Increased sensitivity of teeth (hyperesthesia) is a short-term occurrence of pain under the influence of temperature, chemical or mechanical irritating factors. Usually occurs when drinking cold water, sour, sweet, salty, or touching with a toothbrush. The intensity of pain varies from mild to unbearable.
According to WHO, every second person in the world suffers from hypersensitivity. In Russia it is about the same: 45–65% of adults aged 20–55 years. More often women make complaints.
A little anatomy
A tooth consists of a crown and root part, connected by a neck. The coronal part is covered with enamel, the root part is covered with cement. Beneath the enamel and cement there is dentin, a hard tissue. Inside there is soft tissue - the pulp; blood vessels and nerves pass through it.
Dentin is not sensitive, but consists of many tubules in which fluid circulates. The irritant causes fluid movement, which is detected by the nerve endings of the pulp. A person feels their reaction as pain.
What to do if you lose tooth enamel?
The problem is not always solved by remineralization and dental varnish. In cases where the enamel is worn out or severely cracked, gentle methods will not help. Modern dentistry offers several solutions with complete or partial preservation of the tooth:
- Veneers and lumineers are the most expensive method; they provide good protection, but do not restore chewing functions.
- Ceramic or zirconium crowns are strong and durable. Requires preliminary preparation of the support.
- Artistic restoration - new generation composite materials are practically indistinguishable from the natural shade, but last a maximum of 10 years.
Tooth sensitivity: causes
- Demineralization of enamel. It becomes more loose due to the leaching of calcium, phosphorus, and other trace elements.
- Thinning of enamel. As a result of increased abrasion due to malocclusion and the occurrence of wedge-shaped defects.
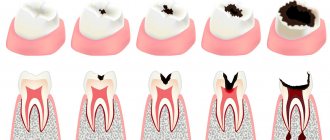
- Untreated caries or violation of the marginal seal of the filling.
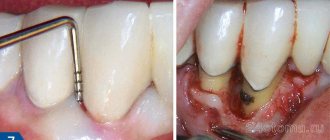
- Exposure of roots as a result of injury, metabolic-dystrophic process or inflammation of the gums.
- Changes in the pH of saliva due to the consumption of certain drinks, foods, and medications. A pH of less than 5.5 is considered dangerous.
- Some diseases accompanied by gastroesophageal reflux and endocrine disorders.
- Vitamin deficiency, exposure to radiation, work in hazardous industries, living in a region with an unfavorable environmental situation.
- Smoking.
More often than not, several reasons are discovered at once. The enamel becomes thinner, loses strength, and cannot protect dentin from irritants. The result is pain.
Causes of hyperesthesia
Dental hypersensitivity occurs under the influence of a complex of endogenous (internal) and exogenous (external) factors. Obvious causes of dental hypersensitivity include:
- carious lesions of tooth enamel;
- demineralization of enamel (loss of minerals);
- wedge-shaped defects of the tooth neck;
- pathological abrasion of teeth;
- periodontitis, periodontal disease;
- traumatic damage to teeth: chips, cracks, crown fracture.
Factors contributing to the occurrence of hyperesthesia are:
- Uncontrolled use of whitening toothpastes with a high RDA abrasiveness index: the higher it is, the larger the size of the grinding particles contained in the paste. With an RDA index of 100-200, toothpaste can be used no more than 1-2 times a week; if this rule is violated, the enamel becomes thinner. The chemical components of whitening pastes can wash out calcium from tooth enamel.
- Drinking sugary carbonated drinks and some fruit juices. Carbonated sweet water contains sugar and acid, which can destroy tooth enamel. Carbon dioxide also, with frequent consumption of soda, disrupts the structure of the enamel, so even unsweetened carbonated water should not be drunk too often. Such drinks are especially harmful to children's teeth.
Fruit acids contained in grapefruit, pineapple, pomegranate, grape and some other juices wash out minerals from tooth enamel, it becomes porous and reacts to various irritants.
- Poor dental care, which leads to deposits of plaque and tartar on them. Cariogenic microorganisms that live in dental plaque produce organic acids that destroy tooth enamel. This not only causes hypersensitivity, but also contributes to the development of caries.
- Professional teeth cleaning. The areas of enamel under dental plaque do not have sufficient amounts of calcium, fluoride and phosphorus necessary to protect teeth from external irritants. Tartar protects these areas from the action of various factors; when it is removed, the teeth become hypersensitive for a while. But teeth cleaning is necessary, so after it, the enamel is coated with remineralizing compounds.
- Poor nutrition. Lack of vitamins A, D, C, B vitamins, minerals, especially calcium and phosphorus in food, negatively affects the condition of the enamel. One of the reasons for sensitivity is the appearance of microcracks in the enamel as a result of simultaneous ingestion of cold and hot food.
