Hemisection is a surgical operation that involves removing the affected molar root along with the adjacent part of the crown. Such surgical intervention is carried out in cases where the pathological process, which cannot be treated, is localized only at one of the roots of the diseased tooth. After the operation is completed, the intact roots and crown part of the tooth can still play the role of support for prosthetic structures during orthopedic treatment.
The essence of the method
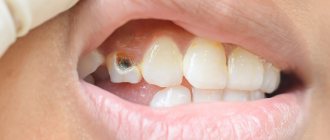
If a tooth has several roots, on one of which a granuloma or cyst has formed, complete removal is not necessary. Hemisection involves amputation of the affected part, leaving healthy tissue unaffected. After the operation, the natural support of the tooth is preserved, so restoration and restoration of chewing function is possible. Your own tooth is better than any modern implant. If it is possible to save it, you should do so.
Hemisection - the real salvation of your molar
The procedure aimed at preserving the unit is carried out in the following cases:
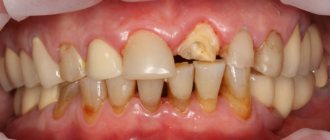
- Advanced periodontitis;
- Localized neoplasm (granuloma, cyst);
- Traumatic damage to one root as a result of trauma, perforation;
- Periodontitis;
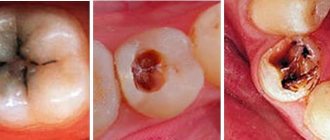
- Caries lesions;
- Infections after unsuccessful therapy.
Surgery for coronoradicular separation is performed after the patient has consulted with an orthopedist. At the DemoStom clinic, patients undergo root canal treatment before hemisection. It is important to do this so that the part that is important to save has a root filling. Allow time to pass between root canal treatment and hemisection to reduce the risk of inflammation. The procedure is recommended in the following cases:
Indications
The operation is performed only on teeth that have two or more roots. After removing the affected area, a root should remain that firmly holds the tooth. Indications for hemisection are:
- inability to treat the root;
- cyst;
- granuloma;
- perforation;
- root caries;
- the impossibility of cleaning the canals due to their irregular shape or small diameter;
- chronic periodontitis;
- mechanical damage.
Hemisection is also performed in childhood. Dentists are often faced with the impossibility of endodontic treatment due to tortuous canals. But preserving a child’s tooth is important, since prosthetics using implants is only possible in adults, and many children refuse to wear a removable denture.
Basic methods and stages of surgical treatment
The partial resection operation meets modern dental requirements aimed at preserving the patient’s own teeth without discomfort and pain. There are two main methods of hemisection.
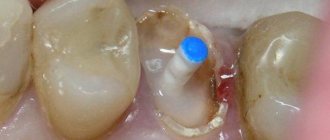
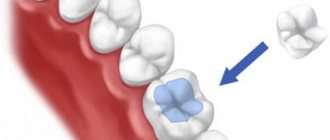
- The first option is removal from above. During the operation, vertical sawing and amputation of a segment of the coronal part of the tooth is performed along with the affected root and tissues affected by inflammation. The resulting hole is filled with osteoplastic material. To restore the tooth crown, a pin is installed, and if necessary, the surgeon sutures the mucous membrane.
- The patch hemisection technique is indicated in cases where the tooth crown is not destroyed, but the root cannot be restored. Access to the affected area is carried out by detaching a gum flap, after which the damaged part of the root is amputated. At the end of the hemisection, the excised tissue is placed in place and sutured with catgut threads. If the remaining part of the crown is mobile, splinting is used.
Very often, to speed up wound healing, instead of osteoplastic mass, blood plasma is transplanted into the socket. The innovative technique eliminates the risk of rejection and significantly speeds up the recovery process. During the operation, radiography and follow-up examinations are required. Healing takes up to four months, after which the healthy part of the molar can be used as a full-fledged support for the installation of an orthopedic structure.
Contraindications
The operation is not performed on teeth that have one root, or when the other roots are also affected. In these situations, it is impossible to save the tooth because it has no support.
Fused roots are another obstacle to tooth-preserving surgery. In this case, it is impossible to separate the affected tissues from healthy ones.
The operation is not performed in elderly patients or in patients with severe somatic diseases: diabetes mellitus, oncology, kidney damage, or cardiovascular disease. If there are doubts that a person will safely undergo hemisection for health reasons, it is better to remove the tooth.
