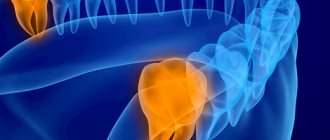
Bartholinitis is an inflammation of the large Bartholin gland. The Bartholin gland, in turn, is a paired organ that is located in the subcutaneous fatty tissue of the labia majora. When a large gland in the vestibule of the vagina becomes inflamed, microorganisms affect the excretory duct of the gland (canaliculitis), as well as the gland itself.
The main function of the Bartholin gland is to produce secretions that maintain constant moisture in the vagina. What is it for?
This secretion is released in large quantities during arousal during sexual intercourse to facilitate penile insertion. In addition, secretion is very important during childbirth. Thanks to it, the vaginal muscles stretch well and the baby can be born without damaging the vaginal walls. If the Bartholin gland does not produce secretions in the required quantity, the vagina will become dry - discomfort, itching and burning in the perineum and pain during sexual intercourse will appear. Normally, this is only possible during menopause due to the age-related decrease in female estrogen hormones.
Causes of bartholinitis:
Bartholinitis occurs due to infection in the Bartholin gland through a narrow opening of the excretory duct on the inner surface of the labia minora. Once deep into the gland, microorganisms actively multiply. This leads to inflammation and suppuration of the Bartholin gland.
Not all genitourinary infections cause bartholinitis. In the vast majority of cases, bartholinitis is provoked by sexually transmitted infections. Most often it is gonorrhea, less often - trichomoniasis and chlamydia.
Bartholinitis of nonspecific etiology is extremely rare - in this case, the causative agent is bacteria - staphylococci, Escherichia coli, streptococci, and so on. This is possible if personal hygiene rules are not followed. It should also be taken into account that even in the presence of sexually transmitted infections, bartholinitis does not develop in everyone and not always.
Immunity plays an important role in the development of the disease: if it is weakened, the chances of developing bartholinitis increase.
Depending on the clinical course of the disease, bartholinitis can be acute or chronic. Acute bartholinitis is characterized by the formation of a true or false abscess of the Bartholin gland (a limited focus with pus).
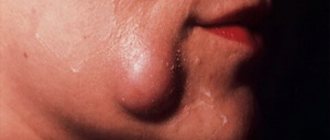
When a false abscess forms, the excretory duct of the gland first becomes inflamed (“canaliculitis”, in scientific terms). The skin over the site of inflammation turns red and swells. If you press on the inflamed area, pus will come out. Next, a blockage of the excretory duct of the gland occurs and pus is no longer released, but accumulates in the Bartholin gland. Because of this, the gland is greatly stretched and protrudes, forming a painful “bump”-shaped formation. During movements - when walking, running, during sexual intercourse - the pain intensifies, and a burning sensation appears in the perineum. Sometimes body temperature rises slightly. If you do not contact a gynecologist for a long time, the disease becomes chronic.
With a true abscess, the infection penetrates directly into the Bartholin gland, and the parenchyma of the gland melts. In this case, the symptoms of the disease are more pronounced than with a false abscess. The labia majora and minora become very swollen. The body temperature rises to more than 38 degrees, the inguinal lymph nodes enlarge, chills, weakness, and “pulsating” sharp pain in the labia majora appear. Spontaneous opening of the abscess with the release of yellow-green pus is possible, which leads to a weakening of the symptoms of the disease. But if left untreated, the inflammation recurs again and gives complications, or, like a false abscess, becomes chronic.
In the chronic form of bartholinitis, the symptoms of the disease temporarily subside and worsen again. Instead of an abscess, a cyst (liquid formation with inflammatory exudate) forms in the gland.
With any form of bartholinitis, you should never self-medicate or try to squeeze out an abscess or cyst - this can lead to blood poisoning . If such symptoms occur, you should immediately consult a gynecologist.
Symptoms of inflammation of the labia
The inflammatory process in the area of a woman’s external genitalia (vulva) is referred to in gynecology as “vulvitis.” This condition has characteristic symptoms, such as redness, itching, swelling of the labia, painful symptoms when urinating, and copious natural female discharge. A woman may also experience a number of additional symptoms:
- the appearance of roughness of the labia minora, which is nodules of enlarged sebaceous glands;
- the appearance of a whitish coating, plaques reminiscent of psoriasis rashes;
- feeling of general malaise and fever.
Like any other inflammatory process, vaginitis is divided into acute and chronic. The acute form is characterized by pronounced symptoms, while the chronic process is more sluggish and unnoticeable.
Expert opinion
You should be especially careful about the development of vulvitis in little girls, since children tend to hush up problems associated with discomfort in the intimate area. For this reason, it is necessary to make it clear to the child that if he experiences any unpleasant sensations, he must inform his elders about their occurrence.
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category Oksana Anatolyevna Gartleb
Gynecologist appointment
Diagnosis of bartholinitis:
Diagnosing bartholinitis is not particularly difficult. The doctor will be able to make a diagnosis during examination at the first appointment. In the presence of an abscess, swelling and redness of the Bartholin gland is determined; palpation of the formation causes sharp pain. In the chronic form of bartholinitis (in the presence of a Bartholin gland cyst), a tumor-like formation is detected, painless on palpation. In addition to the examination, the following tests must be taken:
- a regular vaginal smear;
- PCR diagnosis of major sexually transmitted infections (chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis, herpes, human papillomavirus);
- bacteriological culture of vaginal discharge to establish sensitivity to anitibiotics;
- bacteriological examination of pus when an abscess ruptures (or the secretion can be obtained from the excretory duct of the gland by light pressure).
