One of the most common reasons for visiting pediatric otolaryngologists is inflammation of the tonsils in a child, otherwise known as tonsillitis. Inflammation affects the palates; tonsils are paired lymph glands, often called tonsils. The cause of inflammation of the tonsils in children can be either a viral or bacterial (streptococcal and staphylococcal) infection.
Pediatric ENT doctors at the Miracle Doctor clinic comprehensively assess the child’s condition and develop individual treatment regimens. Experience and the latest equipment allow them to provide high-quality diagnostics and treatment of ENT organs of patients of all ages.
Symptoms
Inflammation of the tonsils in the throat of a child is characterized by the appearance of the following clinical symptoms:
- discomfort in the throat: pain, soreness, rawness;
- increased body temperature (up to 37-38° C);
- appearance of cough;
- sensation of a lump or foreign body in the throat (due to plugs formed on the tonsils);
- general weakness and fatigue, headache;
- white plaque on the tonsils.
Depending on the type and stage of inflammation of the tonsils, the clinical picture may be supplemented by enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes, redness and swelling of the palatine arches, and the appearance of purulent plugs on the tonsils with a specific unpleasant odor.
.
The difference between acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections, colds and flu
There are several key differences:
- Various pathogens
- influenza virus, rhinovirus infections, etc. Identifying the cause of the disease is very important for proper treatment and the absence of complications. - Different clinical picture
: influenza is a sudden onset, a sharp jump in body temperature, symptoms of intoxication (headaches and muscle pain, chills, body aches, adynamia, dry cough against the background of chest pain), inflammation of the mucous membrane lining the upper respiratory tract; - the first manifestation of acute respiratory infections, ARVI is inflammation of the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract (runny nose, sore throat, bronchitis, wet cough) - and only then the temperature rises (rarely above 38°).
Complications
If inflammation of the tonsils becomes chronic, then exacerbations of the disease occur; 6-7 times a year. The presence of frequent exacerbations indicates a weakened immune response of the child’s body to the presence of infection in the tonsils. Inflammation of the tonsils often leads to the development of complications in the ears, lungs and other organs of the child. In the case of chronic inflammation, the tissue of the tonsils becomes scarred, lacunar plugs appear, and the lacunae themselves become foci for the spread of staphylococcal and streptococcal infections.
.
Prevention of acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections in children
Prevention of acute respiratory infections should include, first of all, protection in children from sources of infection with acute respiratory diseases
, during periods of epidemic, it is recommended to wear a medical mask in kindergarten and school. In addition, you must:
- provide the child with vaccinations on schedule and during the epidemic;
- avoid hypothermia;
- carry out hardening;
- feed the child correctly - in a balanced manner, according to a schedule, with food rich in vitamins;
- spend less time in public places during outbreaks;
- at the first signs of illness, consult a doctor, even if you need to miss school or kindergarten;
- walk more with your child in the fresh air;
- introduce general strengthening gymnastics into the child’s daily routine.
Sources:
- S.O. Klyuchnikov, O.V. Zaitseva, I.M. Osmanov, A.I. Krapivkin, E.S. Keshishyan, O.V. Blinova, O.V. Bystrova. Acute respiratory diseases in children (Manual for doctors) // Russian Bulletin of Perinatology and Pediatrics, 2008, supplement No. 3.2008.
- L.A. Balykova, Doctor of Medical Sciences, corresponding member. RAS, T.I. Razdolkina, candidate of medical sciences, associate professor. Acute respiratory diseases in children // Remedium Privolzhye, 2022, No. 3(163), pp. 18-22.
- T.A. Samsygina. Modern treatment of acute respiratory diseases in children // Pediatrics, 2013, No. 3, pp. 38-42.
- Seto WH, Conly JM, Pessoa-Silva CL et al. Infection prevention and control measures for acute respiratory infections in healthcare settings: an update // East Mediterr Health J., 2013, i9 (Suppl. i), p. 39-47.
Markova Daria Olegovna Clinic
Author of the article
Markova Daria Olegovna
Specialty: endocrinologist
Experience: 15 years
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Treatment
Treatment of inflammation of the tonsils can be either conservative or surgical. Conservative therapy for inflammation of the tonsils includes:
- physiotherapeutic treatment
- prescribing a course of systemic antibiotics;
- symptomatic treatment;
- immunomodulatory and restorative drugs;
- treatment using the Tonsillor device.
