Causes and duration of pain Mechanism of pain Localization Stages of healing Possible complications When to see a doctor What to do after removal What not to do How to reduce pain
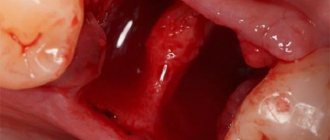
Tooth extraction (removal) is a surgical intervention accompanied by damage to the periodontal tissues (gums, bone socket, mucous membrane). Pain after tooth extraction is a normal reaction of the body to surgery. Depending on the complexity of the clinical situation, the volume of the operation, after the procedure, when the effect of the anesthetic wears off (after 3-4 hours), the patient begins to feel aching pain in the injured area.
Why and how much does it hurt?
Pain occurs due to traumatic swelling of tissues and compression of nerve endings. The more complex and extensive the operation, the more intense the gum pain after tooth extraction. Normally, symptoms after extraction of an incisor or molar are as follows:
- Aching pain persists for 1-3 days
, but subsides day by day; - slight swelling, hematoma, redness around the removed unit (may increase for 2-3 days
and then subside); - formation of a blood clot in the wound;
- the appearance of a whitish coating (fibrin, which accelerates tissue healing).
This is a normal reaction to surgery. How much a tooth hurts after extraction depends on the complexity of the operation, the characteristics of the body, the patient’s pain threshold, the location of the dental unit in the row (after extraction of molars, the injury is more extensive and worries longer). Normally, discomfort lasts
3-5 days
, gradually subsides and disappears on its own.
Tissues are restored
about
10-14 days
. By this time, the mucous membrane has completely healed, new bone begins to form inside the hole, which will completely fill the defect in about six months.
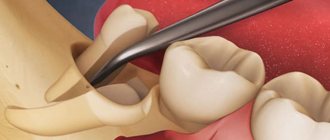
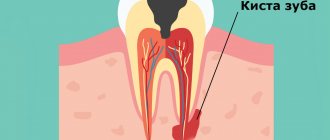
The most difficult to treat and remove is the 3rd molar (figure eight, wisdom tooth). They have very curved, intertwined roots. A wisdom tooth is often completely unerupted (impacted), covered with mucous or bone, and incorrectly erupted (dystopic). The operation is hampered by difficult access to the figure eight. Therefore, healing after a complex 3rd molar extraction may take longer (about a month). But if pain and swelling have not begun to subside a week after the intervention, you need to consult a dentist.
3.Applying ice.
After tooth extraction in our Center, a specialist will give you ice specially prepared for such procedures to apply in the first hours after extraction. Ice is applied for a certain time, at certain intervals, which the doctor will instruct you about. At home, this procedure will need to be continued for some time (the first few hours after removal). This is done in order to minimize or completely eliminate tissue swelling.
Under no circumstances should you heat the area in the area of the extracted tooth; in this case, suppuration will develop.
Mechanism of pain
- Trauma to soft, hard periodontal tissues;
- damage (rupture) of the connective tissue holding the tooth;
- destruction of blood vessels and nerve endings;
- swelling of the injured gum, pressure on nearby areas, poor circulation;
- irradiation of pain along the nerve trunks to other parts of the maxillofacial areas.
Pain after extraction of any dental unit is a natural reaction of the body to the intervention. No matter how carefully the surgeon acts, the integrity of the vessels, nerves, and fibers is inevitably compromised. It is normal for the extracted tooth to hurt for no more than 2-3 days.
, after removing the figure eight, the gums may bother you
for about a week
. If after 7-10 days the discomfort does not disappear, but continues or increases, you need the help of a doctor.
Localization of pain
As a rule, painful sensations are localized in the area of innervation of nerve endings injured during the intervention. Depending on where the hole is located, the pain can radiate to the throat, temple, or ear. Often, after tooth extraction, the neighboring tooth hurts. The most common reason is damage to soft tissues from instruments, which causes the gums around the wound to swell, begin to hurt, and the pain spreads further to neighboring units.
Incisors and canines usually have 1 root, which makes their removal the least traumatic. Chewing units have 2-3 or more roots, which complicates the operation and makes it more voluminous. The back teeth of the upper jaw border the bottom of the maxillary sinuses; after removal, the pain can radiate to the nasopharynx, cheek, orbit, and ear.
If after the removal of the lower tooth the jaw hurts, especially when it comes to multi-rooted chewing units (7, 8 teeth), this is normal. Usually such sensations go away within a few days. You need to go to the dentist if the pain does not subside after 5-7 days and is accompanied by other alarming symptoms.
What should the patient do after the procedure?
After the procedure has been completed, the specialist must carefully explain to the patient his next steps, as well as the rules for caring for the wound during the healing period.
