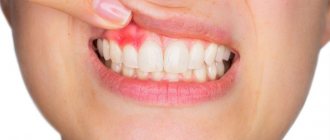
Local swelling of the root zone, compactions of various sizes, throbbing pain, sensitivity to temperature when eating, enlarged lymph nodes may indicate an acute inflammatory process of infectious etiology. In dentistry, there are several types of diseases, among them periapical abscess. It can be caused by advanced caries, chipping of an element of the dental system, overheating of the pulp due to tooth preparation and various pathologies. This can also happen due to poor-quality root canal treatment.
A periapical tooth abscess is an accumulation of pus between the molar and the gums. Purulent exudate can accumulate both in the inner and outer surfaces of the alveolar process of the lower or upper jaw. It most often begins in a tooth with a non-viable pulp, when the nerve dies, causing infection and progressive inflammation. The infection may gradually spread to surrounding tissue. Clinical symptoms are in many ways similar to acute periodontitis. The patient experiences increased sensitivity, acute pain, the mucous membrane may have swelling, there is active hyperemia, and overflow of blood in the vessels of the circulatory system.
Symptoms
- Intense dull throbbing pain.
- Discomfort when chewing food.
- Swelling in this area.
- Painful sensations when swallowing.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Unpleasant sensations when opening the mouth.
- Change in molar color.
Other symptoms also include malaise, fever, weakness, and bleeding. It should be noted that in some cases the inflammatory process can be practically asymptomatic; activation can occur periodically, for example in the case of hypothermia. In this case, immediate assistance from a dentist is required so that he can quickly and accurately diagnose and establish a treatment regimen for effective recovery.
Symptoms of a tooth abscess
The inflammatory process in the tissues of the tooth and gums occurs in stages and is accompanied by different symptoms:
- At the beginning of development, discomfort appears, slight swelling, gum bleeding is possible when brushing teeth, and pain is sensitive when pressed.
- In later stages, swelling increases, and a reaction to hot and cold foods appears. There is prolonged pain and an unpleasant odor. In addition to local changes, the abscess is accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes in the neck, increased body temperature, and general malaise.
A bitter aftertaste is noticeable in the mouth, and a change in the shade of the tooth body is possible. It is important to remember: the symptoms of gum abscess can manifest themselves in different ways - everyone has their own pain sensitivity threshold and perceives signals subjectively. Therefore, you should not wait for acute conditions; a reasonable step is to visit a dental clinic at the first incomprehensible sensation.
Causes of abscess
Complications associated with the inflammatory-destructive process can occur due to the following reasons:
- Poor quality endodontic treatment.
- Carious formations.
- Injuries to elements of the dentition.
- Unqualified prosthetics.
- Infectious diseases in the maxillofacial area, such as sinusitis.
Treatment of a periapical abscess without a fistula may be required in case of violation of the endodontic therapy protocol or incomplete obturation of the canal system. Provoking factors can be serious infectious diseases, hypothermia, and a reduced level of the body's immune defense. Leukocyte infiltration also often causes the formation of an abscess and microabscess.
Causes
The main reasons for the development of a tooth abscess:
- exacerbation of chronic periodontitis;
- accumulation of bacterial infection in the tooth pulp;
- violation of sterility conditions during root canal treatment;
- root cyst;
- vertical fracture of the tooth root.
The bacterial microflora of the oral cavity is represented not only by beneficial bacteria. It is also inhabited by streptococci, staphylococci, cocci, lactobacilli, bacteroides, and spirochetes. The inflammatory process begins with the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms beyond the root apex. Hypothermia, colds and infectious diseases predispose them to increased reproduction.
Kinds
Based on the nature of the localized accumulation of pus in the elements of the dentition and nearby structures, two groups of abscess are distinguished.
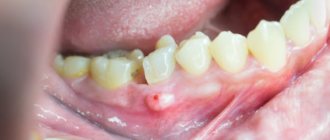
- Periapical abscess without fistula. In this case, transcanal infection of periodontal tissue is observed. The adjacent gum may have swelling, hyperemia is observed, pain is felt when biting on a molar, and the appearance of purulent exudate is recorded. The disease has a pronounced clinical picture.
- Periapical abscess with fistula. With this phenomenon, the inflammatory destructive process spreads to the bone marrow and mucous membrane. The fistula most often opens in the projection of the apex of the root element of the dentition. There may be hyperemia on the mucous membrane, a scar from a fistula, and the gums may be quite sensitive to palpation.
In case of periapical abscess without a cavity and with a cavity, complaints of intense dull throbbing pain, deterioration of general condition, and constant pain are recorded.
Prevention and treatment
Abscess prevention is simple. It is enough to follow the rules of daily oral hygiene and regularly come for examinations to the dentist.
If an abscess does form, it should be treated by a doctor. Even if the abscess opened on its own. Usually, after the pus is released, the pain goes away, and the person considers the problem solved. But even in this case, there is a risk that the infection continues to develop deep in the soft tissues. A visit to the dentist is a must.
Various methods are used to treat an abscess:
- Therapeutic antibacterial treatment. Antibiotics are not always used. Which drugs will best cope with the problem depends on the clinical picture. Usually in the early stages you can do without potent drugs.
