In this article you will find answers to questions such as:
- why does caries appear between teeth?
- how is interdental caries treated?
- photos of the main stages of treatment.
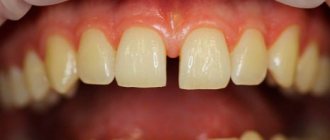
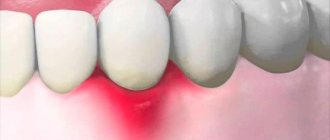
Caries between teeth is a carious lesion that is localized on the lateral surfaces of the teeth (in the interdental spaces). It must be said that this zone is the most favorite for the occurrence of dental caries, which is explained by two reasons. Firstly, after eating, food debris constantly accumulates in the interdental spaces, and secondly, very few people use dental floss every time after eating to clean the interdental spaces.
As a result, carious lesions of tooth enamel occur in the interdental space, which is accompanied by minor pain when eating sour/sweet foods, as well as thermal irritants (cold or hot). As the carious defect deepens, these symptoms then disappear. It should be noted that interdental caries can be difficult to diagnose in time, because this area is difficult to visually observe, and patients usually do not see a dentist in the early stages of caries.
Caries between teeth: photo
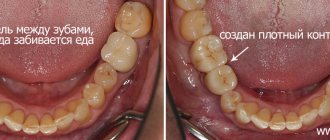
In dentistry, the treatment of interdental caries is not a simple task, because... here, in addition to restoring the side wall of the tooth, it is necessary to restore the contact point between the teeth. This last task is quite difficult for most dentists. Filling a tooth without creating good contact between the teeth in the interdental space leads to the fact that food will actively get stuck in it, and this, in turn, will provoke the development of secondary caries near the filling, as well as periodontal pockets.
Causes of caries between teeth
The causes of interdental caries are determined by the individual characteristics of the tissue structure and certain conditions - previous diseases, diet, location, crowding, hygiene:
- "metabolic explosion"
. Excessive sugar consumption provokes active production and accumulation of acid on the tongue, surfaces and pits. Demineralization occurs, the saturation of saliva with salts decreases, which contributes to the destruction of tooth enamel and the occurrence of caries; - tissue resistance
. The degree of resistance to the action of factors causing pathology depends on heredity, health status, and fluoride content in food/water. Manifests itself in the age-related dynamics of the onset of the lesion, the aggressiveness/prevalence of the process; - ignoring the rules of oral hygiene and dental care.
Clinical researches
Clinical studies have proven that regular use of professional toothpaste ASEPTA REMINERALIZATION improved the condition of the enamel by 64% and reduced tooth sensitivity by 66% after just 4 weeks.
Sources:
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of toothpaste “ASEPTA PLUS” GENTLE WHITENING” Author: doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Clinical and laboratory assessment of the influence of domestic therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste based on plant extracts on the condition of the oral cavity in patients with simple marginal gingivitis. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elovikova T.M.1, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor Ermishina E.Yu. 2, Doctor of Technical Sciences Associate Professor Belokonova N.A. 2 Department of Therapeutic Dentistry USMU1, Department of General Chemistry USMU2
- Report on the determination/confirmation of the preventive properties of personal oral hygiene products “ASEPTA PLUS” Remineralization doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of toothpaste “ASEPTA PLUS” COFFEE and TOBACCO Author: doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky. First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of commercially produced personal oral hygiene products: Asepta toothpaste used in combination with Asepta mouthwash and Asepta gum balm Head. Department of PFS Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor S.B. Ulitovsky St. Petersburg State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova. Faculty of Dentistry. Department of Preventive Dentistry.
Symptoms of interdental caries
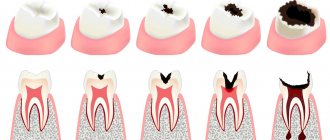
The features of the development and treatment of interdental caries are not very different from other types of carious lesions. There are 4 stages in total:
- Initial interdental caries - a small spot forms on a unit, invisible to the naked eye. To identify the initial stage, a hardware method is used.
- Superficial – the disease destroys the enamel. Darkening forms on it, it turns yellow and becomes rough, and sensitivity increases. But bacteria do not penetrate into deeper layers.
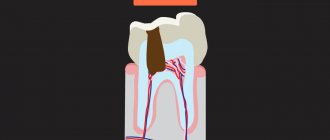
- Medium - at this stage the dentin layer is affected, the tooth reacts to irritants: cold, hot, sweet. The patient experiences severe pain.
- Deep - an advanced form of carious damage, pathogenic microorganisms penetrate into the root part. There is a risk of damage to healthy tissues and the development of periodontitis. At a deep stage, filling or restoration of the tooth is necessary.
