It is no secret that calcium is necessary for the formation of bone and dental tissue. In this regard, a completely logical question arises: is it possible to consume additional calcium to strengthen teeth? Dentists unanimously state that during the formation of teeth (and this is during childhood), this macronutrient is extremely necessary, but in adults calcium will not be able to improve their condition. To strengthen tooth enamel, special dental procedures are recommended for adults. In St. Petersburg they are carried out by specialists from Nurimed dentistry. You can make an appointment with a doctor by calling.
Proper nutrition: calcium for dental health
Lack of calcium in the body leads to multiple health problems, and affects not only the condition of the teeth. A sufficient amount of this macroelement is responsible for the health of the endocrine and cardiovascular systems. Calcium regulates processes occurring in the nervous system and affects blood clotting. If a person does not receive enough of this substance, then the body independently solves this problem by obtaining calcium from the bones.
You can eat many foods high in calcium, but this will not help improve the health of your teeth or slow down tooth decay. However, following the rules of a healthy diet, drawing up a daily diet taking into account all vital vitamins and macroelements is important in order to maintain your body and not aggravate the situation.
What vitamins and minerals are missing if you have bad teeth?
Most often, healthy and strong teeth are associated with calcium. What traditional medicine does not recommend for this is powder from eggshells, from corals, and even ordinary chalk. Unfortunately, the human body is much more complex than an ordinary chemical flask. Regular consumption of ground organic calcium will not always lead to a positive result.
In order to absorb the required amount of this substance, it is necessary to ensure that some other minerals and vitamins enter the body. Moreover, all of them must be either in an active form, or in such a form that our body itself can quickly convert them into such. A prerequisite is the stability of the complex in the aggressive environment of gastric acid, or, on the contrary, it should have a positive effect on the absorption of one or another substance we need.
When it comes to teeth, the presence of calcium, vitamin D3, magnesium, phosphorus and other active substances in the diet is mandatory. Despite the good reviews from adherents of “grandmother’s recipes,” it is unlikely that you will be able to limit your dental care to eggshells only.
Is it possible to get your daily requirement of vitamins and minerals from food?
The calcium content in our usual foods is quite high. With a balanced diet, there is no problem in getting the 1000 mg due to a person. Same with other essential vitamins and minerals. However, one nuance remains: does everyone adhere to a balanced diet, when the diet contains sufficient quantities of sea fish, fresh herbs, various vegetable oils, seeds and nuts?
Most often, the diet of the modern average person is poor in vitamins and minerals, so it is better to buy them. Fortunately, pharmacies have a huge selection of drugs indicating which vitamins and minerals they contain and in what quantities.
It is worth mentioning vitamin D separately. Whatever products contain it, the bulk of it is synthesized in the body under the influence of sunlight. This means, in addition to a balanced diet, we need to spend enough time outdoors on sunny days. How many working people can afford such luxury? This means that a good vitamin complex is simply a must for anyone who monitors their health, and in particular the condition of their teeth and oral cavity in general.
Usage rate
Throughout a person’s life, the required amount of calcium changes:
- Infants under 6 months need 200 mg daily.
- Children from 7 months to one year need 260 mg per day.
- Between the ages of one and three years, a child needs 700 mg.
- Children from 4 to 8 years old need 1000 mg of the macronutrient daily.
- A maximum dose of 1300 mg/day is needed for ages 9-18 years.
- Women aged 19 to 50 years need 1000 mg of calcium per day.
- Men aged 19 to 70 years need 1000 mg per day.
- Women aged 51 years and older need 1200 mg daily.
- Men 71 years of age and older require 1,200 mg of calcium per day.
The greatest amount of calcium is needed by a person in childhood and adolescence, when permanent teeth appear. This is due to the fact that the macroelement accumulates in the teeth only during their formation. And the further condition of the teeth depends on how much this supply is replenished. Unfortunately, it will not be possible to influence the health of molars by consuming calcium-containing foods.
Calcium content in foods: replenishing calcium deficiency
Macronutrient deficiency can manifest itself in different ways. Here are its main features:
- Brittleness of nails.
- Hair fragility and loss.
