Causes Symptoms Treatment Possible complications Prevention
Gum hyperplasia is a condition in which tissue begins to grow excessively. They hang over the teeth, forming false pockets, covering most of them, interfering with hygiene procedures. There are several terms in the literature that describe this condition: gingival overgrowth, hypertrophy, or hypertrophic gingivitis.
The main danger of tissue proliferation is that it promotes the proliferation of bacteria, causing serious diseases such as periodontitis.
Causes of gum hypertrophy
The main reason for tissue hypertrophy in the mouth is poor hygiene. Remains of food and decay products settle on the enamel of the teeth. They accumulate, causing inflammation of the mucous membrane, one of the manifestations of which is hyperplasia.
Other reasons include:
- Taking certain medications
A side effect of some anticonvulsants and immunosuppressants, and some heart medications, is gum overgrowth. However, you should not stop taking them or reduce the dosage if your gums have increased in size and began to bleed, without consulting a doctor.
- Genetic predisposition
Most people experience tissue growth during puberty. In most cases, after the end of hormonal changes, spontaneous reduction is observed. But in some patients, the gums do not shrink and may even increase in size. This phenomenon is characteristic of hereditary fibromatosis.
- General diseases
Leukemia almost always provokes tissue hypertrophy because they are saturated with dense masses of immature leukocytes. The gum turns into a hard surface on which wounds appear at the slightest pressure. This problem is also typical for sarcoidosis.
- Hormonal instability
Pregnancy and diseases of the endocrine system, such as diabetes or hypothyroidism, disrupt metabolic processes in tissues and lead to inadequate growth.
- Crowded teeth
If teeth creep onto each other and overlap surfaces, this interferes with proper cleaning of surfaces and contributes to the formation of microbial plaques. They, in turn, provoke inflammation.
Why is the tooth root exposed?
The reasons for the development of gum recession can be different, and in some cases there is a combination of several factors at the same time.
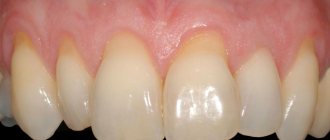
- aggressive brushing with a toothbrush - there is such a thing as brush gum recession. They occur when there is excessive pressure on the toothbrush when brushing, or when using a brush of unsuitable stiffness (hard). If you have increased tooth sensitivity when brushing, if your toothbrush becomes deformed over time (the villi move in different directions), you should consult a dentist about proper self-hygiene.
An example of brush gum recession on the upper jaw.
- incorrect position of the tooth in the dentition. Sometimes even a small bite problem can lead to gum pathology. This occurs because the tooth bears excess load when chewing or when teeth are closed, which over time leads to atrophy of the tissues of the supporting apparatus of the tooth, including the gums. In addition, excessive protrusion of the tooth root from the dentition also leads to gum atrophy.
Multiple gum recessions caused by malocclusion.
- caries - in cases of gingival caries, gum loss often occurs due to the presence of an infectious focus in the immediate vicinity of the gingival margin.
Gum recession caused by tooth decay in the immediate vicinity of the gum margin.
- Tartar can also cause root exposure.
- anatomical features - for example, a thin biotype of gingival tissue in combination with other factors can lead to recession. Shallow vestibule of the oral cavity (in which the muscles of the lips attach very close to the gingival margin and gradually “pull back” it, exposing the roots of the teeth). In addition, improper attachment of the lip and tongue frenulum can contribute to gum recession.
The frenulum of the lower lip, a thin tissue biotype, caused the exposure of the lower incisor root
- bad or professional habits - for example, chewing a pen/pencil, biting threads (for a seamstress), pinching metal objects with teeth, etc.
- lip or tongue piercing - constantly touching the gums and regularly injuring it, metal jewelry can lead to exposure of the roots of the teeth.
- periodontitis - with inflammatory diseases of the gums, the roots are often exposed due to the resorption of the tissues surrounding the tooth, including gum tissue. Unlike “normal” gum recession, periodontitis is treated differently and the prognosis for such recessions is somewhat worse (as a rule, it is impossible to restore the volume of lost gum by completely covering the exposed root).
Symptoms
The growth of the mucous membrane is a gradual process. There are 3 degrees:
- The gingival papillae increase in volume. The gingival contour is disrupted and hangs over the tooth.
- The growth progresses, the tissue covers up to half of the coronal part. Bleeding and discomfort when brushing teeth and eating food develop.
- The gum covers the tooth by two thirds, sometimes completely. Folds form in which microflora accumulate, causing inflammation.
The process is generalized
when the entire gum on the jaw suffers.
Focal
hyperplasia is located around one or more teeth.
The edematous form is characterized by the presence of plaque, there is a lot of it, it is quite soft, but covers the enamel with a thick layer. Gum pockets form. The papillae turn red and bleed when pressed.
Patients complain of itching, discomfort in the mouth while eating, and an unpleasant odor.
With fibrous gingival hyperplasia, patients are only concerned about the unusual appearance of the mucous membrane. There is usually no pain or bleeding, but there are complaints of an unpleasant odor.
