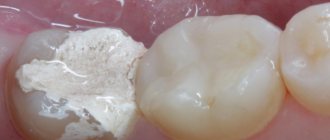
Features of superficial caries
Among the main distinctive features of superficial carious damage to teeth in children in comparison with other forms of pathologies, the following should be noted:
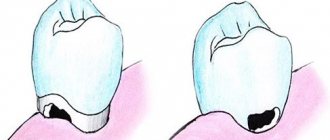
- only the enamel layer is affected by pathogenic formations. The dentin remains intact. With timely treatment, the risks of complications are minimal;
- the occurrence of an acute reaction to external stimuli, for example, sour and sweet foods, low and high temperatures;
- if superficial caries is diagnosed in children, treatment can be carried out without tissue preparation;
- Most often, the superficial form occurs in children aged 3-4 years and in adolescents.
Note! Initial caries and superficial caries are two completely different forms. The first appears as a small spot, the second occurs in the absence of treatment. It can be recognized by the presence of small-sized carious cavities.
Types of acute caries
Acute caries is divided into three types:
Acute superficial (or initial)
With this type, patients either do not show any complaints at all, or talk about tooth reactions to chemical irritants - sweet, sour and salty, less often a slight reaction to cold occurs. The reason is the destruction of the enamel, a violation of its mineral composition. A carious spot is visible, which has already passed into the stage of a shallow hole that has not yet passed beyond the boundaries of the enamel. An x-ray shows a superficial enamel defect.
Spicy medium
This type of caries is characterized by complaints of local short-term pain associated with exposure to a temperature or chemical irritant. The enamel has already been destroyed, further degenerative processes occur in the deeper layer of the tooth, dentin. You can see a hole that has destroyed all the enamel and moved to the border with dentin or to the dentin itself, this can be seen on the x-ray.
Spicy deep
The most neglected option. Characterized by pain in response to chemical, thermal and mechanical stimulation. Upon examination, softened dentin is noticeable, which lines the resulting carious hole. The x-ray shows a significant defect in which the dentin layer is separated from the tooth cavity.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of superficial foci of caries are manifested by the following signs:
- visible defect. On the surface of the tooth there is a small cavity with uneven edges. The color of the formation is dark, the bottom is slightly rough;
- pain syndrome. When exposed to cold, hot, sweet and sour foods or drinks, sharp short-term pain occurs;
- hyperesthesia. When inhaling cold air, while brushing your teeth, increased sensitivity occurs.
These are the main symptoms and in each individual case they can manifest themselves differently.
How is caries diagnosed?
Caries can be detected during an external examination, but some of its symptoms are similar to those of enamel hypoplasia and fluorosis, so differential diagnosis is necessary. To achieve this, dentists use the following methods:
- Treatment of teeth with hydrogen peroxide. Areas of demineralization become more noticeable.
- Caries indicators. The enamel is coated with a special compound that turns the affected areas blue.
- Transillumination is the transillumination of a tooth with a directed beam of light from a special device.
- Fissurotomy: The dentist widens or grinds down the natural grooves on the chewing surface of the tooth to more closely examine the fissures.
- Laser diagnostics. This is the most modern research method. The dentist directs a laser beam at the tooth and illuminates it. The device shows whether there is a carious lesion and how deep it has spread.
- Radiography. It is used for the development of caries at the root or under the gum. The photographs show the carious lesion, its scale and stage.
After the examination, a method of caries treatment is selected.
Factors influencing the development of superficial caries in children
The fundamental factors that result in superficial caries in children are:
- eating foods that contain large amounts of carbohydrates;
- non-compliance with hygiene rules: insufficient brushing of teeth, ignoring periodic rinsing with special means, etc.;
- drinking water with a deficiency of fluoride in its composition;
- deficiency of vitamins and mineral elements;
- severe systemic diseases;
- hormonal imbalance;
- ignoring professional hygiene, the need for which arises every 5-6 months.
Any of these factors or several at once are the primary causes of tooth enamel destruction.
Classification of early stages of caries
At the first and second stages, hydroxyapatite, the main substance of enamel, is destroyed. It forms 5 pathological zones, which differ from each other in the depth of penetration into the tooth tissue. Each of these zones has its own characteristics:
- Superficial: stable and dense zone with small microporosity in the area of demineralization.
- Subsurface: in the affected area of the tooth, the calcium content decreases by 15%. Because of this, the permeability of the enamel increases.
- Central: calcium concentration drops by another 25-30%, and the number of micropores increases by 20%.
- Intermediate: mineralization is at a very low level - 2-4%, but the natural process of enamel restoration has not yet stopped.
