Advantages of glass ionomer cement
By choosing fillings made from this material, you get:
• guarantee of complete safety for dentin and pulp. This type of cement does not emit any toxins, does not react with tooth and oral tissues, and does not cause allergies; • a noticeable reduction in the price of treatment. Availability and relative cheapness; • glass ionomer cement can significantly reduce the overall cost of caries treatment; • increased adhesion. The cement adheres well to the tooth tissue, which ensures complete immobility and tightness of the filling; • additional therapeutic effect. After installing a cement filling, it releases fluoride compounds for a long time, which strengthen the tooth and improve its condition; • low thermal conductivity of the material.
What are the benefits of a glass ionomer cement filling?
Firstly, the material is non-toxic and hypoallergenic, which is why it is often used in children's dental clinics. Glass ionomer cement (GIC) is biocompatible with the human body; its thermal properties are identical to those of dental tissues. This almost completely eliminates depressurization of the seal. Differences between GIC and other types of filling materials:
- Antibacterial action. Fluorides in the composition prevent inflammation and relapses of caries.
- Excellent adhesion. Glass ionomer bonds very firmly to dentin.
- Relatively low price of cement. Treatment using GIC is available to most patients.
- Preservation of teeth. For filling, you do not need to drill a deep hole, so there is no risk of injuring the dental tissues or pulp.
Disadvantages of glass ionomer cement
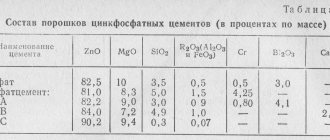
• long time for final hardening of the material. In some cases it can be about a day; • short working hours. In a short period of soft consistency of the material, the dentist cannot always adequately restore the chewing surface of the tooth; • surface roughness. Glass ionomer cement fillings are difficult to polish; • low aesthetics. Most glass ionomer materials are produced in colors that are not entirely typical of natural teeth. This partly contributed to the emergence of colored cements, which have become widespread in pediatric dentistry; • high shrinkage and abrasion of the material; • the need to form a cavity in the tooth with parallel walls.
Popular dental materials
Fillings are divided into permanent and temporary. A permanent one is placed when there is minor damage to the tooth crown, a temporary one is used for long-term complex treatment or diagnostics. A temporary filling is also used to protect medicinal compounds during dental treatment: a medicinal compound is placed under it.
The materials from which fillings are made are divided into several types:
- cement, silicate;
- plastic;
- metal, amalgam;
- ceramics;
- composites.
Depending on the material used, fillings are divided into several main types:
- cement;
- composite;
- compomers.
The dental industry also produces other types of fillings - plastic, metal and ceramic.
The most durable material is made from light-curing composite. Such fillings are expensive, but the high price justifies the long service life. The fillings look aesthetically pleasing and have the ability to change their shade with changes in lighting.
The most popular material is dental cement. These fillings are still in demand among patients due to their low cost, high adhesion and strength. The fillings literally stick to the surface of the crown and do not form air gaps.
Features of the use of glass ionomer cement
Glass ionomer cements are most often used in pediatric dentistry, as they are unpretentious to difficult placement conditions. This type of material is used to fill carious cavities and seal the fissures of recently erupted permanent teeth.
In adult dentistry, glass ionomers are used for permanent fillings, as an insulating lining for more aggressive types of materials, and for fixation of orthopedic fixed structures (crowns and bridges). Also, in some cases, glass ionomer cements are used for filling root canals.
Filling teeth with glass ionomer cement is possible only if indicated. Using them in other situations, guided only by the desire to save on treatment, means creating a serious risk of rapid destruction of the filling and the occurrence of a relapse of the inflammatory process inside the tooth.
Why use dental fillings?
Regardless of whether the tooth was mechanically damaged or as a result of caries, it must have a filling. The absence of a filling exposes the tooth to external factors. This, in turn, leads to further destruction and exposes the patient to pain.
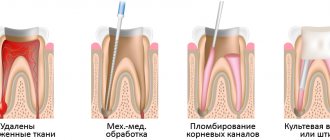
When caries is advanced, pulpitis appears, which in turn leads to health problems. In such situations, endodontic treatment (root canal treatment) is necessary, which is more invasive and expensive than simply installing a filling.
Untreated teeth negatively affect the entire body. The bacteria that spread after it can disrupt the functioning of very important internal organs, including the heart and kidneys. This is a very serious problem, so the use of a dental filling is necessary. Even small cavities can quickly turn into much larger problems.
Which material to prefer
The dental compositions described above have their own characteristics, advantages and disadvantages. Which filling do you prefer? Which is better - light or chemical (ordinary)? The choice will depend on financial capabilities and the location of the tooth in the oral cavity - posterior molar or frontal.
It is preferable to place fillings made of durable, indelible compositions on posterior chewing molars. For example, metal, glass ionomer or nanocomposite materials.
