The need for suturing in dentistry
Surgical intervention and, as a consequence, suturing are indicated for the following manipulations:
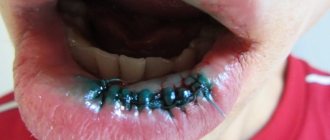
- Removal of wisdom teeth - third molars differ from the rest in the large size of the tooth crown and its root. Late eruption, the position of the “extreme” in the dentition very often leads to a violation of the physiological location of the tooth or even its impaction (partial or complete failure to erupt). In this regard, the procedure for removing a wisdom tooth is often accompanied by complications - extensive damage to the soft tissues of the oral cavity and alveolar process, ligaments, and blood vessels. To avoid this kind of consequences, dentists apply stitches to reduce the wound.
- Implantation - its implementation is always accompanied by the need for surgical intervention. A deep incision in the gum requires suturing.
- Maxillofacial operations - elimination of the consequences of traumatic injuries, congenital defects of the dentofacial apparatus.
- Removal of tumors of various etiologies - the integrity of the soft tissues of the oral cavity is damaged, often requiring layer-by-layer sutures.
Care after sterilization
Many novice dog breeders are concerned about what kind of stitch a dog should have after the sterilization procedure. In most cases, suture removal is not required, since modern materials promote rapid healing and dissolve on their own. The main thing is to keep the operated area clean and timely treatment.
To protect the seams from bacteria and mechanical damage, use a special blanket with ties on the back. Since the thin, breathable material quickly becomes dirty, the bandage should be changed once a day. The new blanket must be ironed and only then put on the dog. When treating seams with chlorhexidine, the device is not removed; it is enough to simply move it to the side by untying several tapes.
The animal may try to rip off the bandage in order to scratch or lick the cosmetic seam. This should not be allowed, as infection may enter the area undergoing surgery. In these cases, an Elizabethan collar is put on the dog.
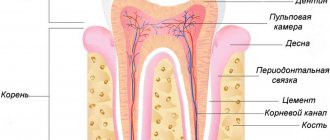
Types of sutures and materials used in dentistry
To facilitate and accelerate the healing process of postoperative wounds in the oral cavity, the following types of sutures are used:
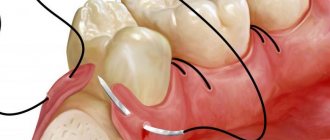
- nodal - used when it is important to ensure equal tension on both edges of the wound (for example, between teeth);
- continuous - when a violation of the integrity of soft tissue occurs along several dental units;
- single - each stitch is knitted separately from each other.
Threads used for suturing in dentistry can be made of absorbable and non-absorbable material.
Absorbable threads:
- from catgut - which contains a foreign protein, which is perceived by the body as a foreign body, and therefore often causes inflammation of the damaged soft tissue of the patient’s oral cavity;
- “Vicryl” is a synthetic material made from polyclatin and polyglycomic acid, which does not cause the risk of developing inflammatory processes even during complex operations.
Threads made of absorbable material do not require the removal of sutures; they disappear within 2-5 weeks.
Material for non-absorbable threads:
- silk is an easy-to-use material, highly durable, but has a significant drawback - it causes inflammatory processes in soft tissues if not removed 7 to 10 days after surgery;
- monofilament is a thread made of polytetrafluoroethylene, which is durable and does not cause inflammation, but has a rigid structure that can damage the mucous membrane. To exclude this possibility, a bandage is applied to the wound surface;
- polyester is a woven thread often coated with silicone for elasticity and smoothness. A very durable material that does not lead to inflammatory processes, but requires careful fixation in the form of knots.
Recovery after intervention
Conventionally, the rehabilitation process consists of 2 periods: early and late. After the procedure, the patient spends a couple of hours in the clinic. The doctor prescribes antibiotics and painkillers. A special compression bandage is applied to the head. Before discharge, the doctor examines the operated area and makes recommendations. The patient goes home.
Dressings are performed 2 more times: the next day after the procedure and at the end of the early period, before removing the suture material. The sutures after otoplasty are removed within 7-10 days.
During the early rehabilitation period you cannot:
- wash your hair for the first three days;
- exercise;
- remove the bandage;
- sleep on the operated ear;
- remove the stitches yourself.
Only strict adherence to the recommendations will avoid complications.
When and how is the procedure for removing sutures in dentistry performed?