- Dryness and itching of the skin.
- Pain in muscles, joints.
- A tingling feeling in the muscles.
- Frequent seizures.
- Loss of energy, lethargy, chronic feeling of fatigue and drowsiness.
If you notice signs of calcium deficiency, you can compensate for the deficiency by adjusting your daily diet.
Calcium is found in milk and dairy products (yogurt, cheese). But what about people who don’t use them? You should know that this macronutrient is also present in other products.
Fish and seafood are known for their beneficial properties. The beloved sardine in oil can rightfully be considered a storehouse of calcium. 100 grams of this canned food contains 383 mg of macronutrients. There is also calcium in shrimp. There are 90 mg of calcium per 100 grams of shrimp.
Calcium is also found in products of plant origin. The record holder among them is sesame. 100 grams of seeds contain 780 mg of calcium. One serving of white beans (approximately 175 ml) contains up to 141 mg of the macronutrient; beans contain slightly more - 194 mg. 100 grams of almonds contain 263 mg of calcium. Cauliflower will replenish 95 mg of calcium in the body with one 125 g serving. Broccoli also contains this macronutrient: 47 mg of calcium per 100 grams.
Good news for those with a sweet tooth is the information that calcium is also found in chocolate. By choosing a 100 gram milk chocolate bar, you will get up to 240 mg of calcium. But here it should be remembered that sweets in themselves are not good for teeth, so you should not choose chocolate as the only source of this macronutrient.
When introducing foods rich in calcium into your diet, you should know that it is not absorbed by the body by itself. To achieve the desired effect, it is necessary that other beneficial substances and vitamins enter the body. In particular, vitamin D3 is responsible for the absorption of calcium (on average, it needs 0.636 mg per day).
Microelements necessary for bones and teeth
The use of calcium preparations in dentistry is mandatory not only for prevention, but also for dental treatment. In order for this element to better penetrate bone tissue in medications and dietary supplements, it is combined with other minerals, vitamins and even Omega-3 fatty acids. Pharmacy drugs are sold under a variety of names, but to choose the best one, you need to carefully read the composition in the annotation.
Calcium
If we consider medications, then calcium and calcium are different. For example, in the instructions for using calcium gluconate injections there is not a word about teeth, which means this drug is not suitable for us. The same can be said about calcium chloride or calcium chloride, which is used in medicine for completely different purposes. Neither calcium oxide nor calcium hydroxide are also suitable for strengthening tooth enamel, since they are practically not absorbed by the body.
Modern pharmacology offers us essentially five types of compounds - gluconate, carbonate, citrate, malate and chelate molecules. The price for them is completely different - from mere pennies for calcium carbonate to impressive sums for glycinates and bisglycinates (chelates).
- Calcium gluconate is the most affordable drug, known since Soviet times. One can say something cheap and cheerful about him. To get the maximum effect, the tablet must be chewed and washed down with plenty of water.
- Calcium carbonate is a good form to absorb. Rapidly breaks down in the body, releasing free calcium.
- Calcium citrate - until recently was considered the most active form. Also releases free calcium in the lumen of the small intestine.
- Calcium malate is similar to the previous one, only in combination not with citric acid, but with malic acid.
- Calcium glycinate and bisglycinate are chelated forms or organic calcium. Even though it is a synthetic molecule, it has the best properties of natural organic calcium compounds. Firstly, it immediately penetrates cell membranes as an organic molecule (free calcium needs to undergo a number of modifications for this). Secondly, it does not affect the absorption and activity of iron ions, zinc and some medications that were previously not recommended to be taken with calcium.
For maximum effect, all calcium supplements should be taken on an empty stomach one hour before meals. This should be done in the evening, since the peak metabolism of this mineral occurs around 18:00. If the daily dose is more than 500 mg, then it is advisable to divide it into 2-3 doses - anyway, more than 500 mg at a time will not be absorbed.
Phosphorus
In order for calcium from the blood to penetrate into the teeth and bones, and to fix it there, phosphorus is needed. In good vitamins for men and women, the dose of this mineral should be about half the calcium content. In general, it is recommended to take up to 1000 mg of phosphorus per day, and approximately half of this figure should come from food.
