ICD - pharyngitis:
- J02 - acute pharyngitis
- J02.0 - streptococcal pharyngitis
- J02.8 - acute pharyngitis caused by other specified pathogens
- J02.9 - acute pharyngitis, unspecified
- J31.2 - chronic pharyngitis
- J31.1 - chronic nasopharyngitis
Pharyngitis is rarely isolated as a separate disease; the diagnosis is usually acute respiratory viral disease (ARVI).
ARVI is a general name; the doctor usually specifies how exactly ARVI manifests itself.
This may be rhinitis (runny nose), pharyngitis (red throat), nasopharyngitis (inflammation of the nose and throat), etc.1,2
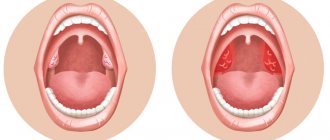
It is important not to confuse pharyngitis with tonsillitis.
To do this, let's understand the structure of the pharynx and oral cavity.
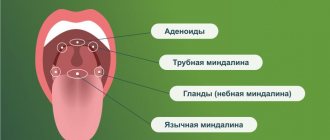
Structure of the pharynx
The pharynx is divided into 3 sections:
- upper (nasopharynx)
- middle (oropharynx)
- lower (larynx)
This division is very conditional, because There are no clear boundaries between departments. When inflammation occurs, it rarely happens that the inflammatory process is localized in one section; usually infectious processes spread and move throughout all sections of the pharynx5,7
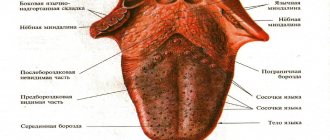
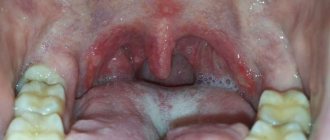
As can be seen in the picture below, the oropharynx is composed of the velopharyngeal arches, the uvula and the soft palate.
Pharyngitis usually affects:
- temples
- tongue
- soft sky
- posterior wall of the pharynx
The doctor uses a spatula to completely examine the pharynx. It is needed to improve visibility of the back of the throat.
The palatine tonsils also become inflamed with pharyngitis, because it is impossible to limit the inflammation process. This widespread nature of inflammation in pharyngitis distinguishes it from tonsillitis, where the tonsils are predominantly affected.
Effective rinsing solutions
• Water with salt, soda.
Dilute 1 teaspoon of salt and soda in a glass of water. You can add a little iodine there, which will have a disinfecting effect. • A solution of chlorhexedine, which has antiviral and antimicrobial activity. It fights well against pharyngitis, streptococcal, and staphylococcal infections.
• Chlorophyllipt is a green alcohol solution for getting rid of staphylococcal and viral infections. They are also good for treating laryngitis, pharyngitis, and sore throat.
• Propolis – helps in case of bacterial sore throat. Drops of propolis tincture are dissolved in 100 ml of water (you can buy it at the pharmacy).
• Medicinal herbs that have bactericidal and anti-inflammatory effects. These include: St. John's wort, calendula, chamomile, eucalyptus, oregano, raspberry leaves, sage. You can use these herbs individually or as a whole collection.
Remember, dear friends. Self-medication for such diseases is unacceptable. Every pimple on the mucous membrane of the throat requires treatment by a professional who can accurately determine the cause of its appearance and prescribe the correct therapy. Be healthy!
Children get sick often, and this is largely due to imperfect personal hygiene, close contact with other children or adults who are sources of infection, as well as the immaturity of the immune system, as a result of which the body becomes susceptible to viruses and bacteria. Redness of the mucous membrane of the pharynx and tonsils is a persistent sign by which a person examining the throat of a sick child can judge the presence and severity of the inflammatory process. Often, parents and practicing pediatricians are faced with cases of classic pharyngitis and tonsillitis, but if the pimples in the child’s throat have a reddish tint, the approach to diagnosis will be different.
Throat diseases are a broad concept, since it includes a whole group of heterogeneous pathologies that can be caused by both viruses and bacteria, and pathogenic fungi (mycoses). The “throat” in the generally accepted sense includes the pharynx, lymphoid formations - the tonsils, and sometimes the larynx, located next to the pharynx. Since during a visual examination without special devices one can see mainly the back wall of the pharynx and the palatine tonsils, complaints about rashes are usually explained by damage to these anatomical areas.