- The turunda or cotton wool that was left by the surgeon in the hole does not need to be removed by yourself. If the tampon placed by the doctor falls out ahead of schedule, the patient must return to the specialist to install a new turunda. If this is not done, an infection may enter the wound cavity.
You shouldn’t remove turunda with medicine yourself
- If after the procedure the cheek is very swollen, you can apply ice or a cold compress to it. After this procedure, it is forbidden to heat the affected area and apply hot compresses.
- You can eat food after tooth extraction only two hours after the procedure. It is recommended to eat only liquid and light foods that do not contain solid pieces.
- A blood clot forms in the hole where the tooth was pulled out. It is prohibited to remove it or touch it. The first time after the procedure, you must brush your teeth with caution and do not use any rinses.
- For 7 days after tooth extraction, it is prohibited to carry out other interventions in the oral cavity.
- During the healing period, it is not recommended to overheat, for example, take a steam bath, and also exercise with caution. It is also strongly recommended to stop drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking cigarettes for two days after the procedure.
- After tooth extraction, pain often occurs at the extraction site. In this case, quite often not only the hole, but the whole head as a whole can hurt. Also, the patient may experience pain while eating, regardless of which side of the teeth he chews on. Experts recommend coping with these problems with the help of painkillers, such as Pentalgin or Tempalgin. In this case, it is advisable to take the drug in combination with Suprastin.
To relieve pain, you can take painkillers
Despite the fact that there is medicine in the hole, a person may still feel pain and some burning. Such unpleasant sensations will have to be ignored.
Important ! If the sensations intensify, it is recommended to consult a doctor again so that he can examine the wound and, if necessary, take action.
Video - Briefly about iodoform turundas
Stages of socket healing
- 2-3 hours
after
a blood clot (thrombus) forms
in the socket . It serves as a barrier to pathogenic microorganisms, preventing them from entering the wound. - The next 2-3 days
- the blood clot thickens, shrinks, the wound
becomes covered with a whitish coating
(fibrin film), the formation of granulation tissue begins inside the hole, the basis for the restoration of mucous membranes. - After 3-7 days
, the thrombus lightens, becomes whitish, the connective tissue has practically filled the hole, swelling and pain are minimal or completely absent. - After 7-10 days
, the hole has shrunk significantly,
new bone begins to form
, which will completely fill the defect after 4-6 months. - After 2 weeks
,
the gums have completely healed
.
What are the possible complications?
The intensity of pain must be carefully monitored. Unpleasant sensations must subside, otherwise it indicates the development of pathology. The gums hurt especially painfully after difficult removal if inflammatory complications develop:
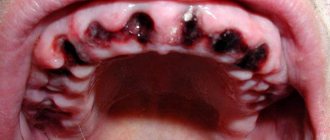
- Alveolitis is an inflammation of the bone socket and surrounding tissues. accompanied by acute, throbbing pain, redness, swelling, the formation of yellow, greenish, dark gray plaque, cloudy pus with a putrid odor. The cause of the complication is poor hygiene in the postoperative period, ignoring the drug therapy prescribed by the doctor.
- Dry socket - there is no blood clot in the socket, it is dry, empty, there is a yellowish-gray coating, a putrid odor. The reason is that the clot was not formed due to a blood clotting disorder; the clot was removed from the socket by the patient during hygiene, intensive rinsing, etc.
- Socket bleeding - may be associated with a blood clotting disorder, excessive damage to tissues, blood vessels, or a fracture of part of the alveoli.
- Facial neuralgia is a rare complication that occurs due to damage to the facial nerve during tooth extraction. Accompanied by numbness in the cheeks, tongue, lips.
- Periostitis is a purulent inflammation of the periosteum that develops for the same reasons as alveolitis. Accompanied by acute, diffuse pain that cannot be relieved with an analgesic. Swelling is pronounced, can spread to the neck, temperature is above 38℃, general intoxication of the body is observed (headache, weakness, etc.).
- Osteomyelitis is a purulent-necrotic lesion of the jaw bone, accompanied by throbbing pain radiating to the ear, temple, fever, swelling of the gums and oral mucosa, spasms of the masticatory muscles, deterioration in general well-being, and enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes.
Cheek pain after tooth extraction is a very common symptom, the duration of which depends on the complexity of the intervention. Normally, aching pain completely subsides after 2-3 days
. The picture is completely different when complications develop. With inflammatory complications, purulent foci form in the tissues, and the risk of spread of purulent contents through the general bloodstream increases many times over. There is a high probability of phlegmon, abscess, and destruction of bone tissue. Serious surgery and long-term rehabilitation are inevitable.
What medications should I take?
The rehabilitation period after bone grafting and sinus lifting includes the mandatory use of certain groups of medications. The doctor prescribes individual representatives individually, but the general scheme during rehabilitation is as follows:
- Antibacterial agents. Every patient takes such medications after bone grafting and sinus lifting, as they represent the main prevention of the development of an infectious process. The standard course involves a five-day intake of broad-spectrum agents.
