In this article we will look at Stanton-Capdepont syndrome, a disease determined at the gene level. It manifests itself as damage to the enamel and dentin, which results in not only an aesthetic defect, but also a subsequent decrease in the height of the bite. The size and shape of teeth are not affected during eruption.
Discoloration is characteristic - staining the enamel grayish or brown. A medical history test, physical examination data, X-ray examination and EDI can correctly diagnose the syndrome. Its treatment usually consists of complex remineralizing therapy and prosthetics. Let's look at this syndrome in more detail.
Causes of pathology
Stanton-Capdepont syndrome is a hereditary disease that occurs as a result of a mutation in the gene that is responsible for a specific matrix protein. It is transmitted in 50% of cases, both in girls and boys. The disease affects not only temporary teeth, but also permanent teeth.
The cause of irreversible changes is a decrease in the thickness of the enamel layer (enamel and dentin dysplasia), which disrupts the connections between the hard tissues of the tooth. Usually there is no predentin layer. Dentinal tubules are less than normal. The production of replacement dentin leads to obliteration of the pulp chamber and calcification of the root canals.
STEINTON-CAPDEPOINT SYNDROME
STEINTON-CAPDEPONT SYNDROME
(Gh. W. Stainton, 1839-1906, American dentist; V. Capdepont, 1867-1918, French dentist; syndrome; synonym:
odontogenesis imperfecta, odontopathia mesodermo-ectodermalis, opalescent dentin, Stainton's syndrome, Capdepon's dysplasia
) - a genetically determined malformation of the development and structure of dental tissues, characterized by a change in the color of the crowns of the teeth, increased fragility of the roots, early obliteration of dental cavities and a decrease in the electrical excitability of the pulp. Described in 1892 by Stainton and in 1905 by Capdepont. It is observed equally often in men and women. Both temporary and permanent teeth are affected. Etiology and pathogenesis are unknown.
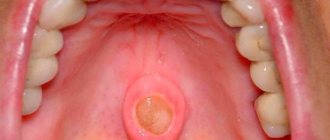
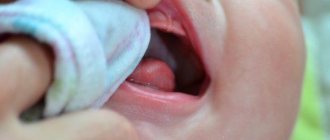
Teeth with S.—K.s. erupt at normal times, the color of the enamel ranges from bluish-gray to dark brown, sometimes with a pearlescent sheen. Soon after teething, the enamel begins to chip, the teeth become transparent (amber), the exposed dentin takes on an increasingly darker color from light yellow to brown, and such teeth quickly wear down to the gums. Worn teeth are usually insensitive to external influences and often have reduced electrical excitability; The cavities of the teeth and the canals of the roots of the teeth become obliterated early. In addition to obliteration of dental cavities, radiographs sometimes reveal changes in the roots (shortened, thickened or thin), and at the apexes of the roots of some (or many) teeth there are foci of destruction of bone tissue.
With histol. examination of teeth (see) in the enamel reveals wider, compared to the norm, interprismatic spaces, and closer to the surface of the enamel - resorption and decay of enamel prisms. The number of dentinal tubules towards the pulp decreases sharply; they are convoluted and of different diameters. The predentin zone is often absent. The layer of odontoblasts is thinned, many cells are devoid of processes. Excessive development of cement is observed on the surface of the tooth roots.
To prevent tooth wear, it is recommended to cover them with artificial crowns; in case of significant tooth abrasion, orthopedic treatment is carried out in order to restore the dentition (see Dentures).
Bibliography:
Borovsky E.V. et al. Therapeutic dentistry, M., 1982; B i x 1 e D. Heritable disorders affecting dentin, in the book: Oral facial genetics, ed. by V. E. Stewart a. G. H. Prescott, p. 227, St Louis, 1976; C apd ep ont C. Dystrophie dentaire non encore decrite е type her £ditaire et familial, Rev. Stomat. (Paris), t. 12, p. 550, 1905; Stainton CW Crownless teeth, Dent. Cosmos, v. 24, p. 978, 1892*
Yu. M. Maksimovsky, L. R. Rubin.
