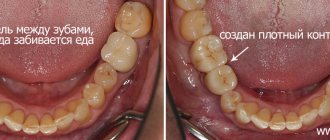
Diastema
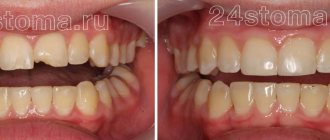
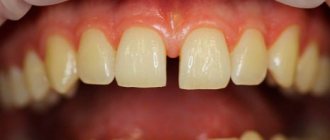
- a gap between the front teeth - is not so rare: 20% of the population has this pathology and most often only in the upper jaw. Diastema is a type of trema, a gap between the teeth. On the front upper teeth. It rarely occurs on the lower jaw. Some people are not bothered by the presence of a diastema; they live with it all their lives and consider it their highlight. Others do not like its aesthetic appearance, or rather the aesthetics of the entire smile, especially if the diastema is very large. According to statistics, the majority of those who have a so-called gap consider it a disadvantage. Diastema develops various kinds of complexes in them. Such people may have difficulty communicating, which has a very negative impact on their personal life and career.
What is a gap from a dental point of view?
In dentists' language, the gap between teeth is called diastema (from Greek - “gap, distance”). According to statistics, varying degrees of this defect are present in every fifth adult on the planet. In childhood, increased interdental space is often temporary; it is observed in 50% of preschool children. Diastema refers to an abnormally large empty space between the incisors (can reach 10 mm).
Patients often confuse a diastema (a gap between “units”) with a trema (a gap between any teeth in a row), although formally these are completely different defects, although similar in essence. Accordingly, the approach to treatment/elimination is different in both cases.
Reasons for the appearance and enlargement of gaps between teeth
The gap between the front teeth is a result of internal or external factors. Most often it occurs as a result of:
The cause may also be the presence of microdentia, which inherently affects the symmetry of the teeth.
An increase in an existing gap occurs for the following reasons:
- abuse of chewing seeds;
- progressive problems with the root system;
- the appearance/development of various types of orthodontic pathologies;
- Frequent chewing of hard food (particularly with the front teeth).
Correct and recommended prevention will help maintain the diastema at the existing level (prevent the distance between the incisors from becoming larger), and the orthodontist will select an individual program for eliminating the defect.
You might be interested in:
Types of teeth bites
Straightening teeth without braces
Treatment and straightening of teeth
Clear braces
For what reasons are the roots of teeth exposed?
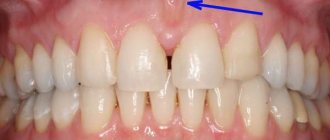
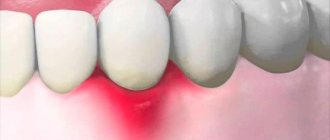
The phenomenon of exposed teeth in dentistry has a name - gum recession, but usually recession is only a symptom behind which another dental disease is hidden. Most often, it is the lower row of teeth that suffers from recession, since it bears the brunt of the load.
A common disease that causes gums to become exposed is periodontitis, during which inflammatory processes begin to occur in the periodontal tissues; if such a disease is started, it can become chronic.
Typically, periodontitis is a consequence of poor oral hygiene. Plaque and food debris that accumulate between the teeth and on the surface gradually enter the soft tissues and provoke inflammatory processes.
Inflammation significantly weakens the gums, making them weak and unable to maintain their shape. Then they descend and expose the neck of the teeth, which can lead to their loosening and loss. Periodontitis can also be caused by natural pathology.
The second most common cause of exposed roots is periodontal disease, which, unlike periodontitis, is not an inflammatory disease. During such a disease, the gums decrease in size due to atrophy of soft tissues, or disruption of metabolic processes in them.
Other reasons that cause denudation of teeth include:
- Improper brushing of teeth, namely too much pressure of the brush on the gums.
- Tooth decay close to the gums due to caries.
- Malocclusion, short frenulum of the tongue and other pathologies of the oral cavity.
- Malfunctions of the thyroid gland and gastrointestinal tract.
- Caries that has penetrated deep into the dental tissue often causes the gums to detach from the tooth.
To eliminate the defect, it is necessary to find out the cause of its occurrence. If the disease is allowed to progress, the gums will eventually recede to the point where the tooth can fall out. Considering that most of the causes of such a defect are not local, but affect the entire oral cavity, refusal of treatment can lead to the loss of all affected teeth.
Types of diastemas
How the gap between the teeth can be removed depends on the reasons why the gap appeared. Therefore, it is very important to correctly identify the species. Diastemas are classified according to three main characteristics:
- By time of occurrence of the defect
:- False
. It is diagnosed in children when the bite is not yet fully formed. The problem disappears on its own without third-party intervention after replacing baby teeth with permanent ones. - True. Diagnosed in adolescents and adults in the period after the formation of the bite. It occurs due to periodontal pathologies, injuries or the absence of some frontal teeth in a row.