How it manifests itself
Among the main signs of caries between teeth:
- increased sensitivity of units;
- intolerance to cold and hot food/drinks;
- frequently occurring sore throat;
- presence of bad breath.
It is important to remember that in the first stages the disease usually does not manifest itself in any way. Discomfort occurs in a person only when the structure of the enamel has already been damaged.
Diagnostics
- visual examination of the oral cavity
. It is performed using special instruments to assess the condition of the oral cavity. A dental mirror allows the specialist to carefully examine the distal surfaces: to detect the localization of spots, stripes/dots of black, brown color, and a carious lesion in the gap. The probe helps differentiate the depth of the cavity; - percussion method
. Intended for diagnosis and identification of pathological segments by tapping. The diseased unit reacts with a muffled sound, the patient experiences pain and severe discomfort; - radiography
. The x-ray image shows the distance of the lesion from the pulp, the level of prevalence of the process; - transluminescence
. Luminescence (transmission through a filter with an ultraviolet beam) and fiber optic exposure (transmission with a light beam) are practiced. Damaged areas appear darker than healthy areas; - coloring
. Application of staining markers (potassium iodide/methylene blue solution). The technique allows you to diagnose pathology and distinguish it from fluorosis/hypoplasia.
In difficult cases, fissurotomy (opening the grooves on the surface of the molars) and electroodontometry are used to determine the degree of pulp damage.
Read more about tooth pigmentation
Discoloration (from the English word “discolor” - “change color”) of teeth is their persistent staining caused by various influences. According to statistics, today it is very common: it is diagnosed in more than 80% of patients in dental clinics. There are more men among them: they account for more than half of the cases, or rather 60%. Of course, it happens that yellow spots on teeth appear due to poor hygiene, which causes increased accumulation of plaque... But sometimes the yellow color of teeth is an anatomical feature of tooth enamel and dentin.
However, if they change color abruptly, then the reason may lie in the effects of sealers, medications or resocin-formalin. A stain on a tooth can also appear due to traumatic damage due to mechanical impact. As a rule, patients with discoloration that has arisen due to the influence of several factors resort to the services of a dentist. Experts have established a relationship between the color of enamel, its resistance, the correctness and regularity of oral hygiene measures.
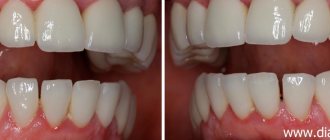
Treatment of caries between teeth
Treatment of caries between teeth is long and complex, since the doctor has to work with two units - to regenerate their anatomical structure and eliminate the carious lesion. When sanitizing the front teeth, it is also important to achieve an aesthetic result:
- remineralizing therapy
. Remineralization is carried out at the spot stage and involves restoration with the help of fluorine/calcium-containing preparations; - Icon technology
. The modern infiltration method is effective for minor dentin deformations (no more than 1/3): a sealing polymer composition is applied to the damaged area, restoring the density of the enamel; - filling
. The classic method involves installing a filling; in case of serious damage, it may be necessary to install an inlay/pin; - prosthetics
. Restoration with crowns/inlays is practiced for volumetric damage, in the absence of alternative options.
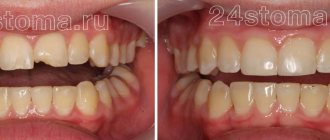
Before and after
Contraindications:
- First trimester of pregnancy;
- Bleeding gums;
- It is not recommended to carry out treatment during the period of illness with herpes and acute respiratory infections. It is better to postpone a trip to the dentist until you have fully recovered.
Why isn't every spot a black tooth decay?
There is no need to think that dentists are being cunning, wanting to deliberately turn an initial carious cavity into mid- or deep-stage caries.
After all, the more complex the problem, the more expensive its treatment. No doctor does this. It’s just that the identified violation has a completely different origin. In reality, dark spots can represent:
- Consequence of hypoplasia. This is a dental disorder in which, during the formation of a tooth, its crown part is underdeveloped. The disease is a consequence of metabolic disorders in the buds of teeth. It can also develop due to improper metabolism of proteins and minerals in the fetal body during its intrauterine development. Rickets, somatic pathologies, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, severe infectious diseases - all these are also factors that provoke hypoplasia.
- The result of fluorosis. This disease occurs due to the constant and prolonged ingestion of large amounts of fluoride into the body. First, whitish spots form on the crowns, and then depressions resembling black caries. During examination, the doctor records destructive and erosive changes in the enamel.
- Erosion of teeth. Another type of non-carious lesion of tooth enamel. Defects occur on the outer layer of the crown and can even affect the dentin. Erosive defects are most often localized symmetrically. They provide an unsightly cosmetic effect and therefore require urgent correction.
