What does thrush look like in a child?
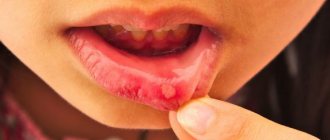
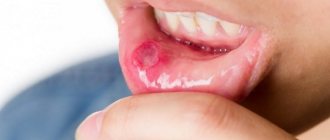
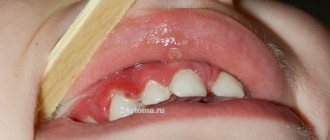
Any part of the oropharynx can be affected: tongue, lips, corners of the mouth, gums, mucous membranes of the cheeks, palate, pharynx, tonsils. White grains (spot coating) appear, reminiscent of curdled milk, or a film (solid coating) of a cheesy appearance. These elements are easily removed by scraping with a spatula, revealing a bright red base, sometimes with a bleeding surface. As a rule, the course of the infection is painless and has only local manifestations. General health is not affected.
Symptoms of thrush in the mouth in infants and children
Signs of candidiasis in babies vary depending on the stage of the disease and may appear 5-10 days after birth.
Symptoms of the first phase of the disease are disturbances in the psycho-emotional state (tearfulness) and the appearance of plaque. It is difficult to remove pathological formations that look like small white dots. The child refuses to take the breast and is capricious.
As thrush develops, deposits spread beyond the mouth and become localized in the throat.
The plaque acquires a cheesy consistency, looks like dense white plaques, and cannot be removed. The child's mouth smells unpleasant.
Stage three thrush in infants is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- deposits cover the throat, lips, tonsils, palate, gums, cheeks;
- upon palpation, enlarged lymph nodes are felt;
- identified ulcers are characterized by increased bleeding.
The baby is worried, constantly cries, and refuses to eat. Additional signs include fever up to 37.5 °C, lethargy, the presence of allergic reactions, and a strong odor from the child’s mouth. The disease spreads to the tissues of the gastrointestinal tract and manifests itself in the genital area. The plaque may take on a yellow or brown tint.
How to treat thrush in a child?
The disease is treated at home. Local medications are used and only as prescribed by a doctor: pediatrician or dentist! Special antifungal agents are used in the form of solutions, sprays, gels, and drops. For maximum effectiveness of therapy, the drug must remain in the oral cavity (on the mucous membrane) for as long as possible. Therefore, the main way to use them is by rinsing or lubricating.
Treatment is long, up to 2-3 weeks.
It is important!
Often thrush in the mouth of infants is associated with candidiasis of the skin of the nipples and areola in the mother. In this case, the woman experiences redness, irritation, and a burning sensation on her chest. In this case, treatment should be comprehensive, for mother and baby.
Symptoms of candidiasis
Most often, candidiasis occurs in newborns and preschool children.
The older the child, the less often the disease is diagnosed. The favorite place for thrush to appear is the oral mucosa. A cheesy coating appears on the gums, palate, and inside the cheeks, and the baby feels pain and itching when eating. Along with these symptoms, candidiasis in children is also characterized by other signs:
- redness of the mucous membrane;
- ulcers that open after removing the cheesy plaque;
- loss of appetite;
- general weakness;
- white coating on the tongue.
The child does not eat well and is often capricious, since any touch to the mucous membrane causes pain.
In advanced cases, bleeding wounds open at the site of the removed plaque. There is another common form of candidiasis - fungal tonsillitis. It develops as a result of improper treatment of protracted sore throat. Characteristic symptoms of the disease are a cheesy coating on the tonsils and a burning sensation in the throat.
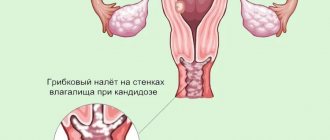
When the skin is infected with fungi, dense spots, redness, and blisters appear on it. In adolescents, thrush often affects the mucous membrane of the genital organs, and the disease is more typical for girls. Vaginal discharge becomes white and thick. In boys, the head of the genital organ turns red, and a discharge similar to sour cream appears in the area of the urethra. Cystitis and urethritis may develop.
If fungi infect the digestive tract, the child begins to suffer from colic, and food is difficult to digest. The baby suffers from constipation and pain in the lower abdomen. If fungi colonize the respiratory organs, the child often suffers from bronchitis, pneumonia, and ARVI. If internal organs are damaged, treatment should begin immediately, in consultation with a pediatrician.
