Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
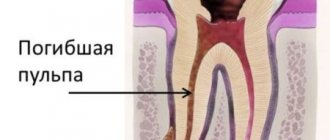
Periodontium is connective tissue located in the gap-like space between the cementum of the tooth root and the alveolar plate. Its inflammation (periodontitis) is one of the most severe and dangerous dental diseases. It often occurs as a result of deep caries of one or more teeth - in this case, the infection most often penetrates the connective tissue through holes in the roots. Other routes of infection are also possible - for example, through the blood in the presence of other inflammatory processes in the body, through gum tissue in case of periodontitis, etc. In addition, periodontitis can occur as a result of a reaction to the effects of certain medications during previous dental treatment. Dental injuries can also serve as a starting point for the development of an inflammatory response.
The periodontium contains a large number of blood vessels and nerve endings, and also performs the most important functions, creating support for the teeth and serving as a shock absorber during chewing. Therefore, its inflammation in most cases is accompanied not only by severe pain, but also by the danger of losing teeth. Periodontitis can become chronic with periodic exacerbations. The symptoms and treatment tactics of periodontitis largely depend on the form of the disease:
- Acute periodontitis
Obviously expressed inflammatory symptoms: swelling and redness of the gums, acute pain, swelling of the tissues in the area of the affected tooth. Occurs for the first time. As a rule, the acute form is not accompanied by destruction of bone tissue in the upper part of the root. - Chronic
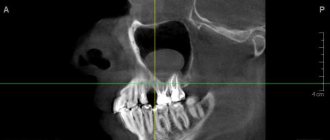
May be asymptomatic or with minor manifestations - periodically occurring mild aching pain, soreness of the teeth or gums when biting. When favorable conditions for microorganisms arise, an exacerbation occurs, during which the symptoms become more pronounced. Also, in the chronic course of periodontitis, an x-ray usually reveals the presence of an abscess (accumulation of pus) in the area of the root apex. In the photographs, the abscess looks like a small clearing. A long course of the disease can also lead to the destruction of bone tissue in close proximity to the source of the inflammatory process.
Indications for treatment of periodontitis
There are two main ways to treat periodontitis: conservative and surgical. Each of them has its own indications and contraindications.
According to modern dental standards, a doctor should give preference to conservative methods. They are indicated for both acute and chronic periodontitis, including the appearance of cysts and granulomas, loose teeth, and increasing inflammation.
However, orthograde treatment cannot be used in all cases. Indications for surgical intervention are:
- obstruction of the tooth root canals;
- the presence of a stump tab or pin that cannot be removed without damaging the roots;
- multiple perihilar cysts or cysts growing into the maxillary sinus;
- wide affected area (over 10 millimeters);
- perforation of the tooth cavity or root wall;
- ineffectiveness of conservative treatment methods.
Important!
When we talk about periodontitis, we often mean apical (also known as periapical or apical) periodontitis - that is, inflammation at the apex of the tooth root. The cause of this disease is endodontic problems. Another type of periodontitis, marginal, affects the gums in the cervical area of the tooth, but it already belongs to the field of periodontology. This material is devoted to the treatment of apical periodontitis only.
Historical reference
Periodontitis, as a concept, did not previously exist, but, of course, this disease has worried humanity, and its history dates back more than one millennium. Thus, in the scientific literature there has been a discussion for a very long time about the methods of dental treatment in Ancient Egypt. The basis for the debate is a number of artifacts, which indicate the predominance of conservative treatment methods in dentistry of that time, and no traces of surgical intervention were identified during the study of the mummies of the pharaohs1. At the same time, a study of mummies showed that the ancient Egyptians suffered from severe damage to the teeth and periosteum, from which we can conclude that periodontitis “flourished” among the first persons of Ancient Egypt, along with other dental diseases. Egyptologist M.A. Raffer wrote that in Egyptian cemeteries it was not uncommon to find diseased teeth that had almost fallen out of inflamed sockets, or carious teeth that were the cause of extensive diseases of the jaws, which could have been avoided and/or cured by performing simple operations 1.