The time for suture removal is determined by the dentist, guided by the process of regeneration (healing) of the soft tissues of the mucous membrane, which depends on:
- on the age of the patient;
- complications of surgical intervention;
- presence of complications.
Usually, sutures are removed 5-10 days after they are applied.
The dentist removes sutures as follows:
- the surface of the wound is disinfected with an antiseptic;
- if the patient has a low pain threshold, local anesthetics are used (but usually this is not necessary);
- Using surgical scissors and anatomical tweezers, the dentist carefully cuts and removes the threads from the healed wound;
- a visual examination is carried out to check the integrity of the wound;
- Disinfection of the suture prevents the risk of wound inflammation.
Sometimes sutures are removed due to the risk of suppuration in the area of the operation. In this case, the sutures are removed, sanitizing procedures are performed and appropriate antimicrobial therapy is prescribed.
Suppurating atheroma on the face
Ordinary atheroma in itself is not dangerous. The exceptions are cases of localization on the face and suppuration. Causes of festering atheroma on the face: infection, complications after a poorly performed operation, advanced form of the disease.
Symptoms of the disease:
- general weakness, enlarged regional lymph nodes;
- temperature increase;
- redness in the area of the tumor;
- swelling;
- cyst enlargement.
Treatment of suppurating atheroma is only surgical. The surgical intervention consists of two stages. Your doctor will tell you at a personal appointment about the day on which the sutures are removed after surgery to remove atheroma.
Hygienic oral care after suture removal
To quickly restore the integrity of the soft tissue of the oral cavity, the patient must:
- Use a soft toothbrush to brush your teeth daily;
- use anti-inflammatory rinses;
- rinse the mouth with warm water or a decoction of medicinal herbs after each meal;
- Avoid eating hard, sour, salty, spicy foods that can irritate the mucous membrane.
Timely removal of sutures, maintaining oral hygiene, and performing procedures prescribed by the dentist will ensure good wound healing and speed up recovery.
When not to remove stitches yourself
On average, healing takes 1-2 weeks, but you should focus on the appearance of the tissue. You can remove stitches yourself only from small, well-healed wounds. It is better to refuse the procedure in the following cases:
- after serious abdominal operations, especially with large-scale blood loss and weakening of the body;
- the incision site is inflamed, painful or suppurating;
- the wound is in a hard-to-reach place or on the face;
- the edges of the tissues are tied together with metal staples (removal of staples after surgery must be carried out by a doctor).
If touching the wound and sutures causes severe discomfort, they should not be touched. Sometimes the threads grow into the tissue, which also requires medical intervention.
Healing time for external sutures on the perineum
It's no secret that all mothers who have just given birth are interested in the question of how long postpartum sutures last. The healing process is directly related to the size of the wound surface, the correctness of care during the recovery period, the general condition of the woman’s body, and the techniques and materials used when suturing. If self-absorbable threads (natural or synthetic) were used during suturing, healing will take about two weeks, and scar formation when using metal staples or non-absorbable threads takes longer - 15-30 days; in the latter case, the sutures are removed in the maternity hospital before discharge, approximately on the seventh day after birth.
How to remove stitches after surgery
If you decide to remove the stitches yourself, please read the instructions below.
You will need:
- surgical or manicure scissors or scalpel;
- tweezers;
- antiseptic (hydrogen peroxide or alcohol);
- magnifying glass;
- sterile bandages;
- antibiotic ointment.
Everything you need must be at hand, so prepare thoroughly before starting the “operation”. Before work, tweezers and scissors/scalpel must be thoroughly disinfected in boiling water and treated with alcohol so as not to introduce infection into the wound. It is necessary to prepare a well-lit place; under no circumstances remove seams in the dark.
When all the tools and materials are prepared, you can start working:
- Rinse the stitched area thoroughly and then clean the wound with alcohol.
- Grab the first knot with tweezers and lift it slightly above the skin.
- Use scissors to cut the suture closer to the skin.
- Carefully pull the thread out of the skin (if bleeding appears, it means removal began before the wound has healed, so you need to consult a doctor).
- Remove the remaining seams in the same way. It is very important not to leave a single piece of thread in the leather.
- For greater safety, cover the wound with a sterile bandage.
Try not to pull the thread that was on the outside through the skin. This way you risk introducing an infection into the wound. To prevent this from happening, cut the suture as close to the skin as possible. Antibiotic ointment will be needed if the wound opens again. In this case, you need to re-stitch the stitches, and you can’t do it without a doctor.
