Caries is a pathological process characterized by damage to the hard tissues of the tooth and further formation of a cavity in it. In recent years, caries of primary teeth has become a fairly common problem. By the age of 6-7 years, until permanent teeth begin to appear, more than 70% of children have lesions on their baby teeth, and most of them go to the dentist with complications or an advanced process. Most often, caries of primary teeth is detected at 2-3 years of age, but sometimes it can also occur in children who are not yet two years old. In different regions of the country, the prevalence of this form of caries by the age of four is 20-80%. How can such problems be avoided and what do parents need to know?
Causes of caries
Most often, caries of primary teeth can form under the influence of several factors simultaneously. Its most common causes are:
- Damage to tooth germs in the prenatal period. In the embryo, tooth buds begin to form in the first trimester of pregnancy. That is why any illnesses of the expectant mother that she suffered during this period, as well as the use of medications, can contribute to the fact that the fetus’s proper development of teeth is disrupted.
- Insufficient oral hygiene or its absolute absence. In this case, food particles remain on the teeth, and this is an excellent environment for the life and proliferation of bacteria.
- Incorrect eating habits - using pacifiers for a long time. Those children who are unable to switch from drinking from a bottle to a sippy cup or cup for a long time, and especially those who have learned to fall asleep every evening with a bottle or pacifier in their mouth, are at risk of developing bottle caries. With this pathology, through prolonged contact with the teeth of the liquid from the bottle (especially if it is sweet), the front teeth are affected by caries, and the process spreads along the circumference of the crown part of the tooth (along the perimeter of its visible part).
- Insufficient amounts of food in the daily diet, which requires intense chewing and leads to increased salivation, due to which the teeth are cleaned naturally. This factor is inherent in children under two years of age; it is one of the causes of early caries.
- Lack of calcium in food and water - the main building material of teeth and fluorides, which strengthen tooth enamel and protect against caries, preventing the possibility of its development.
- Rickets – with this pathology in children, tooth tissue is easily destroyed.
- Physiologically determined low resistance of children's dental tissue to agents that cause caries.
- Anomalies of dentition and bite.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Chronic diseases, as well as frequent respiratory diseases, which reduce the overall resistance of the body.
- Excessive amounts of carbohydrates in a child’s food contribute to the development of caries in two ways simultaneously: they feed bacteria, and in the process of their decay, organic acids are formed that damage tooth enamel. For the formation of caries, it is not so much the total amount of carbohydrates consumed that matters, but the frequency of their intake.
Without a doubt, a child who is not yet three years old should not snack between meals, especially food containing a high amount of carbohydrates (sweets, chocolate, etc.). Instead, it is better to offer your baby fruits, marshmallows, marmalade, pastries, and dried goods. It is better to eat sweets after breakfast or dinner, and then brush your teeth after a while. Almost all children do not grow up without sweets, but their consumption should be limited and reasonable.
What is caries of primary teeth?
Caries affects not only the permanent teeth of adults, it is truly merciless to children’s delicate milk teeth. The principle of development of the disease is absolutely the same as in adults. If there are bacteria in the child’s mouth that cause caries, then they, feeding on carbohydrates from leftover food - and this also applies to breast milk, produce acids, which, in turn, destroy tooth enamel. This process goes much faster in children, because... their enamel is more fragile and cannot withstand an aggressive environment. And if several unfavorable factors confluence at once, then caries in children progresses very quickly.
The Forbidden fruit is sweet…
In order not to tempt your baby with “forbidden fruits,” simply do not buy them or consume them yourself. There is no doubt that your friends and relatives all bring sweets to the child solely with the best intentions. Try to talk to them and explain that instead of candy, you can bring your child, for example, a toy or an interesting book. Due to poor or complete lack of oral hygiene, the plaque that remains on the teeth after eating food turns into dental plaque containing bacteria that produce lactic acid, which damages the enamel and contributes to the development of caries. As soon as a child has his first teeth, he should immediately have age-appropriate toothpaste and a brush. Developing the habit of brushing your teeth at an early age twice a day (in the morning and also in the evening, after meals) will prevent many problems.
