types of tartar – subgingival and supragingival. They are classified according to their location on the tooth surface. Supragingival can be easily seen with the naked eye, is whitish-yellow or gray in color and is easily removed by scraping. Minerals that come from saliva take part in its formation. The predominant localization of such a stone is the area of the buccal surfaces of the upper molars, where the ducts of the salivary glands and the frontal teeth of the lower jaw emerge.
The second type of tartar can only be detected by a dentist during probing. Its formation involves minerals that come mainly from gingival fluid. Most often, it has a dark brown color and a greenish tint, and is localized in most cases on the root cement, on the neck of the tooth (near the gingival groove) and on the root cement. The stone covers the neck of the tooth and is tightly attached to its surface; it can often form protrusions.
Provoking factors
The main reason why tartar forms in young children is poor oral hygiene. Even parents are not always able to thoroughly clean children’s teeth, so, as a rule, large plaque accumulates in hard-to-reach places.
The provoking factor may be:
- lack of solid food in the child’s daily diet;
- bite pathologies;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- gastrointestinal diseases.
It is not always possible to eliminate the provoking causes of tartar in a child, so dentists recommend that parents constantly monitor the quality of their teeth cleaning.