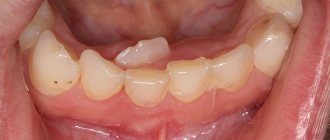
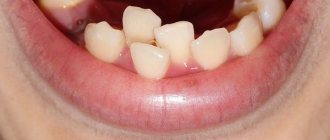
Fibrous pulpitis is one of the types of chronic pulpitis. Its characteristic feature is the excessive growth of connective tissue fibers in the tooth cavity, which ultimately leads to impaired blood supply to the pulp and its death.
Seeking professional help for chronic fibrous pulpitis on time is the key to restoring the appearance and functional characteristics of the tooth. At the same time, an advanced disease can lead to the death of the pulp and the spread of the inflammatory process to the periodontium.
It is worth noting that chronic fibrous pulpitis can develop as a result of the lack of treatment for acute pulpitis, and it can also be a primary process without an acute stage. It can appear and develop on both primary and permanent teeth. Treatment of fibrous pulpitis involves surgery.
Filling made of light-curing material for classes I and V - 2,000 rubles.
Filling made of light-curing material in classes II, III, IV - 3,000 rubles.
Placing a temporary filling - 400 rubles.
Resection of the root apex (frontal group) - 6,500 rubles.
Resection of the root apex (chewing group) - RUB 9,000.
Mechanical and medicinal treatment of canals for periodontitis (1 canal) - 1,100 rubles.
Closing perforations (MTA) - RUB 6,500.
At CELT you can get advice from a dental specialist.
- The cost of a dental consultation is 1,000
- The cost of an orthodontist consultation is 2,000
Make an appointment
Etiology of fibrous pulpitis
The reason for the development of the chronic form of the disease is the opening of the coronal dental cavity during acute fibrous pulpitis
. It is accompanied by the outflow of exudate and some relief for the patient, since the pain that arose during its accumulation will subside. This type of pulpitis is called secondary. As for the primary one, it is an independent form of this pathological condition and develops in a closed tooth cavity. The reasons are a violation of the technique for treating advanced caries (namely, incorrect treatment of the dental cavity, application of a medicinal lining, or mechanical damage to the tooth when opening the pulp chamber).
Treatment prognosis and disease prevention
Dentists at the CELT clinic give favorable prognoses for treatment that was carried out efficiently and on time. In any case, they take all measures to save the tooth.
In order to avoid this disease and keep the tooth healthy, it is necessary to undergo preventive examinations at the dentist every six months and not try to endure toothache. The earlier the disease is detected, the easier and faster it can be cured. Prevention measures also include maintaining oral hygiene. The dental department of the CELT clinic offers services for the treatment of the most complex cases of gangrenous pulpitis. Contact us and be healthy!
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Forms of fibrous pulpitis
There are two forms of fibrous pulpitis: acute and chronic. Most often, the second occurs as a result of the first; in addition, exacerbations of chronic fibrous pulpitis
.
The chronic form can be called compensation, in which fibrous transformation of the nerve of the tooth occurs with a minimal amount of exudate. The process is characterized by the proliferation of connective tissue fibers in the dental canal and a decrease in the sensitivity of the dental nerve. It arises as a result of the reactivity of the body, which tries to adapt to the ongoing processes by changes in the structure of the pulp. The latter does not disintegrate.
Inflammatory processes of the pulp during this period eliminate acute pain. Most often, this is facilitated by tooth destruction under the influence of carious processes, which creates an outflow of fluid through the hole. Despite the fact that the pain symptoms in the chronic form are not severe, the tooth requires immediate treatment. Very little time will pass - and part of the pulp will die, its necrosis will begin, and purulent inflammatory processes will spread to the tissue around the tooth root. Result? Envelopment of the periosteum, development of flux and (often) tooth extraction.
Pulpitis of permanent teeth in children
Pulpitis of permanent teeth in children is a common ailment among adolescents. Surprisingly, newly erupted molars are especially sensitive to external influences, because during the first few years they are not yet saturated with mineral components.
Pulpitis of permanent teeth in children most often develops against the background of deep or medium caries. And if in children with formed tooth roots, pulpitis develops in the same way as in adults, then in adolescents with just developing roots, this ailment is significantly different from what is usual for parents.
Clinical manifestations
Often this type of pulpitis is practically asymptomatic, which is why the patient does not immediately turn to the dentist. But for most cases the following is typical:
- heaviness in a sore tooth;
- pain reactions in response to irritants;
- nagging pain that intensifies when exposed to irritants and does not go away for a long time;
- bad breath due to poor hygiene;
- the presence of a deep carious cavity with softened dentin inside.
With an exacerbation of the chronic form, pain occurs spontaneously, intensifies at night and spreads to the entire jaw.
It is important to understand that fibrous pulpitis is often detected by a dentist during an examination. This happens when carious cavities are “hidden”: for example, located under the gum. In such places they are inaccessible to irritants, so the patient does not feel severe pain that would force him to seek professional help. One more point must be taken into account: if the carious cavity is combined with the tooth cavity, the patient does not feel such a specific symptom as heaviness in the tooth. Moreover: he does not feel any discomfort at all, and therefore does not seek treatment. And this is very bad, since the lack of treatment will lead to destruction of dental tissue, damage to the periosteum and the development of gumboil, the treatment of which often involves tooth extraction.
Why is pulpitis dangerous for a child?
If pulpitis is not treated in time, the inflammation very quickly turns into a purulent form, accompanied by general intoxication of the body. Inflammation spreads to the periodontal tissues and complications appear.