- Endocrine and other diseases of the body. It has been established that endocrine diseases, such as thyroid disease, contribute to the development of hyperesthesia. Patients suffering from these ailments often develop wedge-shaped dental defects. Also, this pathology often occurs in parallel with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Bruxism. Grinding your teeth while you sleep leads to the abrasion of the enamel and the appearance of microcracks.
- Malocclusion. It also contributes to the appearance of areas on the teeth with increased abrasion, which react sharply to external irritants.
- Violation of teeth brushing technique. When brushing your teeth, you should not make horizontal movements, as this leads to wedge-shaped defects in the teeth.
- Menopause, pregnancy. These conditions are accompanied by changes in the hormonal levels of the body, which entails a violation of mineral metabolism: the enamel is demineralized.
Provoking factors
Hyperesthesia does not appear immediately. There are several factors that you need to pay attention to in order to eliminate them in time. Don't wait for discomfort to appear. It is better to initially develop healthy habits that will help you maintain your health so that you never experience acute dental pain. Sensitivity increases when any of the factors listed below are present.
- Insufficient oral hygiene. Soft plaque is an accumulation of microbes that eat food microparticles stuck in crevices, releasing organic acids that dissolve enamel minerals. Externally, the dental unit looks intact, but the density of the enamel is significantly reduced. Its demineralization occurs. The first alarm bell is increased sensitivity, then caries develops.
- Consumption of certain foods. Juices, wine, sweet soda, fruits, candies, and other sweets contain phosphoric and other acids that negatively affect the strength of enamel.
- Constant use of aggressive whitening pastes containing abrasive and chemical components.
- Ultrasonic cleaning. Under a dense coating, the enamel becomes thinner and becomes loose. After professional cleaning, it is exposed, its sensitivity increases sharply. Usually, dentists, taking this point into account, use strengthening pastes at the end of the procedure for the preventive treatment of tooth sensitivity.
Types of hypersensitivity
If sensitivity is increased on one or more teeth, it is called limited. If for everyone - generalized.
Table 1. Types of hyperesthesia
| № | View | Reaction |
| 1. | Light | for cold, hot |
| 2. | Average | as with 1st degree plus for sour, sweet, salty |
| 3. | Expressed | as in grade 2 plus mechanical irritants (when brushing teeth, eating) |
Symptoms and diagnosis of hyperesthesia
Dental hypersensitivity is characterized by a sudden sharp or aching pain, a sore throat when the tooth is exposed to any irritant: when taking sweet, sour, salty, cold or hot liquid, food; when brushing your teeth. After eliminating the irritant, the pain quickly goes away.
Women are most susceptible to hyperesthesia; In the population over the age of 60, hypersensitivity reactions become less pronounced due to the aging of dentin.
The diagnosis of hyperesthesia is made based on a conversation between the dentist and the patient and examination of the oral cavity. If a doctor directs a stream of air or water onto hypersensitive teeth, the patient immediately reacts with a shudder, his face expresses pain, and he reports his sensations.
Sensitivity of teeth. Stages of treatment
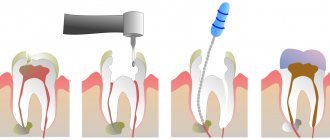
- Eliminate the cause of hyperesthesia: get rid of plaque, deposits, stones, caries, wedge-shaped defects.
- Carry out professional oral hygiene.
- Strengthen the enamel with calcium and fluoride.
- Teach the patient how to use a toothbrush and floss correctly.
- Choose suitable dental care products: toothpaste, mouthwash.
Table 2. Tooth sensitivity: causes and how to treat
| № | Cause | What to do |
| 1. | Soft coating. | Careful hygiene with home remedies. |
| 2. | Hard coating. | Professional hygiene in dentistry. |
| 3. | Caries in the white spot stage. | Deep fluoridation, remineralization. |
| 4. | Caries, pulpitis, periodontitis. | Dental treatment. |
| 5. | Exposure of the cervical part, wedge-shaped defect. | |
| 6. | Malocclusion. | Orthodontic therapy. |
Complications
If increased tooth sensitivity occurs, patients try to injure them as little as possible during brushing, sometimes they refuse it, so the condition of the oral cavity gradually worsens. Over time, the amount of plaque on the teeth increases and tartar forms. Hard dental deposits contribute to the development of inflammation in periodontal tissues and the occurrence of caries. Periodontal disease leads to exposure of the roots of the teeth, resulting in increased sensitivity. It turns out to be a kind of vicious circle.
Elimination of tooth sensitivity
Using ultrasound, the doctor removes soft and hard deposits from the teeth. After removing plaque, teeth become more sensitive for a short time, so remineralization or deep fluoridation is immediately carried out. During remineralization, the enamel is treated with active compounds of calcium and phosphates. Deep fluoridation – coating with sodium fluoride. Both procedures significantly strengthen the enamel's resistance to irritants.