Child nutrition
Simple carbohydrates are the main nutrient medium for fungal growth. Therefore, sweets, sugar, cookies, etc. must be excluded from the patient’s diet. Breastfeeding certainly continues.
If the child is bottle-fed or mixed-fed, then preference should be given to formulas containing probiotic microorganisms, which have the largest evidence base for their effectiveness. These are LGG and BB-12 from Chr. Hansen. It has been proven that LGG and BB-12 inhibit the growth of opportunistic microorganisms and fungi, protect against the development of caries and infections, and effectively prevent atopic eczema. Nutrilak Premium Comfort is enriched with LGG probiotic.
Disease prevention
To get rid of candidiasis completely, you need to adhere to a number of simple preventive measures. Among them:
- compliance with basic hygiene rules: wash your hands thoroughly, care for the skin and mucous membranes of the child;
- maintaining an optimal microclimate in the apartment;
- strengthening the child's immunity.
Thrush in a baby is a serious disease, the recurrence of which can only be avoided by timely consultation with a doctor. It is prohibited to independently treat childhood candidiasis, without undergoing the necessary examinations, based on knowledge obtained from newspaper (magazine) articles.
Candidiasis (thrush) and breastfeeding
Candidiasis (thrush) is one of the types of fungal infection, caused by microscopic yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida (primarily Candida albicans).
All representatives of this genus are classified as opportunistic (that is, they live in the body and can cause disease under certain conditions). Candida is part of the normal microflora of the mouth, vagina and colon of most healthy people. The disease is caused not simply by the presence of fungi, but by their proliferation in large quantities and/or the ingress of more pathogenic species of fungus.
Most people encounter Candida fungi in the first year of life, and according to some data, in utero. The possibility of infection of the fetus is confirmed by the detection of fungi in the amniotic fluid, placenta, and umbilical cord membranes. In the future, contact of newborns with Candida fungi can occur during the passage of the birth canal, with the mucous membrane of the mouth, with the skin of the nipple during feeding, the skin of the hands during care, as well as with food or household items.
Thrush of the nipples and areola has a negative impact on the breastfeeding process. It becomes painful for both mother and baby, the principle of feeding on demand is violated, which can lead to a decrease in the amount of milk. With the development of infection, blockage of the milk ducts and, as a result, lactostasis may occur. Against the background of candidiasis, there is also a possibility of a bacterial infection of the breast. The fungus is easily transmitted to the baby, and it develops oral candidiasis, causing the baby pain when sucking, and in some cases also causes breast refusal. It is necessary to treat candidiasis in the woman and baby as quickly as possible in order to restore the normal process of breastfeeding.
Why does the disease occur?
During lactation, ideal conditions are created for the fungus of the genus Candida on the surface of a woman’s nipples: increased humidity, a nutrient medium for the fungus (sugar in breast milk), decreased immunity in mother and child, postpartum hormonal imbalance, constant favorable body temperature.
Women at risk are most often affected by the disease. Risk factors include:
- taking antibiotics, hormonal drugs during lactation;
- nipple injuries due to improper attachment of the child;
- disturbance of intestinal microflora, as well as disturbance of vaginal microflora (for example, vaginal candidiasis during pregnancy and after childbirth);
- unbalanced diet (excessive consumption of sweets and baked goods);
- fatigue, stress and lack of sleep;
- diabetes mellitus and anemia in the mother.
Under such conditions, breast thrush has maximum opportunities for infection and development. During primary infection, the disease does not appear immediately, so it is important to carefully monitor the condition of the nipples and not miss the manifestations of alarming and rather unpleasant symptoms.
Clinical picture of the mother
What symptoms allow one to suspect the disease?
Upon examination, there may be swelling of the nipples, the formation of scales and films on the areola and nipple, as well as cracks in the nipples, the areola may be moist in appearance with small bubbles, and hyperemia of the skin of the breast.
The disease is accompanied by itching and burning of varying degrees of intensity, sometimes there is even severe pain. Characterized by high sensitivity of the nipple during feeding and between lumps, the breast becomes sensitive, the woman feels discomfort even when putting on underwear and when taking a shower. Pain from the nipple can spread throughout the chest, radiate to the arm or back - feeding the baby becomes unbearably painful. This symptom may indicate a bacterial infection.
