- home
- Useful articles
- Oral abscess: causes, symptoms, treatment
The development of an abscess in the oral cavity is associated with infection entering the pulp and its further spread throughout its entire structure. An inflammatory process begins, leading to tissue swelling and accumulation of purulent deposits. If the infection is not stopped and timely treatment is not started, then it will penetrate through the dental canals into other organs of the body, causing various diseases.
What is it and why does it happen
This disease is a local acute inflammatory process in the oral cavity, which is characterized by the accumulation of pus in the tissues of the gums, teeth or palate. Lack of timely and correct treatment can lead to a transition to a chronic form or cause such serious complications as the appearance of phlegmon or sepsis.
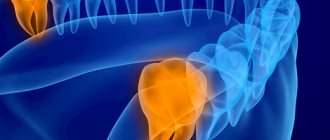
The causes of this disease are the presence of problems with the gums (gingivitis), with the roots of the teeth and adjacent tissues (periodontitis), with the enamel and hard surface (caries), as well as various mechanical injuries, infection, and chronic diseases. People suffering from diabetes and immune diseases are at increased risk of becoming acquainted with this unpleasant disease.
If your tooth is cracked, the roots are exposed, deep cavities appear, do not wait for an abscess to develop - be sure to visit the doctor at our dental clinic in Lyublino, because untreated caries is the main reason for the development of the inflammatory process.
In our clinic you can get a free dental consultation!
Abscess of the palate
Palate abscess is a limited accumulation of pus in the tissues of the soft and hard palate that occurs during inflammation.
It usually occurs as a complication of periodontitis of the teeth of the upper jaw. More often the cause is the second incisor, canine or second premolar. The disease begins with pain in the hard palate and redness of the mucous membrane. When it bulges, the pain becomes most intense.
Based on the site of formation, this type of tumor can be divided into two subtypes: inflammation of the hard palate and soft palate.
Abscess of the hard palate:
- the patient complains of a noticeable throbbing pain in the palate (upper jaw), which intensifies when talking and trying to chew food;
- foci of infection - periodontal pockets of the maxillary teeth, wounds on the mucous membrane of the hard palate;
- may spread in the absence of timely treatment to the soft palate and peripharyngeal space.
Abscess of the soft palate:
- complaints of painful swallowing, sore throat, aggravated by talking. The affected area greatly increases in size;
- sources of infection - damaged lacunae of the tonsils in chronic tonsillitis, microcracks in the mucous membrane of the soft palate, places where local anesthesia was administered;
- further spread leads to damage to the peritonsillar and peripharyngeal space.
Symptoms
Characteristic local signs of abscess of the hard palate:
Complaints of severe throbbing pain in the upper jaw (palate), aggravated by eating and talking.
Objectively: in the area of the hard palate there is a swelling or protrusion with clear contours. The mucous membrane over the source of inflammation is hyperemic, palpation causes pain. Fluctuation may be detected.
Characteristic local signs of an abscess of the soft palate:
Complaints of sore throat, worsening when swallowing or talking.
Objectively: asymmetry of the pharynx with a displacement of the uvula of the palate to the healthy side. The affected part of the soft palate is increased in volume due to inflammatory infiltration of its tissues, the mucous membrane covering it is hyperemic. Pressure on the infiltrate (with an instrument, during palpation) increases pain.
Treatment
Surgical
Treatment of abscess of the hard palate:
1. Pain relief. When the abscess is localized in the anterior part of the hard palate, local infiltration anesthesia in combination with conduction anesthesia at the greater palatine foramen; when the abscess is localized in the posterior part of the hard palate - local infiltration anesthesia in combination with conduction anesthesia at the round opening according to S.N. Weisblat, or subtemporal anesthesia according to A.V. Vishnevsky against the background of premedication.
2. An incision in the mucous membrane of the hard palate through the inflammatory infiltrate along its entire length parallel to the course of the vascular bundle of the palate.
3. Opening a purulent focus and evacuation of pus by spreading the edges of the wound using a hemostatic clamp.
4. Excision of a strip of mucous membrane 2-3 mm wide along the edge of the wound to ensure good constant outflow of inflammatory exudate without introducing drainage into the wound. Hemostasis.
Treatment of abscess of the soft palate:
1. Anesthesia - local infiltration anesthesia (preliminary application anesthesia with a 1% dicaine solution can be performed) against the background of premedication.