Symptoms
Stanton-Capdepont syndrome does not prevent teeth from erupting on time. Early or late appearance is rare. A characteristic symptom of the disease is the color of the enamel - from yellow to gray and brown. It occurs due to the filling of the dentinal tubules with blood. When chipped, the enamel exposes the dentin surface.
An increase in water content and a decrease in mineral components destroys the dentin structure, which affects increased tooth wear. A low bite reduces the lower third of the face. Due to chipped enamel, the edges of the teeth become sharp, resulting in painful damage to the mucous membrane. What is glass ionomer cement used for? More on this later.
Objectives of the Center
- Using a synergistic effect when combining the scientific and clinical potential of the specified departments of St. Petersburg State University and specialists in various fields (cardiorheumatology, pulmonology, neurology, gastroenterology, endocrinology, immunology and allergology, psychiatry, epidemiology) - to clarify the etiology, pathogenesis and development of effective methods for the treatment and prevention of health disorders in persons who have had a new coronavirus infection.
- Development of domestic and international cooperation in biomedical and clinical research of post-infectious autoimmune and immunopathological syndromes and diseases.
- Development of an individualized treatment plan for each patient in a short time within the framework of outpatient consultations, a clinical examination by a team of specialists and a one-day hospital stay.
- Creation of a telemedicine consultation center to work with patients outside St. Petersburg.
Post-Covid syndrome
is a condition that occurs in the form of long-term pathological symptoms after a new coronavirus infection, persisting for three months or more.
Diagnostics
Clinical examination and the results of additional research methods, as well as anamnestic data are taken into account when making a diagnosis. During a physical examination, the dentist determines that the pigmented enamel is opalescent, gray or brown. In this case, the shape of the teeth will be correct. The sizes of the crowns are within normal limits. The enamel will be thin and fragile, quickly chipping after eruption, and the dentin layer will be exposed as a result. The dentin is stained and the teeth become dark brown. Due to the fact that there is increased abrasion, sharp edges appear, injuring the mucous membrane in the mouth. With this syndrome, the pulp chambers become translucent.
The radiograph shows a decrease in the height of the roots, the tooth cavity is narrowed, and the root canals of the tooth are obliterated. Also, in patients with this syndrome, radiographic examination often reveals foci of destruction in bone tissue. Cystic formations are associated with disruption of bone formation processes. This is also caused by the penetration of infection transdentally due to decay or inflammation of the pulp. According to the results of EDI, the sensitivity of the pulp decreases.
It is important to differentiate the syndrome from other genetically determined pathologies of hard dental tissues. These include:
- dentinogenesis imperfecta types 1 and 3;
- dentin dysplasia;
- imperfect amelogenesis.
The examination is carried out by a dentist-therapist. To identify hereditary factors of the disease, a geneticist consults.
Goals of the center:
- improving the quality of long-term observation, planned treatment and rehabilitation of patients who have suffered viral infections, including COVID-19, and who have complications of an immunopathological nature,
- exchange of scientific and clinical experience in the above area with Russian and foreign colleagues,
- diagnosis and rehabilitation of the consequences of autoimmune diseases.
What is the treatment?
For Stanton-Capdepont syndrome, remineralization therapy is carried out, which consists of restoring enamel and dentin. This method prevents subsequent tooth decay.
Most patients are indicated for endodontic treatment and dental crowning. An effective method is prosthetics. In this case, solid crowns are used, as well as metal-ceramic crowns. Removable dentures help solve problems of replacing dentition. How are tooth canals protected?
The patient is prescribed phosphorus-calcium preparations, vitamins, and microelements for oral administration. The surface of the teeth is coated with products containing calcium and fluoride. Teeth restoration with composite materials that are reflective is carried out in case of the syndrome, but this is a temporary measure, since a strong bond between dentin and the photopolymer material does not occur due to reduced mineralization. Subsequently, the tooth is destroyed.
