Typically, the replacement of a child’s milk teeth with permanent ones occurs in two stages. At the age of 5-7 years, the primary incisors (four front teeth) change on the upper and lower jaws. Also at this age, the eruption of 6 permanent teeth (molars) occurs. They erupt without the baby teeth falling out. The second period of tooth change is the age of 10-12 years, when the canines and premolars (3, 4 and 5th teeth) change. For various reasons, a child may lose baby teeth before their natural replacement date. This may be the consequences of caries or injury.
Indications for removal of baby teeth
In the absence of pathologies and good dental health, the renewal of the child’s bite begins at approximately the age of 5-7 years. The permanent molars are already ready to replace the baby teeth, so the latter become mobile and often fall out on their own.
The ideal scenario makes everyone happy, but sometimes the removal (extraction) of baby teeth is an objective necessity. Indications are determined by the dentist:
- Loose baby teeth. The strong mobility of the changing tooth bothers the child. Unpleasant sensations occur when talking or eating. There is a danger of gum inflammation.
- Supernumerary tooth. An extra unit interferes with the formation of a correct bite, so after consultation with an orthodontist it is often recommended to be removed.
- Beginning of permanent molar tooth eruption. In this case, the baby tooth becomes a nuisance, which it is advisable to remove as soon as possible.
- Severe tooth decay due to deep caries, pulpitis or periodontitis. The dentist will make every effort to save the baby tooth, but in case of serious damage to the crown, there is only one solution - removal.
- Crack and mechanical damage. A crown split, root fracture and other consequences of severe trauma are a reason to remove the destroyed unit.
- Bite correction. To ensure the correct positioning of teeth in the jaw, it is often necessary to forcefully remove individual units. But this is done after consulting an orthodontist.
- Inflammatory processes in the area of the tooth root. Granuloma, fistula or cyst is a threat to the health of the root system of permanent elements. Usually, the doctors at AzaBuka Pediatric Dentistry manage to cure the inflammation. If not, removal is inevitable.
The reasons for the removal of temporary teeth can be very different, but modern pain relief techniques make the extraction procedure painless and comfortable for the child. It is best to schedule an adaptation visit as your first appointment. If the baby is already familiar with doctors, then you can immediately make an appointment with a dental surgeon.
Adaptation in dentistry is a series of introductory sessions for children, during which children are introduced to the work of dentists, equipment, and tools. Communication takes place in a fun, playful way with the display of informational cartoons, fairy tales, and interesting dental models. After adaptation techniques, children cease to be afraid of doctors and willingly agree to all types of treatment.
In the absence of lateral teeth
With the early removal of several lateral teeth, depending on the adaptation mechanism, the following may form: - deep bite: the height on the sides is lost, and the lower front teeth begin to reach the mucous membrane of the palate. At the same time, the face is visually shortened. - mesial bite: in the absence of lateral teeth, chewing will be transferred to the incisors - they will experience functional overload and wear out. The jaw will move forward, and in this position it will be fixed at the skeletal level. - open bite: in the absence of two or three teeth nearby, muscle balance is disturbed and so-called “bad habits” are formed: tongue protruding, cheeks sucking into the area of missing teeth. In the future, this will interfere with the eruption of permanent replacement teeth, leading to non-occlusion of these teeth. - Crossbite: Removing side teeth on one side will force the child to chew only on the opposite side. Such chewing will lead to a sideways displacement of the lower jaw, the formation of a crossbite and asymmetry of the face and temporomandibular joints.
Is it painful to remove a child's baby tooth? Anesthesia decides everything!
The question of tooth pain relief during extraction is the most frequently asked question by parents. The wishes of adults vary: some want extraction without medications, others insist on full anesthesia. AzaBuka provides several anesthesia methods for children, and when selecting, the doctor always focuses on the individual characteristics of young patients.
In rare cases, they do without pain relief. This is real if the baby tooth is very mobile, and its permanent replacement is already emerging through the gums. In this case, the doctor removes the tooth during an examination of the oral cavity, and the child does not even notice the manipulation. There is simply no point in worrying about whether it is painful to remove a baby tooth in children, but such techniques are rare.
