Changing children's baby teeth to permanent ones is always an exciting time for parents. This process is quite lengthy and often painful for the child, because it can be accompanied by various inflammations and discomfort. To help parents, for a better understanding of the physiological processes associated with the formation of teeth, dentists offer to look at the pattern of loss of baby teeth in children.
Bookmarking teeth
The formation of baby teeth occurs at approximately 4-6 weeks of fetal development. At the same time, the formation of the fundamental elements occurs much later - during the first months of the child’s life. For this reason, new mothers who are bottle-feeding are strongly recommended to supplement their baby’s diet with calcium. This substance promotes the proper formation of tooth enamel.
At an early age, unprotected baby teeth are extremely susceptible to carious lesions. Parents should monitor this closely, as infection can subsequently cause destruction of permanent teeth. The fact is that the rudiments of permanent teeth are in close proximity to the roots of milk teeth, so as soon as you discover dark spots on your child’s enamel, immediately go to pediatric dentistry.
The main signs of baby teeth
It is quite simple to identify baby teeth by their strictly vertical location in the dentition. Permanent ones, on the contrary, grow a little forward or to the sides. In terms of appearance, baby teeth also have significant differences.
For example, the height of the first and second primary incisors is about 5-6 mm, while permanent teeth can reach a length of up to 10 mm. In addition, the primary incisors have a flat and smooth edge, while the primary ones have a hilly edge. The third milk tooth (fang) is small in size and has a worn edge. The permanent fang is long, with a clearly pointed end. The fourth and fifth primary teeth are easily distinguished by the presence of four chewing cusps raised on the surface of the tooth. Permanent molars have two. And since there are only 20 baby teeth - five on each side of the middle of the row, the “six” and “seven” are a priori molars.
It is also easy to distinguish milk and molar teeth by the following characteristics:
- Baby teeth often have a white tint. This can be explained by the fact that the enamel and dentin layers in them are thinner than in adult teeth. While permanent ones have a natural yellowness due to the mineralization of hard tooth tissues.
- Molars are usually more massive and have an elongated shape, in contrast to the rounded milk teeth.
- The roots of baby teeth are much shorter and thinner than the roots of permanent teeth. They are not so firmly anchored in the bone, so these teeth fall out easily.
If you still cannot determine whether all of your child’s milk teeth have been replaced by permanent teeth, we suggest you contact our dental clinic “IBN-SINA”. Here you can undergo a preventive examination, receive important recommendations on oral care and caries prevention, and, if necessary, treat problem teeth.
Baby teeth in children: loss pattern
Many mothers are concerned about the question of when their children’s baby teeth begin to fall out. As a rule, this process starts immediately before primary school, that is, at the age of 6-7 years. In this case, the pattern of loss of baby teeth in children is similar to the sequence of their eruption. Only the fangs differ, which are replaced later, by the age of 13.
The order in which baby teeth fall out is the same for almost all children. First, molars grow - molars, which were absent in the “milk” set. As soon as there is enough space in the child’s jaw, “sixes” begin to appear. Only after this comes the time to change temporary teeth.
First, the lower incisors fall out, and then the upper ones. After this, the premolars appear at about 9-11 years of age. The last in line are the fangs, which usually fall out by the age of 10-12 years. At the same time, there should already be molars in the child’s mouth. After 18 years, third molars or, as we used to call them, wisdom teeth begin to emerge. However, they do not appear in everyone, which, by the way, does not indicate the presence of any pathologies.
"Shark Teeth"
During the process of root resorption, baby teeth become loose and, pushed out by growing permanent teeth, fall out. But sometimes the mechanism of this process fails. The permanent tooth has time to grow before the milk tooth that precedes it falls out.
Sometimes a whole row of such permanent teeth grows parallel to a row of milk teeth, which, for some unknown reason, do not fall out. Such teeth are usually called “shark” teeth, by analogy with the dentition of sharks, in which the teeth grow in three rows.
Studies have confirmed that “shark teeth” do not cause problems in the long term. When a baby tooth falls out, the “shark tooth” begins to shift and takes its normal place.
What should parents do?
The process of changing teeth in children worries parents, but this is quite natural, and most children do not experience significant pain. However, this does not relieve parents of the need to constantly monitor the condition of their child’s oral cavity. There is no need to remove baby teeth yourself. When the time comes to say goodbye to a tooth, a certain mechanism is activated in the child’s body that dissolves the milk tooth roots. You should seek help from a specialist only if the baby tooth does not want to fall out, but the permanent one is already beginning to appear.