- In case of ineffectiveness of conservative treatment and the development of serious complications, a decision is made on surgical intervention. Removal of tonsils for chronic tonsillitis is called tonsillectomy or tonsillotomy.
Causes of development of exudative otitis media
The cause of ESO is always an inflammatory process in the nasopharynx . If a child has had a runny nose for more than 10 days, frequent colds accompanied by nasal congestion, especially if there is constant difficulty in nasal breathing, snoring during sleep, be sure to consult an otolaryngologist for examination.
The most informative is an endoscopic examination of the ENT organs , when the doctor can accurately assess the condition of the nasopharynx, the degree of adenoid vegetations, the presence of discharge from the paranasal sinuses, and even see exudate in the tympanic cavity.
Tympanometry is very important in diagnosing ESO . This examination allows you to evaluate the results of treatment and restoration of hearing function.
Advantages of visiting the Miracle Doctor clinic
When prescribing surgical intervention, along with traditional surgical methods for removing tonsils in children, the Miracle Doctor clinic performs tonsil removal under anesthesia using the cold plasma coblation method, in which a special device with an electrode is used instead of a scalpel. Removing tonsils with a coblator avoids damage to surrounding tissues; the operation is quick and almost bloodless.
Regardless of whether general or local anesthesia is used, highly effective and safe drugs of the latest generation are used. To ensure comfort during the postoperative period, the patient is provided with a separate room in a 24-hour hospital. Pediatric otolaryngologist surgeons at the Miracle Doctor clinic can not only slow down inflammation of the palatine tonsils, but also, in advanced cases, perform surgery using progressive minimally invasive methods.
Treatment of acute respiratory infections in children, effective relief of symptoms
Recommendations on how to treat acute respiratory infections in children are aimed at relieving clinical manifestations associated with the inflammatory reaction.
Recommendations on how to treat acute respiratory infections in children are aimed at relieving clinical manifestations associated with the inflammatory reaction.
- a diet rich in vitamins;
- drinking plenty of water;
- antipyretic drugs.
Locally, symptoms are relieved by the following means:
- for nasal congestion - with vasoconstrictor drops;
- if the throat is affected - with sprays, local antiseptics, gargles;
- to relieve a wet cough - with expectorants;
- for dry cough - antitussives. Source: T.A. Samsygina Modern treatment of acute respiratory diseases in children // Pediatrics, 2013, No. 3, pp. 38-42
Inhalations and physiotherapy may also be prescribed.
Antibiotic treatment for acute respiratory disease is prescribed to children when the causative agent is a bacterial infection; only a doctor should give clinical recommendations, select the drug and dosage. If a child is prescribed an antibiotic for the flu, it is necessary to relieve complications that arise from bacterial damage (for example, pneumonia). In general, antibacterial drugs are powerless against viruses.
Doctors recommend avoiding antibiotics for uncomplicated respiratory viral infections. Their use is not justified even with mucopurulent runny nose lasting less than 2 weeks. Source: Seto WH, Conly JM, Pessoa-Silva CL et al Infection prevention and control measures for acute respiratory infections in healthcare settings: an update // East Mediterr Health J., 2013, i9 (Suppl. i), p. 39-47
Signs of a bacterial infection for which antibiotics are indicated:
- anaerobic sore throat;
- purulent processes;
- acute tonsillitis when group A streptococcus is detected;
- sinusitis, if clinical changes persist in the sinuses after 2 weeks from the onset of the disease;
- acute otitis media;
- pneumonia;
- chlamydia and mycoplasmosis (respiratory form);
- bronchitis caused by mycoplasma (mycoplasma bronchitis).
The child is required to have bed rest
until body temperature normalizes,
eat a balanced diet, take multivitamins
. You can gargle with decoctions of medicinal herbs, infusions, and antiseptic solutions. If the body temperature is normal, then the following will be useful: dry heat on the lower back and feet, hot foot baths.
How is exudative otitis media treated?