Prevention of caries in young children
Prevention of childhood diseases must begin in the antenatal period, when the child is still in the womb. During the development of the embryo, the structure of its teeth is laid down - already at this stage they are saturated with mineral salts. For this to happen correctly, the expectant mother should:
- Eat right: eat foods with calcium, magnesium and other trace elements.
- Carefully observe oral hygiene: brush your teeth, use dental floss, rinses and irrigators.
- Undergo medical examinations, including by a dentist; cure caries and other dental diseases before conception or at least during pregnancy.
If you take these recommendations into account, the risk of developing dental diseases in your baby will be significantly lower. However, the prevention of childhood caries at this stage is just beginning. In principle, you will have to do it all your life. It’s just that in the first years after the birth of a baby, parents should teach him to take care of his teeth, so that later prevention becomes a part of his life.
Signs of caries
Caries of primary teeth according to the depth of damage can be divided into the following types:
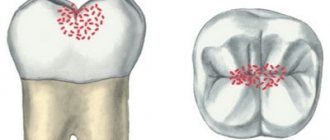
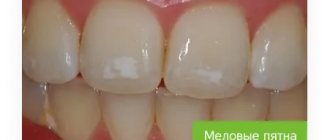
- Initial caries - in this case, white spots of different sizes and shapes appear on the enamel, but there is no pain. If left untreated, the process progresses and the spots darken, become black or brown. If you start timely treatment, you can stop the further development of caries.
- Superficial caries - a defect in dental tissues can be detected exclusively within the enamel. Pain occurs when exposed to sour, sweet, salty foods. A carious cavity can be dark or light. Treatment consists of filling the cavity.
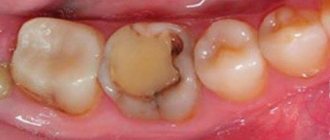
- Medium caries - damage to tooth enamel and part of the dentin (intradental tissue) is detected. Painful sensations arise from hot, cold, salty, sweet. With this type of caries, the cavity is filled.
- Deep caries - the enamel is affected, as well as most of the dentin. When choosing a treatment method, the condition of the pulp is assessed and, depending on whether, filling or conservative treatment is carried out, in which therapeutic pads are used, and then delayed filling.
In children, multiple dental lesions are possible (20 baby teeth may be affected at once). In addition, during childhood, several carious cavities can occur in one tooth. Due to the physiological and anatomical structure of teeth, some children have a thinner layer of dentin and enamel, so hard tissues have a higher permeability, which is why the carious process quickly spreads along the surface of the tooth and deeper. This contributes to the spread of the process to deeper tissues and the development of periodontitis and pulpitis.
Diagnosis of initial caries
So, we have found out what caries looks like on teeth at the initial stage, now we need to tell you how the diagnosis is carried out. This is not as simple as it might seem at first glance. The clinical picture of initial caries is mild. The disease has practically no characteristic symptoms, and this is especially true for pain. Only occasionally the patient may feel slight discomfort after drinking cold drinks. Diagnosis of initial caries today is carried out using several methods.
Methods for diagnosing initial caries
- Drying.
A common visual assessment technique. The tooth is thoroughly dried with peroxide, after which the affected areas become visible. - X-ray.
Not the most reliable method, but dental x-rays are an integral part of the preparation. White spots are especially noticeable in targeted photographs. - Coloring.
After applying a solution of methylene blue, the affected areas turn a characteristic blue color. - Transillumination.
The teeth are scanned with a special fluorescent device, as a result of which areas of demineralized enamel and their boundaries are detected.
In addition, specialists can resort to differential diagnosis. This is a set of procedures aimed at distinguishing diseases that are similar in symptoms and clinical picture. In the case of initial caries, these are non-carious lesions of the enamel (fluorosis, hypoplasia, and the like).
Stay vigilant
If you find plaque forming on your child’s teeth that you are unable to remove on your own, as well as brown or white spots, this indicates that the child urgently needs to be shown to a pediatric dentist. If the baby complains of discomfort that occurs when eating hot or cold food, this indicates the spread of caries into the deeper layers of the tooth. Parents should never ignore such complaints. It happens that a small child is not able to clearly communicate what is bothering him, so if he refuses food or a certain type of food, and also chews on one side, this may indicate toothache.
Prevention, or how to avoid “bottle” caries?
