A. Iandolo (Alfredo Iandolo) Doctor of Dentistry, Professor
The long-term success of endodontic treatment is closely related to adequate cleansing and quality three-dimensional obturation of the complex root canal system. Probably, a significant percentage of failures is due to the presence of residual pulp tissue and insufficient cleaning of the canals.
The endodontic system consists of spaces easily accessible for manual and machine files (main canals) and spaces that are difficult or inaccessible (delta, lateral and auxiliary canals) (Fig. 1, 2).
Rice. 1.
Rice. 2.
Regardless of the technique used, it is impossible to mechanically treat all areas of the root system. For this reason, biochemical purification is necessary. Modern endodontic treatment methods are based on old methods of work: without the help of an operating microscope, with conventional NiTi files, the use of irrigation without activation.
Endodontic treatment can be divided into stages:
- Opening the pulp chamber is the most difficult phase according to the literature, since an error at this stage may jeopardize further processing. Dissection should be performed under constant magnification and illumination.
- Forming stage using new modified NiTi tools.
- Cleansing stage using irrigant activation.
- Obturation stage.
- Of course, treatment should end with restoration.
After a thorough analysis of the X-ray and clinical examination data, endodontic treatment can begin.
Opening the pulp chamber
The first step is to isolate the surgical field using a rubber dam. Then, with constant magnification and illumination, we must begin to open the pulp chamber using rotary instruments and ultrasonic tips.
The main function of an operating microscope (Fig. 3) is the ability to distinguish between two points that are very close to each other. The human eye is essentially unable to distinguish between two points separated by a minimum distance of 0.1 mm; it will sum them up as one image. When using an operating microscope, the resolution power increases from 0.1 mm to 0.005 mm, which is 5 microns and allows the human eye to discern more details.
Rice. 3.
Ultrasonic instruments include different types of tips that have different shapes and lengths (Fig. 4). In addition, with the introduction of new and improved ultrasound sources, it has become possible to optimize the use of each type of nozzle with the ability to control the frequency and amplitude of vibration. Ultrasonic handpieces guarantee greater precision thanks to their reduced dimensions, which provide a greater view of the working area than rotary instruments.
Rice. 4.
Only after identifying the orifices (Fig. 5) is it possible to continue treatment.
Rice. 5.
Medical Internet conferences
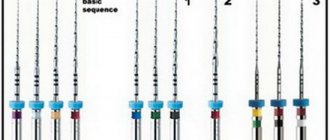
After analyzing the market for dental products, six representatives of MPEI were selected for comparative characteristics of properties. The contenders have different generations of instruments.
We will be the first to study the characteristics of the fifth generation EMR “Protaper universal treatment”, then the representative of MPEI No. 1. This system has three options for the length of the working part of the tool: 21/25 and 31 mm; there are two types of tools: “shaping” and “finisher”. The first is intended for shaping the canal, and the second is for finishing the apical third of the canal. There are also different tip diameters; “shapers” have 3 options: Sx (0.19mm) S1 (0.17mm) S2 (0.20mm); and “finishers” - F1, F2, F3, respectively, “shapers”. The advantages of the “Protaper universal treatment” system include a single sequence and color coding for the use of instruments, regardless of the shape of the root canal. Most clinical cases require only three instruments and, of course, safety due to the rounded guide of the protaper tip.
Representative of MPEI No. 2 replaced the previous test subject and has some improvements. In its work, this propaper uses wave-like movements, which promotes better removal of dentinal filings. This propaper also has an improved alloy, which reduces the likelihood of instrument fracture in the root canal. This tool has five types of dimension/taper - x1, x2, x3, x4, x5. The taper differs along the entire length of the working part, for the first two the taper both increases and decreases, and for x3, x4, x5 it is fixed in the first 3 mm of the length, then it decreases. Representative of MPEI No. 2 is the most famous of the machine files, since the fifth generation of files is the most effective and safe.
Representative of MPEI No. 3 is a fourth generation system. The file moves in different rotational directions (reciprocal movement) to avoid screwing and breaking the file in the root canal. Forward movements begin at a large angle, and return movements have a smaller angle; the full rotation cycle is 360 degrees. As a rule, only one system file is used; only the size is selected depending on the channel.
Let's consider another fourth-generation system that deserves attention - further, representative of MPEI No. 4. This system is a MEI, which is self-adapting and has the shape of a hollow lattice cylinder made of nickel-titanium alloy. This file adapts to the anatomy of the canal and is the most non-invasive method of shaping and cleaning it. The hollow design of the MEI makes it possible, using a special endomotor, to provide constant irrigation, which, in turn, improves disinfection. A special motor provides pecking and vibration movements equal to 5000 movements per minute, as well as very precise adjustment of the micromotor speed. The file is available in 3 standard sizes: 21 mm, 25 mm and 31 mm.