2. An incision in the mucous membrane through the top of the inflammatory infiltrate (swelling) along its entire length parallel to the palatine arch.
3. Separating the edges of the wound and moving towards the center of the purulent-inflammatory focus by tissue separation using a hemostatic clamp, evacuation of pus.
4. Since drainage in the wound of the soft palate is poorly maintained, in order to prevent premature adhesion of the edges of the wound, you can excise a strip of thinned mucous membrane along the edge of the wound 2-4 mm wide, or periodically spread the edges of the wound.
Our doctors
18 years of experience
Baghdasaryan
Armen Evgenievich
Chief physician, dentist-orthopedist-therapist
Graduated from VSMA named after. N.N. Burdenko. Internship on the basis of MGMSU named after. A.E. Evdokimov in “General Dentistry”.
Clinical residency at the Moscow State Medical University named after. A.E. Evdokimov in “Orthopedics”.
More about the doctor...
5 years experience
Sadina
Ekaterina Vladislavovna
Dental therapist, surgeon
Penza State University Medical Institute, specialty “Dentistry”.
In 2016, she underwent professional retraining in the specialty “Therapeutic Dentistry” at the Moscow State Medical and Dental University named after A.I. Evdokimov.
More about the doctor...
8 years of experience
Arzumanov
Andranik Arkadievich
Dentist-orthodontist
Graduated from Moscow State Medical University. Internship - Moscow State Medical University at the Department of Orthodontics and Children's Prosthetics.
Residency at Moscow State Medical University at the Department of Orthodontics and Children's Prosthetics. Member of the Professional Society of Orthodontists of Russia since 2010.
More about the doctor...
Symptoms
The main symptoms of this disease are:
- An increase in acute, throbbing or aching toothache, intensifying with food intake;
- Experiencing a bitter taste or unpleasant odor in the mouth;
- Feeling of general weakness, headache, apathy, insomnia, lack of appetite;
- Increased tooth sensitivity;
- The gums become inflamed, there is swelling, redness, a small compaction or swelling filled with pus is formed;
- There is an enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes;
- As the infection develops, nausea appears and body temperature rises;
- Facial asymmetry may appear, the size of one cheek, lower or upper lip may increase.
It is important to know that an abscess that begins on one tooth, if left untreated, can spread to the next. If the outer shell cannot withstand and ruptures, the pus comes out, it becomes easier and the pain goes away, but there is a risk of purulent masses getting into healthy tissues and teeth, and the sad story repeating. Ignoring purulent seals in the oral cavity can lead to such dire consequences: tooth loss, death of jaw tissue, development of respiratory diseases (pneumonia, sore throat) and vision. This is also fraught with paralysis of the facial nerves, and the entire body is exposed to acute intoxication.
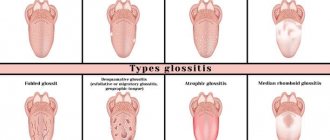
What types are there
Depending on the location of the source of inflammation in the oral cavity, abscesses can be localized to:
- Gums One of the most common types, it forms around the inflamed soft tissues of a certain tooth, without proper treatment it becomes chronic. During an exacerbation, bad breath appears, accompanied by the discharge of pus and general weakness;
- Palate Usually occurs with periodontitis located in the teeth of the upper jaw, quickly spreads to other tissues, and can cause the development of osteomyelitis (bone necrosis);
- Cheeks A very dangerous type of inflammation, if left untreated there is a risk of inflammation spreading to the skin of the face. It affects the inside, and it is possible that the outside of the cheek can also be affected. A possible reason for the appearance is infection in the smallest wounds when biting the mucous membrane with teeth.
- Floor of the mouth Placed under the tongue, characterized by severe pain when eating or talking. An abscess that spontaneously opens can further spread the infection through the throat to other organs of the body;
- On the tongue, the surface thickens and swells. There is redness, it hurts to eat, talk and even just breathe. This type of inflammation causes a feeling of suffocation and lack of air, and therefore requires urgent hospitalization.
