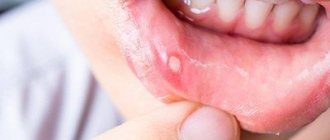
As a result of the development of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the throat and oral cavity, an unpleasant and even cutting pain in the throat often appears. An unpleasant symptom negatively affects general well-being and interferes with normal eating, drinking and talking. The pain most often continues for several days. To alleviate the condition, many doctors advise taking Imudon.
Imudon is a medicine that is of bacterial origin. Has an immunostimulating effect. The drug helps to overcome the emerging disease. Before taking it, you should read the indications, instructions for use and make sure there are no contraindications.
Composition and release form
| Lozenges | 1 table |
| mixture of bacterial lysates (dry matter): Streptococcus pyogenes group A, Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium, Streptococcus sanguis, Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae subsp. pneumoniae, Corynebacterium pseudodiphtheriticum, Fusobacterium nucleatum subsp. nucleatum, Candida albicans, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus fermentum, Lactobacillus helveticus, Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. lactis | 50 mg |
| excipients: lactose; mannitol; glycine; povidone; sodium saccharinate; sodium bicarbonate; sodium deoxycholate; anhydrous citric acid; mint powder; magnesium stearate; sodium merthiolate (preservative) - no more than 12.5 mcg/table. |
8 pcs in blister; There are 5 blisters in a cardboard box.
Imudon 24 pcs. lozenges
pharmachologic effect
Pharmacological action - immunostimulating.
Composition and release form Imudon 24 pcs. lozenges
Lozenges - 1 tablet.
- mixture of bacterial lysates (dry matter): Streptococcus pyogenes group A, Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium, Streptococcus sanguis, Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae subsp. pneumoniae, Corynebacterium pseudodiphtheriticum, Fusobacterium nucleatum subsp. nucleatum, Candida albicans, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus fermentum, Lactobacillus helveticus, Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. lactis - 50 mg;
- excipients: lactose; mannitol; glycine; povidone; sodium saccharinate; sodium bicarbonate; sodium deoxycholate; anhydrous citric acid; mint powder; magnesium stearate; sodium merthiolate (preservative) - no more than 12.5 mcg/table.
There are 8 pcs in a blister; There are 5 blisters in a cardboard box.
Description of the dosage form
White or almost white tablets of flat-cylindrical shape, with a smooth shiny surface, with beveled edges, without pores.
Characteristic
Polyvalent antigenic complex is a mixture of bacterial lysates, the composition of which corresponds to the pathogens that most often cause inflammatory processes in the oral cavity and pharynx.
Directions for use and doses
Inside.
Adults and teenagers over 14 years old.
For acute inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity and pharynx and exacerbation of chronic diseases: - 8 tables. in a day. The tablets are dissolved (without chewing) in the mouth at intervals of 1 hour. The average duration of treatment is 10 days.
For the prevention of chronic inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity and pharynx: 6 tablets. in a day. The tablets are dissolved (without chewing) in the oral cavity at intervals of 2 hours. The course duration is 20 days.
Children from 3 to 14 years old.
In the treatment of acute and exacerbation of chronic inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity and pharynx, as well as for prevention: 6 tablets. in a day. The tablets are dissolved (without chewing) in the oral cavity at intervals of 2 hours. The duration of treatment for acute diseases is 10 days, for the prevention of chronic diseases - 20 days.
It is recommended to carry out preventive courses of taking Imudon 3-4 times a year.
Pharmacodynamics
Immunostimulating drug of bacterial origin for topical use in dentistry and otorhinolaryngology. Activates phagocytosis, helps increase the number of immunocompetent cells, increases the production of lysozyme, interferon and secretory immunoglobulin A in saliva.
Indications for use Imudon 24 pcs. lozenges
Treatment and/or prevention:
- superficial and deep periodontal disease, periodontitis, stomatitis, glossitis, aphthous stomatitis;
- inflammatory and infectious diseases of the oral cavity and pharynx;
- erythematous and ulcerative gingivitis;
- dysbacteriosis of the oral cavity;
- pharyngitis;
- chronic tonsillitis;
- ulcerations caused by dentures;
- infections after tooth extraction, implantation of artificial dental roots;
- preoperative preparation for tonsillectomy;
- postoperative period after tonsillectomy.
Contraindications
- increased individual sensitivity to the drug or its components;
- children under 3 years of age.
