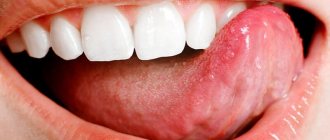
What is tongue swelling, and how dangerous is it?
Edema is an increase in volume of an organ. The tongue may swell and increase in width, and also partially, for example, when a tumor-like lump forms in some place. Such conditions are extremely alarming; they may indicate the progression of a dental disease or an allergic reaction.
Note! Tongue swelling should not be confused with a slight swelling on the tip of the tongue that appears after biting or eating hot, sour foods.
Edema may also be accompanied by the following symptoms of various diseases:
- choking cough and sneezing;
- profuse lacrimation;
- rash on the surface of the face and body;
- feeling of a “lump in the throat”;
- itching in the mouth and sore throat;
- increased body temperature;
- weakness;
- difficulty swallowing;
- speech problems;
- swelling of the tissues of the oral cavity and face;
- feeling of a foreign body in the mouth, etc.
It is important! The most dangerous symptom is swelling of the tongue at its root, when the tissues block the airways, the person feels a sharp suffocation, blushes, and rolls his eyes upward. In such situations, you should urgently call an ambulance or provide emergency first aid to the patient.
Dentistry for those who love to smile
+7
Make an appointment
Diagnosis of tongue neurosis
The fact is that the etiology of numbness, coating on the tongue and other manifestations of oral discomfort is sometimes not associated with stress. The reasons for such unpleasant sensations may be:
- Diseases of the digestive tract. In particular, the backflow (reflux) of intestinal contents into the trachea causes pain and a burning sensation in the throat and tongue.
- Circulatory disorders due to cardiac disorders.
- Neurological and endocrine pathologies.
- Allergic reaction to topical medications (rinses, lozenges, etc.).
- Infection of the oral cavity (usually stomatitis, fungal diseases).
Often characteristic symptoms occur after visiting the dentist. Glossalgia often appears after prosthetics due to injuries during orthopedic manipulations, allergies to the material from which the prostheses are made. The syndrome can also be a consequence of malocclusion, constant injury to the oral mucosa by unsuccessfully placed fillings, or dental plaque.
Many experts forget about the rather rare, but noteworthy syndrome of “galvanism” - insignificant electrical discharges that appear in the mouth in the presence of fillings or prostheses made of metal alloys, due to which the tongue becomes numb and pain appears.
To exclude the somatic etiology of the disorder, consultation with a dentist, ENT specialist, neurologist, cardiologist and gastroenterologist is necessary. The patient is also asked to take a general and biochemical blood test and do an ECG. It is advised to undergo a study to determine the indicators of local immunity of the oral cavity, assess the enzymatic activity of the salivary fluid, the content of protein and other elements in it, and the pH level.
Why does swelling of the tongue still occur?
We list the most common reasons why an organ may swell:
- an allergic reaction resulting in Quincke's edema;
- glossitis disease or an inflammatory process that affects the tissues of the tongue;
- hypothyroidism or diseases of the endocrine system;
- infectious diseases, when the tongue may suddenly swell;
- injury caused by a broken piece of tooth, or incorrect prosthetics;
- disruption of the metabolic process;
- malignant formations;
- complications caused by piercing, etc.
An experienced doctor will help determine the true cause of swelling of the tongue, who will diagnose the oral cavity under the careful supervision of the patient.
If the pain is associated with damage to the frenulum
The hyoid frenulum is a mucous membrane that connects the tongue to the base of the mouth. Inflammation can be caused by:
- Diseases occurring in the oral cavity - stomatitis, gingivitis, periodontitis;
- Using incorrect hygiene products: toothpaste, toothbrush, mouthwash;
- Allergies caused by taking medications.
Inflammation of the frenulum under the tongue can also occur as a result of injury to it during brushing teeth, eating (too hot or cold foods), talking loudly, sharply biting the tongue, or careless handling of cutlery.
The reason why it hurts under the tongue may also be a physiological feature. In cases where the frenulum is short from birth, the likelihood of damage increases significantly, and discomfort can occur even while eating.
A visit to the dentist cannot be avoided if the frenulum under the tongue hurts. The doctor will examine the damage and prescribe treatment. At home, especially if you can’t immediately visit a specialist, in order to relieve pain, you can rinse your mouth:
- Soda solution (a teaspoon per glass of chilled boiling water);
- Chamomile or sage decoction;
- Preparations: Stomatofit, Rotokan, Chorophyllipt.