The representative of MPEI No. 5 has one very big difference, which is that the cross-section is not of the protaper type, but of the convex (convex) type. This type of section increases wear resistance and also provides a torsion load distributed over 3 points. Depending on the anatomy of the canal, from three to five instruments are used. The 02 taper gives this file high flexibility, which is an incomparable advantage for curved canals. ISO color coded, lengths available in 18, 19, 20 and 22 mm.
It is also necessary to consider instrument No. 6, which is the next generation of MPEI representative No. 5 - the new generation has an increased depth of the tubules on the instrument for removing dentinal chips; shortened shank 11 mm, which provides better access to molars.
Upcoming events
2021-09-01BASIC COURSE ON DENTAL IMPLANTATION WITH DR. FRIEDMAN FOR STUDENTS AND RESIDENTS (Annual course)
2022-01-26Predictable results of orthopedic treatment in digital format.
2022-02-05International Implantology Congress
The main properties of NiTi are shape memory and superelasticity (or pseudoelasticity), although the first characteristic is not used in endodontics. Superelasticity, or pseudoelasticity, is particularly useful because it gives the alloy the ability to flex and conform to the shape of the channel, allowing the channel to be formed in rotation while maintaining a centered position even in the presence of accentuated curvature. Thus, negative effects (perforations, steps) on the original channel path are minimized. Superelastic or pseudoelastic behavior depends on changes in crystalline organization. Although the use of NiTi offers several advantages, the use of these rotary instruments in endodontics may increase the risk of fracture compared with the use of steel instruments.
Fracture of a rotating instrument most often depends on bending resistance. There are many NiTi instruments available in dentistry today, in this study we used a new set of rotary instruments - ProTaper Next, as their use in endodontic treatment is very effective (Fig. 6).
Rice. 6.
ProTaper Next is the fifth generation of instruments, created using modern M-Wire technology, with a rectangular cross-section and an asymmetrical center of rotation. This tool, rotating in the channel, has a larger cutting surface than a tool with the same caliber, square cross-section and symmetrical center of rotation.
The rectangular cross-section and asymmetrical center reduce blade-to-wall contact, providing more debris clearance and increased flexibility. In addition, the new alloy improves resistance to tool cyclic fatigue, allowing you to work more safely even in highly curved canals (Fig. 7-10).
Rice. 7.
Rice. 8.
Rice. 9.
Rice. 10.
As shown in the literature, files are not able to contact all endodontic spaces, for this reason active cleaning is necessary to maximize the cleanliness of a complex endodontic system.
Machine method of root canal treatment
The result of endodontic treatment in general largely depends on the effectiveness of mechanical treatment of the root canals. At this stage, the canals are completely cleaned of microbes and dentin sawdust, they are expanded and brought to the shape necessary for fixing the filling material.
There are 2 methods of mechanical treatment of canals: machine and manual. Machine preparation is carried out by rotating nickel-titanium (Ni-Ti) files with special endodontic tips and micromotors that drive them.
The most common Ni-Ti tools are profiles (Pro-File), propapers (Pro Taper), MTU system (Mtwo).
The profiles are made from a super-flexible alloy (nickel-titanium), as a result of which they have high ductility, which allows even curved channels to be processed. Greater Taper (GT-rotating files) are the latest generation of nickel-titanium endodontic instruments. They are maximally adapted for root canal preparation using the Crown Down technique.
Advantages of machine root canal treatment:
- The presence of a special top on machine files, which avoids damage to the root wall;
- The doctor’s labor costs are reduced and the time for canal preparation is reduced;
- Instruments made of a flexible alloy (nickel-titanium) allow them to prepare even curved canals (up to 90 degrees);
- The cutting edges of the instruments have a special shape, which makes it possible to effectively remove dentin sawdust and nerve remains from the canal, and ensure its complete rinsing;
- The canal is given the desired shape for three-dimensional filling with filling material.
Disadvantages of machine root canal treatment:
- special skills are required to operate machine tools;
- tactile quality control of root processing deteriorates;
- high cost of equipment and treatment;
- Initial passage and processing of canals should be performed using hand tools. Therefore, today the most correct method is considered to be a combined preparation method using manual and machine files.
3D cleansing
The most common irrigant used for cleansing is sodium hypochlorite. Several authors have described various methods for increasing the effectiveness of sodium hypochlorite, including using more quantity and preheating.