Treatment of vulvitis
If you notice any alarming symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor. Only a specialist can diagnose the cause and prescribe correct and quick treatment, including a set of measures: relieving inflammation, eliminating factors that are catalysts for the process.
The basis of treatment for vulvitis is the elimination of the causes of the inflammatory process and treatment of concomitant diseases, which may include diabetes mellitus (Diabetes mellītus), gonorrhea (Gonorrhoea), diphtheria (Diphtheria), helminthiasis. After receiving smear test data and checking the sensitivity of the infectious agent, the doctor can prescribe medication, most often antibacterial drugs. Vulvitis responds well to treatment with local remedies, which include all kinds of ointments, gels and suppositories.
In parallel, in the course of treatment of vaginitis, vitamin complexes can be prescribed, including vitamin A to effectively protect the epithelial layer, as well as vitamins E and C, known for their antioxidant properties.
To combat severe symptoms, other drugs may be prescribed:
- Antihistamines that help relieve itching.
- Hormonal, occurring in atrophic vulvitis in the postmenopausal period.
- Anesthetics that relieve pain.
In addition to the medications prescribed by your doctor, you can use Gynocomfort Restoring Gel. This product was created by specialists from the pharmaceutical company VERTEX and underwent clinical trials at the Department of Dermatovenerology with the clinic of the St. Petersburg State Medical University. During testing of the gel, it was proven that it is a very effective additional agent as part of the complex therapy of inflammatory processes of the female genital tract.
As additional therapeutic measures that can be used at home, it is worth mentioning warm baths with herbal infusion.
Chamomile, calendula, string, and comfrey have excellent anti-inflammatory properties.
Baths will help not only reduce inflammation, but also relieve symptoms such as itching, burning and pain.
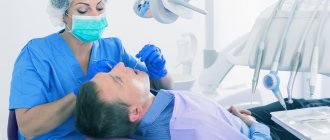
Surgical treatment of Bartholin gland cyst:
Treatment of Bartholin gland cysts is carried out without exacerbation of the inflammatory process. In this case, there are two options for surgical intervention: marsupialization of the cyst (creation of an artificial duct of the gland for the outflow of secretions) or extirpation (removal) of the Bartholin gland.
When performing marsupilization, the doctor opens the cyst capsule with a linear incision. The edges of the capsule are sutured with separate sutures to the edges of the skin wound, forming an external opening. A drainage tube or catheter is inserted to drain the contents of the cyst. After the operation, within two months, the external opening narrows, and a new excretory duct is formed.
Extirpation of the gland is carried out in case of recurrence of bartholinitis. To do this, a longitudinal incision is made on the inside of the labia minora. The gland is carefully isolated with a scalpel and removed, and catgut sutures are placed on the wound.
For any types of bartholinitis, after surgery and complete elimination of the inflammatory process, physiotherapy is prescribed on the 3-4th day - magnetic therapy and ultraviolet irradiation. All patients are advised to abstain from sexual intercourse until complete recovery, since there is a high probability of infection of the sexual partner. In order to prevent a relapse of bartholinitis, it is important to eliminate the cause of the disease, to completely recover from concomitant infections (chlamydia, gonorrhea, etc.), otherwise bartholinitis may occur again.
All patients must observe the following rules of personal hygiene:
- wash your face twice a day;
- wear comfortable underwear, preferably cotton;
- During menstruation, change pads and tampons every 3-4 hours to avoid re-infection.
During the recovery period, it is important to use drugs that enhance the immune system. These include vitamins, a balanced diet, and some herbal immunomodulators.
Causes of inflammation of the Bartholin gland
Typically, the cause of bartholinitis is a bacterial infection. Microorganisms enter the gland through the outlet of the gland duct, where they begin to multiply. As a result, inflammation, suppuration, swelling and blockage of the gland ducts occurs. The mucus in the ducts stagnates, which leads to the formation of a Bartholin gland cyst (accumulation of pus).
The most common cause of inflammation of the Bartholin gland is sexually transmitted diseases:
- gonorrhea
- trichomoniasis
- chlamydia
And:
- failure to comply with intimate hygiene rules (infection with staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli)
- development of inflammation due to candidiasis (thrush)
Factors that can stimulate bartholinitis in women include:
- hypothermia
- weakened immune system
- sexual intercourse during menstruation
- abortion and other uterine surgeries
Prevention of bartholinitis:
- regular visits to the gynecologist;
- protection against sexually transmitted infections - use of condoms, monogamous lifestyle;
- timely treatment of infections;
- strengthening the immune system: good nutrition, exercise, giving up bad habits.
In our clinic you can receive a full range of clinical and laboratory examinations before performing this surgical operation. The equipped operating room allows you to perform the operation both under local anesthesia and general anesthesia, with stay and observation in the ward for several hours.
Bartholinitis and pregnancy
Infections that a woman is infected with and that cause bartholinitis can negatively affect the course of pregnancy and the development of the child. Infected mother's blood, entering the child's body through the placenta, can lead to disturbances in the formation of the baby's organs. In the early stages of pregnancy, infection can cause fetal death.
Do not delay visiting your doctor if you have symptoms of inflammation of the Bartholin gland. You can diagnose bartholinitis in our clinic, and also receive qualified help, advice and recommendations by making an appointment with a gynecologist by phone. or the feedback form at the bottom of the page.
Watch yourself, appreciate yourself and be healthy!