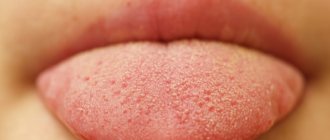
At the first visit, it is important for each patient to receive detailed information about his disease, its causes, consequences, methods of treatment and prevention. The total cost of treatment is also important information for the patient. In order to answer these questions, the doctor conducts an initial examination and diagnosis and, based on their results, develops a treatment plan.
What happens from the time you arrive at the clinic until you receive your treatment plan? View the standard treatment plan that our specialists draw up for patients.
At the first visit, the patient meets his attending physician and expresses his complaints. The doctor studies the noted problem and carries out a number of diagnostic measures. In simple cases, a minimum set of diagnostic measures is required.
What does the dentist do during the examination?
If there are no complaints, the initial examination proceeds according to the standard plan.
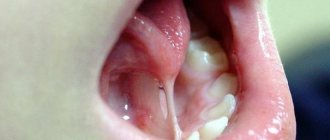
Visual assessment. The doctor examines the crowns, gums, mucous membranes (inner surface of the lips, cheeks), palate, checking:
- the presence of soft plaque and hard deposits on the enamel and in the gum pockets. Tartar accumulation indicates ineffective hygiene and requires professional cleaning. It is removed to check that there are no demineralized areas or caries underneath;
- general condition of the enamel: its color, transparency, gloss, presence or absence of mechanical defects. During examination, the doctor can identify chips, wedge-shaped defects, erosion, demineralization;
- signs of gum inflammation: swelling, discoloration, thickened areas, ulcers, etc.;
- condition of the mucous membranes (assessment of symptoms of gingivitis, traces of frequent mechanical injuries, burns, irritation or inflammation);
- condition of the palate, tongue (signs of injury, plaque deposits, traces of inflammation, erosion).
The color of the enamel is assessed separately. Its changes may indicate pulpitis (becomes gray), the use of certain medications (the shade changes to yellow or pink, may require bleaching), demineralization or caries in the stage of a white or dark spot (enamel lightens, loses its gloss, and then darkens, may turn brown or almost black).
Probing. It is carried out to control the strength of the enamel and evaluate the surface of the crowns. For this, a special tool is used - a probe. Such diagnostics allows us to identify caries, determine its stage, and the degree of tooth destruction. Probing also helps to diagnose non-carious lesions: fluorosis, hypoplasia, enamel erosion. It is carried out both for healthy and already filled teeth. If the crown has been restored, using a probe you can identify secondary caries and assess the condition of the fissures on the chewing surfaces. The tool should be blunt, angular, with a notch at the end. Probing is painless: the dentist simply runs a blunt end over the surface of the crowns, assessing the smoothness or roughness of the enamel and the degree of its hardness. The same technique is used to control gum pockets. The end of the probe is inserted into the groove behind the edge of the gum on all four sides of the crown. The immersion depth of the tool should not exceed 1 mm. If it goes deeper, the gum pocket is enlarged and this may indicate periodontal disease.
Using a probe, the gaps between your own tissues and the edges of the fillings are additionally checked. If they are enlarged (there is a noticeable joint that can be felt when the instrument is passed over the crown), this may require retreatment. When probing, the doctor can detect softening of dentin under the chewing surface, deposits of tartar on the neck of the tooth, under the gingival margin.
Palpation. It is carried out to assess the condition of the periodontium and identify hidden inflammation. With this diagnosis, the tooth is moved with tweezers in different directions, assessing its movement in the alveolus and how much it can move. If even with a slight force the crown moves, this indicates inflammation and swelling of the tissue. They can occur after injury, with periodontitis, periodontal disease, and periodontitis.
Additionally, they check in which directions the crown moves (only in one, two, three, in any direction, vertically, with the possibility of rotation, scrolling around the axis). When performing palpation, the doctor evaluates the patient’s sensations (is there any pain, sensitivity, during which movement of the crown is the pain most intense). When the tooth is rocked, bloody or purulent discharge may appear; the doctor may detect swelling or compaction, and this also helps to make a diagnosis. Traditional palpation (palpation) is carried out for the gums, inner surface of the cheeks and lips, if inflammation or other pathology is suspected.
Percussion. This is tapping the crowns with a probe handle or tweezers. The movements should be light, each tooth is tapped on the sides and on the top surface. The appearance of pain with a horizontal blow may indicate periodontitis, with a vertical blow it may indicate inflammation of the nerve or pulpitis. By assessing during percussion exactly in which places, during which tapping pain appears, and how severe it is, the doctor can make a preliminary diagnosis.
In some cases, radiography may be required during the initial examination. It helps to assess the condition of bone tissue, roots, and the filling density of the root canals if the tooth has already been filled.