Heated sodium hypochlorite has a greater ability to dissolve pulp tissue and clean the canal. The rate at which a chemical reaction occurs increases with increasing temperature, pressure, activation and concentration. Since the pressure within the root canal system cannot be increased, it is possible to speed up the cleansing by increasing concentration, heat and activation.
Activation is easily achieved with sound or ultrasonic sources (Fig. 11, 12). The concentration of solutions available on the market today to prevent possible irritant reactions does not exceed 6%.
Rice. eleven.
Rice. 12.
So let's move on to heating. Usually the solution is preheated to a temperature of 50°. Preheated solutions are of limited benefit as they quickly stabilize at room temperature.
New technique for heating sodium hypochlorite: working protocol
Sodium hypochlorite has a boiling point of 96°-120°. We use a heating plugger (System-B or similar). The temperature is set to 150°. The plugger used will be 30/04 so that the working length can be easily achieved without excessive preparation.
The root canal is filled with sodium hypochlorite through an endodontic needle. The plugger is inserted to a level of no more than -3 mm from the working length, and then activated. Each activation cycle lasts 5 seconds with further intervals of 5 seconds. When activated, the plugger makes short up and down movements of a few millimeters to agitate the irrigant.
The most important aspect is that there is no contact with the canal walls during activation of the plugger. After each cycle, the irrigant is replaced with a fresh solution to have a larger amount of hypochlorite with active chlorine. The activation cycle is repeated 5 times. During each activation, vapors are absorbed by the cannula.
The main indicator is the heating of the outer surface of the root in the coronal, middle, apical thirds and at the level of the apical foramen. When the irrigant was activated, the temperature on the outer surface of the root was measured with an infrared thermometer (resolution 0.1°). Using the values set in the operating protocol, no external heating above 42.5° was detected. In this way, temperatures close to 47°, which are dangerous for the periodontal ligament, can be avoided. After chemical-mechanical cleansing (Fig. 13-15), we proceed to three-dimensional obturation using thermoplastic gutta-percha.
Rice. 13.
Rice. 14.
Rice. 15.
Files
There are many different file types on the market.
As their name indicates (files), this tool is used for filing the walls of the canal. The instrument is inserted to the apex and, when some clamping of the instrument is felt, it is withdrawn, while the walls of the canal are scraped. In this case, the tool is either turned very little or not at all. During the preparation process, the instrument is removed, then reinserted and pressed with the working edge in another part of the perimeter of the root configuration, and in this way most of the walls are prepared from the mouth to the apical third. If necessary, the tool can also be used as an example.
K-type files
These tools are made from high quality steel wire and are sharpened into a square or triangle cross section. Then the workpiece is twisted in a spiral from 0.88 to 1.97 curls (cutting edges) per millimeter.
Recently, K-file microboring technology has been used and the result is an ultra-sharp tool with increased flexibility.
Made from triangular wire, K-files are ultra-sharp and efficient. Thanks to their increased flexibility, they fit into the channel without deviation from their course.
K-flex files
The cross-section of the blanks is diamond-shaped and, after twisting, they form sharp (less than 600) cutting edges and a blunt, non-cutting tip.
The cutting efficiency of K-flex files is higher than other types of files. This is achieved due to increased flexibility and increased ability to remove sawdust, as well as the relatively obtuse angle of the grooves, which act as a reservoir for sawdust.
The main disadvantage is the rapid loss of cutting efficiency.
Flexofile is the same K-file made of triangular wire made of high-quality steel with increased flexibility.
Flex-R file
Many root tools have a sharp tip. Removing the sharp cutting tip of the tool prevents the undesirable effect of creating ledges and perforations. The Flex-R file is deprived of the ability to form ledges, since its tip is deprived of cutting capabilities. This allows the tip to slide along the channel without penetrating into its walls. It is made of triangular wire, is very flexible and can fit even into highly tortuous canals up to the apex. This was a step forward in endodontic instrument design.
Handstrom file
It is made from a round wire billet, has rising cutting edges, and seems to consist of cones that decrease in size. Although the design of the tool may be very flexible, it is very fragile due to sudden changes in diameter, and is prone to breakage. Cutting efficiency, unlike other files, only when moving towards you. These files can be helpful in removing instrument debris and silver pins from the canal. Two files are inserted on the sides of the fragment and can be successfully removed. Effective in removing gutta-percha from canals.
S-file
Proposed by the Swedes and has an S-shape in cross-section. Manufactured by stretching. Tougher than a handstrom file. According to the manufacturers, it can perform both the function of a file with increased cutting efficiency and the function of a reamer. The tip of the instrument is 90* to form an effective canal shape in the area of physiological constriction.