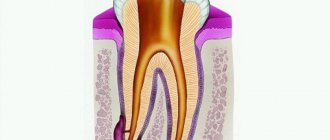
The inlay is a one-piece structure, the lower part of which is similar to a stump (therefore a stump). It takes into account the characteristics of the destroyed tooth, so it can be single, double or triple. In complex cases, it may consist of individual elements. The upper part is made of any shape, in accordance with the impression taken. The inlay can be installed without a crown, completely repeating the shape of the tooth. Such microprosthetics are often used in orthopedic dentistry, because even a severely damaged tooth can be completely restored, obtaining an aesthetic dental unit.
Advantages and disadvantages of tabs
- There is no danger of destruction or cracking - the strength and reliability of the inlays is high.
- Resistance to food dyes, color stability.
- The characteristics of the bite are taken into account.
- The shape of the tooth is completely restored and remains unchanged in the future.
- There are no unpleasant sensations at all.
- The result of tooth restoration is highly aesthetic.
- The possibility of the spread of harmful organisms is eliminated.
Negative aspects may arise if you go to clinics with insufficient equipment or inflated prices. In these cases, patients note the lengthy process of manufacturing and installing the inlay and the high cost.
What is it - a tooth tab?
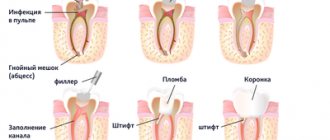
Dental inlays are microprostheses that can be used for different purposes. Restorative or restorative inlays are used like fillings: they help recreate the natural crown of a tooth, keeping it alive. Stump inlays are used in cases where it is necessary to restore a badly damaged tooth under a crown. Let's take a quick look at why restoration and stump inlays are used, and find out the difference between them.
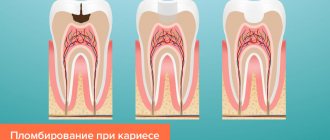
Restoring inlays are stronger than conventional dental fillings and differ from them in the technology of their creation: dental inlays are not made directly in the patient’s mouth, like fillings, but in a dental laboratory, using previously taken impressions. Because microdentures are made in a laboratory setting, they are also called indirect dental inlays.
The inlays exactly repeat the shape of the cavity that needs to be closed for tooth restoration and fit tightly to the natural tissues. The high density of adhesion of the inlay to the tooth tissue eliminates the risk of developing caries in the gap between the installed microprosthesis and the tooth. Restoring a tooth with an inlay will help keep the tooth alive in a situation where a sufficient amount of tooth tissue has been preserved, its nerve is alive and well, but a large filling still needs to be placed. Large fillings do not stick well to the teeth and can break under stress, along with the tooth. Inlays have a long useful life, can withstand chewing loads well, and their use makes it possible not to rush into dental prosthetics with a crown, which often requires preliminary depulpation of teeth.
Stump inlays for a tooth are no longer a restoration element, but a technical one. It acts as a support for the installation of a dental crown in cases where the tooth cannot be restored qualitatively with a conventional filling. In order not to confuse stump and restoration inlays, the easiest way to classify them is as follows: restorative inlays are installed outside the living tooth, stump inlays are always located under the crown.
This is the main classification of inlays, but they can also differ in the type of material they are made of, and below we will definitely talk about all the types of microprostheses and their features. But first, let's find out who and when is recommended to install inlays on teeth.
Indications and contraindications for use
It’s worth putting a tab if there is:
- Extensive caries damage (more than 60%) of the tooth tissue;
- Large cavity size;
- Traumatic tooth damage;
- Hyperplasia, dysplasia;
- Wedge-shaped defect;
- The need for protection against tooth wear;
- Installation of bridges simultaneously with root structures.
The use of inlays is not recommended if the patient has:
- Small tooth cavity;
- Carious processes are active;
- There is no quality oral hygiene.
Reconstruction of the functionality of the dentition using an inlay allows you to cope with high loads. This is a great solution, but it can be painful some time after installation. What to do if a tooth hurts under the tab?
The cause of pain may be high sensitivity. If the situation worsens over time, you need to see a dentist and get an x-ray.
If a tooth hurts under the stump tab, then the following reasons are possible.
- Pulpitis is damage to the pulp of a tooth with a preserved nerve. When installing the inlay, the pulp chamber was accidentally damaged. After the anesthesia wears off, the pain becomes severe and intensifies with chewing and contact with cold and warm foods. The patient feels pain under the tab.
- Pressing the inlay into the tooth tissue. A bursting, aching pain occurs, which does not allow establishing a specific location.