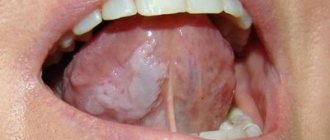
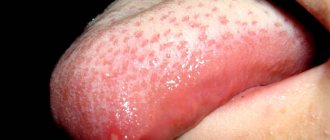
Tongue abscess
Perhaps one of the most dangerous is an abscess of the tongue, as it develops rapidly, causing a sharp increase in the size of the tongue, which can lead to a lack of oxygen and suffocation. When infection gets into microcracks and an abscess forms in the thickness of the tongue, the patient begins to experience severe pain. The tongue swells, swallowing and chewing becomes difficult; these symptoms are especially pronounced in the presence of an abscess of the root of the tongue. The closer the source is to the nasopharynx, the sooner the patient is indicated for hospitalization and surgical intervention by a doctor.
In addition to dislocation at the root, the development of a sublingual abscess is possible. Although it is less dangerous for breathing, it also needs to be opened as soon as possible in order to avoid breakthrough and purulent intoxication of the body.
When this type of inflammation occurs, the patient usually experiences pain while eating and talking. In any case, an abscess of the tongue, no matter in what area it forms, is a very dangerous thing, since all nearby soft tissues, organs and, first of all, the brain are at risk. The first signs of inflammation:
- painful sensations;
- headache;
- hyperemia;
- loss of sleep and appetite;
- general malaise.
Treatment
To get a complete picture of the disease, dentists use modern diagnostic methods, on the basis of which they select the optimal solution to this problem. These include radiography, ultrasound, sampling of purulent mass and their analysis, visual examination of the condition of the pharynx (pharyngoscopy). Based on the results obtained and studying the history of the disease, appropriate therapy will be prescribed.
Before visiting a doctor, you can alleviate your condition a little by taking painkillers and warm antiseptic solutions, but you should not put off visiting the dentist for long, because the process develops very quickly and does not go away on its own.
Treatment of an oral abscess is usually carried out using two methods:
- Surgical intervention Allows you to avoid most of the complications that may arise from an unauthorized breakthrough of a purulent sac. The operation is performed under local anesthesia by a dental surgeon, with the help of special instruments the abscess is opened, the wound is cleaned and drainage is placed, after the operation antibiotics, antihistamines, vitamins and immunomodulators are prescribed;
- Medication Medications (Fluocinonide gel, Chlorhexidine solution, Ibuprofen) are prescribed only in the initial stage; timely consultation with a doctor and timely prescribed medications help avoid surgical intervention.
When the pus comes out, relief comes: there is no more pain, the temperature returns to normal, and the swelling disappears. The course of treatment ends with the necessary physical procedures: electropharesis with the addition of an antiseptic on the gums, UHF heating, and the procedure for silvering teeth affected by caries. Until the wound in the mouth completely heals, the patient must abandon hard vegetables and fruits in favor of soft cereals and liquid soups.
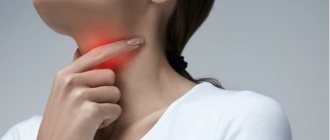
Treatment methods for peritonsillar abscess
A peritonsillar abscess cannot be cured on its own. Methods suitable for treating sore throat are not suitable here. If an abscess is left untreated, it may open spontaneously, but in this case there is a high probability that the pus will not completely come out and the inflammation will resume. Serious purulent complications are also possible: blood poisoning, phlegmon of the neck.
The treatment method for peritonsillar abscess is surgical.
Opening a paratonsillar abscess
The opening of a paratonsillar abscess is performed by an otolaryngologist in a surgical hospital. The operation is performed under local or intravenous anesthesia. The planned operation time is 1 hour. After the operation, you must be under medical supervision for 24 hours.
After opening the abscess, a course of antibiotics, gargling, and physical therapy are prescribed. The first time after surgery, food should be warm and soft (semi-liquid) so as not to irritate the healing wound.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
Prevention
In general, the effectiveness of treatment depends on at what stage of the disease the patient sought medical help and his general health. It is very important to follow all doctor’s orders and treatment procedures immediately after they are prescribed. A timely surgical operation and the absence of complications after it are a guarantee of healing the abscess within one to two weeks.
Preventive measures to prevent this disease are very simple:
- Maintain hygiene, which includes high-quality and proper care of teeth and gums (brushing teeth and tongue at least twice a day, cleaning interdental spaces with dental floss after meals, regular use of mouth rinses);
- Treat carious teeth and other oral diseases in a timely manner;
- Protect the jaws and oral mucosa from injury;
- Have a complete diet, including vitamins and vital microelements.
Simple tips, the implementation of which depends only on your desire, will help in the future to avoid serious consequences caused by an abscess. And remember: oral health directly affects the beauty and charm of your smile.