After reading this, many may accuse me of advocating the abandonment of breastfeeding, or the sudden cessation of feeding during sleep! In no case! Firstly, every mother decides for herself how long to breastfeed her child. In addition, I think no one will argue that there is nothing better than natural breastfeeding, since in addition to nutrients, the child receives passive immunity from the mother due to the IgG immunoglobulins contained in milk.
Ingredients: In addition to xylitol, TeethCleaners™ contain green tea extract, which has a mild anti-inflammatory and anti-edematous effect, which helps reduce itching of the gums during teething. The composition also includes various biological natural components, such as rice and barley decoction.
- Careful oral hygiene. You should start brushing your teeth from the moment they appear as often as possible, and at least 2-3 times a day. REMEMBER: NO PLAQUE - NO CARIES! In addition, this develops in children the habit of brushing their teeth and at an older age they will be more enthusiastic about brushing on their own;
- After each meal, wipe your baby's teeth. For this purpose, there are special dental wipes Spiffies™, ZubkiChistki™, Wakodo™ Tooth Cleaner for Baby. The xylitol they contain has a bacteriostatic effect on Streptococcus mutans, which causes caries and inflammatory gum diseases. By the way, the xylitol contained in the wipes has a sweetish taste, for which children are happy to let you wipe their teeth. If you don’t have them on hand, you can use the “old-fashioned method”: ordinary gauze wrapped around your finger and soaked in water, tea or chamomile decoction. By the way, treatment with various decoctions (chamomile, oak bark, etc.) helps remove gum teeth during teething, as they have a slight anti-inflammatory and anti-edematous effect;
- Try to include solid food in your diet (apples, carrots, cucumber, etc.). Firstly, children like to chew on something, especially when they are teething. Secondly, while the child is gnawing on a carrot, the surface of the tooth is cleansed of bacterial plaque. Plus, some vegetables (carrots, cucumbers, celery stalks) and herbs (parsley) regulate the pH of saliva in the mouth (shifting it to the alkaline side), which creates additional protection against caries;
- At home, you can independently carry out remineralizing therapy to strengthen your tooth enamel. For this, there are special remineralizing gels and creams: ROCS Minerals™ and GC Tooth Mousse™;
- Do not lick the pacifier and spoon, do not give him food you have chewed. Together with your saliva, the bacterial flora of the oral cavity is transmitted, which the child’s body is not always able to cope with;
- Try not to use the pacifier unless absolutely necessary. And especially do not lubricate the pacifier with sugar or jam. Affection and love for a child are better than any pacifier. If your child is crying, contact your pediatrician, there may be a good reason for this;
- Consult a pediatric dentist as soon as your baby's first tooth emerges. The pediatric dentist will always tell you how to properly care for them.
PHOTO: Spiffies™ oral hygiene wipes for young children contain xylitol, which has a sweetish taste and a bacteriostatic effect (inhibits the growth of bacteria).
To learn how to teach a child to brush their teeth correctly and what brushing technique to use, read the article How to properly brush a child’s teeth?
If you find whitish, rough (or any other color) spots on your baby’s teeth, you should not immediately try to self-medicate and remineralize therapy, even if you are sure that this is the initial stage of caries. First, consult a pediatric dentist! A pediatric dentist will always explain and show parents how to properly care for a small child’s teeth, especially if signs of enamel destruction are already appearing, will help select individual hygiene products and, if necessary, will carry out the necessary treatment.
Complications of caries
The most typical complications of caries are pulpitis and periodontitis.
Pulpitis is a pathological process in which the inflammatory process affects the soft dental tissue (pulp). Symptoms of pulpitis can develop over several hours. This is preceded by minor pain, then acute pain occurs, more often at night or as a result of exposure to temperature stimuli. Such signs indicate that the carious cavity is most likely very deep and the dental pulp is affected. In this case, urgent dental intervention is necessary.
In the event that toothache has been observed repeatedly, the child has swelling of the gums or cheeks, and a fistula with purulent discharge is visible on the mucous membrane near the tooth, pain occurs as a result of biting on the tooth, then this indicates the spread of the pathological process beyond the tooth and inflammatory the process developed in the tissues that surround the tooth and a pathology such as periodontitis arose. When treating it, the doctor will choose the treatment tactics individually, but such a baby tooth is unlikely to be cured and will need to be removed.