A rash in the throat in children is a symptom that can only be called relatively specific. Rashes such as spots, nodules or blisters (vesicles) are not characteristic of the typical form of pharyngitis or tonsillitis (sore throat), and these diseases are the most common. Damage to the mucous membrane, accompanied by the appearance of vesicles, is observed during infection with herpes group viruses, enteroviruses that cause:
- herpangina;
- chicken pox;
- herpetic stomatitis.
Pimples in the throat are usually explained by an infectious process.
However, at the same time, other changes that are present in banal (simple, classical) forms of inflammatory processes can be mistaken for a rash. The diseases named in the list are characterized by a blistering rash, often with clear or cloudy exudate, rather than elements resembling pimples or pimples. Therefore, diagnosis should be carried out by a specialist familiar with the features of changes in the mucous membrane of the oropharynx in various pathologies.
It is also necessary to distinguish between infectious and inflammatory pathologies that occur acutely or chronically, provoked by viral or microbial agents. For example, white bumps in the throat may indicate a bacterial throat infection called bacterial pharyngitis. The etiology of the disease during the infectious process determines the choice of treatment, so timely and high-quality diagnosis is necessary for successful recovery.
Why might red formations resembling pimples appear in a child’s throat? This occurs as a result of the development:
- Acute infectious pharyngitis.
- Chronic hypertrophic pharyngitis.
These diseases are caused by an inflammatory process within the boundaries of the pharynx and are most often caused by respiratory viruses or bacteria (streptococci, staphylococci). We cannot exclude the possibility of simultaneous damage to the tonsils (tonsillopharyngitis), which is often observed in children, especially in the younger age group.
How common is pharyngitis?
Pharyngitis, like a common ARVI (viral infection), occurs quite often. The incidence rate increases during the season from September to May, with a peak in February and March. A decrease in the incidence of pharyngitis by 3-5 times is observed in the summer months.10,11
Acute pharyngitis occurs more often in childhood than in adults. Children under 5 years of age suffer viral infections, including pharyngitis, 6-8 times a year.8,9
In the first year of visiting a preschool institution, the incidence of the disease is 10-15% higher than in children at home. But, unfortunately, “home” children subsequently get sick more often at school age.
Folk remedies
A rash in the throat may be accompanied by severe pain. To eliminate unpleasant sensations, traditional medicine, in particular rinsing solutions, will come to the rescue. This procedure should be carried out after meals, at least 4-6 times a day.
Solutions and rinses will help relieve sore throat
- Recipe 1. Dilute 0.5 tsp in 100 ml of milk. soda, add a piece of butter and season with ginger.
- Recipe 2. Dilute 1 tsp in 500 ml of warm water. salt. Exactly the same proportions for preparing a soda solution.
- Recipe 3. Pour 200 ml of boiling water over 2 tbsp. l. mint, chamomile, eucalyptus. After rinsing, you can suck 1 tbsp. l. honey If there is no fever, you can do herbal inhalation or breathe over hot water in which propolis is diluted.
If pimples in a child’s throat are caused by thrush, the plaque should be removed in the following way: wrap a bandage around your finger, dip it in a soda solution and wipe the affected area.
Causes of pharyngitis and tonsillitis
Etiology (origin, cause) of pharyngitis. In 70-90% of cases, pharyngitis is caused by viruses. Pharyngitis can also be caused by bacteria, fungi, allergies, injuries, and exposure to irritating factors.
The most common viruses are rhinoviruses, adenoviruses, influenza, parainfluenza, enteroviruses, Coxsackie A, coronaviruses, a group of herpes viruses (Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, HSV).12
There are pharyngitis, which are classified as a separate diagnosis depending on the pathogen, for example streptococcal pharyngitis ICD J02.0
Treatment methods for white pimples in the throat in children
Child examination
The doctor will determine the cause of the appearance of white bubbles or pimples in the child’s throat through tests, throat swabs and visual examination of the throat. Treatment is prescribed on an individual basis and depends on the cause of the pathology.
Treatment of candidal stomatitis
For candidal stomatitis, a soda solution helps a lot. Gauze is wrapped around the finger, moistened in a soda solution (preparation instructions: 1 teaspoon of soda per glass of boiled water) and the mucous membranes of the oropharynx affected by white pimples are carefully treated.
Preparation of soda solution
Infants should be put to the breast more often, and babies who are already receiving complementary foods should be given boiled water to drink after each meal. In case of severe damage and severe course of candidal stomatitis, the doctor selects an antifungal agent for the child in its age-appropriate dosage.
Children who eat from a common table must limit fast carbohydrates in their diet:
- White bread;
- candies;
- chocolate;
- cocoa;
- baked goods;
- cookie;
- sugar.