Without phosphorus, calcium is absorbed much worse, and most importantly, it begins to be deposited in tissues other than bones and teeth, which leads to the development of various diseases.
Magnesium
The relationship between calcium and magnesium in the body is very complex. Magnesium is directly involved in the mineralization of bones and teeth, being a kind of cement that holds calcium together. At the same time, he is its antagonist - that is, he performs absolutely opposite tasks.
In order to have strong teeth, it is necessary that at least 400 mg of magnesium enter the body daily. It is better to take it separately from calcium supplements, since their competition manifests itself at the absorption stage, so one thing will be absorbed per unit of carrier molecule - either calcium or magnesium.
Fluorine and boron
Fluoride is an essential mineral in the fight against tooth decay. In teeth it is found in the form of a sparingly soluble complex that is very resistant to acids. It allows the enamel to maintain its protective properties even in an acidic environment, when carious bacteria are most active.
Boron also promotes the absorption of calcium and prevents its loss by dental and bone tissue.
For fluoride and boron, optimal daily doses have not yet been established, which exist for most vitamins and microelements, however, when buying a multivitamin complex for dental health, you need to make sure that they are included in it.
Zinc, copper, manganese
Zinc is part of the dentin of teeth. It is involved in the formation of coarse-fiber bone tissue. Its optimal daily dose is 15 mg.
Copper is very important for gum health. In combination with calcium, it is even used to treat inflammatory periodontal diseases in the acute phase. The maximum daily dose is 2 mg.
Manganese plays an important role in the synthesis of chondroitin and is found in tooth dentin. To maintain healthy teeth and bones, it is enough to take at least 2 mg of manganese per day.
Medicines and nutritional supplements with calcium to strengthen teeth
Dentists recommend eating a piece of hard cheese with tea after meals. Although calcium will not enter the tooth enamel, it will provoke salivation. The secreted saliva promotes the self-cleaning of tooth enamel. In addition, cheese neutralizes the acids contained in salivary fluid, which in turn helps preserve tooth enamel.
If you can no longer get calcium from food, what can an adult do? Are there methods that work to strengthen tooth enamel? And here the answer is comforting: such methods exist, and some of them can be used at home.
Using toothpastes with fluoride and calcium allows you to perform superficial enamel remineralization at home. The frequency of use of such pastes is prescribed by the dentist.
To achieve faster and more sustainable results over time, you can perform this procedure in a dental office. The essence of the method is to saturate the tooth enamel with minerals. Typically, calcium phosphate and fluorine are used for such purposes. The procedure helps preserve the aesthetics of a smile, and is also used in the complex treatment of tooth sensitivity and a number of other dental problems.
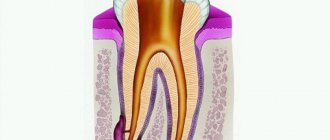
Temporary obturation of root canals
In 90% of cases, infection is the main cause of periodontitis. In some cases, during the treatment of periodontitis, pain and swelling of the soft tissues persist even after intracanal treatment using potent agents.
Changes in the microbial flora or disturbances in its balance lead to clinical exacerbation of periodontitis. Foci of chronic infection in the area of the apex of the tooth root adversely affect the immunological status of the body. At the same time, during a purulent-inflammatory process in the pulp and periodontal tissues, the infection penetrates through the dentinal tubules into the thickness of the root dentin.
Therefore, along with generally accepted technologies for root canal treatment, it is necessary to carry out temporary root obturation in order to have a prolonged antiseptic effect on the root canal system. It should be said that the most thorough medicinal treatment of the canal does not guarantee against its reinfection.
Preparations based on calcium hydroxide, which have been known in dentistry since 1920, have gained widespread acceptance as a means for temporary filling of root canals, but have gained recognition in endodontics only in the last two decades.
Calcium hydroxide is characterized by the following properties:
- antiseptic effect;
- anti-inflammatory properties;
- high chemical activity,
- having a highly alkaline reaction (pH = 12.5);
- stimulation of reparative processes in the apical periodontium due to increased activity of osteoblasts;
- hemostatic effect.