- Antihistamines. These medications help reduce the activity of the inflammatory process and, accordingly, reduce the edema syndrome. They are taken for 3 days in a standard dosage.
- NSAIDs. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs help reduce swelling and inhibit the production of inflammatory mediators. On average, such medications are taken for 3-4 days.
- Analgesics. Painkillers are not included in the course of pathogenetic and etiological therapy during the recovery period, since they relieve only the symptom of pain. They are taken during the first week after surgery (during this period the discomfort should completely disappear) or even less. The doctor himself selects the appropriate drug for the patient and prescribes its dosage. It is forbidden to exceed the maximum daily dose and drink large amounts of medicine at a time. If the doctor forgot to tell you about the rules for taking analgesics, then the patient follows the instructions.
- Healing ointments. Special means to accelerate regeneration are used topically - smeared on the postoperative wound. Their use increases the regenerative abilities of tissues, and epithelization occurs faster. The doctor prescribes one, and sometimes even two drugs, which should be used according to a certain scheme.
- Antiseptic. A solution of Chlorhexidine or any other antiseptic is used for oral care. It is forbidden to rinse your mouth, but it is recommended to treat it and the wound surface in particular with this product after each meal.
- Calcium preparations. Bone grafting involves damage to bone structures. In addition, the condition of the teeth also requires some kind of replenishment. Not only calcium supplements, but also foods rich in calcium do an excellent job of this. This includes: cottage cheese, sour cream, milk and other dairy products.
- Vitamin C. Ascorbic acid helps not only improve immunity, as many believe, but also accelerate regeneration and improve overall metabolism. It is an indispensable component of any course that involves exhaustion of the body.
Each of the listed drugs helps to shorten the rehabilitation period and its successful course. You cannot ignore any of the dentist’s prescriptions, as this can lead to the development of various complications and unfavorable outcomes.
When do you need to see a dentist urgently?
- Severe, acute, throbbing pain that is not relieved by an analgesic, spreads across the face, radiates to the ear, neck;
- bleeding from the socket that does not stop, but rather intensifies;
- absence of a blood clot in the socket;
- bad breath;
- discharge of pus from the wound;
- the formation of yellow, dirty gray, green plaque on the wound;
- temperature rise above 38℃;
- numbness of a part of the face (gums, cheeks) for more than a day;
- pronounced swelling of the gums and cheeks, which does not decrease 2-3 days after extraction.
What medications should you not take?
Some drugs are ineffective or cause complications. Taking them after tooth extraction is not advisable. Such medications include:
- Aspirin. It has a weak analgesic effect and is more aimed at reducing temperature. In addition, it thins the blood, which can cause secondary bleeding and loss of the clot from the socket. Therefore, it is not used if the wound hurts after surgery.
- "No-Shpa." A popular drug, mistakenly believed to be a good analgesic. However, it only relieves spasm, which is completely ineffective in relieving symptoms if a canine, incisor, molar or wisdom tooth is removed.
- Paracetamol. Like aspirin, it reduces fever and has no analgesic effect. Can be used if it is necessary to relieve swelling when a wisdom tooth grows. However, it has a strong effect on the liver. The same applies to paracetamol-based drugs.
After extraction, the wound may hurt, so analgesics must be prescribed. They are taken for several days until the acute symptoms subside. The best remedies are “Ketanov”, “Nimesil”, “Ibuprofen”, “Analgin”.
What can and should be done after tooth extraction
- 20-30 minutes after the intervention, carefully remove the cotton swab
; - use cold compresses
for 2-3 hours after the intervention (take a break every 10-15 minutes to avoid tissue hypothermia); - for 3-5 days, make oral baths
with antiseptic solutions (take the solution, hold it in your mouth for a minute, spit); - When carrying out daily hygiene, avoid the injured area
, you can start using the toothbrush on the 2-3rd day, it should be new, with soft bristles; - chew on the opposite side
; - Eating is allowed after the anesthesia wears off (not earlier than 3-4 hours later
).
What is prohibited?
- To prevent accidental washing of a blood clot from the socket, it is forbidden to rinse your mouth. To treat the cavity, oral baths are quite sufficient;
- Hot compresses are prohibited, this stimulates severe swelling, the development of inflammation, and bleeding;
- You cannot puff out your cheeks, blow your nose too much, or sneeze;
- It is forbidden to touch the wound with your fingers, tongue, or objects;
- You can’t eat hot, cold, irritating foods; preference is for soft, warm, neutral foods;
- you cannot smoke or drink alcohol for at least a week - tobacco and alcohol slow down tissue regeneration;
- Hypothermia and overheating must be avoided - going to the sauna, swimming pool, solarium is prohibited for 5-7 days;
- Do not take aspirin or other blood thinners;
- do not engage in active sports, do not subject the body to excessive physical or sports stress.
