June 14, 2021
Normally, the size and shape of the jaws may vary slightly in accordance with the characteristics of the shape and size of the face of each individual person. These small differences contain the uniqueness of each face, its unique personality and attractiveness. However, in some cases, when there is a sharp deviation of these values from the average parameters that conventionally correspond to the rest of the human face, we can talk about the presence of pathology. Such pathologies include anomalies in the size of the jaws, which we will discuss in detail in this article.
Causes of development of jaw size abnormalities. Definition of disease
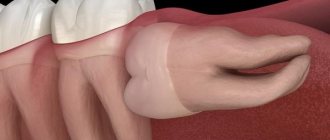
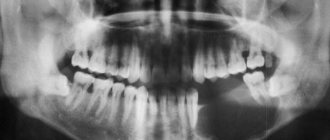
Anomalies in the size of the jaws are expressed in defects in the structure of the jaw bone. These are functional and aesthetic defects affecting the upper or lower jaw . In mild forms of the pathology, the defect does not cause noticeable discomfort. However, serious size anomalies can noticeably distort facial proportions and cause problems with speech, breathing, chewing and swallowing food. Violations in the size of the jaws, their incorrect position in relation to the skull and, accordingly, uneven load on the joints, muscles and teeth often provoke the development of certain dental diseases and serious pathologies of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ).
Anomalies in jaw size are usually classified into the following types::
- Macrognathia (pathology is characterized by an unnaturally large jaw size). Macrognathia can be lower, upper or combined.
- Micrognathia (characterized by a reduced jaw size, its insufficient development). Micrognathia can also be lower, upper, or combined.
Various developmental disorders of the maxillofacial region, including anomalies of shape and/or size, are unfortunately quite common and significantly affect a person’s quality of life. The development of macrognathia or micrognathia can be caused by many factors, but genetics significantly predominates among them. Another common cause of such deformities may be environmental factors , a combination of genetic and environmental factors, or severe trauma .
Most often, jaw size anomalies are detected from birth, since in most cases micro- or macrognathia is a manifestation of hereditary diseases or a consequence of the harmful effects of adverse factors on the fetus during pregnancy.
! The main reasons for the development of dentofacial deformities include:
- Specific inheritance by a child of the anatomy of the dental system. The baby inherits from its parents not only external characteristics and body composition, but also the structure and size of the jaws and teeth. In some cases, teeth (their size, shape) can be inherited from the father, and the structure of the jaw bones from the mother, or vice versa. This can provoke developmental disorders and interfere with the formation of harmonious relationships between the jaws and dentition.
- Poor nutrition of a pregnant woman, neglect of a healthy lifestyle before and during pregnancy (smoking, alcohol), infectious diseases , taking certain medications.
- Unfavorable environmental conditions (a woman carrying a child or a newborn and a nursing mother is in an unfavorable environment (ultraviolet irradiation, increased radiation, mold spores, excess exhaust gases, the content of harmful elements and heavy metals in the air and water)
- Potentially dangerous diseases suffered by a child in infancy that can provoke deviations in the process of subsequent bone formation (rickets, osteoporosis, severe infectious or endocrine diseases, osteomyelitis).
- Disturbances in the infant's sucking process (unnatural latching on the breast, use of a pacifier of improper non-anatomical shape, excessively prolonged sucking of the pacifier or fingers, etc. can lead to pathological inclination of the dentition and improper development of the jaws); untreated diseases of baby teeth in a child (early loss of molars (chewing teeth) can cause a decrease in the activity of growth zones and, as a result, cause underdevelopment of the jaw bones)).
- Pathologies of the otorhinolaryngological system (chronic diseases of the nasopharynx, various rhinitis, sinusitis, etc. or abnormal structure of the nasal septum often lead to “mouth breathing” - a person constantly breathes exclusively through the mouth, which affects the tone of the orbicularis oris muscle, which in turn negatively affects growth upper jaw)
- Serious injuries to the head and facial area , consequences of incorrect surgical intervention in the maxillofacial area, etc.
Definition
The concept of “small lower jaw” in orthodontics is not clearly defined.
This diagnosis is classified into several types, differing in the clinical picture of the anomaly.
Micrognathia
Mandibular micrognathia is a defective or too long-term development of an organ that goes beyond the norm.
The defect can affect both the entire jaw and its individual areas, for example, affecting only one lateral part.
Prognathia
It is considered a phenomenon directly opposite to the case described above.