Inflammation and temperature after dental implantation
Your body may also react to surgery with a low-grade fever, that is, an increase in general body temperature to 37°C. Even if the temperature stays within these limits for several days, this will remain the norm. You should be wary only when there is a persistent increase in temperature to 37.8-38°C. In this case, it almost certainly means inflammation, which requires immediate intervention (for example, in case of peri-implantitis, this should be sanitation of abscesses, bone regeneration, as well as professional oral hygiene).
In this case, you should not delay visiting a doctor: the inflammation can not only worsen on its own, but also lead to implant rejection.
How much does it cost to have stitches removed?
Removing sutures in Russia can cost 100-500 rubles. depending on regions. This procedure can be performed free of charge at a local clinic. But if you want to save time and nerves, go to a paid hospital.
The cost of the procedure depends not only on the region, but also on the complexity and location of the suture. The most expensive services are removal of sutures from the eyeball. Open areas (arms, legs, stomach) will be much cheaper.
Departure is paid separately - from 550 rubles
Request a call
Call:
+7 (499) 455-08-05
If you can’t go to the doctor, and you are afraid to carry out such a procedure yourself, you can use the service of suture removal at home. In Moscow, the price of the service may be slightly higher than in other regions. You don’t need to go anywhere - the specialist will come to you himself.
Withdrawal deadlines and important factors
The sutures must be removed in time, when the wound has healed securely. If the procedure is performed early, the wound may open. If you remove the threads too late, inflammation will begin. Only a doctor can accurately determine whether or not the sutures can be removed.
The approximate timing for suture removal is given below:
- face/neck – 6-8 days;
- abdomen and chest – 10-14 days;
- after amputation – after 12 days;
- legs/arms – 9-11 days;
- after caesarean section – 7-11 days.
In the mouth they are removed after 3-6 days, and permanent sutures are placed on other mucous membranes.
When removing sutures, it is necessary to take into account a number of factors that will affect the entire process: the age and well-being of the patient, the characteristics of the disease and possible complications, the nature of the operation and the recovery characteristics of the body. For example, you are unlikely to be able to remove the sutures in your mouth without causing more harm.
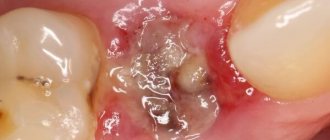
Why did you sew up the hole after tooth extraction?
If stitches were applied after wisdom tooth removal, this will only be beneficial. Repeated studies have proven that a sutured socket is:
- reducing the risk of infection and complications - by 90%;
- rapid stop of bleeding;
- preservation of the blood clot and natural healing of the wound;
- minimal pain after surgery;
- rapid fusion of tissues thanks to sutures.
Sutures are placed on the socket immediately after the removal operation. After which the doctor gives recommendations for accelerated healing and rapid normalization of the general condition.
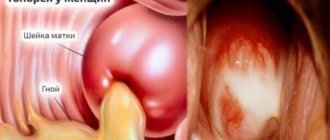
Rules for caring for postpartum sutures on the perineum
While the woman is in the maternity hospital, the sites of ruptures or incisions are treated by a procedural nurse - care consists of washing the sutures with hydrogen peroxide and then applying brilliant green or iodine to them.
Patients with stitches on the external genitalia upon discharge from a medical institution are required to receive recommendations on how to care for the intimate area.
Postpartum instructions include the following important points:
— Choose underwear of the appropriate size to wear. Panties that are too small or insufficiently wide can put pressure on injured areas and prevent stitches from healing. The material from which the underwear is made is also important; give preference to natural materials, preferably cotton - synthetic fabrics often cause skin irritation and various types of inflammation.
— Observe the rules of intimate hygiene: during this period, it is necessary to wash the external genitalia twice a day with simple soap without aggressive components and synthetic fragrances (scented gels should be avoided, but baby soap is ideal), and additionally wash your face every two hours and change your panty liner ; in addition, it is required to treat the genitals with warm water after each visit to the toilet. It is important to wash the seam on the crotch not only carefully, but also thoroughly; you can direct the shower stream at it.
- Douching is strictly prohibited!
— After hygienic manipulations, carefully blot your genitals with a towel; friction can damage already vulnerable tissues.
- Provide air flow to the genitals from time to time - periodically it is recommended to lie on a bed or sofa, take off your panties, spread your legs apart and bend them at the knees.
— Empty your bladder in a timely manner, otherwise the filled organ will put pressure on the uterus and prevent its contraction.