Application of Imudon 24 pcs. lozenges during pregnancy and breastfeeding
There is insufficient information on the use of Imudon in pregnant women. Relevant data from animal experiments and epidemiological studies are not available.
It is not recommended to take Imudon during pregnancy or lactation.
special instructions
Children from 3 to 6 years old dissolve tablets under the mandatory supervision of adults!
You should not eat or drink water, or rinse your mouth for an hour after using Imudon, so as not to reduce the therapeutic effectiveness of the drug.
When prescribing the drug to patients on a salt-free or low-salt diet, it is necessary to take into account that 1 tablet of Imudon contains 15 mg of Na+.
For patients with bronchial asthma in whom taking medications containing bacterial lysates causes an exacerbation of the disease (an attack of bronchial asthma), the use of the drug is not recommended.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
There is no data indicating the need for any restrictions on activities related to driving a car or other machinery during the treatment period.
Overdose
Cases of overdose of the drug Imudon have not been described.
Side effects Imudon 24 pcs. lozenges
Rarely:
- from the gastrointestinal tract: nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain;
- allergic reactions: rash, urticaria, angioedema.
Drug interactions
Imudon can be used with drugs from other groups.
Indications for the drug Imudon®
Treatment and/or prevention:
superficial and deep periodontal disease, periodontitis, stomatitis, glossitis, aphthous stomatitis;
inflammatory and infectious diseases of the oral cavity and pharynx;
erythematous and ulcerative gingivitis;
dysbacteriosis of the oral cavity;
pharyngitis;
chronic tonsillitis;
ulcerations caused by dentures;
infections after tooth extraction, implantation of artificial dental roots;
preoperative preparation for tonsillectomy;
postoperative period after tonsillectomy.
Reviews about the drug Imudon
People who have already tried the effect of the medicine on themselves for medicinal or therapeutic purposes assure that for many diseases that are present in the list of indications for use, the tablets are highly effective. Most reviews are positive. Most often it is taken for stomatitis and tonsillitis.
There are some doctors who are of the opinion that the effect of the drug and its effectiveness have not been fully studied, and some patients claim that no result was achieved after taking it.
Directions for use and doses
Inside.
Adults and teenagers over 14 years old
For acute inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity and pharynx and exacerbation of chronic diseases: - 8 tables. in a day. The tablets are dissolved (without chewing) in the mouth at intervals of 1 hour. The average duration of treatment is 10 days.
For the prevention of chronic inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity and pharynx: 6 tablets. in a day. The tablets are dissolved (without chewing) in the oral cavity at intervals of 2 hours. The course duration is 20 days.
Children from 3 to 14 years old
In the treatment of acute and exacerbation of chronic inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity and pharynx, as well as for prevention: 6 tablets. in a day. The tablets are dissolved (without chewing) in the oral cavity at intervals of 2 hours. The duration of treatment for acute diseases is 10 days, for the prevention of chronic diseases - 20 days.
It is recommended to carry out preventive courses of taking Imudon® 3-4 times a year.
Features of Imudon
The medicine has been sold in pharmacies for more than 2 decades. The drug is one of the local immunostimulants. Once in the oral cavity, it strengthens the immune system. The active components included in the composition are not capable of leading to the appearance of any disease or causing complications of an existing disease. The action of the active components leads to an increase in the number of phagocytes (cells of the immune system). These cells absorb and destroy foreign elements. The action of the active components is supported by the auxiliary elements present in the composition.
special instructions
Children from 3 to 6 years old must dissolve tablets in the mouth under the supervision of an adult!
If necessary, you can rinse your mouth no earlier than 1 hour after administration (so as not to reduce the therapeutic activity of the drug). When prescribing the drug to patients on a salt-free or low-salt diet, it is necessary to take into account that 1 table. Imudon® contains 15 mg sodium.
There is no data indicating the need for any restrictions on activities related to driving a car or other machinery during the treatment period.
Adverse reactions and overdose
Negative effects may occur as a result of taking the drug:
- from the gastrointestinal tract: nausea, vomiting, pain in the stomach;
- from the respiratory system: cough, exacerbation of asthma;
- allergies: skin rash, urticaria;
- from the circulation: thrombocytopenia.
Other reactions include high body temperature.
No cases of overdose have been recorded to date.