The organ corresponds to the normal parameters, but with the pronounced size of the upper jaw, it seems that it is too small.
Experts often call this disease false prognathia.
Prevention of the development of micrognathia and macrognathia
Let's talk about possible measures to prevent the development of maxillofacial anomalies. Since the influence of negative factors on the health of the child’s future dental system is especially active during the mother’s pregnancy and in the first months of the baby’s life, preventive measures must be followed even before the birth of the child and in the first year of life . To promptly prevent the development of dentofacial deformities, you should adhere to the following:
- carefully monitor the course of pregnancy, try, if possible, to avoid the risk of infectious diseases of the expectant mother;
- try to avoid long stays of a pregnant woman, mother and baby in an unfavorable ecological environment;
- eat a nutritious and varied diet and lead a healthy lifestyle during pregnancy;
- give up bad habits in the process of planning pregnancy, during pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- adhere to proper feeding of the baby (use an anatomically correct nipple and discard it in a timely manner; when artificially feeding, make sure that the bottle with the mixture does not put pressure on the alveolar processes);
- if possible, stop bad habits (sucking and biting fingers and cheeks, tongue, various objects) that provoke deformations of the dentition, disturbances in the growth of the jaw bones;
- observe the timing and sequence of teething, monitor the development of speech;
- promptly identify and eliminate congenital pathologies in the form of a shortened frenulum, cleft lip, palate, etc.;
- wean the child from sucking fingers, objects, etc.;
- conduct myogymnastics with the child to prevent disorders of respiratory, swallowing, and speech functions; ensure that the child does not breathe through his mouth;
- timely treatment of baby teeth and periodontal diseases;
- adhere to preventive measures and promptly treat common diseases (rickets, diseases of the ENT organs, endocrine pathologies, etc.)
Thus, in the prevention and timely identification of risk factors that contribute to the occurrence of various dental anomalies, the most important thing is the active and careful participation of parents at all stages of the child’s growth and development.
How is it diagnosed?
Pruzansky classified mandibular hypoplasia as grade 1, 2, or even 3. Class 1 refers to the small size of the lower jaw, regardless of the average configuration. Some patients were diagnosed with congenital hypoplasia of the mandible, devoid of any recognized syndrome. Diagnosis of the lower jaw includes:
- Hypoplasia of the lower jaw;
- Hyperplasia of the lower jaw;
- Hypoplasia of the lower jaw with dentoalveolar hyperplasia;
- Hyperplasia of the lower jaw with dentoalveolar hyperplasia;
- Dentoalveolar hyperplasia;
- Neonatal enamel hypoplasia associated with premature birth or possibly early febrile illness.
Significant signs are also rib rupture defects, which can contribute to rib fracture. This jaw hypoplasia occurs in children with a special focus on the respiratory tract. Mandibular hypoplasia can be classified according to the Pruzansky classification system developed in 1969. The underlying pathology is actually mandibular hypoplasia, which throughout fetal life creates an inability for the tongue to migrate caudally, causing abnormal tongue positioning and obstruction of regular palate growth.
Surgery. Forecast
The doctor assesses the need for correction of macrognathia and micrognathia based on detailed diagnostic data, medical indications, and the wishes of the patient himself, taking into account his state of health and emotional state.
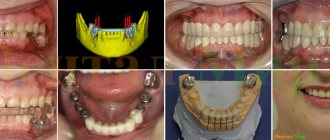
The solution to most problems associated with unexpressed disorders can consist of conservative treatment , the use of various orthodontic systems. In case of pronounced skeletal disorders, in cases where there are also concomitant significant functional and aesthetic disorders, it is advisable to resort to combined orthodontic-surgical treatment , which will be aimed comprehensively at simultaneously eliminating both aesthetic and functional disorders. During complex treatment, including orthodontic preparation and subsequent orthognathic surgery, extensive joint work is carried out between the orthodontist and the surgeon, aimed at correcting the bite, changing the shape and position of the bone structures of the face.
Orthognathic surgery requires high-quality orthodontic preparation (on which the correct closure of the dentition after surgery and the final predicted result of the entire combined treatment depend) and detailed planning. Orthognathic surgery is performed under anesthesia through intraoral access. The surgeon moves the jaws, changes their shape if necessary, gives the jaws the correct position and secures them with special fixing elements. Upon completion of the rehabilitation period and the end of the orthodontic treatment stage, the final result no longer requires any additional correction and remains stable throughout life.