First visit to the pediatric dentist - how to put your child in a positive mood
Caries is considered one of the most common dental diseases, affecting the vast majority of children. According to statistics, carious cavities occur in 80% of all children in Russia1. The first visit to the dentist is an important event, the success of which directly determines the child’s future attitude towards dental treatment. Experts in this field insist that your baby should make an appointment with a specialist immediately after the first teeth erupt. Read on in our article to learn how to prepare for this difficult test, especially if your child is afraid of the dentist.
How to arrange a child's visit to the dentist
Dentist consultation
It is carried out in two stages. Before the examination begins, the doctor talks with the patient, interviews him, collects information about existing complaints, previous treatment, the presence of concomitant or systemic diseases, possible contraindications for certain treatment methods. The goal is to collect general information about your health status.
The second stage of consultation is carried out after the examination. The dentist talks about identified dental problems, offers treatment options, and schedules the next appointment. If the appointment was preventive and the patient is healthy, the doctor can give recommendations on dental care and set a date for the next examination (usually every six months or more often if there are indications for this).
Treatment methods used in dentistry
Depending on the problem that has arisen, the following methods of treatment, restoration, restoration of teeth and other oral tissues can be used:
- Treatment of caries using remineralizing drugs or drills and filling materials.
- Treatment of pulpitis using vital/devital amputation or pulpectomy.
- Treatment of periodontitis – resection of the root apex, coronal-radicular separation, root amputation, tooth extraction.
- In surgery – tooth extraction, tooth-preserving operations, surgical operations on bone or soft tissues of the oral cavity.
- In periodontics – splinting, curettage of periodontal pockets, treatment of gums using the Vector apparatus, deepening the vestibule of the oral cavity.
- In orthopedics – installation of implants, prostheses and microprosthetics (veneers, lumineers, inlays, crowns, bridges, complete prosthetics). As well as bone grafting and bioreconstruction.
- In orthodontics – treatment using braces, mouth guards, removable and non-removable plate devices.
- Preventive measures - hygienic cleaning with removal of plaque, fluoridation of teeth. Sealing of fissures, remineralization of teeth (in pediatric dentistry).
- Teeth whitening – Zoom, Amazing White, Beyond Polus systems, custom-made mouth guards.
A dentist is a doctor who will effectively and painlessly cure/correct any pathology, anomaly, disorder, disease, or injury to the tissues of the oral cavity. If your tooth hurts, your gums bleed, ulcers appear on your tongue, or your enamel has darkened, you should consult a dentist with all these problems.
Modern dentistry has a wide range of methods, techniques and treatments in its arsenal in order to make therapy as effective, safe and comfortable as possible. And also so that the client receives not only high-quality, but also aesthetically perfect, durable results.
Useful tips for parents
How to prepare a child for the first preventive examination at the dentist and set him up in a positive way? First, you need to talk to him and it is better if the conversation is with a family member who himself is not afraid of treatment at the dentist. So, child psychologists offer the following advice in this regard:
- try to talk about going to the dentist as an interesting event, but at the same time ordinary and completely natural,
- During the conversation, call the child's doctor by name. For example, you can say: “This is Viktor Petrovich, he wants to see what beautiful teeth you have,”
- it is better to conduct the conversation within 1-2 days maximum - this way the child will not have time to start worrying or hear enough “horror stories” from peers,
- Make an appointment in the morning so that your child does not have a reason to worry all day about the upcoming visit. In addition, young children are usually calmer in the morning,
- One parent is sufficient to accompany the child to the clinic. Bring your baby's favorite book or toy with you. While waiting, he can be distracted by reading, looking at pictures or, for example, playing a game.
Before going on a hike, it is also advisable that the child is well-rested and does not have colds or other diseases. If this happens on the day of your planned visit to a specialist, then it is better to postpone the visit until better times.
The importance of prevention
Many mothers and fathers are subject to the mistaken opinion that it is not worth treating baby teeth at all, because their service life is very short and soon the baby teeth will be replaced by a permanent one. However, this belief is fundamentally wrong, since the formation of the rudiments of permanent teeth directly depends on the condition of temporary teeth. Caries or pulpitis in an advanced form can negatively affect the rudiments and lead to more serious dental problems in the future.
Teach children about oral hygiene
Therefore, it is extremely important to be on guard of the health of the baby’s teeth and gums from a very early age. Teach your child to perform thorough oral hygiene twice a day using a soft-bristled brush and toothpaste. For very small children, you can use special wipes or a fingertip designed to carefully remove deposits from the enamel surface. Consult your pediatric dentist about choosing an appropriate toothpaste. Make sure your baby's diet is rich in solid fruits and vegetables. Take your child to the dentist regularly for checkups.
Answering the question why children are afraid of dentists, it is worth noting that most often the parents themselves are to blame. Many adults still experience an overwhelming fear of the dental office, and excitement and anxiety are inevitably passed on to the baby. In this state, it will be very difficult to calm the child, so before going to the dentist, you should first deal with your emotions and experiences.
- According to the World Health Organization (WHO).