In many non-carious pathologies, it is possible to improve the aesthetics of a smile through remineralization. The patient is prescribed vitamin and mineral complexes, calcium and phosphorus supplements, and local applications. Electrophoresis is used in many clinical situations.
Only with voluminous cavities reminiscent of black caries do they resort to filling material. If the damage is very severe (which happens when a person puts off visiting the dentist for a long time), even prosthetics may be required.
It is important to understand that caries is always a cavity of microbial origin. That is why it has to be drilled out to remove all damaged tissue and prevent further spread of pathogens. From this position, not every even point on the tooth requires the use of a drill.
Features of the treatment of caries between the front teeth
When treating front teeth, it is important to preserve not only their functionality, but also their aesthetics. Therefore, the dentist is required to have extensive experience and skills in artistic restoration. Treatment of anterior teeth has several nuances:
- Carious lesions develop quickly due to the thin layer of dentin and enamel.
- During sanitation, it is necessary to achieve high aesthetic indicators, which is quite difficult with interdental caries.
The dentist carefully removes the affected tissue from the walls, and then restores the damaged teeth and interdental space. All medical procedures are performed under local anesthesia. There is an opinion that caries between the anterior units of the lower jaw is much easier to treat than on the upper jaw, but this is only a myth. There are no particular differences in the treatment protocol for the lower/upper dentition. To preserve beauty, a durable filling with high aesthetic indicators is installed on the front and side units. The most popular option is artistic restoration using compomer and reflective filling materials that preserve the aesthetics and natural appearance of the tooth.
Painfulness of the procedure
Most people are afraid of the procedure precisely because of toothache, but modern technology and the use of anesthesia eliminate this ailment.
The session is completely painless. To reduce the likelihood of discomfort, all manipulations are carried out after the administration of an anesthetic. If there is no nerve, the procedure is performed without anesthesia. The patient may feel slight pressure on the gum.
An exception is intolerance to certain medications used for anesthesia. The choice is made in favor of a similar drug with a different active substance.
After the injection, no painful sensations are observed.
It hurts if there is a strong inflammatory process at the root apex and in the canals. Unpleasant sensations occur only when the drug gets into the periodontal tissues. They go away instantly after increasing the dosage of the painkiller.
Some pain is possible if there is a deep stage of carious lesions, depulpation or canal treatment is performed, or sensitivity is increased.
Features of the treatment of caries between chewing teeth
Although molars are located in the lateral part of the jaw and are practically invisible when smiling, interdental caries is especially dangerous for them, as it is often diagnosed already at the stage of deep damage, when the dentin layer of one or more chewing units is affected. Very often the disease affects the pulp of two teeth. This situation is the most unfavorable, since endodontic treatment of canals is a long and expensive process and is performed only by an experienced dentist. If you do not start fighting the disease in a timely manner, the patient may encounter complications in the form of periodontitis, pulpitis (nerve inflammation), etc.
When filling molars, special attention is paid to the strength and durability of the filling material. To restore them, high-quality glass ionomer fillings are used.
Content:
- Why isn't every spot a black tooth decay?
- When there is black caries, but it is still not treated
- How to deal with little black caries
- When black caries still needs to be filled?
Sooner or later, small dots or dark-colored depressions appear on the teeth of any person. They are usually perceived as caries. But, when visiting a dentist, the patient may be told that he does not need to treat his teeth. Why is this happening? Is it true that not every black spot on the crown of a tooth is a cavity?
Prevention
Preventing the development of interdental caries is quite simple. To do this, it is enough to follow the recommendations of dentists:
- It is recommended to clean your teeth after each meal, moving the brush up and down to remove as much food debris as possible in hard-to-reach places. For care, use pastes that improve the protective properties of enamel.
- Rinse your mouth several times a day. It is not necessary to use special solutions; boiled water will be enough for cleaning. Additionally, use an irrigator.
- It is better to avoid foods such as chips, chocolate, and crackers, as their particles settle tightly in the interdental space and become a haven for bacteria. As a last resort, carry dental floss with you.
- Visit your dentist's office every six months for a checkup and professional cleaning.
To find out the cost of treating caries between teeth, sign up for a consultation at Dr. Razumenko’s dental clinic in Moscow by phone.
Preventive measures for “white caries”
The main component of dental health and prevention of caries development is compliance with the rules of prevention:
regular and proper oral hygiene. It is necessary to brush your teeth not only with a brush, but also after each meal you should use dental floss. After removing pieces of food with a thread, it is advisable to chew chewing gum for 5 minutes;
- Maintain a nutritious diet and try to avoid frequent snacks between meals. A common cause of caries is frequent consumption of sweets, flour, candies, chips, fast foods, and carbonated drinks. For dental health, the diet should contain fish, vegetables, fruits, kefir, nuts, cottage cheese, milk and other products with a high content of fluorine, phosphorus and calcium;
- periodically carry out professional teeth cleaning and treat the enamel with fluoride-containing preparations.