- Surgical intervention. The surgeon opens the abscess and cleans the abscess cavity. After this, anti-inflammatory therapy is mandatory. It is necessary in order to eliminate the risk of inflammation.
Lack of qualified medical care for an abscess can lead to the development of serious complications. Suppuration is fraught with the development of tooth mobility, their loss, and bone destruction. If any alarming symptoms appear, contact our clinic. The dentist will make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of an acute inflammatory process of infectious etiology with localization in the hilar region includes a visual examination and radiographic examination. In some cases, thermography may be performed. The dentist assesses the condition of the mucous membrane, hyperemia of the tissue, and changes in tooth color. X-ray examination helps to assess the location of the pus. At the diagnostic stage, the specialist determines the viability of the pulp.
A clinical study allows us to determine the degree of pathology and select the correct endodontic treatment or surgical intervention. If necessary, additional examination methods may be required to determine the condition of the periapical tissues. In each specific case, the treatment method is selected individually depending on the history and clinical examination. The patient’s age, local symptoms, and the presence of general diseases are also taken into account. Additionally, microbiological diagnostics can be performed to identify various types of microbial pathogens.
After tooth extraction
Tooth extraction is a dental operation during which the gums are injured. If antiseptic rules have been violated or the patient does not provide the necessary postoperative care, infection can enter the wound. Bacteria will multiply quickly. Suppuration forms. If there is no treatment, the abscess affects the soft tissue.
Suppuration as a result of medical error after removal is rare. At the ARDC clinic, dentists use modern equipment, consumables, and medications. You can be confident in the quality of the procedure and compliance with the treatment protocol.
Improper postoperative care is a more common cause of abscess after removal. After the operation, the dentist must give recommendations on how to care for the wound. Careful adherence to all these rules will reduce the risk of suppuration at the site of the extracted tooth.
Treatment of periapical abscess
Depending on the stage and form of the pathology, the specialist selects a therapeutic or surgical method of treatment. At the initial stage, the canals are usually cleaned, in particular the elimination of pathogenic microflora between the teeth and gums, and the cavity is treated with antibacterial components. Endodontic therapy may include the installation of a temporary filling and the application of an antiseptic dressing with antimicrobial properties in the root canal. Antibiotics may be prescribed to stop the inflammatory process.
High-quality endodontic therapy allows you to eliminate the infectious focus. As inflammation increases, an element of the dental system can be removed. In some cases, the specialist performs appropriate tooth-preserving procedures, for example, hemisection, that is, removal of one of the molar roots.
The opening of an abscess is always performed using anesthesia; discomfort and pain are excluded during high-quality endodontic treatment. After the abscess removal procedure, drug therapy and surface treatment with special bactericidal compounds may be prescribed. The final step is to take an x-ray to ensure complete recovery.
The specialists of the AlphaDent clinic are always ready to help if you have complaints about a periapical abscess without a fistula or with a fistula. Dentists have the necessary knowledge and sufficient experience to provide high-quality endodontic treatment.
Qualified treatment will eliminate the recurrence of the infection that caused the abscess. Timely dental care will help keep your teeth and mouth in good condition. It is recommended to make visits to the dentist for preventive examinations in order to exclude complex endodontic treatment associated with the removal of an abscess.
Treatment
Treatment tactics for periodontal and periapical abscess are different.
Treatment of periodontal abscess
The primary goal of treating a periodontal abscess is to eliminate acute inflammation. To do this, periodontal pockets are washed with antiseptic solutions. It may be necessary to open the abscess, in which case the doctor will first perform anesthesia.
After this, curettage of periodontal pockets is carried out - scraping out granulations, dental plaque, epithelial particles, and necrotic tissue. Finally, the doctor applies stitches. In most cases, the patient is prescribed to wear a periodontal bandage. This is the application of medicinal substances to the area of periodontal pockets.
Treatment of periodontal abscess must be comprehensive. The patient is also prescribed rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions and taking broad-spectrum antibiotics. As a rule, the inflammatory process can be stopped.
Treatment of periapical abscess
To ensure the drainage of pus, the doctor opens the tooth cavity and creates access to the root canals. Also, drainage of pus can be carried out through an incision in the gum tissue, which does not eliminate the need for endodontic treatment (canal treatment).
After opening the tooth, the pulp or filling material is removed, if the pulp was removed earlier, and root canal treatment is performed.
It is important to completely remove purulent masses and infected dentin tissues and rinse the canals with disinfecting solutions. Then an anti-inflammatory medicine is placed in them and a temporary filling is installed. The chances of saving a tooth depend on the quality of endodontic treatment. Broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed for oral administration. After the inflammatory process has been completely eliminated, the canals can be filled with permanent filling material and the crown of the tooth can be restored. If treatment is ineffective and the inflammatory process increases, the tooth will have to be removed. Both types of abscesses are usually accompanied by swelling of the soft tissues, and swelling may also persist after tooth extraction. Physiotherapy helps speed up recovery: UHF therapy, magnetic therapy, laser therapy.