The doctor uses agents that reduce the movement of fluid in the dentinal tubules. It “seals” them using desensitizers or reduces their volume through remineralization. Protecting exposed dentin reduces the force of transmission of the irritant impulse from the enamel to the nerve.
Diagnosis and treatment methods
The first, and most important, step in the treatment of any disease is diagnosis. The dentist performs it through a visual and instrumental examination. In addition, it conducts two tests: exposure to cold water (air) and physical touch with a probe. Another important examination method is electroodontometry - measuring the response of the pulp to the influence of electric current. With hyperesthesia, the pulp reacts to a current of 2 to 6 microamps. Also, the doctor must collect an anamnesis, during which the presence (or absence) of systemic problems with the patient’s health is revealed.
There are several methods for treating hyperesthesia. The choice of a particular one depends on the cause of sensitivity. If the problem is caused by caries (or another violation of the integrity of the enamel layer), then the doctor prepares the tooth, cleans out the carious cavity and places a filling. In case of recession (recession) of the gums, surgery is necessary to raise it to the desired level. If the recession was caused by periodontal disease, then periodontal treatment is carried out using conservative and surgical (if necessary) methods. Increased abrasion of enamel caused by bite pathologies is eliminated by orthodontic therapy.
In the absence of all the listed pathologies, fluoridation is used to relieve excessive sensitivity. It consists of applying applications to the enamel surface or covering it with fluorine-containing varnish. This technique helps strengthen the enamel and seal the dentinal tubules. As a result, the speed of fluid movement in them is significantly reduced, and this, in turn, reduces the response (pain) to external stimuli. The purpose of another technique is to block impulses from the nerve endings of the dentinal tubules using potassium salts. This substance creates a protective sheath around sensory fibers and blocks the transmission of impulses.
Basic points of proper hygiene
Use a synthetic, medium-hard or soft brush. Change it every three months.
The toothpaste should be suitable for very sensitive teeth. Typically, such products contain hydroxyapatite, strontium chloride, fluorides, potassium nitrate, or a combination of calcium carbonate and arginine.
Take enough paste. For children under 3 years old - the size of a grain of rice, from 3 to 14 years old - the size of a pea, for adults you need to squeeze out about one centimeter.
Brush your teeth for 2 minutes: 30 seconds on each surface, top and bottom. Monitor time using an hourglass or mobile phone timer. Electric toothbrushes emit a short beep every 30 seconds and a long beep every 2 minutes from the start of brushing.
Cleaning sequence
- Using sweeping movements, clean the outer and then the inner surfaces of the bottom row. Move from molars to incisors. Then do the same on the top row. Hold the brush at a 45-degree angle and do not use a sawing motion. This leads to damage to the enamel.
- Brush chewing surfaces with small circular movements.
- Close your jaws and walk along your gums in a circular motion.
- Brush your tongue using a leisurely four to five strokes from root to tip.
- Treat the interdental spaces with dental floss.
- Rinse your mouth.
It is more effective to clean with an electric brush or irrigator. The quality of hygiene increases 3–4 times. Hyperesthesia can be dealt with faster.
Is it possible to strengthen sensitive teeth at home?
Yes. If you can’t get to the dentist, you can try to help yourself. There are several remedies that can solve the problem of hyperesthesia at home.
Table 3. Popular products for home use
| № | Name | Mechanism of action | Age category |
| 1. | ROCS Medical Minerals, GC Tooth Mousse | Remineralizing gels | Adults and children |
| 2. | Colgate Duraphat 2800 ppm | Fluoridating paste | 10–15 years |
| 3. | Colgate Duraphat 5000 ppm | From 16 years old | |
| 4. | ELMEX junior | Fluoridating paste | 6–12 years |
| 5. | ELMEX | From 13 years old | |
| 6. | LACALUT Extra Sensitive | Paste that reduces tooth sensitivity | For adults |
| 7. | Colgate Sensitive Pro-Relief | ||
| 8. | PRESIDENT Sensitive | ||
| 9. | LACALUT Sensitive, 300 ml | Rinse for sensitive enamel | From 15 years old |
Dental hyperesthesia
Therapy for hyperesthesia of hard dental tissues has its own history. Proposals for the use of many medicinal substances to eliminate hyperesthesia indicate its insufficient effectiveness. Substances that destroy the organic substance of hard dental tissues were used. This group includes solutions of silver nitrate and zinc chloride. For hyperesthesia of hard tissues, pastes containing alkalis were widely used: sodium bicarbonate, sodium carbonates, potassium, magnesium, as well as substances capable of restructuring the structure of hard dental tissues: sodium fluoride, strontium chloride, calcium preparations, etc. According to modern ideas, Fluorine ion is able to replace the hydroxyl group in hydroxyapatite, transforming it into a more stable compound - fluorapatite. Indeed, after applying 75% fluoride paste to a dried area of sensitive dentin, pain relief occurs, and after 5-7 procedures, pain may disappear. However, after a short period of time the pain occurs again, which is a significant drawback of the method.