After a tooth falls out, you may experience some bleeding. If desired, have your child rinse his mouth with a solution of soda with a drop of iodine as a preventative measure.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
What you should pay attention to
The child’s body prepares in advance for the period of teeth change. Here are the main signs of the changes taking place:
- mobility and loosening of primary teeth
- redness and swelling of the gums
- the appearance of interdental spaces due to jaw growth
- the rudiments of a permanent tooth become visible
When a baby tooth is replaced with a permanent one, the root gradually dissolves. The process is helped by a new tooth pushing out the temporary one from below.
Usually children and their parents remove the loose tooth themselves. But we recommend contacting a specialist who will provide professional assistance.
How many baby teeth do children lose?
The very first teeth appear between the ages of six months and one year. First, the incisors appear, located below and in the center, then the upper ones, and only then the lower lateral and upper lateral ones. This is followed by the first molars, canines and second molars. In pediatric practice, such a concept as a dental formula is used, that is, a standard dental set for children: 2 incisors, 2 molars and a canine. Multiplying the data obtained by four, we get 20 – the number of baby teeth is normal. Accordingly, the same number of baby teeth fall out.
Dental clinic "32 Dent" offers a full range of services in the field of pediatric dentistry. To receive complete and detailed answers to all your questions, call the numbers listed on the website.
Schedule for changing baby teeth to permanent teeth.
Primary teeth are a set of 20 primary teeth. Typically, replacing them with permanent teeth looks like this:
- 6 – 8 years – upper and lower incisors (units)
- 7 – 9 years – upper and lower lateral incisors (twos)
- 8 – 12 years – fangs (threes)
- 10 – 13 years – first and second premolars (fours and fives)
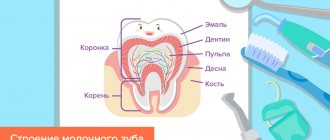
Baby teeth differ from “adult teeth” not only in size, but also in structure: their enamel is about 2 times thinner and not so saturated with minerals. Therefore, adults need to control that the child brushes his teeth thoroughly - caries on baby teeth develops quickly and quickly develops into pulpitis.
Useful tips for parents
- If a loose tooth begins to interfere, you can pull it out yourself. To do this, wrap it in a piece of sterile gauze, gently swing it to the sides and pull it up. Do not apply too much force, otherwise you may cause serious injury to the baby. If the tooth does not give in, it is better to leave it alone for a while or consult a dentist.
- Sometimes baby teeth sit firmly in the gums and interfere with the growth of permanent teeth - in this case, it is recommended to consult a doctor who will remove the tooth. If this is not done in a timely manner, the permanent tooth may grow incorrectly or “stand out” from the general row, causing the child’s bite to deteriorate.
- Many parents are faced with the phenomenon of caries of baby teeth. The decision to treat the disease should be made exclusively by a specialist (sometimes such a procedure is simply impractical). It is necessary to remember that after filling baby teeth, their roots dissolve much more slowly.
- If blood comes from the wound after a tooth falls out, you should cover the wound with a clean piece of bandage or cotton wool and hold it for several minutes. For two hours after the loss, it is better to avoid eating food, especially cold, hot, sour and salty foods.
- You can rinse your mouth after a tooth falls out, but not too actively - a blood clot forms in the hole that remains in place of the tooth, which protects it from germs.
- If changing teeth causes discomfort for your child, you can buy a special toothpaste that eliminates the discomfort.
- During the period of changing teeth, it is important to pay attention to caries and other dental diseases. If a baby tooth is affected by caries, there is a risk that its permanent “brother” will also be sick. In addition, the child’s diet at this time should be balanced and contain a sufficient amount of vitamins and microelements, especially vitamin D and calcium. It is better to limit the amount of sugar and sweets so as not to create an environment favorable for the growth of bacteria. To cleanse and strengthen teeth, you can give your child hard fruits and vegetables, such as apples or carrots.
- To protect your child’s permanent teeth from negative effects, you should contact a dentist who will perform fluoridation of teeth or fissure sealing (protecting areas that are in hard-to-reach places).
- Even if the process of changing teeth is easy and without discomfort, the child should visit the doctor at least once every six months - this will help identify caries in the early stages, as well as prevent its occurrence.
If a permanent tooth does not appear in the place of the milk tooth within 3-4 months, parents should consult a dentist. The reason for this may be a rare pathology called adentia - the absence of tooth buds. If the examination indicates this diagnosis, prosthetics will be necessary to maintain a beautiful bite and facial shape.
What reactions of a child’s body are possible during the period of loss of baby teeth and growth of permanent teeth?
Replacing teeth is almost painless. The loss of baby teeth occurs on their own after their root is completely absorbed or removed at home, and if the permanent tooth is already growing, but the permanent one has not yet fallen out, the help of a pediatric dentist is required. When permanent teeth erupt, pain usually does not occur. Very rarely, there may be a slight increase in body temperature, itching of the gums or discomfort in the abdomen. In this case, the child does not need treatment, but it is recommended to visit a dentist.