The mother may have symptoms of vaginal candidiasis, especially if the woman suffered from it before giving birth.
Clinical picture in a child
If the disease is transmitted to a child, the fungus develops in his mouth.
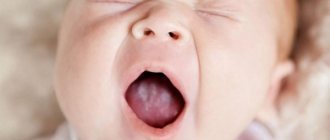
In this case, a whitish, cheesy coating can be found in the baby’s mouth, which develops on the baby’s tongue, gums, upper and lower palate. White films, unlike normal milk deposits, are difficult to remove when trying to treat the baby’s mouth; small wounds and erosions may appear under the white coating.
Also, characteristic rashes can be found around the anus, on the buttocks and inguinal folds of the child. To clarify the diagnosis, you need to contact your pediatrician.
Treatment of thrush
Since the fungus is easily transmitted from mother to child, and can then be transmitted back, therapy must be carried out simultaneously by both the nursing woman and the baby, even if one of the couple (mother or baby) does not have obvious signs of the disease.
- During treatment, feeding should be reduced in time, but feeding more often so that the baby receives a sufficient amount of milk. If pain is severe, temporary weaning and feeding with expressed milk may be necessary, and manual expression may be less painful than using a breast pump. It is recommended to feed the baby in alternative ways (not from a bottle).
- Careful adherence to the rules of personal hygiene will help speed up recovery - frequent hand washing with soap before and after feeding, before and after changing the baby's diaper and going to the toilet.
- If a mother suspects vaginal candidiasis, then she should contact a gynecologist for an examination, tests and timely treatment. In this case, systemic drugs can also be prescribed, most often fluconazole (Diflucan and its analogues). This drug is compatible with breastfeeding and does not require weaning during treatment.
- In some cases, relief is provided by treating the nipples with a soda solution, since the alkaline environment prevents the active proliferation of the fungus in the affected areas.
- Underwear should be cotton and breathable, not tight. In cases of severe pain during the acute period, wearing ventilated silicone breast shells helps when it is necessary to prevent contact of the nipples with underwear.
- Excluding simple carbohydrates (sweets, baked goods, baked goods and sugary drinks) from the mother’s diet will speed up recovery.
- Drug treatment (local and systemic) is prescribed only by a doctor after examination and diagnosis. Of the modern medications, the most commonly prescribed are creams and ointments containing an antifungal component - clotrimazole (Candide), natamycin (Pimafucin). In case of severe inflammation, swelling and suspected bacterial infection, combination drugs containing an anti-inflammatory (hormonal) and antibacterial component (Pimafucort, Triderm) can be prescribed. When used correctly as prescribed by a doctor, these drugs are safe during lactation. The need for systemic therapy is determined by the doctor. In some cases, you may also need to take pain medications.
As mentioned earlier, treatment is required not only for the mother, but also for the child to avoid re-infection.
- Wiping the oral mucosa with gauze soaked in soda, as recommended in many articles, can further injure the oral cavity and cause pain to the child. A solution of borax in glycerin is also prohibited for use due to toxicity to children.
- All items that may be in the child’s mouth (nipple covers, toys, teethers) must be thoroughly washed with soap and hot water or a soda solution.
- The pediatrician will prescribe medications to treat the oral cavity. Of the modern remedies, drops with clotrimazole (Candide) are most often prescribed. If there are rashes on the skin, use the same creams as for treating nipples. The baby's skin must be kept dry, ventilated more often, and washed with baby detergent when changing a diaper. Wet wipes can make the situation worse, delaying recovery.
Thus, if you consult a doctor in a timely manner and follow the recommendations, treatment of candidiasis can be successful. Stopping breastfeeding is not required.
Measures to prevent candidiasis of the nipples and areola
- Correct attachment and timely treatment of abrasions and cracked nipples.
- When using absorbent breast pads, change them as often as possible to keep the skin dry, and provide air baths.
- For breastfeeding women, it is recommended to wear cotton underwear that does not compress the breasts.
- In the diet of a nursing mother prone to recurrent thrush, the intake of simple carbohydrates should be reduced.
- Compliance with hygiene measures (washing hands), as well as timely treatment of other foci of thrush.
Thrush in children: causes
In adolescents, the main cause of thrush is a hormonal imbalance, which occurs due to the growth and development of the child or due to disruption of the endocrine system.