- The tab is too large. The patient feels pain only when chewing. The pain is dull, there is no reaction to hot and cold food. The sensations are more like discomfort. In the absence of correction, inflammation of the periodontium or gums develops.
- Infection. Before installing the inlay, the doctor cleans the carious cavity to prevent further spread of the destructive process. If at this moment there is already an infection in the tooth, but has not yet been identified externally, after installing the tab the process will spread deeper, to the pulp and to the roots. If left untreated, the pain under the ceramic inlay will become very severe, the nature of the “sensations” will be pulsating and sharp.
Causes of pain after dentures
All inflammatory processes are accompanied by pain, redness, swelling and dysfunction of the affected organ. However, each pathological process has its own symptoms and cause. For example:
- Incorrect or incomplete preparation of teeth for prosthetics. This means the lack of professional hygiene, root canal treatment, oral sanitation and treatment of chronic foci of infection and periodontal diseases.
- Errors in the choice of design, as well as its manufacture. Incorrect installation leads to the formation of too large gaps between the gum and the prosthesis, or vice versa - to its too tight fit. In the first case, there is a constant accumulation of food debris, inflammation, pain and an unpleasant odor. In the second - the formation of bedsores, with similar symptoms.
- Failure to comply with the rules of operation of the structure and oral hygiene, which entails complications in terms of breakage and damage to the dental structure, accumulation of hard and soft plaque, the development of periodontal diseases and carious processes with its complications.
- Allergy to prosthetic materials. Sometimes such an individual reaction occurs to the residual monomer of the base of removable structures.
Oral hygiene
Any of the above reasons leads to the development of complications, which are often accompanied by toothache after dentures . It can be:
- Caries and its complications – pulpitis, periodontitis, periostitis.
- Acute or aggravated forms of periodontitis.
- Prosthetic stomatitis.
- Mechanical injury to the soft tissues of the oral cavity due to dental structures.
What complications are possible?
An incorrectly installed inlay can result in the development of a cyst. Treatment will be lengthy and expensive - resection of the root apex will be required.
If you have pain under a microprosthesis or the inlay under the crown hurts, contact dentistry at amazing prices. An endodontist will examine the oral cavity and prescribe additional examination.
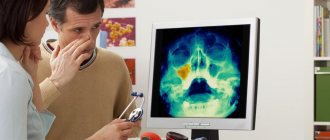
- X-ray - to assess the condition of the root and surrounding tissue (the image will show whether there is a cyst;
- EDI – Electroodontodiagnosis to assess the condition of the pulp – the doctor has the opportunity to determine:
- The degree of damage to nerve tissue;
- Is it necessary to open root canals, treat or remove the pulp?
Taking into account the results obtained, effective treatment will be carried out.
How are restoration inlays installed on teeth?
Installing a restorative inlay on teeth is a multi-step process that always begins with a detailed diagnosis, which will include examination, radiography and computed tomography. After the diagnosis, the type of inlay is selected and a detailed treatment plan is drawn up.
The tooth on which the inlay is planned to be placed is ground down and then an impression is taken from it and sent to a dental laboratory. An inlay will be made based on the impression and the average production time is 5-7 days.
When the inlay is ready, the patient is invited to the clinic for fitting and installation of a microprosthesis. The inlay is fixed in the tooth cavity using special dental cement.
Emergency help
If you can’t see a doctor, and the tooth under the tab hurts, the following measures will help.
- Chewing and temperature stress on the teeth should be completely avoided. Food should be consistent with body temperature and should not require chewing or biting. Broths and pureed soups are the best solution.
- For unbearable pain, take an analgesic or anti-inflammatory drug. The main thing is that the product does not cause allergies. It could be Nimesil, Nise or Analgin.
- If the situation worsens, accompanied by headache and chills, you should contact the nearest medical facility. The staff will call an emergency dentist, and the problem will be solved.
Author:
Mayorov Andrey Mikhailovich
Specialization:
orthopedic dentistry, dental prosthetics, implant installation
Why does a tooth hurt under a crown and what to do about it?
The crown is the most popular type of prosthetics in modern dentistry.
Today, several types of prostheses, materials and installation tactics are used, thereby minimizing the risk of complications. However, there are cases when prosthetics are completed, the crown is installed, and after some time the tooth becomes sore under the crown.
Why does the tooth under the crown hurt and what to do about it?
It is difficult to find an exact answer to this question, since there are many reasons that can provoke pain syndrome after crown placement. However, the symptoms and types of pain will also be different. In any case, you should hurry to meet with your dentist.