In general, the existence of these dental artifacts inexorably indicates that such a pathology of the dental system as periodontitis has existed for more than one century. But in those days, the symptoms by which today medical science classifies and treats this disease were symptoms of simply a “sick tooth.”
More than a century and a half later, in 1889, a Swiss mechanic and formerly an experienced watchmaker, August Maillefer, who was seriously interested in dentistry, together with his three sons founded a company that was engaged in the creation of high-precision mechanical instruments and gave it his family name - Maillefer. Maillefer used his extensive experience working with watch movements, characterized by unsurpassed “Swiss” precision, to expand the capabilities of dentistry.
Perhaps the first serious treatise, which described about 130 dental diseases caused by various reasons, was the work “The Dentist-Surgeon, or Treatise on Teeth” by P. Fauchard, published in 1728. He also became the author of a number of new filling materials and dental instruments 2. As if anticipating the role endodontic instruments would play in the future, the Maillefer company was the first in the world to invent trimers, pulp extractors, files - tools for working in dental canals. Since 1995, this company became part of the DENTSPLY concern, later called DENTSPLY IMPLANTS, and today it is DENTSPLY SIRONA. And it was the developments of August Maillefer’s company that became the “first signs” of modern endodontic instruments, without which effective, efficient and reliable treatment of periodontitis is impossible today.
Treatment methods for dental periodontitis
| Conservative treatment | Surgery |
Therapeutic:
Physiotherapeutic:
Conservative treatment of periodontitis is accompanied by the use of antibiotics. | Surgical treatment:
|
Important!
The probability of successful conservative treatment of periodontitis is 70 - 90%
Inspection and primary treatment of dental canal cavities
Treatment of periodontitis begins with a thorough examination of the patient by a dentist, after which the specialist prescribes an x-ray for the patient. The image will help make the diagnosis as accurately as possible, as well as study in detail the number of dental canals, their length and shape. Next, an anesthetic injection is made into the area of the diseased tooth, without which treatment of periodontitis can be a very painful and uncomfortable process for the patient.
After the drug takes effect, the doctor will perform the following manipulations:
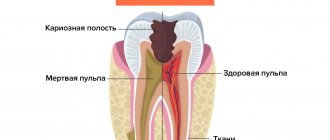
- It will remove from the diseased dental unit all tissues damaged by the carious process, as well as some healthy enamel and dentin. This is necessary to gain access to the mouths of the dental canals;
- If the tooth has not been treated before, the doctor will remove the inflamed pulp from it. If treatment of the unit with the removal of nerves has previously been carried out, the tooth canals are unfilled;
- Expand the tooth canals manually, using specialized instruments for this purpose. After expansion, the tooth canals are thoroughly washed with an antibacterial solution;
- Place a medicine with enhanced antiseptic action into the channels.
After applying the antiseptic to the dental unit, a temporary filling is installed, and the specialist thoroughly advises the patient on oral care, prescribes anti-inflammatory drugs and medications that reduce the risk of allergic reactions. The next time you will need to visit the doctor approximately three days after completing the first stage of periodontitis treatment.
Stages of periodontitis treatment
The number of visits to the clinic for the treatment of periodontitis depends on the stage of the disease (acute periodontitis, chronic, chronic in the acute stage) and the chosen technique. Often, therapy is carried out in several stages and requires at least 2 - 3 visits to the attending physician, since it is not recommended to install a permanent filling until the inflammation is completely removed.
- Preparation for treatment: diagnosis using an x-ray, anesthesia injection.
- Drilling a tooth to access canals, removing a nerve, or removing an old filling.
- If necessary, expand channels.
- Antiseptic treatment of canals, application of medications, physiotherapeutic procedures.
- Installation of a temporary filling.
- Removal of the temporary filling, antiseptic treatment of the canals (this stage is repeated until the source of inflammation is completely eliminated; sometimes this may take several months).
- Installation of a permanent filling, control x-ray.
In parallel, the patient is prescribed antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy, as well as home rinses with disinfectant solutions.