In order to relieve pain sensitivity, we used dicaine liquid, proposed by E.E. Platonov. 1-2 minutes after applying the liquid, tissue preparation becomes possible. However, the analgesic effect is short-lived.
A more effective method of relieving hyperesthesia was proposed later by Yu.A. Fedorov and V.V. Volodkina. For local exposure, they used calcium glycerophosphate paste on glycerin (6-7 procedures), along with oral glycerophosphate or calcium gluconate 0.5 g 3 times a day for a month, multivitamins (3-4 tablets per day), phytoferolactol (1 g per day) for a month. The authors suggest using the proposed scheme 3 times a year.
The systematic use of remineralizing paste “Pearls” has a therapeutic effect.
Currently, for hyperesthesia of dental tissues, remineral therapy is widely used. The theoretical basis for the method is that in some types of hypersensitivity, in particular in the erosion of hard tissues, surface demineralization is detected. If this procedure is carried out, the teeth are isolated from saliva, thoroughly dried with a cotton swab and plaque is removed from the enamel surface. Then a 10% calcium gluconate solution or Remodent solution is applied for 5-7 minutes. During every third visit, after two applications of remineralizing liquid, the surface is treated with a 1-2% sodium fluoride solution. Instead of this solution, you can use fluoride varnish. Calcium gluconate is prescribed orally, 0.5 g 3 times a day for a month. Along with this, it is recommended, if possible, to exclude juices and acidic foods from the diet, and to use fluoride-containing toothpastes to brush your teeth. As a rule, after 5-7 procedures, improvement occurs, and after 12-15 procedures, hyperesthesia disappears. It should be borne in mind that after 6-12 months it may occur again. In such cases, it is recommended to repeat the course of treatment.
Algorithm of actions for hyperesthesia
- Adjust your diet. Avoid completely or significantly reduce the consumption of foods and drinks containing acids and sugar. Especially fruit and berry juices, wine, candies. Eat more green vegetables, fiber-rich foods, and whole grains.
- Change your toothpaste. Never use bleach. Choose from those labeled "Sensitive".
- Check if you are practicing proper oral hygiene. If it's wrong, correct it.
- Make an appointment with your dentist to find out the type of tooth sensitivity, find out the cause and get treatment.
- Visit the dentist twice a year, even if nothing hurts.
Tooth hypersensitivity after caries treatment
Hyperesthesia after medical intervention is associated with the use of phosphoric acid to treat the prepared cavity. This makes it possible to increase the adhesion of the filling material to the tooth tissues, but when it comes into contact with healthy enamel, the acid washes out calcium from it, so sensitivity increases. To avoid this phenomenon, the dentist treats the enamel after installing the filling with a special preparation.
Also, after caries treatment, tooth sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures may persist for several days due to the fact that when drying the prepared cavity before treating it with orthophosphoric acid, the surface was overdried, resulting in increased dentin sensitivity. After some time, the necessary moisture comes from the dental tissues into the surface layer of dentin, and the unpleasant sensations disappear.
If tooth hypersensitivity persists for a long time after treatment of caries, it is necessary to repeat the visit to the dentist to find out the reasons.
Treatment of hyperesthesia in the “Family Doctor”
If hyperesthesia occurs, make an appointment with a dentist by calling the contact center in Moscow +7 (495) 775 75 66 or using the online appointment form. Our clinic has been operating for more than 26 years. Experienced doctors help patients cope with pressing problems, including hypersensitivity.
The doctor will find out the cause of tooth sensitivity and provide effective treatment. In most cases, it is enough to select suitable oral care products and carry out proper hygiene procedures. In more complex situations, full treatment is used, and if necessary, surgical treatment.
The clinic takes a gentle approach to patients. All procedures are accompanied by adequate pain relief, which eliminates the occurrence of discomfort and pain. Increased sensitivity of teeth is not just a feature of them. This is the beginning of a disease that must be cured. And it's better to do it as quickly as possible.
Classification of hyperesthesia
In terms of prevalence, dental hypersensitivity can be limited or generalized. In the first case, the problem affects only one or several closely spaced teeth. In the second we are talking about a larger number or all teeth at once.
Based on severity, there are three degrees of severity of the condition:
- the first is pain in response to temperature exposure;
- the second is pain when exposed to cold, hot, sweet, sour, bitter food;
- the third is pain in response to all types of irritants, including the touch of a toothbrush.
The intensity of unpleasant sensations depends on individual susceptibility.