Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
Inflammation of the periosteum (periostitis) is a disease that brings many painful symptoms. As a rule, acute pain and severe swelling immediately bring the patient to the dentist, and rightly so: not only the condition of the oral cavity, but also health in general depends on the timeliness of treatment.
Typical symptoms
Symptoms of inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth are quite pronounced:
- redness and swelling of the gums;
- increasing severe pain radiating to the ear, temple and other areas, depending on the location of the inflammation;
- swelling of the face on one side (cheeks, lips, cheekbones);
- high body temperature;
- symptoms of general intoxication (headache, dizziness, dry mouth, fatigue and weakness, general loss of strength);
- white or gray plaque on the gums;
- change in tooth position, tooth mobility;
- in some cases, the appearance of purulent discharge.
With a prolonged inflammatory process, a fistula can form: pus finds its way into the oral cavity, which is accompanied by the appearance of blood, but the pain and fever temporarily subside. This is due to the fact that the contents stop accumulating in the tissues and begin to flow out, but you should definitely consult a doctor.
Causes of occurrence.
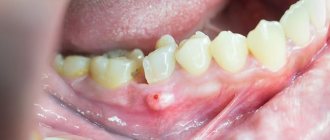
The periosteum is a thin vascular tissue that consists of many nerve endings that completely cover the jaw bone. It securely connects the teeth together with the muscles and ligaments in the oral cavity. If the gum is damaged and an infection gets into it, inflammatory processes begin in the periosteum, the mucous membrane swells, and the person experiences pain. Many patients consider gumboil to be a temporary problem and try to get rid of it using folk remedies. Such an attitude and untimely professional treatment can cause an abscess in the periosteum area. Also, pathology occurs due to difficulty in the eruption of “eights”, i.e. wisdom teeth or as a result of a growing cyst. In addition to these factors, there are several other causes of periostitis:
- Complications of caries.
- Poor oral hygiene.
- Poor quality treatment and improper canal filling.
- Mechanical injuries of the jaw.
- Diseases (sinusitis, sore throat), due to which the infection penetrates the gum tissue through the circulatory system.
- Mistakes during tooth extraction.
Why does inflammation of the periosteum occur?
There are three ways that pathogenic bacteria enter the periosteum:
- odontogenic factor - dental diseases become the source of inflammation: caries, cysts and granulomas of the tooth root, pulpitis. Bacteria penetrate deep into soft tissues. Quite often, periostitis is observed as a result of a long and complicated process of eruption of “eights”;
- hematogenous factor - infection occurs as a result of bacteria entering the tissues from the bloodstream or lymph flow. As a rule, this happens in connection with ENT diseases, furunculosis of the face, neck, abscesses, etc.;
- traumatic factor - mechanical damage to the periosteum during fractures, impacts, complex tooth extractions leads to inflammation.
Methods of pain relief
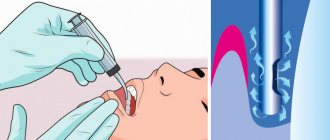
The surgical procedure is performed under local anesthesia. Before performing the manipulation on the upper jaw, bilateral anesthesia is administered by infiltration. This anesthesia involves administering the drug to both sides of the jaw.
To perform intervention on the mobile jaw, torus or mandibular anesthesia is used. The anesthetic is injected into the area of the mandibular ridge.
Reference! With extensive foci of inflammation, the effectiveness of pain relief decreases. In this regard, it is recommended to administer potent anesthetics.
Types of inflammation
Symptoms of inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth depend on the form of the process. In the acute form, pain and swelling are severe, difficulty swallowing, spreading of swelling to the face and neck, and enlarged lymph nodes may be observed. Acute inflammation occurs over several days.
The chronic form may bother the patient for several months. Symptoms are more moderate; a fistula may appear - an opening through which inflamed tissues get rid of purulent contents.
There are also two types of both acute and chronic inflammation:
- serous - more often provoked by traumatic injury, swelling forms quickly, but the pain is more moderate and tolerable, relief occurs, on average, after 5 days;
- purulent - more dangerous, characterized by severe throbbing pain, severe swelling and redness of soft tissues, and higher body temperature.
In both cases, you should definitely consult a doctor, since the risk of complications is very high.
Forms
- Diffuse
. Accompanied by attacks of severe toothache and signs of general intoxication: high fever, lethargy, lack of appetite. Fibrous thickening of the periosteum is observed on the lower and upper jaw. - Purulent
. The most common form of periostitis. Accompanied by high temperature (up to 39°C), the appearance of an abscess and the formation of fistula tracts. In the absence of therapy, it forms severe swelling, phlegmon, and acute osteomyelitis is possible. - Ossifying
. A common form of chronic periostitis, which is characterized by the formation of new bone and hyperostosis. Progresses very quickly. - Chronic
. It proceeds slowly without pronounced symptoms, sometimes worsening, sometimes subsiding over several months and even years. At the site of inflammation, thickening of the bone is possible. As a rule, the lymph nodes become enlarged.
Features of treatment
Treatment of inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth should only be carried out by a doctor. The specialist chooses tactics depending on the type and form of the disease.