What is the price of hemisection of a tooth?
The cost of hemisection surgery may vary based on the price segment of the dental clinic, the qualifications of specialists and the level of complexity of the work in a particular case. The price of hemisection of a tooth in Moscow clinics will range from 2 to 7 thousand rubles. However, when calculating the amount for treatment, the patient must take into account that, in addition to the operation itself, it will require a doctor’s consultation, X-ray diagnostics (before the operation, immediately after it and a month later), possibly a computed tomography. Only the attending physician can plan the exact cost of treatment, taking into account the indication for hemisection of the tooth, the patient’s characteristics and other nuances.
Advantages and disadvantages
The technique allows us to ensure the safety of even hopeless teeth. The restoration will have to be done with a crown, but it will have natural support. It is safer and more reliable than the introduction of an artificial implant.
The operation rarely leads to complications. With the correct technique for performing the procedure and proper preparation, the dentist can achieve results.
The remaining part of the root cannot restore the tooth to its former strength. For this reason, it is recommended to limit chewing loads and not use teeth after hemisection as support for bridges. There is no guarantee that the root will maintain its integrity for several years.
Postoperative complications include: bleeding, secondary infection, suture dehiscence. This often occurs when the rules of asepsis and antisepsis are violated during manipulation and the patient does not comply with the doctor’s recommendations during the rehabilitation period.
Recommendations for patients in the postoperative period
Persons who have undergone hemisection are recommended:
- avoid any physical activity for 3 days;
- protect yourself from stressful situations and factors that provoke psycho-emotional stress;
- refuse to eat for 2 hours after surgery;
- appear for preventive examinations on the second and fifth days after completion of the operation, undergo an x-ray control procedure.
The average recovery period after surgery is 5 days. Complete healing of damaged tissue occurs after 2.5 weeks, and engraftment of bone material occurs after 5 months.
Operation technique
Hemisection refers to volumetric surgical interventions. The procedure lasts 1.5-2 hours. For pain relief, local or general anesthesia is used. The choice depends on the individual characteristics of the patient and the technique used.
Hemisection can be performed by two methods: access from above or by peeling off a skin flap.
When choosing the first method, the crown is sawed to the point where the roots emerge. In this way, the affected root, together with part of the crown, is separated from healthy tissue. After separation, the damaged area is removed.
The second method is carried out by cutting the gums. In the area of projection of the affected area, the flap is peeled off, part of the root is sawed off and removed. Stitches are applied.
After removing one of the roots, a void remains in the jaw. If left, it will fill with granulation tissue, which is considered an unfavorable outcome. To prevent this, artificial bone is poured into the cavity and covered with a membrane. The material is biocompatible and is rarely rejected.
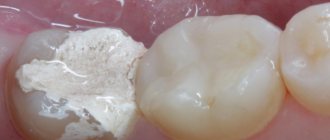
Prosthetics are not performed immediately after surgery. We need to wait for complete healing. This takes at least a month. If the recovery period passes without complications, a crown can be installed. Sometimes, to increase strength, stump inlays are used to evenly distribute the load on the root and protect it from fracture.
Stages of implementation
Geminsection is performed by two methods, which differ in the volume of tissue removed. But the preliminary stage in both cases is identical and includes the following steps:
- removal of the inflamed nerve;
- filling of canals that will be preserved;
- sanitation of the cavity (if necessary).
The patient is recommended to donate blood, which will provide plasma to further fill the root removal area. This reduces the risk of rejection to a minimum.
Patchwork technique. In this case, the maximum volume of tooth tissue is preserved, but the method is considered more traumatic due to the need to dissect and peel off a flap of soft tissue. Direct removal is carried out as follows:
- anesthesia is administered;
- an incision and detachment of soft tissue is performed to access the area of inflammation;
- sawing off a diseased root with a cystic formation or granuloma with a drill;
- cleaning the cavity from tissue debris and disinfection;
- filling the cavity with a polymer that imitates bone tissue and installing a membrane to prevent overgrowth with soft tissue;
- the flap is returned to its place and stitches are applied.
The recovery period is 4-6 weeks.