- Internal: the carious lesion is located closer to the dentin, although within the enamel. There is a risk that superficial caries will progress to the third stage.
Initial and superficial caries can be cured without preparation and filling. However, treatment should be started as early as possible.
Principles of treatment of superficial caries
When superficial caries is detected in children, treatment should be aimed not only at eliminating formations on the tooth enamel, but also at preventing the re-development of the pathology. To prevent complications, comprehensive and immediate therapy is necessary.
When talking about treatment, it should be understood that it is just beginning in the dentist’s office, and it will also need to be continued at home using special means and traditional medicine recipes.
Features of treatment in the pediatric dentist's office
If baby teeth are damaged by caries, then it is quite possible to treat them conservatively without the use of drills, which almost every child is afraid of. Modern dentistry offers more gentle and comfortable methods:
- Children under 3 years of age undergo silvering or deep fluoridation of their teeth. If the enamel has already been damaged by caries, it is cleaned of plaque and treated with a laser. If necessary, cracks in the chewing and frontal teeth are sealed;
- at the age of 3 to 5 years, ozone therapy can be performed to eliminate the first stage of superficial caries, and in case of major complications, treatment is carried out using the method of depophoresis. Its essence lies in the introduction directly into the root canals of a special composition with calcium and copper;
- Children from 5 to 9 years old undergo filling. Glass ionopolymers or colored compomers are used for fillings;
- Children aged 9 to 12 years already have molars and adult technologies can be used to treat them with minimal trauma. But in most cases, therapy of chewing teeth is carried out by sealing fissures.
When superficial caries in children requires complex dental procedures, local anesthesia is mandatory before such procedures are performed. If removal is necessary, such an intervention can be performed under intravenous anesthesia.
Treatment at home
Along with professional treatment of caries by a pediatric dentist, proper oral care at home will also be required to obtain an effective result. For this purpose, special rinsing compositions and toothpastes with anti-caries effects are used.
For children under 4 years of age, dental and oral care products should not contain fluoride. The therapeutic effect is provided by antibacterial active components and calcium ions.
Children over 4 years old are allowed hygiene products containing fluoride, only the concentration of the element must be minimal.
LACALUT kids, PresiDENT Baby, SILPA Putzi, Splat junior are considered good toothpastes for children. You need to brush your teeth with them twice every day. Among the rinses, Drakosha for children, Active Kids, and LACALUT Teens have proven themselves well. When treating caries with such solutions, it is necessary to rinse your mouth after every meal and always before going to bed.
In addition to professional medications, you can also use remedies prepared according to alternative medicine recipes:
- An infusion of chamomile is perfect as a rinse. To do this, pour a glass of boiling water into 1 tbsp. l. dried flowers, leave and cool to room temperature;
- a weakly concentrated solution of sea salt has a positive effect on the condition of teeth. Dissolve 0.5 teaspoons of salt in a glass of water and use for rinsing.
Important! Rinse aids can only be used after the child reaches 1.5-2 years of age, when he can already rinse and spit out liquid on his own, rather than swallow it.
How is the treatment carried out?
During treatment, a drill is used and the dental nerve is affected, so it is impossible to do without anesthesia if you want to achieve high-quality treatment. If the nerve was once removed from the tooth, then you do not need to use an anesthetic.
Modern anesthetics are used as anesthesia - Ultracain, Septanest and other drugs with a similar effect.
Removal of infected tissue
Since patients turn to the dentist when caries has already penetrated not only into the enamel, but also into the dentin, it is necessary to remove tissue damaged by putrefactive processes in order to prevent the further spread of bacteria, as well as to form a cavity suitable for filling.
Modern technologies suggest replacing the drill with a laser, but this method is not characterized by reduced pain, and its cost is often unreasonably high, since laser tissue removal is not common in all clinics and is used extremely rarely.
After cleansing the caries-pigmented tissues, it is necessary to rinse the cavity and treat it with an antiseptic.
Treating the cavity with an antiseptic
Chlorhexidine or drugs with a similar effect are used as an antiseptic, which disinfect tooth tissue and reduce the activity of enzymes, which are a breeding ground for bacteria.
Dental nerve extraction
Removal of the dental nerve is indicated only in the case of a complicated form of acute caries, when destructive processes have already reached the nerve, exposing it. In this case, the patient experiences acute pain.
Now the removal of a nerve, both partial and complete, is most often completed in one visit to the dentist; the procedure is assisted by an X-ray machine, which allows you to evaluate the accuracy of the manipulation during the treatment process. Thanks to modern painkillers, there is no pain when the nerve is removed.