- By location
:- Symmetrical
. The location is determined relative to the conditional center of the dentition (usually oriented along the frenulum). The position of the incisors relative to each other is also taken into account. - Asymmetrical
. Most often, one of the incisors is in its place, and the second is deviated relative to the conditional center. - According to the position of roots and teeth
:- Literal deviation of crowns
. The defect is most often observed in people with a superset of teeth. In this case, the position of the roots is correct, but the incisors themselves deviate. Usually the gap in this case is no more than two millimeters. - Hull literal offset
. A common cause of the defect is excessively compacted bone tissue of the middle suture, which does not allow teeth to erupt in the place where they are needed. It is expressed in the lateral displacement of both the root and the incisor. - Medial tilt
. The most complex defect that can occur with the central incisors. As in the previous case, teeth and roots shift, but they can grow not only to the sides, but also with a displacement around their own axis.
To understand how to remove the gap between the front teeth and which method is best to choose, the dentist must correctly determine the type of diastema. Keep in mind that it is impossible to get rid of a gap on your own or at home - you cannot do this without the help of a specialized doctor.
Do I need to get rid of the gap?
To correctly answer this question, you need to understand what kind of diastema we are talking about. It may be true or false. Is there any way to eliminate the space between a child’s teeth?
False diastema is not uncommon in children with baby teeth. After their shift, she can leave on her own.
A true diastema is one that arose after the formation of a bite and the replacement of baby teeth. Visible space will no longer disappear on its own. Its owner may experience malocclusion, poor diction, and dental problems. Also, for many, the cause of complexes is a gap. Therefore, you should definitely get rid of this diastema.
How can a gap be dangerous?
A small gap between the teeth can be a highlight and be regarded solely as an aesthetic defect. This problem does not bother some people, even those who are often under the gun of video cameras (for example, E. Temnikova, Madonna, K. Novikova, V. Paradis, K. Raikin, etc.). However, in some cases, diastema can cause serious functional disorders. Without therapeutic intervention, the size of the gap will increase, which has the following consequences:
- speech defects (their degree depends on the size of the diastema);
- violation/change in bite (due to uneven chewing load on the upper and lower jaw);
- caries (pathogenic bacteria and hard deposits accumulate in the interdental space; regular home cleaning is not always enough to combat them);
- inflammation and other gum diseases (due to direct contact of the gums with chewed food).
An experienced orthodontist can determine exactly how to remove the gap between the front teeth and whether it is necessary for medical reasons. If the defect is purely aesthetic, then only you can decide whether it needs to be eliminated.
Diastema and trema - what is it and how do these pathologies differ?
Dental diastema is the visible gap between the front teeth of the upper or lower row. The size of the gap can range from 1 mm to 1 cm. This is not only an aesthetic drawback, it causes speech impairment and serious discomfort while eating. Diastema is often a consequence of abnormal development of the labial frenulum.
Trema is one or more spaces between teeth in the entire dentition. It often occurs when baby teeth erupt, or if their size is too small.
Despite the fact that trema and diastema are characterized by the presence of gaps in the dentition, there is a significant difference between them. Diastema forms only between the front teeth, and trema can form between any dental units.
It is important to know. Orthodontic correction should be started as soon as possible, since the presence of gaps in the dentition significantly increases the risk of developing diseases of the teeth and gums.
How to remove a gap between teeth
The main task that a dentist faces when solving the problem of diastema is to achieve the most even alignment of the central incisors. Depending on the chosen method, this process may take 2-3 dental procedures or last several years (the duration of treatment depends on the complexity and causes of the problem, the age of the patient and other factors).
Modern dentistry offers as many as 10 progressive methods of combating the gap between the front teeth:
- Surgical plastic surgery.
- Bracket systems.
- Records.
- Veneers.
- Lumineers.
- Cosmetic correction.
- Artistic restoration.
- Crowns.
- Implants.
- Mouthguards.
It would not be superfluous to study in detail the features of each technique, comparing their effectiveness and other characteristics.
Surgical plastic surgery
This method is used in the case of a congenital defect associated with an incorrect position of the labial frenulum (it is because of this that the incisors cannot close correctly). Surgical plastic surgery of the frenulum will not remove the gap, but will create conditions under which the teeth will be able to take the correct position. And after this, the dentist selects an effective method of correction. This technique has several nuances related to the patient’s age:
- This procedure is most effective for children 5-8 years old - after the operation, the incisors will close on their own without additional dental intervention.
- After surgery, older patients will be forced to wear orthopedic structures (some of which are fixed not temporarily, but permanently).
