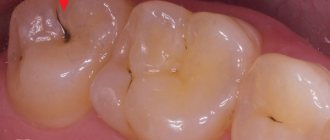
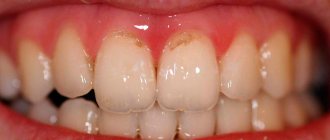
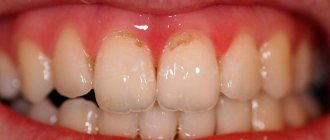
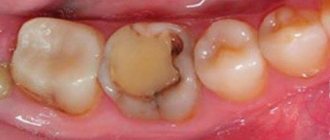
Types of caries localizations
Caries (lat. caries rotting) is a slow and hidden pathological process occurring in the hard tissues of the tooth. It is characterized first by focal demineralization of the enamel, then by the destruction of hard tooth tissues with the appearance of a cavity in the dentin. If left untreated, the tooth is lost or complications arise - pulpitis and periodontitis.
Cervical (circular)
The structure of a tooth is divided into a root, a neck and a crown - the latter is located above the gum. The neck and root are located in the gum and are protected by soft mucosal tissue.
When the carious process begins to destroy the tooth in the area of contact of the crown with the mucous membrane, we can talk about the cervical form of caries.
This category is the most difficult to diagnose and treat. It most often affects the incisors. When biting food with incisors, the food is not only “cut off”, but also gets clogged into the gum pockets, moving towards the gums.
Crown caries
Caries has the ability to affect not only healthy, but also already treated teeth - under a filling or crown. If there is a crown, it is difficult to detect, because the tooth does not have a nerve and pain is not felt. There are no external signs for a long time.
The causes of this type of caries are:
- defect of the dental crown with the appearance of access to the tooth tissue underneath it
- poorly treated tooth before prosthetics;
- gum disease;
- poor oral hygiene.
The problem is that the process spreads into the deep layers and spreads to the bone structures, as a result of which the tooth is often completely removed. That is why preventive examinations and an orthopantomogram - a panoramic image of the entire jaw - are so important.
Radical caries
Basal and cervical caries are similar. Both incisors and chewing teeth are affected. Destruction begins with the enamel, gradually moving to the nerve in the root canal. When the process touches bone tissue, it threatens with osteomyelitis.
The main reason for the occurrence is a cariogenic situation in the oral cavity, when plaque accumulates especially quickly. The enamel in the root part of the tooth is much thinner and more easily destroyed. It is most often diagnosed between the ages of 30 and 60 years.
Root caries
Root or subgingival caries occurs hidden. It can be with or without a cavity. Along the flow - active, suspended, secondary. It most often affects molars.
Stages of caries development
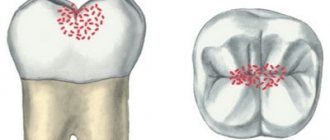
Caries is usually classified according to location and severity. From the point of view of determining treatment tactics, the stage of disease development is of greatest importance. In dentistry, there are 4 stages of development of dental caries:
- Elementary. The enamel layer gradually changes color - white spots appear on the surface of the teeth. Otherwise, caries occurs without a trace for the patient.
- Surface. Dark spots are visualized on the enamel. A damaged tooth does not react for a long time to cold, hot, sour and sweet foods.
- Average. The development of the disease leads to damage to dentin. Pain in response to external irritants is more pronounced and prolonged.
- Deep. The disease is accompanied by extensive damage to enamel and dentin. The pain does not go away even after using analgesics.
The earlier the stage of development of caries, the greater the likelihood that the disease can be cured with few sacrifices.
What is the danger of this disease?
Caries is dangerous because there are no symptoms for a number of years. It is detected more often in an advanced stage, when tooth extraction becomes the solution.
Visual diagnosis is difficult because all destructive processes occur inside the tooth. Pronounced plaque or tartar hides any stains on the enamel.
The root is hidden under the gum and external irritants do not affect it until a certain time. On the other hand, the root walls are thin, so they are destroyed quickly and with complications.
Photos before and after
InformationAge, diagnosis, treatment methodMale, 47 years old
Diagnosis: partial edentia
Treatment: All on 4 dental prosthetics in the upper and lower jaws, with immediate loading.
are presented “before” and “after” prosthetics .
Woman, 45 years old
Diagnosis: partial loss of teeth
Treatment: All-on-4 implantation of the upper and lower jaws, followed by immediate loading.
All on 4 prosthetics: photos “ before” and “after” the procedure.
Woman, 64 years old
Diagnosis: partial edentia
Treatment: prosthetics according to the All on 4 protocol for the lower and upper jaws, followed by loading.
are presented “before” and “after” prosthetics .
Male, 53 years old
Diagnosis: partial edentia
Dental prosthetics: in the photo, the All on 4 method of the upper and lower jaws, with immediate loading.
are presented “before” and “after” prosthetics .