Also, if the frenulum under the tongue is inflamed, it is recommended to treat the affected area with Iodinol or place a cotton swab dipped in sea buckthorn oil at the damaged area. Such measures can only be used in cases where you know for sure that the cause of the pain under the tongue is an inflamed frenulum.
The tongue is connected to the lower jaw thanks to the frenulum - a thin membrane of skin. It holds the tongue and participates in the formation of the correct pronunciation of sounds. It contains a large number of nerve endings and blood vessels. Therefore, with the development of a pathological condition, the frenulum becomes especially sensitive. During the inflammatory process, doing familiar things - talking, chewing food - becomes painful.
Inflammation of the hyoid frenulum can be provoked by various dental diseases, injuries associated with active work of the oral cavity, inflammation of the lymph nodes or tissues of the tongue, and bad habits. The painful sensations that arise in this case negatively affect the quality of life. To identify the true etiology of the syndrome, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
First aid for angioedema of the tongue
We have already spoken above about first aid - here we will give an example using a specific clinical case with a patient.
Angioedema is considered one of the most dangerous, often leading to death, as it occurs extremely quickly. Not only does a person’s tongue swell, but the neck, inner surface of the mouth, larynx, cheeks, eyelids, lips, and the entire face may also swell. The skin becomes blue, the tongue turns white, and tearing occurs.
What can be done first in case of angioedema of the tongue before the ambulance arrives?
- clear the airways of mucus;
- raise your head a little so that the swollen tongue does not block the airways;
- give an antihistamine, preferably administered intravenously;
- monitor the patient's condition and wait for an ambulance.
The tongue itches - what to do if the organ literally itches
The tongue can itch not only in a figurative sense. If you experience unpleasant irritating sensations, the first thing you should do is figure out what could be the reason for the appearance of this symptom. The organ is a muscle containing a huge number of nerves and blood vessels. The occurrence of discomfort, burning, soreness, swelling and itching in the tongue always indicates some pathological condition, and the symptom itself may be associated with dental disease and disturbances in the functioning of internal organs.
Why might my tongue itch?
In any case, if this symptom develops, you should immediately see a specialist. Further in this article we will find out why the tongue may itch, what preconditions contribute to this, and what to do in such a situation.
First aid for allergic swelling of the tongue
Another common picture is when the cause of swelling of the tongue is taking medications or foods that cause allergies.
The first aid for allergies is to stop taking the food or medication that caused the swelling.
You should definitely take antihistamines and report the situation to your doctor. If your allergy does not allow you to go to an appointment on your own, call a doctor at home.
You should also remember the drug or product that provoked the swelling and allergy, and exclude its presence (and drugs with a similar active ingredient) from your life for the future.
Principles of treatment
The treatment regimen proposed by the doctors of the Leto clinic is aimed at restoring normal psycho-emotional status, eliminating symptoms that bother the patient and preventing secondary complications. If the tongue twitches during neurosis or other symptoms of the syndrome are pronounced, drug treatment is indicated. It includes:
- sedatives;
- non-benzodiazepine anxiolytics;
- according to indications (for example, for severe insomnia) - antipsychotics;
- B vitamins, tocopherol, omega complex;
- nicotinic and ascorbic acid, drugs based on adenosine triphosphoric acid, glycine;
- iron supplements.
Various physiotherapeutic procedures that have a relaxing and calming effect have proven themselves well. We recommend:
- massage of the collar area;
- ozone and oxygen therapy;
- transcutaneous and transcranial electrical stimulation;
- hirudotherapy;
- laser therapy.
Regardless of clinical manifestations, neurotic disorders are an indication for consultation with a psychologist. The doctor will help the patient understand the cause of such unpleasant sensations, tell him how to properly respond to conflict and stressful situations, and help him find a solution to the problems that bother him.
Tongue neurosis is a rare disease, but quite amenable to outpatient treatment. You can get more detailed information from our consultants by calling 24/7 anonymous phone number 8(969)060-93-93 .
Causes
The causes of tongue swelling can be very diverse, ranging from injuries to allergies. It can be:
- mechanical trauma of the tongue;
- inflammation of the tongue or glossitis (causes and treatment of glossitis);
- infectious diseases;
- allergic reaction;
- anaphylactic shock;
- metabolic disease;
- thyroid disease (hypothyroidism);
- genetic disorders (Down syndrome);
- malignant tumors (sarcoma, oral cancer);
- injury due to uncomfortable dentures;
- piercing;
- pellagra;
- pernicious anemia;
- pituitary disorders.