The plastic surgery itself is safe for health and painless. Does not require long time for rehabilitation and recovery.
Bracket systems
They are non-removable orthodontic structures designed to straighten the dentition. Parts of the structure are fixed directly on the teeth (from the outside or inside). The use of braces to eliminate gaps between teeth has its own nuances:
- The method is most effective for patients under 16 years of age, when the jaw tissue is not yet fully formed. For older patients, wearing braces may not help (depending on the individual characteristics of the problem).
- The duration of treatment can be up to three years. Braces cannot be removed until the end of the period prescribed by the doctor. In addition, regular visits to the dentist are required (to tighten the braces and change the arches).
It is worth noting that to eliminate a diastema, it will not be possible to place braces only on the incisors - the structure is installed on the entire dentition at once.
Records
One of the most affordable and effective methods for correcting interdental space. These removable structures are made of high-quality plastic and are secured to the teeth using screws, hooks and springs. Due to the created load, the incisors are gradually attracted to each other. The features of this technique include the following facts:
- Efficacy is guaranteed in patients under 12 years of age. It is up to this age that the bone tissue of the jaws is perfectly amenable to correction.
- The plates are not able to cope with significant defects. For example, when the gap is caused by serious dental diseases.
It is worth keeping in mind that, in fact, the plates do not move the teeth like braces, but simply hold them in a given position.
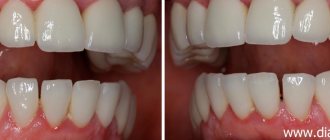
Veneers
Installing veneers can be considered the most efficient option for solving the problem with a chip. They are thin ceramic plates that are used to cover the front surface of teeth. That is, formally the gap is not removed, but closed. The procedure has its own characteristics:
- Veneers do not correct, but disguise the gap, therefore they are suitable only for those cases where the diastema is not a medical, but an aesthetic defect.
- Average service life is about 10 years. After this, the veneers will have to be changed.
- Before installing veneers, a small grinding of the incisors will be required.
Ceramic plates come in a variety of colors, so you can choose ones that will not differ from natural enamel.
Lumineers
Orthopedic onlays are as similar as possible to veneers, but thinner. They are also fixed on the teeth, closing the gap. Features include:
- longer than veneers, service life - up to 20 years;
- installation does not require extensive grinding of teeth.
As in the case of braces, lumineers do not solve, but mask the problem. In addition, they are not suitable for everyone, so you need to pay attention to the list of contraindications.
Cosmetic correction
A budget option that allows you to get quick results. The essence of the procedure is that the gap between the teeth is filled with a filling, which makes the diastema visually invisible. This correction is safe for health, painless and is carried out in one visit to the dentist. The features include the following facts:
- the problem is solved temporarily - the seal has a relatively short service life (5-7 years), so it will need to be replaced;
- The filling material changes color over time, which visually begins to differ from the native enamel;
- There is a risk of developing caries at the junction of the incisors.
Those who choose cosmetic correction to eliminate the gap will have to control the load on the “units” so that the filling remains unchanged and does not break.
Artistic restoration
The method is similar to cosmetic correction, but guarantees a longer lasting result. Using composite materials, the dentist builds up the tissue of the front teeth, closing the gap. As a result, the visual impression is created that the incisors are tightly closed. Features of artistic restoration:
- the most natural appearance after the procedure (photopolymers are matched to the color of the native enamel);
- Just one visit to the dentist is enough to get the desired result;
- the procedure is safe for health and has no contraindications.
The main similarity with cosmetic correction is that after artistic restoration you will also have to control the load on the incisors when eating.
Crowns
Plastic, ceramic or metal-ceramic crowns perfectly solve the problem of diastema. In this case, the cap-shaped design completely covers the teeth (in the case of a gap, it is necessary to apply crowns to both) and does not stand out in any way in the row. Features of installing crowns:
- average service life 10-15 years (depending on the material);
- safe for health;
- preliminary turning of the cutters is required.
The installation of crowns for diastema is not used as often as other methods.
Implants
Implantation is used if the cause of the gap between the incisors is the absence of one or more teeth in a row. Filling the empty spaces will not allow the “ones” to continue to “spread out.” But, even if the dentition is replenished, the gap will remain and will have to be eliminated using some other of the listed methods.
Mouth guards
They are removable orthopedic structures that are manufactured using 3D technology. They look like original “cases” that are put on the teeth and are visually invisible. The mouthguard creates pressure, forcing the “ones” to move in the desired direction, which leads to their closure.
The duration of use of mouth guards (depending on the complexity of the problem) is from three months to three years. During this period, sequential replacement of the aligners is carried out, carried out as the “ones” move. From time to time, the mouthguards are allowed to be removed.