Treatment quality criterion
High-quality, effective treatment of periodontitis requires pinpoint precision when working in tooth canals that have a complex shape and individual anatomical features. Obturation (sealing) of canals is based on the principle of “three pillars”: the canal must be sealed to its entire length, along all micro-branches, without pores and air cavities. This requires high qualifications and extensive experience of the attending physician, as well as the use of modern equipment - endomotors, apex locators, files, dental microscope. Modern endodontic treatment is a high-tech medical procedure and is based on new medical, technological and ergonomic principles, which obliges clinics to be equipped with modern equipment, and doctors to regularly improve their level of professional competence.
Features of the treatment of periodontitis with fistula
Odontogenic fistula is one of the complications of periodontitis, mainly granulating. It consists of holes in the mucous membrane, which are formed due to the proliferation of granulations and destruction of the tissues surrounding the tooth. In severe cases, a fistula can appear not only in the gum, but also in the cheek, and even on the skin of the face. Purulent contents are released through the hole, which appears due to the inflammatory process in the periodontium.
On the one hand, the formation of a fistula facilitates the course of the disease, since inflammatory products are eliminated through it (which means that the patient most likely will not suffer from severe pain). On the other hand, non-intervention over time can lead to tooth loss.
You can get rid of a fistula only by eliminating its cause - damage to periodontal tissue. Treatment follows a standard scheme: mechanical treatment of the canals, disinfection and thorough filling. Due to the outflow of pus through the fistulous tract, treatment is most often successful and takes less time. After creating suitable conditions, the fistula goes away on its own, but in severe cases, surgical removal of overgrown granulations may be necessary.
Signs
Clinical manifestations of periodontal inflammation depend on the form of the disease.
In the acute course, the symptoms are pronounced, often accompanied by the formation of a painful abscess on the gum, gumboil (deeply located abscess with intense swelling of the soft tissues of the gums and face), increased body temperature, etc. Acute inflammation can occur in two forms:
- Serous periodontitis occurs without the formation of a purulent cavity. Accompanied by constant aching pain that does not intensify when touching a tooth or biting food.
- Purulent periodontitis is accompanied by the formation of an abscess. Accompanied by sharp, bursting or throbbing pain, the intensity of which may vary. Flux is noticeable on the gum near the diseased tooth, and the soft tissues of the face on the affected side swell. The mobility of the tooth is increased, the pain intensifies when biting and touching the tooth.
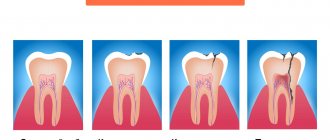
In the chronic form, periodontitis is not as severe as acute periodontitis. There are three forms of the disease:
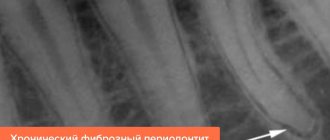
- Fibrous , the symptoms of which are sluggish inflammation without the formation of an abscess and fistulas. Pain with this form rarely occurs. An external sign is a change in the color of the enamel to gray, a change in its transparency. Signs of inflammation are visible only on x-rays.
- Granulomatous , the symptoms of which are periodic formation of an abscess. As it “ripens,” a duct opens on the gum, from which purulent contents pour out. Such ducts can form permanent non-healing fistulas. On x-rays, this form of periodontitis looks like a lesion with a diameter of up to 5 mm at the root apex.
- Granulating , the symptoms of which are chronic toothache, aggravated by biting hard, hot or cold food with a sore tooth. The gums near the tooth are constantly swollen and hyperemic. The opening of the fistula can open both on the oral mucosa and on the skin of the face.
Symptoms of any form of periodontitis tend to subside when the purulent cavity is cleared of its contents.
It is important to know! The main difference between periodontitis and pulpitis is the nature of the pain. With pulpitis, it is acute, painful, reminiscent of electric discharges, intensifying when the diseased tooth comes into contact with solid food particles, hot or cold air.
Treatment of chronic forms of periodontitis
There are three types of chronic periodontitis: fibrous, granulating and granulomatous.
- In fibrous periodontitis, the tissues surrounding the apex of the tooth are replaced by fibrous tissue. The patient usually does not feel pain, and the disease can only be determined by an x-ray.