Restoration of the anatomical shape of the tooth
The last stage of restoring a tooth that has undergone caries is restoring its original shape. The materials used for this are composites, which are placed into the hole, and then ground and polished so that the finished filling does not cause any inconvenience to the patient, does not rub the cheek, does not injure the gums and tongue, and does not interfere with neighboring teeth.
For chewing teeth, which are subject to increased load, composites and ceramic inlays and onlays are used as cement. There are times when a doctor uses several types of material to restore the function and shape of a tooth.
Possible complications
Some parents are in no hurry to visit a pediatric dentist because they consider it useless to treat baby teeth. This approach is explained by the fact that permanent ones will grow instead of them anyway.
Although the carious process itself does not transfer from baby teeth to permanent ones, untreated caries lesions have a detrimental effect on the condition of the latter. If you ignore superficial caries in children , complications may very soon manifest themselves:
- caries progresses rapidly in the absence of adequate therapy. This leads to the development of periodontitis and damage to the molar tooth germ. The inflammatory process significantly slows down the eruption of permanent teeth and complicates their growth;
- premature loss of baby teeth leads to the formation of malocclusion and disrupts the structure of the maxillofacial system;
- If at least one tooth is missing in the dentition, this complicates the process of chewing food. As a result, problems arise with the functioning of the digestive system.
Remember! Even the smallest stain can lead to complete tooth decay. There is no need to risk your child's health. It is much easier to visit the dentist and, if necessary, treat caries.
What is caries: types and causes of the disease
Caries is the process of destruction of hard tooth tissues. Childhood caries develops rapidly: if in adults the transition from initial to deep caries takes years, then a child’s teeth can be affected in just a few months. As a rule, caries affects several baby teeth at once.
Types of caries of primary teeth according to the depth of damage:
- Superficial caries: a small cavity appears, the lesion affects only the tooth enamel. The child may experience sharp pain when eating sweet or sour foods. Treatment of the affected areas with fluoride-containing preparations is required.
- Medium caries characterizes the destruction of dentin. Damaged teeth react to thermal and taste stimuli. Treatment of moderate caries of primary teeth involves filling. If a tooth is loose and a permanent tooth is in a hurry to appear in its place, filling is pointless.
- Deep caries is the last stage of the disease, often accompanied by periodontitis, cyst formation, and gumboil.
Prevention
Proven methods for preventing superficial caries stem from the causes of its occurrence. So, take on board the basic measures to prevent it:
- The main rule
: carry out thorough and systematic hygiene of teeth and oral mucosa. A medium-hard toothbrush and fresh-smelling toothpaste are classics that we all know from childhood. But don’t forget about dental floss: it will be a good protection if you use it after meals. Don’t ignore chewing gum (sugar-free, of course!) – combine business with pleasure. - Try
to avoid unhealthy snacks between meals, especially sweet and carbohydrate ones. Sweets, cookies and cakes are bad for your teeth, because rarely does a person immediately rush to brush their teeth after eating them. It would be worth it! - Take care
of your dental health. Check your mouth regularly. If you see abnormal pigmentation or surface deformation, do not delay in any case, but contact us for help! - Visit
the dentist once, or better yet twice a year, even if you have no complaints. The doctor will detect the slightest violation that cannot be noticed by yourself. This will allow you to begin to take measures at the very first stage, including dealing with caries at the early stage of the stain conservatively - without a drill or filling, as well as promptly treating superficial caries without affecting the dentin. In addition, the specialist will recommend procedures to maintain dental health, such as professional cleaning or treating teeth with special calcium-containing products and fluoride varnish, and will also remove tartar. - Remember
, the sooner you see a doctor at our medical center, the faster and more successfully superficial caries will be cured, which means you won’t have to suffer and be afraid of dire consequences!
In our center, qualified, understanding and most friendly
doctors !
Why does tooth decay occur?
The main reason
The occurrence of caries, including superficial ones, is the appearance and reproduction in the oral cavity of putrefactive microorganisms that come into contact with food particles.
Digesting them, pathogenic bacteria release organic acids that disrupt the chemical balance and wash away the most important building element of the tooth, calcium, from the enamel. poor hygiene
thus creates favorable conditions for the development of caries .
So, scientists identify factors contributing to pathology:
- violation of the microflora of the oral cavity;
- poor dental and oral hygiene, leading to the formation of soft and hard plaque;
- reduced immune defense;
- imbalance in the composition and properties of salivary fluid in a number of chronic diseases, for example, gastrointestinal;
- lack of vitamins and microelements: calcium, fluorine;
- tartar;
- genetic predisposition.
However, few people are resistant to caries.
(caries resistance) even in the presence of pathogenic factors.