Let me immediately note a situation where tooth pain under the crown occurs immediately after installation of the structure; there is no need to panic; most likely, the pain will subside within 2-3 days. This is due to the adaptation of tissues to the new structure in the oral cavity.
However, if a tooth begins to ache under a crown that was installed quite a long time ago, this is a reason to visit a doctor as soon as possible.
There are several common reasons why a tooth hurts under a crown.
- Deep caries.
- Pulpitis is inflammation of the neurovascular bundle of the tooth.
- Periodontitis is an inflammation of the periodontium - the tissues connecting the cement of the tooth root and the bone tissue of the alveoli. Chronic inflammation is characterized by resorption of bone tissue from small sizes to the formation of granulomas and large cysts.
- Gingivitis is inflammation of the gums around a tooth.
- Periodontitis is inflammation of the periodontium - the tissues surrounding the tooth and holding it in the alveolus.
The inflammatory process and its symptoms, in particular when a tooth hurts under the crown, does not develop without reason. It is preceded by:
- A loose fit of the crown, when food particles and bacteria get into the gap between the prosthesis and the tooth, the carious process and its complications begin - if the nerve in the tooth is preserved, pulpitis develops, if not, then periodontitis. In addition, in both cases the gums may become inflamed or periodontal pockets may form.
- Incorrect canal filling. Complications such as incompletely sealed or perforated canals, as well as fragments of instruments remaining in the canal, can lead to an inflammatory process in the periodontal tissues, as a result of the proliferation of pathogenic flora in the root canal.
- Insufficient oral care, when hygiene rules are not followed, the carious process develops much faster. Unrecognized at the very beginning, it progresses and can lead to the loss of the tooth along with the crown. Excessive dental deposits are always the cause of gingivitis and periodontitis. Deep periodontal pockets can cause premature tooth loss.
- Too much stress on the tooth, for example due to missing adjacent teeth. This causes chronic inflammation and loss of tooth attachment; the tooth appears normal from the outside, which is misleading to the patient. As a result, overload can also lead to tooth loss.
- Failure to attend scheduled preventive examinations - a patient with crowns installed on his teeth, if he wants to preserve them, must visit a dentist once every six months for preventive purposes, and if there are alarming symptoms, he must immediately contact a specialist. Otherwise, consequences cannot be avoided.
If a tooth hurts under a crown, you should not ignore the symptoms, “drown out” the pain with painkillers and “get treatment on the Internet.” If you consult a doctor, solving the problem will be much more effective. After all, as we have figured out, there are many reasons why a tooth under a crown may hurt, and first you need to carry out a diagnosis.
An X-ray plays a key role here; if necessary, a more detailed examination is prescribed - computed tomography. This allows us to determine the main question: a vital (“living”) tooth hurts, a non-vital (“dead”) tooth hurts, or there is a problem with the periodontal tissues. Then the treatment tactics are determined.
If a vital tooth hurts , then everything is usually obvious to the patient.
Therapy is carried out in the usual way. The inflamed pulp must be removed, the root canals disinfected and tightly obturated. Treatment can be carried out both after removing a poorly fitting crown, and through the crown, if its fit is not broken. The issue of crown replacement is decided individually.
If the cause of pain is in the tissues surrounding the tooth , then treatment is aimed at relieving inflammation. Removal of dental plaque, medicinal treatment of soft tissues, cleaning with the “Vector” device, and curettage of the periodontal pocket if necessary are carried out. In this case, crown replacement is always required, since it is the one that causes inflammation. Namely: deformation of the crown, discrepancy in size, for example, the edge of the crown overlaps the gum or, conversely, does not significantly reach it. Traumatization of soft tissues and their inflammation occurs, after removal of which the crown is replaced to avoid relapse.
And now we come to the most interesting part. Can a devital (“dead”) tooth under a crown hurt? Most patients are under the misconception that if there is no nerve in the tooth, then there is nothing to hurt there. And this is the most common misconception and at the same time the most common problem.
the cause of chronic inflammation in the area of the tooth root and the prerequisites for it earlier. If a devital (“dead”) tooth under a crown hurts, the tactics may be different. Such a tooth can be treated either therapeutically or with a combined method of therapeutic canal treatment plus apical surgery. In the worst case scenario, the tooth will have to be removed. The choice of treatment tactics is determined based on symptoms, anatomy, and the previous method of treating a given tooth. But the key in this matter is, of course, the size of the inflammation. Therefore, for a more accurate diagnosis, especially if the question is whether to save the tooth or remove it, a computed tomography is performed.
According to the results of x-ray diagnostics, if the diameter of the lesion is insignificant, then the chances of saving the tooth increase significantly. Next, the doctor will evaluate the possibility of root canal retreatment.