Female, age 45 years.
Diagnosis: partial loss of teeth
Treatment: All on 4 upper and lower jaws, with immediate loading.
are presented “before” and “after” prosthetics .
Male, age 62 years.
Diagnosis: partial edentia
Treatment: one-stage dental prosthetics (pictured) All on 4 upper and lower jaws, with immediate load on the dentures.
are presented “before” and “after” prosthetics .
Male, age 61 years.
Diagnosis: partial edentia, crowded teeth
Treatment: All on 4 upper and lower jaws, with immediate loading.
are presented “before” and “after” prosthetics .
Female, age 59 years.
Diagnosis: partial absence of teeth, periodontitis
Dental prosthetics: All on 4 upper and lower jaws, with immediate loading.
are presented “before” and “after” prosthetics .
Causes of the disease
There are 3 main provoking factors that must act in a complex manner; none of them acts independently:
- Cariesogenic microflora - this includes Mutans streptococci, actinomycetes and certain types of lactobacilli. They should dominate the oral cavity. Bacteria produce organic acids from food carbohydrates, which cause demineralization of cement.
- Consumption of simple carbohydrates is the most cariogenic. Their breakdown produces glucan, which contributes to the appearance of plaque.
- Reduced caries resistance is a deterioration in the resistance of tooth tissue and the body as a whole. This is facilitated by a decrease in calcium content in hard root tissues, bad habits, and lack of saliva.
In addition, the anatomical features of the mouth can also have an effect - a small vestibule, a short frenulum, and bite pathology.
Gum disease, pocket formation
Gum pocket or otherwise periodontitis is a common occurrence in many patients. Many people do not treat it because it does not bother anyone for a long time.
The first manifestation of pathology is bleeding when brushing teeth, although outwardly they may look healthy. Dental pockets or depressions are normal, but their anatomical size should not exceed 3 mm.
Then the pocket is able to self-clean from food debris and epithelial particles. Reservoirs of bacterial accumulations form in deep gaps. This is accompanied by bad breath. Conventional treatment with antibiotics and brushing teeth with toothpaste have no effect.
Causes of periodontitis:
- insufficient hygiene;
- poor quality fillings;
- abnormal position of the dentition, malocclusion;
- hereditary predisposition;
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals;
- immunosuppression.
Lifestyle
If you have learned about the risk group for root caries (older age), this does not mean that you can relax. Caries has many causes and can occur at any age if basic precautions are not followed.
Those at risk include smokers, diabetics, pregnant women and even children. The provoking factors in this case are:
- smoking and lack of oral hygiene;
- infrequent brushing of teeth and lack of fluoride;
- poor nutrition with preference for desserts;
- frequent stress;
- alternating hot and cold;
- structural features of the oral cavity;
- alcohol abuse - alcohol breaks down into sugars and acids;
- abuse of coffee and strong tea, which creates an acidic environment in the oral cavity;
- lack of water intake, and therefore lack of saliva;
- gum injuries.
Symptoms of the disease
The process usually occurs without symptoms, but pain may occur when brushing a toothbrush, eating sour, salty, sweet, cold or hot foods.
After eliminating the irritant, everything goes away. The patient can see a doctor if a stain is found on the front surface of the incisors, but often it is hidden under plaque or tartar.
The ongoing carious process gradually reaches the dentin junction, penetrating first into its surface layers and then further. The cavity deepens with bacteria and food debris. There is a smell from the mouth. Irritants cause pain more and more frequently.
With cement caries, teeth become mobile and lose their support, and bleeding gums occur. These are already symptoms of periodontitis. Now, even when chewing food or brushing teeth, severe discomfort occurs.
Digestion begins to suffer. Teeth become hypersensitive to hot or cold.
Next, the process follows the Leus classification:
- Active lesion - the edges of the cavity are undermined. The cavity is filled with softened tissues and tends to grow.
- Suspended caries - no increase in the affected area is observed. The cavity is clean, the bottom is shiny and smooth, the edges are even and dense.
- Secondary caries - occurs under a filling.
The main advantages and disadvantages of dental extensions
Advantages of dental extensions
Some of the benefits of tooth augmentation over other restorative dental procedures include:
- high aesthetic results of restoration;
- the ability to select composite materials that do not differ in color from natural dental tissues;
- no need for preliminary grinding of teeth;
- painlessness of the extension procedure;
- high service life of materials used for the restoration of destroyed or damaged teeth;
- the ability to restore a damaged tooth in one visit to the dentist.
The main disadvantage of tooth augmentation is the relative cost of the procedure. However, in most cases, building up the crown of a tooth costs dental patients less than installing a crown or implanting an implant.
If you have any questions, you can contact our dentists through the on-line connection on the website or call the phone numbers on the website.