Plaksina Margarita
“One young gentleman had his upper tooth so loose that it was turning in all directions. But it didn't fall out. The boy did not let his parents pull the tooth, but he allowed himself to be examined at the reception and quite willingly opened his mouth. Imagine his surprise when I put the pulled out tooth on his palm literally a minute later. He left happy - with a reward for courage and a milk tooth in his hand.”
Most often, dentists resort to local or thorough anesthesia - they use one of the types of modern anesthesia:
- Superficial. The doctor treats the gums with a special gel that gives a slight freeze. This is done for easy removal of highly mobile teeth or at the site of a future anesthetic injection.
- Local (infiltration). To administer the anesthetic, the doctor uses a syringe with a very thin needle, so the discomfort is minimal. The selection of the drug is carried out in the presence of parents to eliminate the minimal likelihood of an allergic reaction.
- Sedation, shallow sleep. The technique is becoming increasingly popular - both children and adults enjoy it equally. Using an inhalation mask, the child is offered to breathe a special gas - a mixture of nitrous oxide and oxygen. The relaxing effect puts the patient into a state of semi-sleep. The baby understands everything, can follow the doctor’s requests, but does not panic, is not nervous or worried.
The dangers of early absence of baby teeth
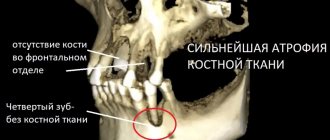
The dentition in children consists of a certain number of teeth, and if it is disrupted ahead of time, this can disrupt the formation of a correct bite. This happens because nearby milk teeth may shift to the place of the missing one, which means that the permanent teeth will begin to grow unevenly .
The absence of baby teeth complicates the process of chewing and biting food, and also makes it difficult for a child to develop correct sound production and diction.
In addition, the absence of a tooth does not look aesthetically pleasing and can lead to psychological problems for the child and low self-esteem.
General anesthesia.
Removal or treatment of teeth in a dream is prescribed for certain indications. The appointment is carried out under the supervision of an anesthesiologist with the mandatory use of monitoring equipment.
Dolotova Marina
“Is it painful to remove a baby tooth for a child under sedation - if it doesn’t wobble? Absolutely not. Usually during the appointment, the children watch cartoons while I carefully remove the tooth. And before that, we play superheroes with them and be sure to try on a real mask - a prototype of the Iron Man helmet!”
Function of primary teeth
Primary teeth are temporary structures in the body. The first very small teeth erupt 6 months after the baby is born, when his jaws are not yet fully formed. As a result, the baby’s feeding style changes – from sucking to chewing. Chewing movements promote the development of jaws and facial muscles. The correct proportional relationship between the parts of the facial skeleton is formed.
The bones under the roots of primary teeth undergo successive stages of maturation of their permanent counterparts. From the age of six, baby teeth begin to fall out and are replaced by larger permanent teeth. In the jaw bones, a synchronous process of resorption of milk roots and advancement of permanent teeth to the alveolar ridge occurs. The last chewing milk tooth falls out at 12-14 years of age.
Carrying out the procedure, simple tips
On the Internet you can find a lot of advice on removing temporary teeth, containing both descriptions of traditional methods and absurd proposals using improvised means. It is always important to think about the safety of the action for the child’s health and the possible consequences; it is better to give preference to one of the following two methods:
- use fingers and a handkerchief;
- apply thread.
Regardless of which manipulation it is decided to remove the milk duct, both participants in the procedure need preliminary preparation aimed at preventing infection. Before pulling out a baby tooth, an adult should thoroughly wash their hands with soap, and a child should rinse their mouth with warm water.
You can remove the milk jug like this: take a clean cloth, grab it and sharply pull it up if the tooth grows from the lower jaw or down if it grows from the upper jaw. This manipulation usually scares children, so they often resort to a more popular method. How to pull out a child's baby tooth using floss:
- Position the light source so that the oral cavity is well illuminated.
- Take a nylon thread about 30 cm long; tie one end to the loose tooth, making 4–5 turns around it; wrap the other around the index and middle fingers of an adult.
- Make a sharp movement with your hand, jerking your hand down if the milk duct grows on the upper jaw or upward for cases where the tooth is on the lower jaw.