If you follow these basic rules, you can keep your teeth strong and healthy. But in order to avoid complications and prevent the pathology from becoming severe, you need to regularly visit the dentist and, if necessary, carry out proper and effective treatment of caries in the spot stage.
Prices for treatment of caries between teeth
| Code no. | Name of procedures | Unit of measurement | Cost, rub. |
| 101 | Repeated treatment and diagnostic appointment of the patient | 650,00 | |
| 300 | Application anesthesia | 150,00 | |
| 301 | Infiltration anesthesia, conduction | 550,00 | |
| 303 | Treatment of medium caries (ultrasound, cavity formation) | 650,00 | |
| 307 | Placement of a light-composite filling (Sonicfil, Estelite) | 3 950,00 | |
| 310 | Recovery from significant damage is complex | 1 unit | 5 500,00 |
| 313 | Artistic restoration (front, side teeth) simple | 1 unit | 11 000,00 |
* The prices indicated on the website are not a public offer. The exact cost can only be determined by visiting a doctor.
Prices for treatment in Moscow full price list
Share on social media networks:
Article Expert:
Ustinova Elena Fedorovna
Doctor of the highest category. Root canal treatment (complex, repeated retreatment), microprosthetics with ceramic restorations.
Work experience 15 years
Case from practice
I remember a patient who came to see me with advanced caries between her teeth. The destruction was significant, the girl was nervous, afraid not only of the dissection, but also of the injection. It is difficult to work with frightened patients; fears must be dispelled. Before administering the anesthetic, I treated my gums with Lidocaine, the girl realized that it wouldn’t hurt, and she calmed down a little. Fortunately, the pulp was not exposed, and the treatment was successful. But due to deep lesions on the lateral surfaces, both dental units had to be restored with ceramic crowns.
We recommend that you read
Dental treatment during pregnancy
Treatment of anterior teeth
Dental filling
Canal filling
Types and clinical manifestations of dental pigmentation
According to the etiological factors, two groups of discoloration are distinguished:
- Endogenous – caused by the influence of internal factors (diseases, tetracycline intake);
- Exogenous – caused by external factors (exposure to dyes, traumatic injuries).
The symptoms of pigmentation are difficult to confuse with any other:
- Loss of tooth enamel of its natural transparency and shine;
- The appearance of anatomical grooves on it;
- The appearance of white, yellow, brown or black spots on it;
- Its color is pinkish, yellow or gray.
The diameter of the spots can vary: from small dots on the enamel to changes in the color of the entire tooth. Discoloration is often accompanied by halitosis, bleeding and soreness of the gum tissue, and tooth mobility. They talk about the development of periodontal tissue diseases. Specific manifestations and the speed of their appearance depend on the general condition of the patient’s body, as well as the causes of the pathology:
- With hemolytic disease, tooth enamel and dentin look grayish-blue, green or brown, the enamel structure is damaged, there are signs of hypoplasia (partial/complete absence of enamel);
- Taking tetracycline antibiotics is accompanied by a gray-yellow coloration, the intensity of which depends on the total volume of the drug taken. Possible combination with hypoplasia;
- Erythropoietic uroporphyria is characterized by red staining of the enamel, hair loss, and increased sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation.
As for discoloration due to exposure to food pigments, the change in enamel color directly depends on what kind of food it was stained with.
Is it possible to independently determine the disease?
Lateral dental caries can be determined by personally completing the following steps:
- With the help of a mirror and good lighting, you can see the color differences between the main and infected parts of the tooth. The dark spot is visible through less transparent enamel.
- Painful sensations after contact with thermal and chemical irritants.
- Unfavorable odor from the mouth. Carious bacteria, together with food debris, “trigger” the process of decay, which is accompanied by a bad aroma.
Diagnosis of dental discoloration in CELT
Before making a diagnosis, our dentists conduct comprehensive diagnostic tests, which include:
- Taking anamnesis and performing a dental examination;
- X-ray (allows you to identify violations of the internal structure);
- Rheodentography (determines the condition of the pulp and the depth of the lesion);
- Computed tomography (providing images of teeth in three-dimensional format);
- Microscopy (multiple magnification makes it possible to assess the condition of the enamel);
- Electroodontodiagnostics (determines the condition of the tissues located around the tooth root).
Pigmentation must be differentiated from necrosis and erosion of tooth enamel, as well as from Capdepont disease.