When is the outcome of treatment of initial caries considered successful?
The initial stage of caries is the easiest to correct, but incomplete or poor-quality treatment almost always leads to the transition of the disease to the next, more serious, stage. The outcome of treatment of initial caries is considered successful when:
- the carious stain disappeared, the tooth color became uniform;
- repeated diagnostics confirms the absence of traces of enamel demineralization;
- there is no reaction to temperature stimuli and the feeling of soreness, which sometimes appears at the stage of initial caries, disappears.
Methods for treating caries
For caries in children at the initial stage of its development, enamel silvering can be used. In this case, a special solution containing silver ions is applied to the carious cavity (untreated). This is usually a temporary measure used to combat tooth decay. When using silver preparations, areas of the tooth affected by caries, that is, the carious stain itself, are persistently painted black, and this does not look very aesthetically pleasing. However, you don’t need to think that the entire tooth will turn black. Only the part affected by caries will darken, while the healthy part will remain unchanged white.
The most traditional methods of treating caries in primary teeth are removing the affected dental tissue with a drill using local anesthesia. The dentist decides on the need to use local or general anesthesia (anesthesia) individually in each case. Sometimes neither parents nor a doctor can persuade a child to open his mouth in order to treat or show his teeth. Most often, children under three years of age or those suffering from concomitant pathologies face this problem. Then it becomes necessary to treat teeth under general anesthesia. A child should not have any fear of the dentist. It is advisable that he become friends with him and understand that it is necessary to treat his teeth. After all, he will have to deal with this for the rest of his life. The child’s psychological mood largely depends on his parents and loved ones, who can convey to him their fear of visiting the dentist. Try to explain to your child the importance of a visit to the dentist and convince him that there is no need to be afraid of such a procedure.
Treatment of initial caries
Most patients are interested in how to get rid of initial caries if you have signs of its manifestation? Initial caries in the spot stage is quite easy to treat, and, importantly, today this rarely requires the use of a drill. Modern dentistry offers non-invasive methods that cope with the disease and do not require tooth preparation.
Non-invasive methods for treating early caries
- Remineralization.
Before starting therapy, professional hygiene is carried out, which is designed to remove plaque and carious stains, as well as dry the teeth. The most common method is application with a solution of 10% calcium gluconate, as well as other drugs, for example, fluorides. To eliminate a stain, 10 to 20 procedures are usually required. In modern clinics, remineralization is often carried out using electrophoresis technology. It is also possible to carry out remineralization at home (for mild forms of the disease and for prevention). Usually special gels and pastes are used for this. - Deep fluoridation.
Application of preparations containing fluoride, copper hydroxide and calcium to the surface of teeth. To consolidate the result, fluoride-containing pastes are used. Fluoridation reduces the body's ability to absorb sugar, so the procedure is not recommended for people with diabetes, as well as for those with excess fluoride in the body. - Treatment using Icon technology.
This is an infiltration technique that involves treating the tooth with a special polymer composition that seals the carious cavity and prevents the development of the disease.
How to brush your teeth?
Each specialist has his own opinion about when to brush a child’s teeth using toothpaste. The composition of the toothpaste must correspond to the age of the baby - all information about this can be found on the packaging. Toothpastes for children under three years of age should not contain fluoride. Children at this age, not having the skills to rinse, swallow the paste. If a large amount of paste containing fluoride enters a child's body, serious health problems may arise, so in this case you should consult a doctor immediately. Children from about 4 years of age after brushing their teeth can partially spit out the remaining toothpaste. This is why toothpastes for this age contain fluorides. The maturation of tooth enamel is accelerated if hygiene products containing active fluoride are regularly used. This has been proven to help reduce the risk of tooth decay.
Children's toothbrushes are varied. For very small children, you can use special finger brushes, with which mother can easily remove plaque from her child’s teeth. By the age of 2.5-3 years, you gradually need to give the child a toothbrush in his hand and teach him to brush his teeth on his own.
Choose a toothbrush with soft bristles, the width of which corresponds to 2-3 teeth. It is recommended to change it every month, because frayed bristles can hurt your gums and are also a source of bacteria. The child should have an individual toothbrush; it should be stored separately, without a case, with the bristles facing up. Before brushing your teeth, as well as after the procedure, the brush should be rinsed well with running water. Oral care with additional hygiene products
- You can use dental floss or floss when all 20 baby teeth have erupted (most often at the age of 2-2.5 years). Dental floss should be used if the teeth fit tightly together. This must be done very carefully so as not to accidentally injure the gums.