How gums heal after plastic surgery
Depending on the nature of the operation, gum tissue is restored within a period of several days to several weeks. The doctor provides you with a list of recommendations that must be followed for a speedy recovery. You will also be prescribed anesthetics.
In the postoperative period, physical activity and hard, too hot or cold foods are contraindicated. We'll have to forget about spicy dishes for a while. Of course, standard daily hygiene procedures cannot be ignored. Until the tissues have completely healed, it is recommended to wear a special mouth guard.
Tissue swelling after plastic surgery persists for several days, but, as a rule, it subsides after the third day. If this does not happen, and in addition headaches, bleeding and other suspicious symptoms occur, you should contact your dentist as soon as possible.
Gum grafting is a surgical procedure with its share of risks. The most common ones include an allergic reaction to painkillers and relapse of gum recession. In the first case, you should warn the specialist in advance about a possible allergy; in the second, you will need to repeat the procedure after six months.
Treatment of gum hyperplasia
Any medical intervention is preceded by diagnosis. The clinic conducts a visual examination using dental instruments. An X-ray is taken and, in some cases, a tissue biopsy. Collect information about current diseases and what medications the patient is taking.
Gingival hypertrophy is differentiated from papillomas, granulomas, epulis (neoplasms) or swelling of the gums as a result of periodontitis.
The treatment plan is drawn up taking into account the degree, course and reasons for which the gums have grown.
For concomitant diseases, procedures should be agreed with the attending physician. Sometimes, simply changing the drug leads to a reduction in overgrown tissue.
Therapeutic methods
They are used mainly after replacing the drugs that caused hyperplasia.
- Decoctions and applications
from oak bark, chamomile, St. John's wort, calendula. Tannins in these plants narrow and strengthen the walls of blood vessels, reducing their permeability. As a result of combining with proteins, tannins form an insoluble film on the mucous membrane. This protects nerve endings from breakdown products and reduces pain.
- Installations in gum pockets.
Plant-based preparations are placed in pockets for 15-20 minutes, for up to 3 weeks.
- Dorsenval therapy.
After the elimination of the inflammatory process, physiotherapy is carried out to strengthen blood vessels.
The main treatment measure is professional teeth cleaning.
If the effect of the procedures is insignificant, as well as with fibrous hyperplasia, gingivectomy
.
Surgery
In cases where the gum has grown on the tooth so much that it covers half of the surface or more, the excess tissue is removed. For fibrosis, therapeutic treatment is not used at all; in other cases, the decision depends on the clinical picture.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia. Apply:
- Classic way
. The tissue is excised with a scalpel. The surface of the roots is polished with instruments, and the wound is treated with an antiseptic. Finally, a special bandage is applied (septopak, vokopak). - Laser
removal of overgrown gums . This is a minimally invasive operation, after which healing occurs much faster. During surgery, the vessels are sealed with a laser beam, which eliminates bleeding. At the same time, pathogenic flora is destroyed. Complications after such operations are extremely rare.
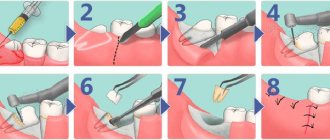
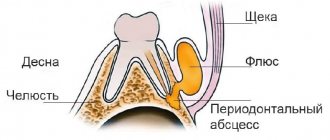
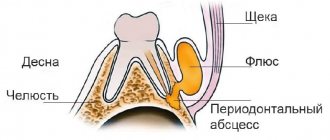
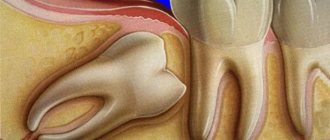
How is removal carried out?
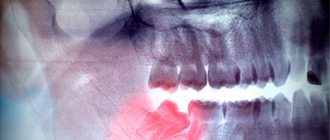
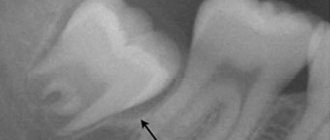
Before the operation, an x-ray is prescribed and a diagnosis is made based on laboratory tests. From the image, the doctor determines a certain type of growth, an abnormal location of the wisdom tooth. It also examines infectious and inflammatory foci in this area and prescribes preliminary treatment. The dental surgeon performs the operation under local anesthesia, which begins to take effect within 10 to 15 minutes. After exposure to anesthesia, he begins to excise the excess mucous membrane hanging over the tooth with a scalpel. Removing a wisdom tooth hood involves several main steps:
- Disinfection of gums and segments of the oral cavity;
- Excision of the “hood” with a scalpel;
- Rinsing the cavity with an antiseptic;
- Stopping bleeding and disinfection with iodoform turunda;
- The use of anti-inflammatory drugs, wound healing ointment.
Complications
Hyperplasia is dangerous because without treatment it provokes inflammatory processes in the periodontium: gingivitis and periodontitis. This leads to loosening of teeth and their loss.
Due to the fact that it is impossible to clean teeth well, caries often develops. Enamel demineralization occurs. Metabolic processes are disrupted.