To restore crowns in childhood, glass ionomer cement is most often used in dentistry due to the good adhesion of the material to dentin and enamel, caries protective effect, and high biocompatibility.
If periapical changes are detected in patients with this pathology, endodontic treatment is carried out with the teeth covered with crowns. These are serious methods.
Treatment of dysplasia
Today, medicine does not have methods that could allow patients to permanently get rid of all manifestations of dental dysplasia. The main goal of treating this pathology is to maximize the preservation of hard dental tissues from destruction by performing the following therapeutic procedures:
- filling;
- remineralizing therapy;
- artistic restoration of teeth;
- vitamin therapy.
In the absence of the expected effect from the treatment, as well as in the case of a significant loss of hard dental tissues, dental prosthetics are performed using the most modern and effective prosthetic devices.
Do not delay treatment, contact the 24-hour A.Dent dentistry and our doctors will provide you with decent treatment.
How can prosthetics help?
Prosthetics is the optimal method of restoring the function and aesthetics of teeth. Solid crowns are made for the lateral teeth, while the front ones are covered with metal-ceramic crowns. Prosthetics can also be carried out by veneering, lamination of the anterior group of teeth and cheek surfaces using ceramic onlays. If the root of a tooth is fractured or if endodontic therapy is poorly effective, the tooth is removed. To replace defects in the dentition, removable dentures are often used.
Post-Covid syndrome can manifest itself as:
- general physical weakness, dizziness,
- prolonged low-grade fever, fluctuations in body temperature,
- heaviness in the chest,
- difficulty breathing,
- vascular symptoms (vasculitis, microcirculatory disorders),
- heartbeat, fluctuations in blood pressure and pulse,
- pain in joints, muscles,
- headaches,
- loss and distortion of smell and taste,
- digestive disorders, including diarrhea,
- sleep disorder,
- anxiety, panic attacks,
- cognitive decline, memory loss, brain fog
- hair loss, tooth loss, cystic formations of the jaws,
- thermoregulation disorder, etc.
The severity and duration of manifestations depends on the course of the infectious process. Treatment consists of symptomatic therapy and includes medications, exercise therapy and physiotherapy.
Hereditary enamel dysplasia
Amelogenesis imperfecta is understood as a genetically determined pathology in which the structure of the enamel is disrupted. The disease develops at the stage of laying ectodermal sheets, from which the bone structure, blood vessels and a number of internal organs are subsequently formed.
Amelogenesis imperfecta is more often diagnosed in women. This fact is due to the fact that the abnormal development of teeth of this type provokes damage to other structures, resulting in the death of the male fetus.
The anomaly first appears in children when the growth of baby teeth begins. The latter have an uncharacteristic structure with thinned enamel, which acquires a yellow or brown tint.
Provoking factors
Amelogenesis imperfecta develops through the transmission of mutated material (the amelogenin gene) via the X chromosome or autosome. These changes lead to the formation of thin crystals, from which tooth enamel is subsequently formed.
Mutations of other genes also influence the development of enamel dysplasia. In particular, due to the imperfection of MMP-20, the fermentation of calcium-dependent proteinase is disrupted. The latter is responsible for the formation of the enamel matrix.
Type of enamel dysplasia
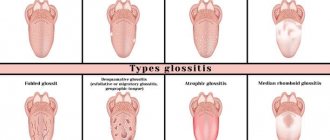
In medical practice, it is customary to distinguish four types of amelogenesis:
- Hypoplastic . It occurs at the stage of formation of dental tissues. The hypoplastic type is characterized by dysfunction of ameloblasts.
- Hypomaturation . Occurs against the background of disruption of the enamel formation process. In this case, the normal thickness of tooth enamel is maintained. However, it lacks minerals.
- Hypocalcification . It develops due to a failure in the mineralization process of tooth enamel. This type is characterized by active growth of crystallites. As a result, this anomaly leads to a decrease in the volume of minerals in the enamel.