- Dental rinses (elixirs) can be used as an additional hygiene product for children with a high risk of developing caries. Special children's elixirs contain fluoride in the amount that a child of a given age needs. You can use it twice a day after brushing your teeth or eating foods that contain a lot of sugar. Chewing gum should not be given to children until after 3 years of age. The sweeteners they contain (sorbitol, xylitol, etc.) have a beneficial effect on tooth enamel and prevent the occurrence of caries. Chewing gum also promotes increased salivation and self-cleaning of the oral cavity. They can be given to children regardless of the presence or absence of a filling in the mouth. Chewing duration is no more than 10-15 minutes.
Dental caries in children: features of the disease
Considering the prevalence of caries in children, from the moment the first teeth appear, parents should pay special attention to the child’s hygiene and nutrition, as well as regularly visit the dentist for examinations and preventive procedures. All this is necessary in order to protect baby teeth as much as possible until the moment when they are replaced by molars. Look at the statistics: in children aged a year and a half, caries is diagnosed on average in 10 - 15% of cases, and by the age of five, more than 70% of children already suffer from this disease. Moreover, caries in preschool children develops at a much faster rate than in adults, so if left untreated, the child risks losing all of his baby teeth even before they begin to be replaced by molars. The causes of caries can be very different, which is largely why it is a widespread dental disease. Below we will talk about the most common causes of caries in children.
How to brush your teeth correctly?
It happens that trying to brush your teeth can sometimes cause a negative reaction. But you don't need to get upset about it. Better be patient and play. Remember that a child under three years of age, and older children too, learn about the world through play. Therefore, do not insist on brushing your teeth; it is unlikely that the baby will understand that this is important. Just play. For such games, a battery-powered brush and a toy on the handle are perfect. The movements performed by the brush for different groups of teeth should differ from each other. Cleaning the front teeth should be done from the gums with unidirectional vertical movements. Move the brush behind the cheeks in a circular manner, while the teeth should be closed. Cleaning the chewing surface of the teeth is carried out with horizontal movements from the inside (from the palate and tongue), back and forth, sweeping upward like a “broom”. But not only the movements that are performed are important, but also how much time is devoted to it. There are two ways to check whether your teeth are being brushed adequately:
- – in terms of time (you need to spend about 7-10 minutes brushing all your teeth), for this you can use an hourglass or any other clock
- – by the number of movements (for each area occupied by the bristles of the brush, 5-6 movements are needed).
Fluoridation as a method of treating caries in the spot stage
The method is somewhat similar to remotherapy. But if remineralization preparations usually contain calcium and phosphates, then the main component of fluoridation products is fluorine. It has the property of strengthening tooth enamel and ensuring its strength.
Fluoridation can be simple or deep. In the first case, you will have to visit the dentist four to fifteen times. During each procedure, the doctor coats the teeth with fluoride-containing gel or varnish for 20 minutes. After the manipulation, you should not drink or eat for an hour.
The deep fluoridation method is considered simpler and more effective. It is carried out using two drugs. One contains magnesium, fluorine and copper, the other contains calcium hydroxide. By reacting with each other, these agents seal the enamel, which allows the concentration of fluoride ions in it to increase several times. A significant advantage of deep fluoridation is the smaller number of procedures - from one to three.
Due to fluoridation, the resistance of tooth enamel to destruction by acids increases, the activity of cariogenic bacteria decreases, and the balance of mineral substances is normalized. To achieve maximum results in the treatment of initial caries, the dentist may recommend the combined use of remineralization and fluoridation methods.
Proper nutrition
One of the preventive measures for dental diseases is a balanced diet - one in which the daily diet contains proteins, carbohydrates, fats, minerals and vitamins that are necessary for the formation and proper growth of dental tissues. In infants, this is breastfeeding. Older children need to include in their diet all the necessary types of complementary foods that are recommended for this age. Additional sources of fluoride can also be water and fluoridated salt; their use does not require special indications. The main sources of calcium are fermented milk products (cottage cheese, milk, cheese, etc.), buckwheat, gooseberries, potatoes, peas, oats, mineral water (some of its types).