Due to increased sensitivity, patients try not to chew on the side where the gum has grown. The chewing load is distributed unevenly, and the risk of losing teeth increases.
When to carry out the procedure and when to refrain from it
Indications for the procedure:
- strong pain;
- the appearance of putrid odor from the mouth;
- discharge of pus from the gums;
- swelling, bleeding and soreness of the gums;
- general weakness, elevated body temperature, dizziness and nausea (such symptoms are a sign of intoxication of the body).
Contraindications:
- mucosal infections (stomatitis, herpes, gingivitis, periodontitis);
- infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract (sore throat, pharyngitis, laryngitis, etc.);
- exacerbation of chronic diseases.
Prevention
Simple measures will help prevent gum overgrowth. Dentists recommend brushing your teeth with a soft brush, using dental floss or interdental brushes. Using a rinse aid reduces the number of bacteria settling on the enamel. But all these measures will not help if there is plaque on the teeth. Therefore, professional teeth cleaning in dentistry is where the prevention of hyperplasia begins.
Author of the article Voznyuk Vladimir Aleksandrovich Maxillofacial surgeon-implantologist of the highest category
Work experience: 28 years.
Gum plastic surgery during implantation
Gumplasty is performed when the root is exposed, after tooth implantation. Often the need for this operation arises when an implant is installed in place of a long-missing tooth. In this case, the correct gum line is not only aesthetic. It protects the implant from infection and the development of peri-implantitis, which without proper treatment can lead to the loss of the entire structure. In addition, it allows you to prevent further exposure of the roots, reduce tooth hypersensitivity, reduce the likelihood of root destruction and, of course, improve the aesthetics of your smile.
Indications for surgery
Formation of periodontal pockets
Lack of high-quality oral hygiene, improperly performed prosthetics or dental treatment often cause disruption of the periodontal ligaments and penetration of pathogenic microflora deep into the periodontium. As a result, deep periodontal pockets are formed, in which food debris accumulates and dental plaque settles.
The pathology is manifested by bleeding, soreness and swelling of the gums. In this case, gingivectomy is prescribed in advanced situations (moderate and severe periodontitis), when other treatment methods (professional hygiene, curettage, anti-inflammatory drug therapy) have not given a positive result.
During the procedure, necrotic tissue is removed in order to reduce periodontal pockets and prevent the spread of the infectious process to bone structures .
Gum hyperplasia
Pathological growth of the gum mucosa or hyperplasia occurs for various reasons: against the background of hormonal imbalance, chronic injury or inflammatory process. It is characterized by an increase in the volume of the gums, raising the gingival margin to the surface of the teeth, and filling the interdental spaces with gingival tissue.
Gingivectomy is prescribed if conservative treatment aimed at eliminating the causes of the disease is unsuccessful. Allows you to remove excess tissue and restore the aesthetics of your smile.
Methods of conducting
The choice of technique depends on the severity of the disease
- Partial The least traumatic option involves excision of only the affected part of the periodontal tissue.
- Simple The entire volume of overgrown mucous membrane is removed, leaving only a 1 mm margin from the gum pocket.
- Radical Performed in severe cases, not only necrotic soft tissue is removed, but also the affected part of the bone.
Any surgical intervention on the gums should be carried out extremely carefully, with minimal tissue trauma. For this purpose, our Center uses a dental microscope, which increases visibility, increases the accuracy of manipulations, allows you to make neat cuts with special micro-instruments, and use the finest threads to apply sutures that do not injure the mucous membranes. All this ensures quick recovery, shortens rehabilitation time, and prevents possible complications.
What is gum gingivectomy
Gingivectomy is a surgical operation in dentistry aimed at excision of overgrown gum tissue due to the formation of periodontal pockets and chronic inflammation. Provides for reducing the volume of gingival pockets by removing affected areas of the mucosa, forming an aesthetic gingival contour.
After the procedure, the natural process of tissue regeneration begins. In combination with other measures carried out as part of the treatment of gum diseases, it allows you to stop the source of infection and eliminate inflammation.
Gum treatment should be carried out by a specialized specialist with deep knowledge in the field of periodontology. Only an experienced doctor can correctly make a diagnosis, determine the form and severity of periodontal damage, identify concomitant pathologies, and on the basis of this choose an effective protocol depending on the specific clinical situation.
Otherwise, you can make many irreversible mistakes - deterioration of the condition, progression of the disease in a complicated form with suppuration, loss of surrounding bone tissue, and as a result - loosening and loss of teeth.
In our Center, therapeutic and surgical treatment of gums is carried out by an experienced, qualified periodontist surgeon who has the necessary knowledge in the occurrence and course of gum diseases. Using theoretical knowledge, practical experience and his own developments, he determines the tactics and strategy of treatment measures, assessing their effectiveness in each specific case.
Medvedeva Tatyana Alexandrovna
Dentist-periodontist, 6 years of experience
Specialist in the diagnosis and treatment of gum diseases. Conservative, surgical, regenerative treatment. Microsurgical operations without pain under sedation.
More about the doctor