Diagnosis of the disease
The diagnosis is made in stages. Listening to complaints and visual examination make it possible to diagnose caries only in 13% of cases. Classic probing with a sharp probe and inspection with a mirror are informative. This allows you to examine the dentition.
Thermal diagnostics, electroodontometry and x-rays are also performed. If the patient has massive dental plaque, changes in the enamel will not be visible. In this case, professional teeth cleaning is first carried out to remove plaque and stone. All this is possible in a dental clinic.
At the dental clinic
The following types of studies can be performed at the clinic:
- Probing with a thin probe with a curved end - it is inserted under the gum, while the doctor has the opportunity to examine the structure of the tooth, its integrity, the presence of irregularities and chips. With rapidly progressing caries, the edges of the cavity are uneven and sharp. In the remission stage, the surface of the pathological focus is shiny, smooth, hard with smooth edges.
- Electroodontometry - can determine nerve damage and the depth of inflammation. The pulp reacts differently to the current strength.
- Thermal diagnostics - treatment of different areas of the tooth with a stream of water and heated wax. Unpleasant sensations that disappear after removing the irritant indicate caries.
- X-ray - a targeted photograph of one tooth or computed tomography. The presence and localization of obvious or hidden inflammation is determined with millimeter precision.
- Visiography is a special device - a visiograph scans the received data and transfers it to a computer, where the picture is studied from different angles and in detail, revealing the hidden process of inflammation.
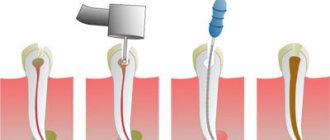
Treatment of average caries in stages
Step-by-step treatment of caries includes the following steps:
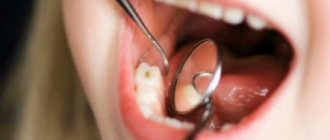
- Cleaning the surface from plaque . How are caries treated in dentistry? First, be sure to clean the damaged tooth and the teeth adjacent to it. To remove plaque, the dentist can use an abrasive brush or floss; to remove the stone, ultrasonic attachments will be required.
- Drilling out affected tissues . Since enamel is hard and durable, it is destroyed less than dentin. It is for this reason that the entrance hole of the cavity may be small, expanding as it deepens. If cervical caries occurs, how to treat it? The doctor drills the edges of the enamel and removes dentin affected by caries. If even a small area of affected tissue remains, on top of which a filling is placed, this is fraught with problems in the very near future, because caries will begin to develop rapidly, which can ultimately lead to pulpitis.
- Isolating the tooth from moisture and saliva . Unfortunately, some dentists (in fact, most of them) neglect this point and skip it. When carious tissue is eliminated, the doctor, in preparation for filling, must isolate the tooth from contact with saliva. It might seem like a small thing, but it affects how long the filling will last. For a long time, ordinary cotton wool or gauze was used for isolation, which was used to cover the tooth, but this method was found to be ineffective. Modern dentistry recommends the use of rubber dam - a thin latex material in which holes are made. Its installation is quite labor-intensive, so dentists avoid this procedure in order to save their own time. The use of a rubber dam by a doctor is a sign that the dentist is conscientious about his work, putting the patient’s health above the profit received.
- Treatment of the cavity with antiseptics.
- Recreating the side wall . How is caries treated if it has affected the surface of the tooth in contact with another tooth nearby? Then you will need to install matrices and wedges to restore the side wall. The procedure cannot be called simple.
- Using acid to condition enamel . To ensure that the adhesive material applied to dentin penetrates into the deep tissues, phosphoric acid is used. At the end of the procedure, the gel must be completely washed off and the surface dried.
- Treatment of enamel with adhesive . In order to ensure ideal fastening of the filling, the enamel is thoroughly impregnated with adhesive material, and after its absorption, it is illuminated with a polymerization lamp.
- Installing a gasket for a seal . A gasket made of a special material is placed at the bottom of the drilled cavity. The need for this action is explained by the peculiarity of the shrinkage mechanisms of the filling material.
- Direct filling , restoring chewing function and aesthetic appearance. To do this, photopolymer materials are laid layer by layer, with each layer illuminated by a lamp, which gives greater strength.
- Surface grinding and polishing . Immediately after installation, the filling is uneven, as a result of which it not only causes a feeling of discomfort, but can even damage the tongue. Polishing will make the tooth smooth.
For many people, it is important not only to undergo caries treatment in Krasnodar, getting rid of pain and discomfort, but also to look attractive. Therefore, the dentist selects the filling material by color, trying to achieve 100% shade similarity with the natural tissue of neighboring teeth. The doctor’s task is to make sure that the filling does not stand out from the rest of the teeth, which is especially important when smiling.