If we consider from an aesthetic point of view, it is better to put light or ceramic fillings on the front teeth, which are identical to tooth enamel and are invisible when smiling. Light dental products are characterized by a certain fragility, and therefore cannot withstand heavy chewing load on the rear molars.
To restore a chipped or damaged tooth in the front rows, light fillings are used. Using a composite material, you can completely restore the shape of a tooth, which will look organic. A distinctive feature of the light composite is the versatility of choosing a color to match the tone of the natural enamel of the teeth.
If we consider the quality of the composition from the standpoint of durability, then the most durable materials are metal and photocomposite - a service life of more than ten years. All other trains last from four to five years.
Sources used:
- Klyomin V. A., Borisenko A. V., Ishchenko P. V. Combined dental fillings. MIA, 2008
- Practical therapeutic dentistry" (Nikolaev A.)
- Scheller-Sheridan C (8 May 2013). Basic Guide to Dental Materials. John Wiley & Sons.
- https://www.dentalhealth.ie/
Plastic, metal and ceramic compounds
Plastic fillings are also at the peak of popularity, also due to their low price. Plastic has many disadvantages:
- gives significant shrinkage after curing;
- changes its color over time;
- quickly wears out and becomes unusable;
- poorly protects against secondary caries.
Important! Cement and plastic fillings are placed in free dental clinics.
Ceramic compositions
The distinctive characteristics of this material are high strength, lack of shrinkage and aesthetics. Ceramics does not darken during use and is not painted. In modern dentistry, ceramics is considered an almost ideal filling material. Types of ceramics include:
- transparent material;
- pressed material;
- metal ceramics.
The disadvantages include the difficulty of installation: the composition fills the hole in the tooth, like an inlay. The inlay is formed using an impression of a previously sanitized tooth.
Metal alloys
Amalgam material includes a mercury compound along with silver. The dangers of exposure to mercury in the body pose a certain health risk. The advantage of amalgam is its long service life and abrasion resistance.
Another disadvantage of this material is expansion during hardening. If the dentist does not correctly calculate the volume of the filling, the possibility of slight destruction of the crown cannot be ruled out.
Due to the unaesthetic appearance of metal structures, they are used on back teeth or the hidden surface of the crown.
Types of dental fillings, their cost, pros and cons
They are an alloy of metals with mercury. Yes, yes, you heard right - until recently, such fillings were installed en masse on chewing teeth. Silver amalgam contained up to 60% silver and very little mercury, and was more dangerous for the doctor during the manufacturing process than for the patient. The finished mass could not be called particularly toxic, but there was little joy from it aesthetically. And it took 3-4 hours to harden, not to mention the fact that sudden changes in cold and hot could lead to cracks in the amalgam. Even the obvious plus - excellent wear resistance - cannot cover the other disadvantages of any type of metal fillings. Currently, they are practically not installed even in public dentistry, not to mention elite clinics.
Cement fillings
A budget option when you simply don’t have enough finances for anything more. They are considered “better than nothing” and will at least cover the tooth cavity until they fall out. Permanent cement fillings should not be confused with dental cement, which is used to fix orthopedic structures and microprostheses: they use a special, especially durable material. Standard cement fillings are made from phosphate or glass ionomer cements. They are easy to knead, they are very cheap, but that’s probably where their advantages end. Even if the doctor performs the filling with exceptional care, he will not be able to achieve a perfect fit of the filling to the walls. The doctor does not have the opportunity to work with this type of material inside the tooth cavity, because... the cement sets in a matter of minutes. Over time, a gap will form between the filling and the tooth wall, where food debris and bacteria will find a home. The strength of cement fillings also leaves much to be desired; they wear out quickly. To be fair, it should be noted that glass ionomer cements have found their use in pediatric dentistry and are installed on baby teeth, but they cannot be seriously considered as full-fledged restorations in adults.
Plastic fillings
They are produced on the dental market:
- acrylic based;
- based on epoxy resins.
Acrylic fillings made of plastic have proven themselves well in aesthetic terms, because... the material has a wide color palette to choose the desired shade. Sufficient professionalism of the doctor will allow the filling to last for several years and withstand normal chewing loads. But, alas, this type also has disadvantages. Plastic is a porous material where bacteria settle, contributing to the development of dental pathologies. Acrylic fillings cannot be installed in case of deep caries, because... There is a high risk of pulpitis occurring after some time. If the patient often consumes dyes or smokes, the filling will quickly darken and lose its appearance.
Fillings based on epoxy resins have better characteristics than acrylic polymers. Toxicity still occurs, but here it is much less. Fillings of this type are more durable and safer, but they cannot be used to restore the frontal group due to the fragility of the material. And the resin-based composition darkens after just a couple of years. Thus, the object of their use remains chewing teeth.