- Granulating periodontitis is characterized by the growth of granulation tissue: the process of bone resorption (resorption) starts, fistulous tracts are formed, through which inflammatory products are separated. As the granulations expand, the patient begins to experience periodic aching pain.
- Granulomatous periodontitis is accompanied by the appearance of a granuloma - a neoplasm at the root apex. It is a chamber of connective tissue filled with granulations. If the disease is not treated, the growth of granuloma can even lead to a jaw fracture.
Treatment of chronic periodontitis is often carried out using conservative treatment methods. According to modern standards, doctors, as a rule, do not carry out separate treatment for granulomas, cysts and fistula tracts: if the canals are disinfected and properly sealed, the neoplasms will disappear on their own. In advanced cases, surgical intervention is permissible.
Complications
Periodontitis is dangerous due to rapidly developing serious complications, so it is extremely important to immediately consult a dentist at the first symptoms. The initial form of acute periodontitis very quickly, within a few days, turns into a purulent form, and then into an abscess. At the stage of chronic periodontitis, fistula tracts are formed, which cause suffering to the patient and significantly increase the treatment period.
In addition, we must not forget that periodontitis destroys the bone tissue surrounding the tooth, and is also a chronic odontogenic inflammatory focus, therefore it significantly reduces the patient’s immune status and contributes to the complication of various somatic diseases. In addition, Swedish scientists from Orebro University recently discovered and proved the effect of periodontitis on the cardiovascular system. The reason for this influence is the activity of the bacterium Porphyromonas gingivalis, which is a common pathogen of periodontitis. This bacterium disrupts the functioning of the gene responsible for controlling inflammation in the coronary arteries, contributing to the occurrence of atherosclerosis and heart attacks 8.
Features of the treatment of periodontitis in the acute stage
Exacerbation of periodontitis goes through two phases: intoxication and exudation (appearance of discharge). As the disease progresses, the patient first experiences aching and episodic pain, and then constant throbbing and tearing pain, so treatment cannot be delayed.
Acute periodontitis can be serous or purulent. In the second case, purulent exudate accumulates in the apical part of the tooth root, and the main task for the doctor is to remove it. Sometimes this is enough to clean the tooth cavity and treat the canals, but in severe cases it may be necessary to cut the periosteum for drainage.
Permanent canal filling
Permanent canal filling in the treatment of periodontitis is performed during the third visit to the dental office. Before proceeding with any manipulations, the specialist sends the patient for a control x-ray. The image will help determine the effectiveness of periodontitis treatment. If the percentage of bone tissue destruction has decreased significantly, permanent filling of the canals is performed.
The procedure begins with the removal of the temporary filling from the crown of the tooth, and then the canals are freed from the previously placed composite. The doctor will carry out an antiseptic rinse and then fill them to the apical part of the root with a composite. Upon completion of the work, the patient is given another x-ray to monitor the quality of the filling performed. Gutta-percha must be tightly packed into the canals to the very apex of the root, otherwise there is a high risk of relapse of periodontitis.
A couple of days later, the patient comes to the doctor for the fourth time and during this visit the crown part of the tooth is restored with a permanent filling to restore its aesthetics and functionality.
Treatment of periodontitis at home
Periodontitis cannot be cured at home, since the disease is caused by bacteria that colonize the dental canals. The only way to get rid of them is to carry out antiseptic treatment and sealing of the canals, and this can only be done by a doctor, but by waiting for a visit to the clinic, you can alleviate the symptoms and reduce pain.
Disinfectants that do not irritate the mucous membranes can be used for rinsing 4 - 5 times a day. Doctors also recommend rinsing with a solution of salt and soda, including after treatment, to relieve swelling and reduce inflammation. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are suitable for pain relief. All this will help relieve symptoms, but is not a cure.
You may experience pain after periodontitis treatment. Normally, they last 3–5 days and gradually fade away. If the pain does not subside or returns with renewed vigor, re-therapy is necessary.
Price
The cost of periodontitis treatment is always strictly individual and consists of a combination of factors. These include diagnostics at the initial and intermediate stages of treatment, the diagnosis made and the algorithm of treatment measures adopted on its basis, the number of visits, drugs, equipment and technologies used in treatment, the work of specialized specialists if necessary, the level of qualifications of the doctor.