Is it possible to treat caries on the front teeth without pain? Absolutely yes. Long gone are the days when going to the dentist and the treatment process was accompanied by physical suffering. Modern means of anesthesia make it possible for the patient to feel nothing at all. The anesthesiologist is able to select the concentration of the anesthetic so that it will act for several hours. The only unpleasant moment is the insertion of a needle into the gum: the faster the drug enters the tissue, the more painful it is for the patient. Although much here depends on the characteristics of the nervous system of each individual person. For people with a high pain threshold, going to the dentist can be an enjoyable experience.
Treatment or removal - what determines the outcome
The doctor makes a decision on treatment or tooth extraction after determining the depth of spread and the area of localization of the inflammatory process. It is mandatory to first carry out professional cleaning using an ultrasonic scaler, an AirFlow water-abrasive device and hand tools.
Initial caries is treated with conservative retherapy. For hard tissue defects, preparation and filling are performed. In severe cases, the tooth is removed.
Treatment of the initial stage of root caries
Conservative retherapy includes:
- fluoridation of teeth;
- covering teeth with protective agents
- training in proper oral hygiene
Caries in adults
Caries in adults develops quite slowly. Most patients seek help from a dentist at the stage of medium and deep caries. After a detailed diagnosis, the doctor most often resorts to the traditional method of treatment; in case of deep tissue damage against the background of complicated caries (pulpitis), endodontic therapy cannot be avoided.
Cleaning in dentistry from stone and plaque
1243900247100
Professional teeth cleaning involves removing the accumulation of all pathogenic microflora around the root.
It involves not only removing plaque, but also stones. This elimination of negative factors protects teeth for a long time.
Antiseptic treatment of affected areas
Treatment of root caries involves drilling out all affected areas with a drill and treating the carious cavity with antiseptics and special preparations. A 2% chlorhexidine solution or a gel based on it is used as an antiseptic for the treatment of carious cavities.
Modern dentistry – does it hurt?
Today it is logical to position the patient’s comfort on the same level as the results of therapy. Proper use of anesthesia in a dental clinic allows you to achieve the best results even in the most difficult cases.
Today's best method of pain relief in dentistry is the introduction of formulations based on articaine, a component that has minimal effects on the human vascular system and has a long-lasting effect.
In practice, there are several techniques for pain relief:
- applique. The doctor does not use a syringe or needle; the drug is applied to the mucous membrane in the form of a spray or using a gel-soaked tampon. This method of pain relief is used for relatively painless manipulations, for example, when giving injections to children;
- infiltration The doctor injects an anesthetic into the upper part of the tooth root. This anesthesia allows a person to be relieved of pain when treating deep caries of one tooth. The only condition for ensuring maximum effectiveness of the procedure is the introduction of the drug into the root of the upper tooth (due to the anatomical features of the jaw structure);
- conductor. The doctor injects the drug into the nerve or near the nerve trunk. The patient loses sensitivity in the local area for 2-3 hours;
- intraligamentary. Otherwise, the technique is called intraligamentous. The dentist injects an anesthetic with a special thin needle into the periodontium itself. This anesthesia allows you to “freeze” half of the jaw and lasts about 40 minutes. The method is most common in pediatric dentistry.
What to do to protect your gums
If the gum is not treated, inflammation will remain and all treatment will become meaningless. The gums are protected by diathermocoagulation and retraction.
Diathermocoagulation
Diathermocoagulation – excision of excess areas of periodontitis with a coagulation knife. The knife immediately cauterizes the bleeding edges. The procedure is performed when there are severe changes in the gums. In such cases, filling is postponed until the soft tissue is completely regenerated.
Retraction
If the condition of the gums is advanced, treatment of caries becomes impossible - the mucous membrane bleeds and interferes with tooth treatment. This gum is excised or a special device is applied to move the gum back. But more often, retraction is performed - lowering the gingival contour or moving apart the overhanging edges of the gums using special hemostatic threads. A temporary filling is placed until complete healing.
What preventative measures are there?
To keep your teeth healthy for many years, you need to brush your teeth twice a day, use floss and a tongue scraper. After sweets, you should rinse your mouth and chew gum for 5-10 minutes.
Prevention also includes the removal of tartar. A sufficient amount of saliva is also important, so it is necessary to maintain a water regime.
Like any other pathology, caries is better prevented than treated. Therefore, it is important to visit the dentist twice a year for preventive examinations. People at risk should approach this especially responsibly.
Other
Treatment of the disease
Caries between teeth is treated in the same way as regular one, with the only difference being that two units have to be “fixed” at once. In some special cases, in order to get to the affected part, the dentist is obliged to get rid of healthy tooth tissue by drilling. First, the specialist must prepare the cavity and then treat it.
It is important to be careful about the process so as not to touch or even damage the nerve. After which the doctor installs a plate that separates the teeth and inserts a filling. At the end of the process, it is put in order by grinding and polishing.