Other causes that act as factors in the occurrence of childhood vulvar candidiasis:
- reduced immunity;
- antibiotic treatment (uncontrolled);
- poor or unhealthy diet (especially abuse of sweets, fast food, etc.);
- smoking and alcohol;
- early onset of sexual activity;
- improper hygiene or its complete absence;
- hypothermia;
- anatomical features of the reproductive system;
- infection from the inside (for example, from the intestines);
- after contact with household objects or in public places (swimming pool, etc.);
- during childbirth from the mother;
- excess weight (at the stage of obesity);
- anemia and other diseases;
- allergic reactions.
As you can see, there are a lot of answers to the question “Where does thrush come from in children?” Moreover, as a rule, a whole complex of problems leads to thrush. Another factor is age. In infants, thrush usually appears as a result of parental neglect, in teenage girls - as a result of changes in the hormonal system, etc.
If there is any suspicion of candidiasis or another infection, it is necessary to take the child to a doctor who will conduct an examination and prescribe a course of treatment and recovery, as well as give useful tips on how to prevent infection or relapses. The medical center employs specialists in pediatric gynecology and uses modern diagnostic equipment.
Initial appointment
At the initial appointment, the doctor examines the child’s genital organs to assess the disease and state of health. The doctor also finds out the possible causes of thrush in a child, prescribes tests to understand how to treat, since the course is prescribed individually for each specific clinical case.
Diagnosis of the disease
In some cases, tests and examinations are required:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs
; - blood and urine tests;
- taking smears and culture for fungi of the genus Candida;
- stool analysis for worms and intestinal dysbacteriosis
If children are suspected of having any diseases other than thrush, additional tests are prescribed. Also, if thrush has caused a nervous shock and affects the psychological and mental development of the child, then a consultation with a psychotherapist is prescribed.
Procedure and treatment regimens for vulvovaginal candidiasis in school-age children and teenage girls
The procedure and treatment regimen are determined individually and depend on the type and stage of development of the disease, the causes of infection and the presence of concomitant diseases. A visit plan is also assigned individually, since for one patient the first consultation and follow-up appointment will be enough, while for others several appointments will be needed.
Diagnosis of thrush
“SM-Doctor” is a multidisciplinary medical center specializing in the identification and treatment of all types of diseases in children from 0 to 18 years old.
Thanks to modern equipment and experienced staff, our clinic provides patients with a full range of diagnostic services. This ensures quick and high-quality detection of thrush. The doctor can diagnose fungal infection of the mucous membranes during the initial examination of the child. After collecting anamnesis and analyzing the patient’s complaints, the doctor assesses the condition of the affected area of the body. If a characteristic plaque is detected in combination with the above symptoms, a preliminary diagnosis is made. To confirm it, the following additional procedures are used:
- microscopic analysis of scrapings from the affected area of the mucous membranes;
- traditional laboratory tests - general and biochemical analysis of blood and urine.
If there is a suspicion of concomitant somatic pathology, the doctor may refer the child for consultation to related specialists. Sometimes weakened immunity can be a consequence of gastritis, cholecystitis or other diseases of the internal organs.
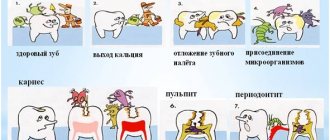
What is thrush?
Thrush is one of the clinical forms of a disease called candidiasis. This is a fungal disease of the mucous membranes, skin, nails, and internal organs of a person, caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. The appearance of the name “thrush” is due to the fact that during illness, the entire mucous membrane of the affected organ is covered with a whitish coating, which resembles curdled milk, and a curdled discharge is formed.
Newborns most often have to deal with oral candidiasis - thrush of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
Treatment plan
How to treat vulvar candidiasis (thrush) in children of school age, and not only?
Basically, treatment involves eliminating the pathogen and stopping its reproduction, which will therefore eliminate the symptoms. Only a good specialist can treat the disease correctly and effectively, who can prescribe:
- antifungal drugs and antiseptics (topically);
- antibiotics;
- ointments and medicinal baths;
- therapy to restore and strengthen the immune system;
- therapy to restore the microflora of the reproductive system.
Which course of treatment will be chosen and prescribed depends on the specific case and the reasons that led to vulvovaginal candidiasis in a teenage girl and a smaller child.