What does bottle caries look like and where does it develop?
Bottle caries always begins its development in the most vulnerable part of a baby tooth, in the cervical area, since it is in this area that bacterial plaque accumulates. The vulnerability of the cervical part of the teeth is due to the fact that mineralization of the enamel here occurs after the birth of a child in new and not always favorable conditions. The mineralization process can be negatively affected by the nature of nutrition (natural breastfeeding or artificial), social conditions, as well as various diseases: acute respiratory infections, intestinal infections, etc. The neck of the tooth becomes weakened and after eruption the enamel becomes vulnerable.
Why bottle caries
develops only on the upper central teeth of the child? To do this, you need to remember how the sucking process occurs in young children. During the process of sucking and swallowing, the tongue is located between the lower teeth and the mother's breast (or pacifier, respectively), so the main load (impact) falls on the upper front teeth. It is in this area that food debris and plaque accumulate.
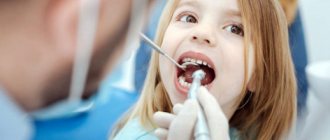
First visit to the dentist
A child’s first visit to the dentist is most often necessary for the following reasons: for a preventive examination upon admission to a preschool or if complaints arise. Don't wait until after the age of four to visit the dentist for the first time. Subsequently, the child needs such visits twice a year. If the baby has already begun the carious process, then during this time it will not be able to spread deeply, caries complications such as periodontitis and pulpitis will not arise, and the tooth can be saved. The sooner the doctor can detect caries, the more successful and painless the treatment will be. Sometimes, in the initial stages of superficial caries, treatment can be carried out without instrumental intervention using mineralizing agents. In this case, medicinal solutions of calcium and phosphorus are applied to damaged areas of enamel. The dentist’s task is not only to provide dental treatment, but also preventive measures that will help keep teeth and gums healthy:
- professional oral hygiene (removal of dental plaque);
- treatment of teeth with calcium and fluoride preparations
- prescribing general treatment if necessary (internal intake of vitamin and mineral complexes);
- teaching your child how to properly brush their teeth;
- correction of the composition and diet, identification of bad habits together with parents;
- sealing fissures (grooves that are located on the chewing surface of the tooth) is a prevention method that is aimed at preventing caries from affecting permanent teeth.
How does childhood caries differ from adult caries?
The structure of a baby tooth and its enamel is somewhat different from an adult tooth. The baby tooth has wider tubules, thinner and more delicate, not yet sufficiently mineralized enamel.
Therefore, the process of tooth decay in children begins and proceeds a little differently than in adults:
- The disease develops very quickly.
- Caries in children is practically asymptomatic, so it is very difficult to diagnose in the early stages.
- The disease can begin against the background of a decrease in the child’s immunity and other common diseases.
- Children experience special forms of caries that are not typical for adults:
- circular caries - a carious lesion is located in the form of a ring at the base of the tooth, which leads to a fracture of the crown;
- Planar caries affects a significant surface of the tooth, but does not penetrate into its depth.
- Children are prone to a generalized process in which caries affects all teeth and develops very aggressively.
Only early prevention of dental caries in children and early diagnosis will help to cope with these problems. We recommend safe non-X-ray diagnostics for children using the Diagnocam device, which does not expose the child to radiation, so it can be done every 6 months. We provide this examination to all our young and adult patients for preventive examinations absolutely free of charge.
The process of treating childhood caries
- Step 1: The cavity is treated with a water-cooled high-speed handpiece to remove decayed tooth tissue.
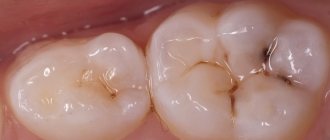
- Step 2. The resulting cavity is treated with an antiseptic solution and filled with filling material. To restore baby teeth, the Grandmed clinic uses special materials that release fluoride ions into the tooth. At the request of the parents and the baby, the filling can be colored.
- Step 3. Excess filling is removed and polished.
- Step 4. The final stage is to coat the filling with protective varnish.
In our clinic, during all stages of treatment, a small patient can watch cartoons. This is done to make dental treatment easier for children to understand.