Analogs
There are no complete analogues of Imudon tablets on sale; there are substitutes for it according to the pharmacotherapeutic group. For a sore throat, doctors prescribe:
- Lysobacter;
- Grammidin.
The following medications contain bacterial lysates:
- IRS19;
- Broncho-munal;
- Ismigen.
Which is better Broncho-munal or Imudon?
Broncho-munal (available from 12 years of age) and Broncho-munal P (designed for children from 6 months to 12 years) are available in capsules that are used for the treatment and prevention of respiratory tract infections. This is an immunostimulating agent, it prevents exacerbation of chronic bronchitis. Capsules are contraindicated if you are allergic to their composition. Broncho-munal and Imudon have different indications for use, and the doctor must decide which remedy is best for a particular patient.
Washing the lacunae of the palatine tonsils
Recommended by doctors for chronic tonsillitis, including for the prevention of exacerbations of the disease. It can be carried out with a syringe with a special attachment - a cannula or using a vacuum method.
The palatine tonsils are accumulations of lymphoid tissue in the pharynx; their important anatomical feature is the crypts. Crypts are branching depressions in the tonsils, due to which the area of contact of lymphoid tissue with infectious agents increases and, as a result, the immune response is carried out faster.
Tonsilloliths also form in the crypts - caseous plugs, which are dense formations consisting of desquamated epithelium and food debris. Usually the plugs are small and come out on their own; this process goes unnoticed by humans. In some cases, plugs linger in the crypts, and when bacteria and leukocytes join them, they increase in size and become denser. The presence of tonsillitis is associated with a feeling of discomfort in the throat, sore throat, reflex cough, and very rarely, only in 3% of cases, halitosis (bad breath). Among the normal microflora of crypts, anaerobes stand out separately, producing volatile sulfur compounds; it is because of them that the cork acquires a characteristic unpleasant odor.
It is believed that caseous plugs do not have a negative impact on health, which means they do not pose a danger. Only in Russia and the post-Soviet space is the detection of traffic jams associated with the presence of chronic tonsillitis. In other countries, this disease is classified as persistent inflammation and swelling in the throat, accompanied by pain, in some cases requiring systemic antibacterial therapy.
In our country, doctors usually recommend a course of rinsing, consisting of 5 procedures, which are carried out every other day or less often. This approach is not based on evidence of effectiveness, but on the preferences of a particular specialist, “his personal experience” and the desire of the patient. A wide variety of washing solutions are used - from furatsilin to systemic antibiotics and bacteriophages.
Foreign doctors offer patients to remove plugs themselves in a variety of ways. It has not been proven that a course of washing the tonsils reduces the incidence of tonsillitis. If caseous plugs cause a person significant discomfort, or he or she is bothered by bad breath, it is suggested that you discuss the possibility of tonsillectomy (tonsil removal) with your doctor. Sometimes, unfortunately, this is the only way to get rid of traffic jams. A one-time rinsing of the tonsils is allowed to remove tonsillitis (not during an exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis!), if they cause severe discomfort, including psychological, and the patient is unable to do this on his own.
The therapeutic effect of washing the palatine tonsils in the prevention of exacerbations of chronic tonsillitis has not been proven. There are also no clear recommendations determining the number of procedures.
It is important to know : washing the lacunae of the tonsils is not a therapeutic or preventive procedure.
“Cuckoo” or nasal lavage using the Proetz fluid movement method
A method developed by American otorhinolaryngologist Arthur Proetz more than a century ago. For many years it was used by ENT doctors to treat acute diseases of the nose and paranasal sinuses.
Russian ENT doctors prescribe “cuckoo” for almost any patient complaint, from acute rhinitis and sinusitis to acute adenoiditis and eustachitis. Washing technique: the patient lies on his back (less often sits), an antiseptic solution is pumped into one half of the nose, and removed from the other using suction. During the procedure, he is asked to pronounce the word “cuckoo” to reduce the likelihood of the solution getting into the throat and larynx (this causes the soft palate to rise, closing the nasopharynx). However, there is still a high risk of liquid entering the respiratory tract, especially in children who do not always understand what is required of them and behave restlessly.
Due to the creation of negative pressure in the nasal cavity, “cuckoo” can be traumatic for the inflamed mucous membrane of the nasal cavity, and if there is severe swelling in the nose and nasopharynx, it can be painful for the ears.