The antiseptic effect of a paste based on calcium hydroxide lasts for 2–3 weeks, until its pH drops below 8. It is believed that this time is sufficient for complete disinfection of the root canal. This is a period of short treatment for teeth with pulp necrosis, after which permanent root canal filling is performed.
Sandquist (1992) found that after the introduction of phenol-containing drugs into a temporary dressing, it was possible to completely free the canal from bacteria in 66% of cases, and after using calcium hydroxide, this effect was achieved in 97% of cases.
For use in endodontic practice, calcium hydroxide preparations are available in the form of liquid, powder, and ready-to-use pastes. When using preparations containing calcium hydroxide, one should take into account its high chemical activity, since when interacting with carbon dioxide in the air, inactivation of Ca(OH)2 occurs. In this regard, manufacturers to one degree or another protect preparations with calcium hydroxide from air contact.
The use of non-hardening pastes based on calcium hydroxide is indicated as a temporary intracanal agent:
- in acute forms of apical periodontitis;
- destructive forms of chronic apical periodontitis;
- cystogranulomas and radicular cysts;
- progressive root resorption;
- treatment of teeth with unformed root apex in pediatric practice.
For different conditions of the apical periodontium, the technique of temporary filling of root canals with calcium hydroxide is different. This is due to the different goals that are set at different stages of treatment. In acute forms of apical periodontitis, calcium hydroxide is introduced into the root canal loosely, without compaction, for 1–3–7 days, depending on the clinical picture.
The main purpose of temporary filling is anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effect.
In case of chronic destructive processes in the apical periodontium, calcium hydroxide is injected into the root canal with compaction to the walls for 1.5–2 months, the material is renewed depending on the clinical situation until the desired result is achieved. The duration of dental treatment is calculated for a period of 0.5 to 1 year and depends on the degree of infection of the root canal, the body’s resistance, the patient’s age, and motivation for treatment.
The main purpose of temporary filling is to stimulate regeneration processes.
The following scheme for using pastes with calcium hydroxide to restore the periapical lesion is proposed:
- The paste is injected into the prepared canal for 7–10 days under an airtight bandage;
- on the next visit, the canal is cleared of paste, washed with sodium hypochlorite solution and filled with a new portion of paste for 1 month;
- subsequent visits are carried out after 3 months, the same manipulations are performed
It is recommended to take the first control x-ray to assess the effectiveness of treatment no earlier than after 3 months. after the first visit.
Restoration of the zone of destruction of the apical periodontium then continues for 3–5 years after permanent filling of the root canal with a sealer based on calcium hydroxide.
Currently, manufacturers modify preparations based on calcium hydroxide by introducing additional antiseptic additives into their composition, potentiating the antimicrobial effect of temporary filling. Both domestic and foreign manufacturers introduce iodoform into pastes based on calcium hydroxide, bringing its content to 40%.
Omega Dent produces two preparations based on calcium hydroxide for temporary filling of canals for periodontitis. These are “Calcept” and “Calcept with iodoform”.
“Calcept” contains sterile calcium hydroxide, and “Calcept with iodoform” contains calcium hydroxide and iodoform, which significantly enhances the bactericidal properties of the drug. The drugs are supplied in syringes and equipped with convenient cannulas for administering the drug directly into the mouth of the root canal.
Lack of calcium in the body in pregnant women
Lack of calcium in pregnant women manifests itself in the form of the symptoms described above. There is no scientifically confirmed evidence that during pregnancy calcium is “washed out” and used to form the fetus from the teeth. However, in addition to the fact that the lack of a macronutrient threatens a woman’s health, it also increases the risk of caries in a child in the future. Studies have shown that children of women who received sufficient amounts of this macronutrient during pregnancy were less likely to suffer from caries.
The required daily calcium intake for pregnant women is needed not in order to preserve their teeth, but in order to provide the required supply of macronutrients to the unborn child. The same applies to the period of feeding the baby.
Knowing how important calcium is for teeth, try to adhere to a healthy lifestyle and maintain the recommended balance of vitamins, macro- and microelements in your diet for your age. To maintain your smile, see your dentist at least twice a year.