- Hypomaturation with hypoplasia . The intensity of the symptoms is determined by the summation of the signs of both pathologies.
Features of symptoms
Regardless of the type of disease, it is accompanied by the following manifestations:
- thinning of enamel;
- darkening of its surface;
- the formation of depressions on the teeth located near the cheeks;
- partial or complete erasure of enamel and dentin.
The hypoplastic type of the disease is characterized by:
- darkening of the enamel surface;
- delay in teething;
- decreased bite height;
- displacement of the head related to the temporomandibular joint.
With the hypomaturation type, the following are observed:
- low X-ray density of enamel caused by its low mineral content;
- The upper parts of the tooth are covered with small dots or stripes.
The hypocalcification type occurs accompanied by the following phenomena:
- the enamel becomes soft, which leads to its peeling;
- the appearance of frequent chips on the surface of the teeth;
- the shine of teeth is lost.
Due to the fact that amelogenesis leads to thinning of the enamel, due to its gradual destruction, teeth acquire various abnormal shapes.
What does modern medicine offer?
Treatment of amelogenesis imperfecta takes about one year. For this disease the following are indicated:
- applications with preparations containing fluoride and calcium, this procedure is repeated every three months;
- use of casein phosphoprotein and amorphous calcium phosphate;
- restoration and prosthetics of teeth in case of diagnosis of significant damage.
Timely treatment, during which problem teeth are covered with crowns, can also achieve a positive effect.
Pathogenesis
The mechanism of occurrence of post-Covid syndrome is poorly understood and is presumably related to the morphological structure and properties of the virus and its effect on human tissues and organs.
One of the reasons is the tropism of the virus to the vascular endothelium of nervous, renal, and pulmonary tissue and the ability to cause chronic vasculitis in it with the development of thromboembolism, tissue hypoxia and organ ischemia.
The development of a pathological immune response cannot be ruled out, leading to the development of chronic autoimmune inflammation that affects human organs and systems.
Separately, one should take into account the influence of the SARS-CoV2 virus on the development of autonomic dysfunction, which is clinically manifested in dysfunction of the cardiovascular system, gastrointestinal tract, respiratory and nervous systems.
Types of myotonia
Myotonia congenita
Myotonia congenitis is the most common non-progressive form of myotonic syndrome and is caused by a mutation in the gene responsible for muscle sodium ion channels. This form of myotonia has no effect on life expectancy and has little effect on body structure or musculoskeletal growth. There are two forms of myotonia congenitis depending on the type of inheritance.
A common and rather severe type of myotonia congenitis is generalized Baker's myotonia, and the inheritance of this disease occurs in an autosomal recessive manner. The debut of this form of myotonia occurs in childhood or early adolescence, but sometimes with a severe course the debut can occur in early childhood. Symptoms may increase progressively over several years after diagnosis or gradually increase until the patient reaches twenty years of age.
The autosomal dominant form of inheritance is called Thomsen's disease. The disease is named after the Danish physician Asmus Julius Thomsen, who had the disease and traced the disease to his family. Symptoms of Thomsen's myotonia are usually much milder than with Baker's myotonia, although the onset of the disease occurs earlier, and the first signs become noticeable in early childhood and sometimes at birth. In rare cases, symptoms may be mild for many years after diagnosis.
The main symptom of both diseases is generalized myotonia caused by voluntary movements. As a rule, such symptoms are provoked by significant physical activity or, conversely, by a long period of rest and muscle relaxation. Myotonia is more severe in the legs, causing difficulty walking and sometimes even falling. Myotonia also affects the muscles of the shoulder girdle and head, which can cause difficulty grasping objects, chewing, or blinking. In rare cases, Baker's myotonia may have immobilizing weakness that appears after the myotonic attack.
After a myotonic attack, in both types of myotonia, stiffness can be relieved by repeated movements in the stiff muscles. Typically, stiffness increases after the first few contractions of the muscles involved, and then after five contractions, myotonic stiffness disappears, allowing normal muscle function to be restored for a certain period of time. This effect is called the warm-up effect and allows people with myotonia to engage in strenuous physical activity and strength sports.