Thus, once having corrected the functional and aesthetic disorders of the maxillofacial area and restored the harmony of facial features at the level of not only the dentition, but also the jaw bones, a person forever forgets about the problems that previously bothered him.
Prices
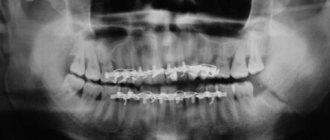
The approximate cost of treating a defect of abnormal development of the lower jaw is given in the table:
| Character of the bite | Correction method | Average price (in rubles) |
| Lactic | Sanitation of the oral cavity | From 3 500 |
| Lactic | Orthopedic therapy | From 30 000 |
| Lactic | Fissure grinding | From 11 000 |
| Lactic | Operation | From 15 000 |
| Constant | Bone grafting | From 19 000 |
| Constant | Bone grafting pole liposculpture | From 50 000 |
| Constant | Endoprosthetics | From 40 000 |
| Constant | Lipofilign | From 35 000 |
HAAS device
The most common and convenient to use for both parents and doctors is the non-removable HAAS device. The device is fixed to the temporary teeth on the upper jaw by an orthodontist; it is absolutely invisible to others, but clearly and quickly performs its task. The most successful and appropriate time to work on it is when the central incisors are replaced with permanent ones, i.e. at the age of 7-8 years. The expansion of the upper jaw is carried out through the work of a screw, which the parents themselves tighten based on the recommendations of the attending physician.
Possible consequences
In addition to the aesthetic aspect, underdevelopment of the lower jaw can cause serious harm to a person’s health. The following problems may occur:
- malocclusion;
- disruption of the auditory and respiratory organs;
- persistent problems with chewing and swallowing, which ultimately leads to problems in the gastrointestinal tract;
- the absence of some teeth and deformation of existing ones;
- weakening of the immune system in general, and, as a result, frequent illnesses.
For adults, the treatment process may take longer. If microgenia is congenital, then it is necessary to contact a professional as soon as possible.
A small lower jaw is a cosmetic defect or a serious pathology
What malocclusions are encountered in dental practice? And a small lower jaw is not uncommon.
Such a defect is not only an aesthetic problem, but also serious risks for the health of the entire body.
What prevents the normal development of bone tissue, and what can cause this disease? Let's try to sort out all these questions today.
The content of the article:
Signs
The main sign indicating the presence of this disease is the visual observability of an anomaly - such a defect is visible to the naked eye, and you do not need to be a specialist in orthodontics to determine such a deviation in a person.
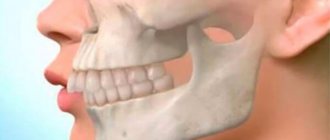
In addition, pathology deforms the natural proportions of the maxillofacial apparatus. The chin becomes sharp and slightly raised upward. Doctors even defined this phenomenon as “bird beard.”
It is important to understand that this is not just a cosmetic defect; micrognathia threatens its “owner” with the development of the pathology of tongue retraction, which is considered a serious disease.
The anomaly causes frequent uncontrollable attacks of suffocation and poses a serious threat to the patient's life.
The disease is often diagnosed based on this characteristic feature - excessive retraction of the chin leads to wrinkling of the skin in its area, and the horizontal fold between the chin and lip is smoothed out.
In addition, underdevelopment of the lower jaw often goes hand in hand with chromosomal mutation processes, which leads to Patau syndrome.
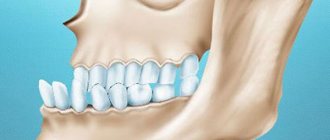
A clear sign indicating the presence of this defect is also the incorrect location of individual fragments of the dentition.
In the case when some organs are missing, neighboring teeth change the direction of growth, trying to spontaneously fill the free space.
Symptoms of microgenia
Dentists consider the following signs of microgenia of the lower jaw:
- Recessed lower lip;
- Formed cleft palate;
- Glossoptosis (underdeveloped tongue, often recessed);
- Difficulty in breathing;
- Deformation of the lower row of teeth;
- The lower teeth erupt in the wrong places, get out of the general line (this happens against the background of a well-formed upper row of teeth);
- With a pronounced anomaly of the lower jaw, a violation of facial proportions is observed. Symmetry will be preserved if the pathology is mild;
- Limited mobility of the lower jaw (this causes problems with fully chewing solid foods and biting).