Complications of pulpitis of baby teeth can be:
- General intoxication of the body. Its symptoms are fever, weakness, headache, sleep disturbances, and refusal to eat.
- Enlargement of the submandibular and postauricular lymph nodes (lymphadenitis).
- Transition of the disease into a chronic course.
- Formation of fistulas on the gum next to the diseased tooth.
- Periodontitis is inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tooth that hold the tooth in the socket; periostitis (flux) is purulent inflammation of the periosteum.
- Sepsis is blood poisoning.
Diagnostics
Fibrous pulpitis must be differentiated from the following diseases:
- deep caries;
- acute focal pulpitis;
- chronic gangrenous pulpitis.
It is necessary to understand that only a qualified, experienced dentist can make a correct diagnosis after an examination and a series of diagnostic studies. Here are just a few signs that help distinguish one disease from another:
| Symptom | Caries | Focal pulpitis | Gangrenous pulpitis | Fibrous pulpitis |
| Pain | Short-term pain when exposed to irritants of different nature | Severe pain that lasts a long time even after the irritant is eliminated | Long-term painful symptoms of aching nature from irritants of different nature | Aching pain that is mild, moderate pain when exposed to irritants |
| Type of defect | Carious cavity with food fragments and softened dentin inside | Large and deep carious cavity with a large amount of dead dentin | Large and deep carious cavity with a large amount of dead dentin | A large carious cavity filled with destroyed dentin. Violation of the tightness of the dental cavity |
In order to correctly make a diagnosis, the dentist conducts a visual examination of the oral cavity, prescribes radiography and electroodontodiagnostics. The inspection reveals the following:
- severe pain when probing the tooth cavity;
- pulp bleeding;
- severe pain when percussing the tooth;
- reaction to a thermal test.
X-ray examination reveals the presence of communication between the carious and dental cavities, and sometimes the expansion of the periodontal gap.
Prevention of gangrenous pulpitis
Due to the fact that gangrenous pulpitis is a consequence of an acute inflammatory process, a mandatory condition for its prevention is a visit to the doctor for symptoms of pulp damage - the appearance of throbbing pain in the tooth. It is fair to note that a visit to a specialist must be made even before pain appears - it is important to treat caries in a timely manner, without waiting for it to reach the internal structures of the tooth.
In order to prevent gangrenous pulpitis, like any other form of it, it is important to be attentive to oral hygiene, visit a dental hygienist twice a year, and undergo professional teeth cleaning.
Reviews about our doctors
I would like to express my gratitude to the dentist Elena Nikolaevna Kiseleva and her assistant Svetlana - they are real specialists and at the same time sensitive, not burnt out by years of practice.
Thanks to them, I have been coming back here for many years. Thanks to the management for such doctors! Read full review Svetlana Nikolaevna
13.08.2021
I am very grateful to Evgeniy Borisovich Antiukhin for removing my three eights. Especially considering that the lower tooth was not the simplest (it was located in an embrace with a nerve). The removal took place in 2 stages, one tooth under local anesthesia, two under general anesthesia. I had no idea that wisdom teeth could be... Read full review
Sofia
28.12.2020
Treatment of fibrous pulpitis
As already mentioned, treatment of chronic fibrous pulpitis is carried out using surgical methods. It is aimed at eliminating the source of inflammation, preventing the spread of the disease and restoring the appearance and functionality of the tooth.
One of the methods of treating chronic fibrous pulpitis is vital extirpation, which is performed under local anesthesia. The procedure consists of several stages:
- removal of carious cavity tissues;
- carrying out treatment using antiseptic drugs;
- removal of pulp first from the coronal and then from the root part of the tooth;
- root canal filling;
- tooth filling.
All these manipulations require one visit to the dentist and are considered gentle and physiological. But if the patient has allergic reactions to local anesthetics or root canal obstruction, devital extirpation is required. It is carried out in two steps, in the first of which the pulp is opened and a special paste is applied to it, followed by the installation of a temporary filling. The second measures are carried out after 1–10 days and consist of removing dead pulp, filling canals and teeth. Experienced dentists at the CELT clinic treat fibrous pulpitis, achieving excellent results.
What symptoms indicate pulpitis of primary teeth?
The following will help you tell if your child has pulpitis:
Complaints about toothache
As a rule, it worsens in the evening and at night, as well as during the process of chewing food. There is almost always a reaction to cold or hot drinks. Painful sensations may occur when tapping the tooth. With an exacerbation of the inflammatory process, the pain becomes aching and constant.
However, it should be borne in mind that the rapid transition of the disease into a chronic form, characteristic of childhood, often leads to the disappearance of pain. Which does not mean there is no problem. And you should visit a doctor even if the tooth stops hurting.
Cheek swelling (swelling)
This symptom can often be found in photographs of pulpitis in baby teeth. However, it is not always observed. And, in addition, it can signal diseases such as periodontitis or periostitis. But pulpitis should not be ruled out. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis. And you may have to take an x-ray.
Increased body temperature and deterioration of general condition
If the child has a strong immune system, then a high temperature may also indicate the development of the disease. In this case, the body reacts to the inflammatory process that began in the pulp. And if there are no suspicions of other diseases accompanied by an increase in body temperature, be sure to show the child to the dentist.
If your baby has a toothache, or you observe any of the above symptoms, you should immediately visit a doctor. Perhaps it's time to start treating baby tooth pulpitis. In any case, there is definitely a reason to visit the dentist’s office.