And although myotonia congenitis does not significantly affect the formation of the musculoskeletal system, at the same time, myotonia affects the size of certain muscles. Both Baker's and Thomsen's myotonias can cause an unusual increase in the size of skeletal muscles, especially in the leg region of the buttocks, but also in the region of the arms, shoulders and back muscles. This increase can be considered muscle hypertrophy and sometimes such patients look like real athletes. With Baker's myotonia, muscle hypertrophy is more pronounced than with Thomsen's myotonia.
Paramyotonia congenita
This myotonia is a rare pathology associated with a disorder of sodium channels and is transmitted in an autosomal dominant manner. This type of myotonia does not shorten life expectancy, and the intensity of myotonia remains stable throughout life. The onset of the disease occurs between birth and early childhood. The characteristic symptom of paramyotonia congenitis is generalized myotonic stiffness, which mostly affects the hands and face, as well as the neck and arm areas. Just as with other non-progressive myotonias, paramyotonia congenitis is provoked by intense voluntary exercise, and in some cases provoked by low temperature. In many cases, cold-induced myotonic attacks and associated muscle stiffness can be relieved by heat.
Myotonic stiffness attacks are often accompanied by immobilizing weakness in the affected areas. The weakness may be longer lasting than an episode of myotonic stiffness, weakening the muscles for a period of minutes to several hours. But weakness is not characteristic of paramyotonia congenitis. In addition, unlike other non-progressive forms of myotonia, paramyotonia does not have a warm-up effect, in which stiffness decreases after several muscle contractions. Conversely, myotonic stiffness usually increases after continued muscle activity, further reducing motor performance. This phenomenon is usually called paradoxical myotonia.
Schwartz Jampel syndrome
Schwartz-Jempel syndrome is the most severe form of non-progressive myotonia. This very rare type of myotonia is transmitted in an autosomal recessive manner. The onset of the disease occurs either immediately after birth or a short time after birth. The nature and intensity of symptoms may have individual characteristics. One of the main symptoms is myotonic stiffness, most pronounced in the face and hips. With this myotonia there is a tendency to falls, speech disorders and facial changes. As with myotonia congenitis, additional muscle contractions cause a warm-up effect and reduce stiffness. But the warm-up effect is insignificant, and in some cases absent. Schwartz-Jempel syndrome is characterized by various skeletal deformities. These deformations cause a growth problem in the body and, as a rule, this is manifested by a decrease in height, as well as facial abnormalities, which gives the face a mask-like shape. Other symptoms include hypertrophied hips, atrophied shoulder girdles and prolonged muscle twitching, and sometimes intellectual impairment.
The cause of Schwartz-Jempel syndrome is not known. It is possible that this type of myotonia is a type of muscle disorder, and it is also possible to have a connection with disorders in the nervous system or is a combination of disorders in the muscles and nerves.
Causes
The main cause of post-Covid syndrome is a new coronavirus infection. The duration of the disease depends on the severity and can be 2-3 weeks for mild cases, and 4-6 weeks or more for moderate and severe cases.
With this disease, the patient may retain certain symptoms, which researchers associate with:
- persistent inflammatory process,
- possible long-term presence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in the body,
- development of autonomic dysfunction,
- chronic stress caused by lifestyle changes (introduction of quarantine measures).
Treatment
Currently, there are no treatment methods that can completely get rid of any myotonic syndrome . Treatment is symptomatic. If myotonic attacks become intense, it becomes necessary to use medications to reduce symptoms. The most well-known drug is mexilitene, as well as drugs such as guanine, procainamide, tegretol, phenytoin. But all these drugs have a lot of side effects and therefore their long-term use is not advisable. It is most optimal when the patient knows the factors that provoke myotonic attacks and tries to avoid provoking situations whenever possible, and after the attacks allows the muscles to recover through rest.