Tooth extraction, if all conditions are met, takes no more than 5 minutes and is not accompanied by pain or other unpleasant sensations. Correctly performed manipulation does not leave the child afraid of the dentist and manipulations in the oral cavity.
Tips on how to pull out a tooth yourself correctly:
- position the thread so that it does not touch the lip, otherwise there is a risk of injury;
- do not use improvised means and tools;
- make sure the milk jug is ready to be removed.
If the tooth is well loosened, but the child is afraid to remove it with floss or fingers, and does not want to go to the doctor, you can give it an apple to chew on - solid food will cause the duct to fall out quickly and without pain.
Removal of molars during pregnancy
Let us say right away that any surgical intervention during pregnancy is extremely undesirable. If a molar tooth hurts at this time, then ideally it would be best to simply heal it. Unfortunately, sometimes this is no longer possible and the diseased tooth has to be removed.
It is highly undesirable to remove molars in the first and last months of pregnancy. It is at this time that the fetus is most vulnerable.
If it is possible to postpone the removal of a molar until the birth of the child, then this is exactly what should be done.
Under no circumstances should you hide your pregnancy from your dentist. On the contrary, this should be said immediately. In this case, the doctor will select a harmless anesthetic that will not cross the placental barrier.
If a pregnant woman is facing a complex molar tooth extraction, then this should only be done in a hospital setting. After removal, the patient should be under medical supervision for at least two to three days. This is due to the fact that very often, after the removal of a molar, pregnant women experience a sharp increase in body temperature, and this is extremely harmful for the fetus.
Care after tooth extraction
In order to avoid complications after extraction of a dental unit, you must follow the doctor’s recommendations:
- Eating is allowed only two hours after surgery;
- on the first day, carry out hygiene procedures, and you need to rinse your mouth very carefully, otherwise the blood clot will fall out;
- you need to limit physical activity for several days;
- until the wound heals, food should be liquid or puree, at a comfortable temperature;
- You cannot drink liquid through a straw or lick the wound.
Pain that occurs in the first hours can be relieved with painkillers approved for children. Swelling is relieved with a cold compress. If after two days the swelling does not subside and the pain continues, then infection and inflammation of the wound may have occurred. In this case, you need to urgently consult a doctor.
Molar removal technology
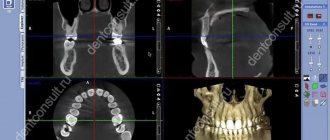
Before proceeding with the removal of a molar, the doctor must make sure that there is no curvature of the roots. For this, an x-ray is taken. If the roots are not bent, the patient is given an anesthetic injection. After 10 minutes, the tooth can be removed.
First, the dentist carefully separates the gum from the body of the tooth. Then he grabs the tooth with pliers and begins to swing it and rotate it at the same time. After several such manipulations, the doctor pulls the tooth out of the alveoli.
In this sequence, both the upper and lower root teeth are removed. However, it is somewhat more difficult to grasp the upper molars with forceps.
Sometimes, when removing a molar, the doctor must first cut it into two or three parts and then pull out each part separately. This usually happens when the roots are bent.
In case of severe curvature of the roots, when they intertwine with the roots of neighboring teeth, removal must be done in fragments and under general anesthesia. In this case, the doctor completely exposes the gum around the diseased tooth.
If there is a cyst in the area of a diseased molar, the doctor is required to be highly qualified. This removal is done under both local and general anesthesia.
Two days after the removal of a molar, the patient must visit the dentist again to take an x-ray. This is necessary to ensure that all tooth roots have been removed.
Indications for tooth extraction in children
The absolute indications for the removal of baby teeth are:
- Neoplasms (cyst, phlegmon).
- Damage to the tooth with further development of a fistula.
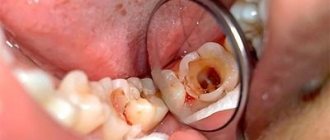
- Severely advanced caries, as a result of which the crown of the tooth is completely destroyed.
- Chips and carious lesions in the crown of the tooth result in the formation of a sharp edge that injures the mucous membrane.
- Inflammation of the tissues adjacent to the tooth.
- The permanent tooth has already begun to erupt and the milk tooth interferes with it.