Only an experienced doctor can differentiate oral diseases that cause swelling of the tongue.
Swelling of the tongue and throat can be dangerous to the health and life of the patient. Don't self-medicate! At the first sign of swelling, you should consult a doctor for help. If swelling develops too quickly and begins to make breathing difficult, call an ambulance to avoid suffocation.
What can cause an itchy tongue?
A phenomenon such as itching of the tongue and lips can be caused by one of many different factors. Here are the most common causes of this unpleasant symptom:
- mechanical injury: the tongue of both a child and an adult may begin to itch due to banal biting or damage of another nature, for example, as a result of a burn. Very often, the culprit is rubbing the mucous membrane with the sharp edges of a crown, an incorrectly fitted prosthesis or an incorrectly adjusted brace system. Also, this symptom may well be a consequence of the use of low-quality cosmetics or oral hygiene products,
Tongue injury can cause itching
- Oral diseases: one of the most common causes of itching is a disease such as glossalgia. In this case, it is usually the tip of the organ that begins to itch, but in some cases patients experience severe itching on the sides. Associated symptoms include burning, pain, tingling in the tongue, as well as dryness of the oral mucosa. Quite often, the disease develops against the background of strong emotional experiences and stressful situations, but the disease can also be triggered by injury to an organ, taking certain medications, or malfunctions in the internal systems of the body,
The photo shows glossitis of the tongue - Gastrointestinal pathologies: problems in the gastrointestinal tract in most cases are reflected specifically in the condition of the tongue. For example, pathologies such as gastritis, ulcers or pancreatitis can provoke itching and burning in an organ,
- stress and depression: against the background of severe nervous exhaustion, some changes occur in the composition of saliva and the volume of its secretion,
- deficiency of vitamins and microelements: sometimes due to a lack of B vitamins, iron and folic acid, the tongue begins to itch very much,
- allergy: such a manifestation may well be an allergic reaction of the body to some irritant, for example, to hygiene products, the presence of an allergen in the oral cavity in the form of metal parts of braces or a prosthetic device,
- candidiasis: the development of a fungal infection often becomes the body’s response to a sharp weakening of the immune defense. In this case, along with itching, burning and tingling occurs, and a dense cheesy coating appears. Quite often, the cause of this problem is long-term use of antibiotics. By the way, in children the disease in question develops almost twice as often as in adults.
This is what a fungal infection on the tongue looks like
Other possible provoking factors include the constant irritating effect of tobacco smoke, abuse of too spicy, salty or acidic foods - in such cases, it often begins to tingle and itch directly under the tongue. Excessive consumption of low-quality alcoholic beverages can also lead to the development of this symptom.
How to determine inflammation of the salivary gland?
The disease is characterized by the manifestation of certain symptoms. First of all, the amount of saliva produced decreases and dryness appears in the oral cavity. Pain increases when eating, talking, opening and closing the mouth.
Inflammation of the salivary gland under the tongue is accompanied by redness and swelling of the mucous surface in the area of the outbreak. The secretion secreted by the gland may contain pus and mucus. With purulent inflammation, there is a danger of melting the salivary capsule of the gland and spreading the disease to nearby tissues.
The appearance of pain under the tongue while eating may indicate a short frenulum. Parents of young children usually face this problem. Doctors recommend cutting the frenulum at an early age so that the child does not have problems pronouncing certain sounds in the future.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytdev
In cases where a person feels pain on both sides of the tongue, the cause may be inflammation of the sublingual salivary gland. It arises as a result of:
- Complications of another disease (inflammation of the tonsils, acute respiratory viral infections, anemia, vitamin deficiency, dental diseases);
- Insufficient hygiene;
- Obstruction of salivary flow caused by stones or pathogens.
The main symptoms indicating inflammation of the salivary gland:
- Dry mouth – it always seems like there is not enough saliva;
- Pain that is observed not only under the tongue, but also in the ear area;
- Redness of the mucous membrane, thickening or swelling under the tongue;
- Putrid taste.
If you observe such signs in yourself, you should immediately go to the dentist and undergo a course of therapy. Otherwise, an abscess may develop or the disease may become chronic.