Drug treatment is only advisable if you consult a doctor immediately at the first symptoms of the disease. Therapy includes:
- taking antibiotics prescribed by a specialist: this will stop inflammation and prevent the spread of infection;
- taking anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers;
- local effect: use of antiseptic rinses, chlorhexidine baths, ointments and gels with an anti-inflammatory effect.
The course of treatment is at least 5-7 days. If relief does not occur, surgical methods are used.
Symptoms and treatment of inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth are individual. In case of advanced inflammation, ineffectiveness of conservative methods and other indications, the doctor performs a tissue opening - periostotomy. It is carried out in several stages:
- anesthesia: local infiltration or conduction anesthesia is sufficient.
- Making an incision in the gum in the projection of the source of inflammation.
- Washing and cleaning tissues.
- Treatment of the wound with antiseptic agents.
- Installation of drainage - a small rubber band in order to prevent premature fusion of the mucous membrane and the re-formation of pus inside.
The drainage is removed by a doctor after a few days; you should not do this yourself. The specialist must make sure that the contents of the inflamed tissue are released and the wound can be allowed to heal. If the incision is small, no stitches will be required.
If the cause of the disease was a damaged tooth, it is treated: restoring its shape using filling materials, filling root canals. Sometimes removal is required; it is performed simultaneously with surgical treatment of periostitis.
Additionally, physiotherapeutic procedures may be recommended. They will speed up inflammation relief and healing. These include UHF, darsonval therapy, infrared radiation, and magnetic therapy. During the healing period, it is advisable to use vitamins and restorative medications.
Diagnostics
Only an experienced dentist can accurately determine the form of the disease and prescribe competent treatment after a comprehensive examination.
1. Visual inspection.
The dentist will examine the oral cavity, paying special attention to severely damaged teeth.
2. X-ray of the jaw.
In order to differentiate periostitis from pathologies with similar symptoms (for example, from a dental cyst or acute periodontitis), the doctor may prescribe an X-ray examination.
X-ray allows not only to accurately diagnose periostitis, but also to determine the boundaries of the source of inflammation.
3. General blood test.
If purulent periostitis is suspected, a general blood test is required. An increase in leukocytes and ESR values confirms the purulent form of periostitis.
How to help yourself before visiting a doctor
If the periosteum of the jaw is inflamed, you should forget about such traditional methods as heating: any hot compresses will aggravate the situation. If you open the formation, take antibiotics without a doctor’s prescription, or remove the pus yourself, this can lead to dire consequences.
You can alleviate your condition by doing the following:
- rinse your mouth with a weak saline solution at room temperature or an antiseptic with an analgesic effect;
- apply a cool compress to the cheek on the side of the inflammation;
- Take an over-the-counter pain reliever.
These measures will help relieve pain and slightly reduce swelling, but you should contact a specialist as soon as possible. As an antiseptic rinse, you can use ACTIVE mouthwash. It does not contain alcohol, so there is no risk of burning inflamed tissues, and the chlorhexidine and benzydamine in the composition will help relieve the condition before you see a doctor.
How to relieve tooth inflammation
If inflammation of the root does not give you peace, then it is best not to delay a visit to the doctor. Traditional medicine at home is not intended to treat such a complex disease - we can say with confidence that self-medication will not bring the expected results. Relieving painful spasms and swelling with herbal infusions will only bring calm to the patient for a while, but the inflammatory process will develop and return after a while with more severe consequences.
The following will help to tame the pain for a while:
- Painkillers. They will help you endure acute pain, which is not advisable to endure, but it is best to drink them 12 hours before going to the doctor so that he can make a correct diagnosis;
- To relieve pain, you can rinse your mouth several times with a special solution, mixing a teaspoon of salt and soda in a glass of water, adding four drops of iodine;
- Using calendula tincture, you can relieve inflammation, mix a tablespoon of tincture with a glass of water, rinse your mouth up to 5 times;
- One of the modern recipes for relieving toothache: place two drops of propolis tincture on cotton wool and apply to the painful tooth, the pain should subside within an hour;
- Boil one teaspoon of chamomile and oak bark in a liter of water, leave for 20 minutes, cool slightly, rinse for inflammation;
It is important to remember that applying warm compresses to a sore spot is strictly prohibited! Rinsing and taking painkillers cannot be considered treatment, because even if you managed to relieve the pain, the inflammatory process has not been stopped, it will proceed unnoticed and will resume with renewed vigor, the consequences of which can be unpredictable.
Clinical researches
Repeated clinical studies have proven that the two-component mouth rinse ASEPTA ACTIVE more effectively combats the causes of inflammation and bleeding compared to single-component rinses - it reduces inflammation by 41% and reduces bleeding gums by 43%.
Sources:
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- The use of drugs from the Asepta line in the complex treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (N.V. Berezina E.N. Silantyeva S.M. Krivonos, Kazan State Medical Academy. Kazan.) N.V. BEREZINA, E.N. SILANTIEVA, S.M. KRIVONOS Kazan State Medical Academy
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of commercially produced personal oral hygiene products: Asepta toothpaste used in combination with Asepta mouthwash and Asepta gum balm Head. Department of PFS Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor S.B. Ulitovsky St. Petersburg State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova. Faculty of Dentistry. Department of Preventive Dentistry.