The presence of a pin and the patency of the root canals play an important role here, since if it is not possible to qualitatively unseal, disinfect and tightly obturate the root canals, the success of the treatment is called into question. Treatment is usually long-term and takes several visits to the doctor.
In this case, the doctor will warn you that there cannot be a 100% guarantee for treatment. However, in case of successful treatment, a crown will be re-installed on the tooth and it will be possible to save it.
For the anterior teeth of the upper jaw, combined treatment tactics are often used. Therapeutic retreatment of the root canal is carried out, and then the dental surgeon performs a minor operation - resection of the root apex along with the granuloma. After complete healing, the tooth is restored with a new aesthetic crown. The prognosis for the tooth with successful treatment is also favorable.
Unfortunately, if the focus of inflammation is of significant size, neither therapeutic treatment nor apical surgery will be successful, and such a tooth will have to be removed, but the focus of inflammation is removed along with the tooth, and subsequently, after healing, an implant can be installed in place of the missing tooth, preserving chewing efficiency.
If the tooth under the crown hurts badly and the gums are swollen, and even more so in cases where there is swelling of the cheek, I think no one will delay a visit to the doctor. Indeed, if left untreated, swelling can develop into serious complications! Even if the symptoms subside, a relapse is inevitable, and after a while a fistula may form on the gum. This happens because the pus accumulated at the apex of the root requires release - after its outflow is established, the symptoms may subside, but this does not mean that the disease has passed. The infection has not gone away. The disease will simply occur with periods of exacerbation and remission and at the same time constantly progress, exposing the bone tissue surrounding the tooth to destruction. Such foci of chronic infection will sooner or later make themselves felt, and with a high degree of probability such a causative tooth will have to be removed.
Don't let the problem get so complicated. Only a dentist can understand the causes of pain in a tooth under a crown and provide assistance appropriate to the situation. And in order to save a tooth, with a crown installed on it, and not only, you must follow a number of simple rules:
- carefully observe personal oral hygiene;
- regularly visit a dentist for preventive purposes;
- perform professional oral hygiene;
- perform X-ray examinations at intervals prescribed by your doctor so as not to miss foci of chronic infection;
- timely change failed orthopedic structures.
Toothache is the most severe and unpleasant - this is a well-known fact. Teeth with or without a crown, “living” or “dead”, can hurt, and there are many reasons for this. But to the question: “what to do?” There is only one answer - contact a specialist. Take care of yourself and your teeth.
Stump inlays: what do you need to know about them?
At the very beginning of our article, we said that stump inlays should not be confused with restorative microprostheses - they are used to restore pulpless and severely damaged teeth, in which they will serve as the basis for installing a crown or dental bridge.
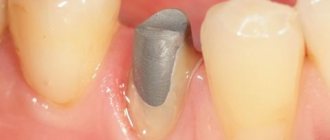
Stump inlays are structures consisting of two parts: a pin installed in the root canal and a support on which the crown will be fixed. Stump inlays can be monolithic or collapsible, and most often this type of structure is used when the tooth has less than 50% of healthy tissue left.
Many people are interested in the question: why is it best to use core inlays rather than fillings on a pin to restore severely damaged teeth? The fact is that the pin may not withstand the load and begin to wobble in the canal, and this will either lead to the filling breaking or falling out, or, worst of all, to damage to the tooth root, in which the tooth is most often removed. Stump inlays allow you to avoid such risks because they distribute the load more correctly and themselves have much greater strength compared to pins.
Stump inlays are also made in the laboratory and the construction material is selected to match the type of dental crown that is planned to be placed in the future. Metal core inlays are used for metal-ceramic crowns, and zirconium inlays are used for ceramic crowns. If you make a metal inlay for a ceramic crown, it can shine through the thin and transparent material of the crown, which will have a bad effect on the aesthetics of the restoration.
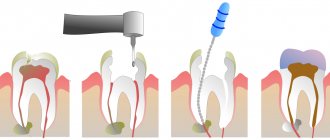
Tooth restoration using a core inlay will also be divided into several stages: diagnostics, preparation, during which a cavity is formed in the tooth for the inlay, manufacturing of the inlay, and its installation. After installing the core tab, the crown is fixed on it and this completes the process of tooth restoration.
If the tooth is destroyed, but there is a living nerve in it, before installing the stump tab, depulpation is carried out, as well as treatment and filling of the root canals. It is important that these procedures are carried out without errors, since poor canal processing leads to various kinds of complications, the elimination of which requires complex and lengthy treatment.