Repeated appointment
At the follow-up appointment, the doctor assesses the child’s condition and checks how effectively the chosen regimen works. If no positive dynamics are observed, then repeated diagnostics and selection of new methods for treating thrush in the child are prescribed.
Control reception
The control reception is an important point. The doctor prescribes it to see how the child recovers after a full course of treatment, to see if there are any relapses or suspicions of them. It is also possible to prescribe physiotherapy and rehabilitation (for example, if a long course of antibiotics has been prescribed). A follow-up appointment is usually scheduled after 21–30 days or later.
Treatment result
The disease can be cured, but the timing of treatment is individual and depends on the stage and causes of thrush in young children or teenage girls. All details of treatment are discussed individually at a doctor’s appointment. If there is a suspicion that the parents are infected, then both parents are treated.
Prevention
Thrush in children is a fairly common occurrence, especially under “favorable” conditions for the disease. To protect the child, it is necessary to take preventive measures:
- carry out proper personal hygiene of the child in accordance with age;
- wear the correct underwear;
- normalize nutrition (moderate or limited consumption of sweets, starchy foods and fast foods, more fruits, vegetables, etc.);
- Strengthen your immune system by taking vitamins and exercising.
Compliance with the rules of personal hygiene at home and in public places will also help avoid the occurrence of vulvar candidiasis and other unpleasant diseases in a teenage girl or young child.
Treatment of thrush
In treatment, the primary goal is to identify and eliminate all factors that led to the development of the disease. For initial, superficial, local forms of thrush, only local, external therapy should be carried out by irrigating the lesions with freshly prepared anti-candidal, disinfectant, alkalizing drugs.
The affected areas are cleaned with a sterile cotton ball soaked in an aqueous solution of potassium permanganate (pale pink solution), a 0.25% aqueous solution of borax, a 2% aqueous solution of soda (for 1 glass of boiled water at room temperature - 1 teaspoon spoon of baking soda), 1-2% aqueous solution of tannin, 0.25-1% solution of hydrogen peroxide. After each such treatment of the oral cavity, the affected areas should be lubricated (but no more than 5 days in a row) with a 1-2% aqueous solution of aniline dyes: gentian violet, methylene blue; 0.25% solution of silver nitrate; Iodinol diluted with boiled water 1:2, Lugol's solution diluted with boiled water 1:3. This procedure must be repeated every 2-3 hours.
You can treat the oral mucosa with an aqueous suspension of nystatin or levorin; you can prepare them yourself: crush the tablet and mix with water. levorin is prepared at the rate of 100 thousand units per 5 ml of boiled or distilled water. A suspension of nystatin at the rate of 250 thousand units per 5 ml of boiled or distilled water, alternates with a 5% solution of sodium bicarbonate. Treatment is carried out every 6 hours.
The mucous membrane is treated with a suspension of 2.5% pimafucin for local use 4-6 times a day, depending on the extent of the lesion. A 1% solution of clotrimazole (canesten, candide) is also used for external use 2-3 times a day.
All manipulations in children of any age should be performed gently and gently, without pressure. Care must be taken to ensure that the child cannot inhale or swallow the cotton. There is no need to start processing immediately after feeding, so as not to provoke vomiting.
If the mother is breastfeeding, then during the treatment period it is advisable to wash the breasts with water after each feeding, then treat the nipples with a 2% soda solution (1 glass of boiled water at room temperature, 1 teaspoon of baking soda) or an infusion of herbs (eucalyptus, calendula, oak, chamomile). Before feeding, you should also wash and treat the nipples with a soda solution. During the period of thrush, it is necessary to boil any object that may end up in your child’s mouth.
Treatment is carried out until complete clinical recovery, but not less than 14 days, since the disappearance of symptoms does not guarantee the elimination of the pathogen. The attending physician decides on the need to extend the treatment period.
But at the present stage, it is considered the most effective and convenient method of treating any form of candidiasis in children of any age, fluconazole (Diflucan, Diflazon, etc.) used orally (orally) 6 mg/kg once and then 3 mg/kg once every day. To do this, you can use injection powder. The powder can be mixed with a small amount of milk or boiled water. It is better to give the medicine from a teaspoon, while simultaneously lubricating the affected areas of the oral mucosa. When using fluconazole, the treatment period is reduced to 3-5 days.
In severe cases of candidiasis and lack of effectiveness of therapy, treatment in a hospital is necessary, with possible intravenous administration of antifungal drugs.
Advertising