Treatment of sore throat
White pimples in the throat with a sore throat most often indicate damage to the mucous membranes by staphylococci. Treatment in this case is necessarily comprehensive.
Depending on the age and characteristics of the child’s body, the doctor prescribes:
- antibiotics to which the pathogen is sensitive (this is determined in the laboratory after inoculating smears from the oropharynx on a nutrient medium);
- aerosols and sprays with local analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects;
- rinsing solutions (you can prepare them yourself at home or purchase ready-made ones at the pharmacy);
- dissolving tablets with antiseptics.
For small children under 4-5 years old, the doctor selects antibiotics in the form of a suspension. The drugs in this dosage form come with a syringe or measuring spoon, with which you can easily measure a single dose of the medicine.
Abscess treatment
A pimple in the throat of a child, which rapidly progresses in growth and is accompanied by signs of intoxication of the body, in most cases is a retropharyngeal abscess. The lesion most often occurs on one side of the pharynx (right or left) and develops against the background of untreated pharyngitis, tonsillitis, or tonsillitis.
Treatment of a child's throat
In pediatric practice, a retropharyngeal abscess is treated surgically; doctors do not wait until the abscess opens on its own, as this entails additional complications in the form of inflammation of the digestive tract, lymphadenitis, and sepsis.
After surgical opening of the abscess, the child must be prescribed conservative treatment, which includes:
- antibiotics;
- gargling with antiseptic solutions, for example Furacilin (the price of tablets in the pharmacy is lower than the cost of the finished solution);
- treatment of the pharynx with aerosols and sprays that contain an antiseptic or antibiotic.
The video in this article explains where pimples in the throat come from, what causes the growths, and what measures should be taken to prevent the development of the pathological process. Please remember that this video is for informational purposes only and cannot replace the advice of a qualified specialist.
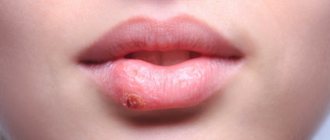
Pimples that appear suddenly in the throat often cause severe discomfort.
Small red sores or purulent rashes interfere with the enjoyment of food, cause pain, and sometimes bleed.
According to medical professionals, a rash on the tongue, inside the cheeks and on the back of the throat is always a symptom of an infectious disease.
- All information on the site is for informational purposes only and is NOT a guide to action!
- Only a DOCTOR can give you an ACCURATE DIAGNOSIS!
- We kindly ask you NOT to self-medicate, but to make an appointment with a specialist!
- Health to you and your loved ones!
The disease can be viral, bacterial or fungal in nature.
But mechanical damage to the mucous membrane is also possible.
It’s a good idea to learn to understand the signs of the most common infections yourself.
This will help avoid unnecessary worries in non-dangerous cases or unforeseen complications in a serious illness.
Classification of pharyngitis
Pharyngitis can be acute or chronic. Acute is inflammation that just arose (suddenly), and chronic is a disease that persists for a long time, and it may not bother a person, but under certain circumstances again cause complaints and anxiety.3
| CLASSIFICATION | A COMMENT | ||
| classification: | Classification of pharyngitis due to its occurrence: | a comment: | viral bacterial fungal allergic traumatic caused by exposure to irritating factors caused by gastrointestinal diseases (gastroesophageal reflux, stomach diseases, etc.) |
| classification: | Pharyngitis associated with specific pathogens: | a comment: | Epstein Bar virus for infectious mononucleosis Yersinia enterocolitica for yersinial pharyngitis gonococcus for gonorrheal pharyngitis Leptotrix buccalis for leptotrichosis of the pharynx |
| classification: | Types of chronic pharyngitis: | a comment: | hypertrophic (enlargement of the mucous membrane) atrophic (depletion of the mucous membrane) catarrhal (standard inflammation) mixed |
Diagnosis of pharyngitis
Acute pharyngitis can be determined by patient complaints and examination of the oropharynx (pharyngoscopy).
Objective symptoms of pharyngitis, which are assessed by a doctor when examining the throat:
- swelling and hyperemia (redness) of the pharyngeal mucosa
- purulent or mucopurulent plaque on the walls of the pharyngeal mucosa
- the presence of inflammation in the arches, tonsils, orifices of the auditory tubes
- the presence of bright red tubercles on the back surface of the pharynx and on the side - hypertrophied (enlarged) lymphoid follicles
- thinning of the mucosa with areas of exfoliating epithelium, crusts and viscous mucus (atrophic pharyngitis)
Based on this, the doctor can make not only a diagnosis of pharyngitis, but also suggest its cause (viral inflammation, fungal infection, etc.).