How to get rid of diastema? Treatment options
There are several treatments for diastema. From surgery to orthodontic treatment. The choice of method for closing a gap between teeth depends, of course, on the cause of its occurrence, as well as on the severity of the problem. The wishes of the patient himself are also important here. If the cause of the gap between the central incisors is the frenulum of the upper lip, first of all its surgical plastic surgery is done, that is, it is trimmed. But subsequent actions will depend on the wishes of the patient.
The gap between teeth can be eliminated using the following methods:
- Therapeutic
, through artistic restoration with composite veneers. - Orthopedic
, when the defect is closed with ceramic veneers or crowns. It looks better than with composite material. - Orthodontic
method. The most durable, but also the most loyal and high-quality in relation to dental tissues, because they are not ground or sharpened in any way. Transparent dental aligners used nowadays can easily cope with diastema. They are completely invisible to others and do not cause any problems to the patient. Today, treatment of diastema with the help of aligners is the most invisible and fastest way to correct the defect of empty dental space - the gap between the teeth, which causes so much discomfort to its carriers.
By the way, you can find out in 1 minute whether aligners are right for you at all or whether doctors will forcefully offer only braces: you need to answer only 9 express questions
.
Preventive actions
As you know, preventing the onset of a disease is always easier and cheaper than treatment. To prevent the appearance of gaps between teeth, you must follow basic rules:
- control the habit of chewing hard objects (for example, seeds, nuts, crackers, threads, wire, etc.);
- carry out proper hygienic care of the oral cavity (to maintain the health of the gums and prevent the spread of bacteria, it is very important to brush your teeth correctly, carefully brushing not only the chewing units, but also the canines and incisors);
- Conduct timely examinations with a dentist (this allows you to diagnose any deviation in time and begin treatment at an early stage).
If the cause of the appearance of interdental gaps is a genetic predisposition, it is very important to begin correction as early as possible. Maximum effectiveness is possible during the period when the teeth are still mobile in the gums and can be rebuilt.
Now you know exactly how to remove the gap between your front teeth, what methods are used for this and how long it takes to eliminate the defect. All that remains is to consult with an orthodontist and, after examination and research, choose a method for eliminating the diastema that is right for you.
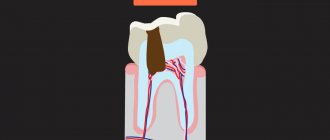
Stages of development of a wedge-shaped defect
The wedge-shaped defect develops gradually. The following stages of process development can be distinguished:
- First changes in enamel. A small area at the base of the tooth darkens slightly and loses its shine. Over time, it will develop pigmentation. At this stage, the future defect can only be seen using a special device.
- Superficial lesion. At the base of the tooth there is a noticeable crack, at its widest part not exceeding 3.5 mm. The gums sag, the neck of the tooth is exposed. The patient is uncomfortable with food that is too hot or cold, but the pain quickly goes away.
- Progressive stage. The wedge-shaped defect deepens to 4 mm, becomes yellowish-brown, matte. The shape of the triangle is already clearly visible - the two affected planes of the tooth converge at an angle of 45 degrees. Teeth react painfully to temperature stimuli and acidic foods. It is painful for the patient to brush his teeth. He feels the defect as a kind of step at the base of the tooth, where the remains of soft food are retained. At this stage, the diseased tooth is already noticeable to others when smiling and talking.
- Launched form. The enamel becomes thinner, dentin is affected, and in difficult cases, even the pulp. The wedge deepens to 0.5 cm, the neck of the tooth is exposed. If the destruction reaches the pulp, the neurovascular bundle of the tooth becomes inflamed. Acute paroxysmal pain appears, the tooth reacts to the temperature and taste of food, touch, the chewing process and causes a lot of inconvenience.
Read also
How to place veneers
The installation of veneers is performed for the purpose of aesthetic restoration of the dentition.
How long do you wear braces and what affects the timing?
When deciding on the use of orthodontic structures, patients are often interested in how long they wear braces on their teeth.
Diagnostics
A wedge-shaped tooth defect is usually identified by a dentist during a routine examination or treatment. He evaluates the location and shape of the pathology, the density of the tooth tissue. It is important to confirm that we are not dealing with dental erosion, superficial, cervical caries or enamel necrosis.
The doctor examines the patient’s dental status (oral hygiene, number of caries-affected, filled and extracted teeth, gum condition) and conducts a thermal test. This is a tooth reaction to temperature stimuli.
Vital staining helps in establishing the diagnosis: the wedge-shaped defect is well stained with iodine solution, but retains its color when treated with methylene blue. It is also important to determine what malocclusion pathologies exist and how they affect the occurrence of the pathology.
To exclude the influence of somatic diseases, the doctor may refer the patient to an endocrinologist and gastroenterologist.