Treatment of exudative otitis media always begins with restoring nasal breathing, relieving acute or chronic inflammation of the nasopharynx, and restoring the patency of the auditory tubes. This can be a long process, sometimes up to a month or more, but it is very important to go through this path and achieve recovery. If exudate (liquid that forms as a result of inflammation) is in the tympanic cavity for a long time, more than 1 month, it becomes increasingly thick, viscous, as if “gluing” all the structures of the middle ear together, adhesions form in the tympanic cavity, which leads to persistent hearing loss, development of chronic otitis media. If conservative treatment does not give a stable result, and each cold leads to a relapse of exudative otitis media or it is not possible to restore hearing within 2-3 months, surgical treatment is necessary - removal of the adenoids (adenotomy) , sometimes with partial removal of the tonsils (adenotonsillotomy), shunting, when a small tube is inserted into the eardrum, through which the eardrum is aerated and medications can be administered.
Dear Parents! It is very important to consult an ENT doctor in time so that a common runny nose does not cause serious complications. Even if you think that you have dealt with a runny nose on your own, come and make sure that your child does not have ear problems. After all, normal hearing is the key to a normal quality of life!
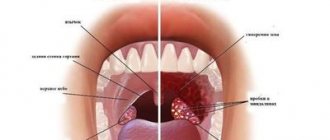
Pus plugs in the throat
The appearance of bad breath, difficulty swallowing, headache and a sore throat indicate the presence of purulent plugs. In addition, patients develop a high temperature, corresponding to the severity of the inflammatory process. Take a close look at the oral cavity: if in the mirror you see whitish neoplasms of a multiple or single nature located on the surface of the tonsils, then these are purulent plugs that need to be removed and the sore throat treated under the supervision of an otolaryngologist.
Causes
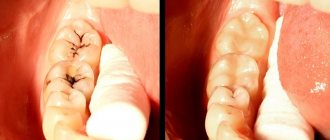
Congestion in the throat accompanies a sore throat that has not been completely cured and has become protracted. The appearance of traffic jams is characteristic of the acute period, as well as the manifestation of the chronic form of the disease. Tonsillitis occurs in both children and adults, and almost always it characterizes a worsening of the pathology. Externally, the corks vary in size - there are whitish dots that look like semolina, or corks with a diameter of about one centimeter. They are visible to the naked eye.
The appearance of plugs is possible only on the palatine tonsils, since they have lacunae - special depressions that are obstructed by purulent discharge. The only way to get rid of traffic jams is to remove your tonsils. However, medical doctors also approach this issue selectively. They carefully study each clinical case and suggest removing the tonsils if the disease cannot be cured conservatively. You should not delay your visit - it is more effective to treat any pathology at an early stage, so as not to resort to radical methods.
Factors in the appearance of purulent plugs
It is necessary to distinguish not only the reasons why plugs appear, but also those factors that provoke an exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis and the resumption of purulent plaque in the lacunae. This process is not always associated with hypothermia and the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms. Traffic jams may occur due to:
- lifestyle - poor oral hygiene, incorrect or incomplete treatment of the disease, bad habits, smoking;
- chronic diseases of the nasal sinuses, which provoke an additional source of infection, and because of this, local immunity is reduced, existing pathologies are aggravated, including tonsillitis;
- a sharp decrease in immunity as a result of a previous serious illness, surgery, chemotherapy, stress or hypothermia;
- food addictions, poor diet - for example, eating large amounts of protein foods helps maintain the inflammatory process;
- injuring the tonsils, for example, when removing plugs on your own, which is strictly prohibited, because the slightest cracks or wounds contribute to the penetration of infection into the blood.
Complications
Despite the fact that angina is a common diagnosis and is traditionally considered a “childhood disease,” it carries serious consequences for the body that can affect much later. Complications are especially severe when a sore throat is not completely cured, when the pathology becomes chronic, and the inflammatory process is sluggish, with seasonal exacerbations.
Among the complications are:
- peritonsillar abscess - inflammation of not only the tonsils, but also the tissues around them, while the fiber is involved so quickly that this leads to an exacerbation of the pathology, a sharp rise in temperature and a deterioration in the patient’s condition;
- phlegmon - an exacerbation of the pathological process, which is associated with the involvement of the subcutaneous tissue of the neck, and in the absence of timely assistance, death can occur;
- degeneration of tissue and replacement of lymphatic tissue with connective tissue, which represents scars and cannot perform its previous protective functions;
- sepsis - blood poisoning when pathogenic microorganisms enter the bloodstream, which quickly spread throughout the body and provoke suppuration of other organs and tissues, and the body’s defenses do not have time to cope with the spread of infection;
- kidney damage is also a complication associated with infection, since the kidneys filter the blood and accumulate not only a lot of pathogens, but also decay products and toxins, which significantly affects the production of urine and filtering of the blood;
- inflammation of the joints and heart - often these are delayed complications that do not appear immediately, as the body tries to fight the infection, turns on protective and compensatory forces, but after some time such consequences still make themselves felt.