How to reduce pain?
Analgesics will help relieve pain after removal of a molar (or any other tooth) - it is better if it is one of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Antihistamines will help remove swelling, and antibiotics will help prevent inflammation. The doctor will prescribe effective medications according to the clinical picture. Medicines should be taken strictly as prescribed. Treatment for pain after tooth extraction depends on the cause of its occurrence. The most important thing after the intervention is to scrupulously follow the dentist’s instructions and recommendations. This will help reduce recovery time and avoid complications.
Author of the article Voznyuk Vladimir Aleksandrovich Maxillofacial surgeon-implantologist of the highest category
Work experience: 28 years.
The best painkillers
Non-narcotic analgesics are used to relieve toothache. Most of them also have anti-inflammatory effects. Units should be pulled out with the obligatory subsequent administration of analgesics with anti-inflammatory effects.
Important! Painkillers after tooth extraction cause irritation of the gastric mucosa and the likelihood of increased bleeding. Therefore, they are stopped as soon as the intensity of symptoms decreases.
Most often, one of the following medications is prescribed.
"Ketanov"
Its effectiveness is tens and hundreds of times higher than that of other analgesics.
The most powerful medicine. Its effectiveness is tens and hundreds of times higher than that of other analgesics. It is especially useful if you need to numb a wound after a complex operation or a wisdom tooth. It has 2 release forms - tablets and injections. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and antipyretic drug based on ketorolac. Its analogue is “Ketorol”.
Capsules are taken symptomatically or 3 to 4 times a day at regular intervals with at least 100 ml of water. If necessary, increase the dose by 2 times. The maximum duration of the course is 1 week.
Injections are given intramuscularly, preferably in the thigh or shoulder. The daily dose is 3 mg for young people and 2 mg for older people.
Important! "Ketanov" should not be taken together with glucocorticosteroids, other anti-inflammatory drugs and drugs containing calcium. This combination will instantly lead to side effects from the digestive system.
"Nimesil"
The active ingredient is nimesulide. Relieves inflammation, swelling, reduces temperature and pain after wisdom tooth removal. Available in the form of powder, tablets, gel, suspensions and syrup for children. The optimal dose is 100 mg, which can be slightly increased when wisdom teeth are bothering you.
The optimal dose is 100 mg.
Analogues - “Nurofen”, “Ibuprofen”, “Diclofenac”, “Nise”, “Affida Fort”.
Important! "Nimesil" is contraindicated during pregnancy, lactation, people with pathologies of the liver, kidneys, heart, blood vessels, and children under 12 years of age. Often causes side effects from the gastrointestinal tract and nervous system.
"Analgin"
They produce capsules, suppositories, and pain-relieving injections for intramuscular and intravenous injections. Relieves fever and pain. The active ingredient is metamizole. Take 500 mg twice or thrice a day, including when wisdom teeth are cutting. If a fang, incisor or molar hurts in children, the dosage is calculated in the proportion of 5 – 10 mg per 1 kg of weight.
Relieves fever and pain.
Important! "Analgin" is not recommended for people with pathologies of the cardiovascular and hematopoietic systems, bronchial asthma, allergies to preservatives, and pregnant women.
Medicines with a similar effect are “Baralgin”, “Spazmalgon”, “Tempalgin”, “Antipirin”.
"Osksadol"
Non-narcotic analgesic based on nefopam. Does not affect blood clotting and does not have an antipyretic or anti-inflammatory effect. Available in tablets, sold by prescription. Can be used after tooth extraction during pregnancy under medical supervision.
Contraindications include: migraine, nausea, dry mouth, drowsiness, tachycardia, sweating. Take 60 mg 3 times a day.
"Movalis"
Powerful anti-inflammatory and analgesic agent.
Release form: injection, capsules, rectal suppositories. Powerful anti-inflammatory and analgesic agent. Not used during pregnancy and when planning it, as it reduces fertility, as well as during breastfeeding.
Important! Movalis causes adverse reactions from the nervous, digestive, respiratory, cardiovascular systems, and allergic reactions.
The medicine can be replaced with Meloxam, Xefocam, Amelotex, Diclofenac.
"Rofika"
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, available by prescription. The active ingredient is rofekoxide. Available in tablet form. The main indications are rheumatic diseases, but you can drink it after tooth extraction.
Important! "Rofika" should not be used by patients with bronchial asthma, cancer and severe cardiovascular diseases, children under 12 years of age, pregnant and lactating women.
Aspirin, No-Shpa and Paracetamol are ineffective after tooth extraction.
Analogs - “Artoxib”, “Denebol”, “Ranselex”, “Roff”, “Celcox”.