Despite the fact that 70% of acute pharyngitis is a viral disease, sometimes it is necessary to exclude a bacterial cause. This is very important for further treatment tactics and prevention of complications. To do this, you should conduct a rapid test to exclude the streptococcal nature of pharyngitis.
In some cases, with fever, long-term complaints, or a temperature exceeding 3 days, it is also necessary to take a general blood test to understand the cause of acute pharyngitis.
Complications of pharyngitis
Acute pharyngitis usually responds well to treatment. The prognosis for viral pharyngitis is recovery.
Bacterial (streptococcal pharyngitis) can be complicated by the formation of a retropharyngeal abscess, and subsequently have a negative effect on the heart and kidneys, causing endocarditis and glomerulonephritis.
Symptoms of pharyngitis can persist even with proper treatment, if the true cause of pharyngitis is not eliminated. For example, if gastroesophageal reflux disease (damage to the gastrointestinal tract) is not treated, then pharyngitis will constantly remind itself.
Acute pharyngitis can become chronic.
Prevention of pharyngitis
To prevent pharyngitis, it is recommended:
- avoid hypothermia and dress appropriately for the weather
- avoid contact with tobacco and chemical irritants
- carry out frequent ventilation of working and living spaces
- walk outdoors more often. Walking will help strengthen the body's defenses in the fight against pharyngitis.
- don't drink ice water
- do not share food and cutlery, cups
- avoid crowded places and, if possible, stay in them for as little time as possible
- use disinfectants, including in public places,
- transport, etc.
- wash your hands often
Video: “Aphthous stomatitis”
Pimples in the throat are signs of diseases, usually of an infectious nature. The most common diseases that result in white rashes or appear as a white pimple in the throat are follicular tonsillitis, inflammation of the tonsils, which is chronic. Also, pimples on the mucous membrane occur as a result of stomatitis, but they are red in color, and the localization of the rashes is usually in the mouth and occasionally in the throat.
If a child has a white pimple in the throat, on the tip of the tongue or on the tonsil, which is accompanied by no fever, then the treatment will be the same as for an adult, unless of course it is a completely newborn.
Pimples in the throat are usually painful; the patient feels a sharp pain when swallowing. In addition, this disease is characterized by soreness, which causes severe discomfort to the person.
Typically, pimples are located on the tonsils (or tonsils), which perform a protective function in the body and recognize and trap pathogenic microorganisms that enter the human body through the oral cavity. If, as a result of stress or some other reason, the body’s immune status decreases, the tonsils are the first to be attacked, and as a result of the ingress of bacteria, a sore throat occurs, the manifestation of which is a rash in the form of blisters or pimples in the throat.
A white pimple in the throat is accompanied by other symptoms, which manifest themselves as pain in the ears, fever, enlarged lymph nodes, general weakness, headache, etc. If the rash in the throat is purulent in nature, then an unpleasant odor from the mouth will be noticeable.
What to do if a white pimple pops up in your throat
Pimples in the throat should be treated after consulting a doctor and finding out the cause of the disease. However, there are several folk methods that will help relieve inflammation and speed up the healing process. My patients took advantage of the doctor’s advice, thanks to which they can get rid of problems in 2 weeks without much effort.
To gargle, you can prepare an infusion of 1 tablespoon of eucalyptus mixed with linden and chamomile flowers. Pour boiling water over this mixture and leave for 30 minutes. It is recommended to gargle with this infusion 5 times a day.
Mixed aloe juice with water in a 1:1 ratio, which should be used to gargle a sore throat, will also help relieve inflammation. An infusion of willow bark will help speed up the healing of the affected mucosa. Gargle with this infusion 5 times a day.
In addition, you can prepare inhalations by boiling two tablespoons of a mixture of mint, sage and chamomile, then remove the decoction from the heat and breathe in the steam for 10-15 minutes. 10-minute inhalations of propolis will also be effective. To do this, place 1 tablespoon of propolis in a liter of boiling water.
As a rule, if you have acne in the throat, the doctor prescribes antibiotics appropriate to your condition, anti-inflammatory drugs, gargles, soft foods, and plenty of fluids. Also, if the condition requires it, then bed rest may be prescribed. To prevent the development of the disease, you should take care of your immunity. Take vitamins, stay cool and avoid stress.
Pharyngitis in pregnant women
During pregnancy, a woman's body's protective properties decrease. In this regard, the risk of contracting infectious diseases, as well as exacerbation of chronic diseases, greatly increases.