Resection of the apex. This method requires the removal of a larger volume of tissue, but is less traumatic. There is no tissue detachment, so healing is faster. The operation is a heminsection through a crown and has the following procedure:
- anesthesia is administered;
- the crown is sawed with a drill into several parts along natural lines until the roots branch;
- an element with a destroyed root, cyst or granuloma and part of the crown is removed with surgical forceps as with a standard tooth extraction;
- the cavity is cleaned and filled with a polymer and a preparation that prevents the germination of soft tissues;
- the crown is restored using an extension or an orthopedic prosthetic crown.
Possible complications
Bleeding may occur during the operation or after the intervention. This is relevant for people with poor blood clotting, taking antiplatelet drugs, and smokers. For this reason, intervention is not recommended for patients with bleeding disorders. If you are taking some medications regularly, you may need to temporarily stop them. You will have to give up cigarettes before hemisection and in the postoperative period.
The tooth, part of which is removed, usually shows signs of inflammation and serves as a source of infection. Insufficiently thorough sanitation of the lesion during surgery can lead to the development of a secondary inflammatory process. The reason may also be improper treatment of the dentist’s hands and unsterile instruments. The infection can be caused by the patient himself after treatment. Failure to maintain oral hygiene and ignoring doctor's recommendations often lead to serious purulent complications.
Even after a successful operation, there is no guarantee that the remaining root will cope with the increased load. Sometimes the tooth has to be removed several months after hemisection.
Complications after hemisection procedure
The main complications that a patient who has undergone hemisection may encounter are:
- bleeding in the surgical area;
- divergence of applied sutures;
- infection on the wound surface with subsequent inflammation of the soft tissues.
If you identify symptoms that signal the development of complications, you must contact an orthopedist and undergo a course of therapy at the 24-hour dentistry “A.Dent” according to the program he has drawn up.
What can become an obstacle to hemisection?
This operation has a general list of absolute contraindications:
- Presence of cancer;
- Allergy to anesthesia drugs;
- Diabetes;
- Psychical deviations;
- Cardiovascular diseases.
Hemisection is not carried out in case of significant destruction of the unit, when the roots are fused, and they are close to the maxillary sinuses. The operation is not recommended for people over 60 years of age. At this age, recovery processes are slowed down, as the risk of complications is high.
Consequences and complications
Sometimes it happens that after hemisection, a natural root may not last for years, but only for a couple of months. This is unpredictable; no dentist can make an accurate forecast. If there are only two roots, then after removing one of them, the remaining roots are usually no longer used for bridges. More stable options will be those in which it is possible to leave two or more roots, but even these should not be subjected to heavy chewing pressure.
Hemisection can also lead to gingival bleeding, and in very rare situations, suture dehiscence may occur. To minimize the risk of complications, it is necessary to carefully monitor the hygiene and condition of the oral cavity, and also not miss follow-up visits to the doctor.
Technique for performing hemisection of the tooth root
Before performing hemisection of the tooth root, the doctor takes an x-ray and assesses the condition of the damaged tooth. Next, the canals that turn out to be healthy are filled. The patient is given the required dose of anesthetic, after which the operation itself begins.
The infected canal is removed along with half of the crown on which it is located. Canal filling is a mandatory procedure; is performed to avoid the spread of infection to the remaining part of the tooth, after which there will be no point in treatment. In some cases, the surgeon has to lift the mucoperiosteal flap and extract the root using a special tool - a drill attachment.
The operation of hemisection of the tooth root, depending on the condition of the tooth to be saved, can take several hours. The hole left after the removed diseased root is filled by the surgeon, after which a suture is placed on the gum.
Rehabilitation after hemisection of a tooth
After the operation, the patient, having received recommendations, goes home and comes to see the doctor at the appointed time. Typically, examinations are performed on the second and fifth days after the procedure to ensure that healing is progressing as planned. The sutures from the gums are removed after 14 days.
If the hemisection was completed without complications, the remaining tooth can be used as a supporting element for building up a full-fledged tooth - it retains its natural functions. With the help of hemisection, dental surgery has already saved hundreds of patients’ natural teeth.
Please rate this article
Stanislav Mezheritsky
Chief physician, surgeon, orthopedist
The author of the article is Stanislav Mezheritsky, a practicing dentist with 19 years of experience, chief physician and one of the founders of the Matisse Dent clinic. The main focus is orthopedic and surgical dentistry. Author of numerous publications, regular participant in specialized seminars.