The use of “complex compounds” for rinsing is less preferable than saline solution. Antiseptics can additionally dry out the inflamed mucous membrane of the nasal cavity. Adding antibiotics to the solution also does not provide a therapeutic effect (in “cuckoo” it is often the reserve antibiotic dioxidine; its side effects are dangerous: experimental studies have shown that it has a mutagenic and damaging effect on the adrenal cortex). The addition of hormonal drugs such as dexamethasone or hydrocortisone is also not justified - there are more suitable hormones for use in the nasal cavity (mometasone, fluticasone, budesonide, etc.). If indicated, these sprays can be successfully used; however, they have low bioavailability, that is, they act only in the nose, without having a systemic effect on the body and without significant side effects.
It has been proven that nasal rinsing with positive pressure (Dolphin balloon, Neti pot) is more effective. Such rinses are especially effective for allergic rhinitis and chronic sinusitis.
Important to know : in acute bacterial sinusitis, it makes sense to discuss the use of oral antibiotics only. Neither topical antibiotics nor local antiseptics are indicated, even as an adjunct to treatment.
What is better Ismigen or Imudon?
Ismigen is available in sublingual tablets, which can be used by patients over 3 years of age with infections of the respiratory tract and ENT organs: inflammation of the ears, bronchi, larynx, tonsils, mouth, paranasal sinuses, runny nose. The medicine is not used in dentistry. It is prohibited in case of hypersensitivity to its composition. Treatment with it can cause allergies, inflammation of the salivary glands, larynx, and runny nose. Ismigen has a more convenient dosage regimen compared to Imudon. You need to take only 1 tablet per day for 10 days.
Doctor Komarovsky's opinion on immunomodulators
Evgeniy Olegovich believes that taking pills is useless, and to strengthen the child’s immunity, the following rules must be followed:
- feed him according to his appetite;
- do not give a lot of sweets, which lead to excess weight, diabetes, and weaken the body’s defenses;
- play outdoor games with him;
- maintain in the room where the child is located the air temperature from 18 to 20 degrees, and the humidity from 45% to 60%;
- give him ice cream and cold drinks, which harden the throat and increase local immunity;
- Make sure your child has regular bowel movements.
Despite the fact that the medication can be purchased without a prescription, self-medication is prohibited. Before starting treatment, they need to consult a doctor who will tell you how to drink Imudon.
By
What is better Imudon or Grammidin?
Grammidin contains the antiseptic cetylpyridinium chloride and the antibacterial agent gramicidin as active substances. It is produced in a spray, which is permitted from 18 years of age. In pediatrics, Grammidin for children is used, which contains the same active ingredients as Grammidin, but in smaller doses. It is available in the form of a spray and lozenges. They can be given to children over 6 years of age for oral infections. Grammidin for children is prohibited if its composition is intolerant. During treatment, they may experience allergies, diarrhea and nausea. Despite the general indications for use, Imudon and Grammidin for children have different compositions and mechanisms of action and can be used together to achieve a faster effect.
Which is better Lizobakt or Imudon?
Lyzobact is a combination drug, the therapeutic effect of which is explained by lysozyme and vitamin B6. It is available in tablets. Lysozyme is active against fungi, bacteria and viruses. Vitamin B6 prevents the formation of ulcers on the oral mucosa. Lizobact can be used for children over 3 years of age with infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity. It is allowed to be used in combination with other medications for herpes in the mouth. Lizobact is contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to its composition, in which case it can cause allergies. The cost of 30 antiseptic tablets is approximately 250 rubles. Imudon and Lizobact are not completely interchangeable and the doctor should decide which is better depending on the clinical picture and characteristics of the patient’s body.
Which is better Imudon or IRS 19?
IRS 19 is a Russian medicine that is available in the form of a nasal spray. Compared to Imudon, it has a wider scope of application; it is used not only for diseases of the ENT organs, but also for respiratory tract infections: sinusitis, bronchitis, rhinitis, tracheitis. It can be used to increase local immunity after acute respiratory viral infection. Compared to Imudon, it has a more convenient treatment regimen; depending on the diagnosis, it needs to be sprayed 2 to 5 times a day. The spray can be used in children older than 3 months. But this does not mean that IRS 19 is better than Imudon, since it can cause fever, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, inflammation of the bronchi, larynx, paranasal sinuses, blood vessels of the skin and subcutaneous fat, thrombocytopenic purpura, and possibly tablets for resorption are more suitable for a particular child than an aerosol.