Self-cleaning of traffic jams
Doctors insist that purulent plugs on the tonsils cannot be removed on their own, because this must be done according to a certain method, and the patients themselves often neglect basic safety rules. This can only worsen the course of the pathology - lead to extensive bleeding when tissue is damaged or the spread of the pathological process deep into the tonsils and onto healthy tissue. Self-medication for sore throat is extremely undesirable.
A relatively safe way is to cleanse the tonsils with the tongue. It is necessary to slightly press the tongue on the plugs, and they can easily come out, after which the throat is gargled to remove the purulent discharge. The tongue does not injure the mucous membrane as much and is not able to push the plugs inside, damaging the delicate tissue of the lacunae. Doctors also do not recommend using cotton swabs or pads to remove accumulated deposits. This is dangerous primarily due to damage. It is best to do the procedure in an office under the supervision of a medical specialist.
However, if you can’t visit a doctor, and the traffic jams have formed quite large and quickly, then two hours after eating you can gargle with an antiseptic and try to remove them with a gauze swab. To do this, soak the tampon in the antiseptic solution and, without applying pressure, try to gently move the plug up. Do not press on it under any circumstances, or point the tampon towards your throat, so as not to swallow the plug. Rinse your mouth every time the discharge is successful. Watch for pain or excessive bleeding. If after two or three attempts the plug does not come out, you should not continue the procedure.
Treatment
Therapy consists primarily of removing purulent discharge and inhibiting the inflammatory process in the tonsils, followed by powerful prevention and restoration of the body's defenses. Treatment begins with washing the tonsils.
Washing
Deposits are removed using a syringe or vacuum method - it depends on the patient’s health condition. If the doctor uses a syringe, then rinsing occurs under the pressure of the liquid with which it is filled. This is usually an antiseptic drug. Using a curved cannula, you can wash out purulent plugs even from hard-to-reach places. Since all the gaps are interconnected by passages, it is enough to act on two or three of the largest of them to wash out all the passages. The procedure is carried out every other day, and the course of treatment takes up to 15 procedures.
Vacuum rinsing is performed under anesthesia. A special device with a nozzle is fixed on the tonsil, which, when creating negative pressure, removes pus from the lacunae. After cleaning with a vacuum, they are washed with an antiseptic. Treatment also requires 10-15 procedures.
Physiotherapy
To assist with the main therapy, doctors also include physiotherapeutic procedures in the treatment regimen, which are aimed at reducing the inflammatory process and speedy regeneration of tonsil tissue. Physiotherapy is prescribed only in those moments when the pathology is not in an acute stage. Treatment methods include:
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- laser irradiation;
- ultrasonic aerosols.
The number of procedures, prescription of drugs and duration of sessions are strictly regulated by the doctor. It depends on the severity of the disease and the extent of tissue damage.
Laser treatment
The procedure does not require anesthesia and causes only minor discomfort. The laser burns out pathologically altered tissues, and the scars tightly close the lacunae, preventing further accumulation of purulent discharge. In most cases, one session is enough, but for advanced disease with frequent relapses, three sessions are required. You may experience a sore throat for some time after laser treatment.
Treatment of purulent plugs in medical settings is carried out conservatively, and only if it is impossible to help patients in other ways, doctors resort to removing the tonsils.
Prevention
Prevention of purulent plugs should primarily consist of proper treatment of sore throat and prevention of its recurrence, manifestation of the disease during a latent course. Proper prevention will help prevent exacerbation and get rid of purulent plugs. To do this you need the following:
- thorough oral hygiene, proper cleaning, elimination of carious lesions;
- rinsing your mouth after eating;
- drinking enough water;
- to give up smoking;
- proper and varied nutrition;
- refusal of alcoholic beverages;
- complete treatment of pathologies of the throat and nose.
Remember that tonsillitis requires long-term treatment, the use of antibiotics, and physiotherapeutic measures. Therefore, all doctor’s recommendations must be followed in full so that plugs on the tonsils do not appear later.
Author
Yampolsky Sergey Zigfridovich
otorhinolaryngologist (ENT)
Candidate of Medical Sciences
40 years of experience
+7