Periodontitis is a very serious disease of the teeth and the dental system as a whole. Failure to consult a doctor in a timely manner and attempts at self-medication can lead to serious complications, including those that can threaten your life. At the first appearance of symptoms, you must urgently visit the dental clinic! Be prepared for long-term treatment, which involves multiple visits to the doctor, since the treatment of periodontitis consists of several stages, each of which cannot be started without diagnostically proven effectiveness of the previous one. Only this approach to treatment, combined with the professionalism of the doctor and the patient’s strict, vigilant attitude to all prescriptions and recommendations, is a guarantee of high-quality treatment and reliable protection against relapse for several years.
According to antiplagiat.ru, the uniqueness of the text as of October 16, 2018 is 99%.
Key words, tags: caries, pulpitis, bone tissue destruction, cyst, odontogenic cyst, flux, OPTG image, tooth-preserving operations, resection of the apex of the tooth root, cystectomy, root amputation, dental microscope, preservation, tooth extraction .
1 I. Zimin “From the history of dentistry.” 2 “Teeth and dentistry. Essays on history” / K.A. Pashkov. – M.: Veche, 2014. – 240 p.: ill. 3 Britova, A. A. Endodontics. Diseases of the dental pulp and periapical tissues: textbook. manual, 3rd ed., rev. and additional / A. A. Britova; NovSU named after. Yaroslav the Wise. – Veliky Novgorod, 2016. – 171 p. 4 https://elestom.ru/recommends INTERNATIONAL CLASSIFICATION OF DENTAL DISEASES ICD-C-3 BASED ON ICD-10. 5 https://elestom.ru/recommends INTERNATIONAL CLASSIFICATION OF DENTAL DISEASES ICD-C-3 BASED ON ICD-10. 6 https://mkb-10.com 7 Kleshchenko A. V. Improving the technique of unfilling root canals of teeth obturated with gutta-percha: Dissertation of a candidate of medical sciences: 01/14/14 / Kleshchenko Alexander Viktorovich; (Place of defense: Moscow State Medical and Dental University). - Moscow, 2011 - 93 p. 8 Report of the American Society of Microbiology based on the work. Author: Tobjörn Bengtson, presented by the Faculty of Clinical Medicine, School of Health Sciences, Örebro University, Sweden. * NOS is an abbreviation for “not otherwise specified,” meaning “unspecified” or “unspecified.”
Answers to popular questions
How long can it take to treat periodontitis?
Treatment of inflammation of periodontal tissues is a very long process. On average, 3–5 visits to the dentist may be needed (depending on the clinical case). The entire process sometimes takes several months.
Why is periodontitis dangerous?
The danger of the disease lies in its consequences. If inflammation is not treated, the following may develop: 1. periapical abscess; 2. diffuse purulent inflammation of the subcutaneous tissue (phlegmon); 3. fistula in the gum; 4. destruction of the jaw bones (osteomyelitis); 5. blood poisoning; 6. unit falling out of the hole, etc.
How can I tell if I have chronic periodontitis?
The following alarming signs may indicate the chronicity of the process: • wave-like appearance of aching pain; • the appearance of a fistula opening on the gum with purulent discharge; • increasing the sensitivity of the segment when chewing. At the first suspicion of the presence of a pathology, consult a doctor and undergo diagnostics.
Temporary and permanent root canal filling
After the operation to remove pus for acute periodontitis, 3-4 days should pass, and then the patient visits the clinic again. During the second appointment, the doctor performs the following manipulations:
1. Thoroughly rinses the canal cavities with antibacterial solutions, and then puts an antiseptic in them.
2. Places a temporary filling on the tooth.
The patient is sent home, but is warned: at the slightest sign of pain, he should immediately seek professional dental care.
Permanent filling of the canals is carried out during the third visit. The treatment procedure can be carried out in the absence of complaints from the patient about any discomfort, as well as in the complete absence of pus in the canal cavities. The canals are filled with gutta-percha composite to the upper root zone. Restoration of the aesthetics and functionality of the tooth is done on a subsequent visit, and at this point the course of periodontitis treatment is considered complete.