Pregnant women need to carefully monitor their health and prevent diseases: avoid contact with people with respiratory diseases, avoid crowded places, wash your hands, eat regularly and properly.
If you develop acute pharyngitis or exacerbation of chronic pharyngitis, treatment is required. It is not recommended to use drugs that can affect the entire body. They can pass through the placenta to the baby and cause harm to him. To treat pharyngitis, pregnant women are advised to consult a doctor and use saline mouth rinses.
FAQ
Can pharyngitis be treated at home?
Pharyngitis usually does not require hospitalization (hospital treatment). You can treat strep throat at home on your own by using topical remedies to relieve sore throat and sore throat. If, after self-treatment, the sore throat does not go away within 3 days, then you should consult a doctor. If you have a fever in addition to a sore throat, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Which doctor should I contact if I have a sore throat?
If you have a sore throat, sore throat, or difficulty swallowing, you should first consult a therapist or pediatrician if you are a child. If there are indications, the doctor will prescribe a consultation with an ENT doctor.
Very severe sore throat. Are you sure I don't have a sore throat?
With pharyngitis, the pain syndrome may be more pronounced than with tonsillitis (tonsillitis). To treat pharyngitis, it is good to use a remedy that has an analgesic effect, for example Tantum® Verde. To exclude sore throat (streptococcal tonsillitis) or streptococcal pharyngitis, it is recommended to conduct a rapid test (streptotest).
Do you need an antibiotic for pharyngitis?
The antibiotic is indicated ONLY for bacterial pharyngitis. For a quick diagnosis, perform a rapid test for streptococcus. It will allow you to exclude or confirm the bacterial nature of pharyngitis. If streptococcus is detected, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics.
Is strep throat contagious?
Most often, strep throat is a viral disease, so a person can shed the virus and infect other people. A sick person is contagious, so you should stay at home until you recover.
What happens if pharyngitis is not treated?
Complications may arise. If pharyngitis is not treated, complaints persist much longer, inflammation does not go away and begins to become chronic.
Is it possible to get vaccinated for pharyngitis and when?
Against the background of an acute illness or exacerbation of chronic pharyngitis, vaccination is contraindicated. Wait until you have fully recovered and then you can get vaccinated. The exception is vaccination against influenza. It can be done when the temperature is normalized, i.e. There is no need to wait for all symptoms to disappear.
Is it possible to eat cold food if you have a sore throat?
If you have pharyngitis, it is not recommended to eat very cold foods, including ice cream. This can increase inflammation and slow down recovery.
Sore throat in children: forms and clinical manifestations
Depending on the nature of the change and the degree of damage to the tonsils, several forms of angina are distinguished.
Catarrhal sore throat
A mild form, characterized by enlargement and redness of the tonsils, as well as the absence of purulent lesions. The child feels dry mouth, a whitish coating appears on the tongue, and the cervical lymph nodes are slightly enlarged. In addition to a sore throat that gets worse when swallowing, the child feels a sore and burning sensation. The temperature rises to 38 degrees, children complain of weakness and headache.
Follicular tonsillitis
A serious disease in which the tonsils become covered with purulent pinpoint follicles. On days 2-3, the ulcers open, leaving wounds that heal quickly. There is severe pain in the throat, radiating to the ear, making it difficult to swallow, children refuse to eat and drink. The lymph nodes are enlarged and painful when pressed lightly. Fever and chills are accompanied by a temperature of up to 40 degrees, vomiting, convulsions and fainting are possible.
Lacunar tonsillitis
In the lacunae, between the lobes of the tonsils, islands of yellow purulent plaque appear, which tend to unite into wide purulent foci. The symptoms are similar to those of purulent follicular tonsillitis, but are more pronounced and are accompanied by severe intoxication of the body. It hurts the child to turn his head, his mouth opens with difficulty, which makes speech slurred.
Viral (herpetic) sore throat
Most often, the development of the disease is facilitated by vitamin deficiency and weakened immunity. The tonsils become covered with red blisters, which burst, leaving small ulcers in their place. In addition to a sore throat, symptoms are acute respiratory in nature: cough, runny nose, abdominal pain, indigestion, as well as stomatitis and conjunctivitis. Lack of timely treatment of herpetic sore throat in children can lead to serous meningitis.
Fungal tonsillitis
A relatively mild form of sore throat that occurs in children under 3 years of age. It is distinguished by a coating of white, curdled flakes on the tonsils and, with proper treatment, goes away within a week.