Also watch: Dental treatment under a microscopeTreatment of dental cariesEndodontic dental treatment
Any type of dental treatment is aimed at alleviating the patient’s condition and restoring oral health. Pain after dental treatment is a common problem that every person has encountered at least once. In some cases, pain and discomfort are an inevitable consequence of the treatment procedure itself and pass quickly, while in others they indicate the development of complications and poor-quality treatment. You should never ignore pain after dental treatment, but this symptom does not always require repeated dental treatment.
Main causes
Dental treatment can be therapeutic or surgical, and pain can appear after any type of intervention. In most cases, mild or moderate pain is a physiological reaction of tissues to the manipulation, can be easily eliminated by taking anti-inflammatory or painkillers and lasts several days after a visit to the dentist.
Also, pain after dental treatment appears due to complications and violations of the technique of performing medical manipulations. Pain is most often observed after:
- dental fillings;
- root canal treatment;
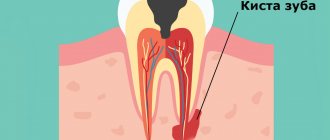
- removal of a diseased tooth, cyst or granuloma.
The dentist must advise the patient about how the recovery process will occur after treatment and for what symptoms it is necessary to come for another appointment. Also, for comfortable well-being after treatment, anti-inflammatory and, in some cases, antibacterial drugs are prescribed. If, despite following all the doctor’s recommendations, the pain continues to bother you, then it is best to undergo another examination by a specialist.
What to do if swelling appears after treatment at the dentist
If after tooth extraction your cheek is swollen from the tooth, there is no need to worry - this is a normal reaction. You can take a pain reliever that your dentist recommends. When a pathological condition is accompanied by pain and weakness, the temperature should be measured.
Edema does not always indicate a complication; it is worth distinguishing a simple reaction of the body from a pathological condition. Don't worry if:
- the flux disappears 3 days after surgery;
- the swelling is not pronounced and does not increase in size;
- no temperature or it does not exceed 37.5 degrees;
- the pain is aching, slight, gradually goes away, eliminated with analgesics;
- in the hole there is a bloody dense clot, which is covered with fibrous tissue within 2-3 days.
On a note! Do not apply hot lotions to the injured area, release pus yourself, or massage the gums. This will provoke further development of the infection, which will lead to serious consequences.
The following symptoms indicate complications:
- the flux grows;
- there is severe pain that cannot be relieved with analgesics;
- tension together with surgery;
- temperature over 37.5-37.6 degrees;
- it hurts to swallow, speak, open your mouth;
- there is no blood clot in the hole or it is covered with a green, gray or yellow coating;
- unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- itching, hyperemia, shortness of breath - indicate an allergic reaction.
Attention! If you have any of the symptoms, you should consult your doctor. Such signs indicate infection. If an operation was performed, the treatment is carried out by a dental surgeon or an endodontist if the root canals were cleaned.
Pain after dental filling
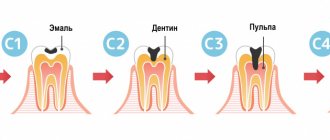
Dental filling is the most frequently performed treatment procedure in any dental clinic. Due to the high prevalence of caries, each dentist installs several fillings per day. However, even such routine dental manipulation in some cases leads to complications and pain in the patient after treatment.
Slight pain when putting pressure on a filled tooth normally goes away a few days after the filling is installed. To reduce discomfort, you can take anti-inflammatory medications as prescribed by your doctor. But if the pain does not go away and intensifies over time, then this may indicate a complication after dental filling. The main causes of pain are:
- Improper grinding of the filling . Grinding is one of the final stages of tooth restoration using filling materials. This procedure is performed to make the filling smooth and consistent with the patient's bite. If the dentist incorrectly polished the filling and it remains too high, this leads to improper closure of the jaws and injury to the mucous membrane. Also, an unsuitable filling increases the sensitivity of teeth to various irritants (exposure to cold, sour or sweet foods). In such cases, you need to contact your dentist again so that he can adjust the height of the filling and the associated discomfort will no longer bother you.
- Allergy to filling materials . Materials for filling teeth are being improved every year, but the use of even the most modern filling materials cannot completely eliminate the occurrence of an allergic reaction. Symptoms of individual intolerance include swelling, pain, redness of the gums, and a strange taste in the mouth. It is important to understand that similar symptoms occur if you are allergic to a local anesthetic drug. If you suspect that you are allergic to a temporary or permanent filling, you should immediately contact a dental clinic, where the placed filling will be removed from the tooth and filled with other materials.
- Violation of filling technique . Pain after dental treatment sometimes appears if the dentist performed one of the filling stages incorrectly. Pain may occur due to overheating of dentin when preparing a carious cavity with a drill, which leads to inflammation of the pulp. Pain also appears if a special acid is applied for a long time, which improves the fixation of the filling on the tooth, or if the drying technology is disrupted. Any mistake when installing a filling can lead to increased tooth sensitivity and pain. The method for correcting complications is selected individually.
- Development of secondary caries . In some cases, an infectious process can develop under a previously installed filling. This occurs due to insufficient treatment of the carious cavity before installing the filling, as well as due to the loose fit of the filling to the natural tissues of the tooth. The danger of this process is that it is more difficult to visually notice secondary caries. Signs of pathology are darkening of the enamel and pain in the tooth affected by caries. In such cases, the dentist removes the old filling and re-treats the caries.
- Incorrect diagnosis . Pain after filling teeth occurs in cases where the dentist missed the presence of pulpitis in the patient and did not check the condition of the root canals of the tooth. Moreover, even after a high-quality filling is installed, complaints may remain of aching, intense pain of a bursting nature, which intensifies with chewing and biting. To prevent further spread of the inflammatory process, cleaning and treatment of the root canals and removal of the nerve are required. After these manipulations, the canals are filled and the tooth is restored.
To avoid complications and pain after dental filling, a thorough preliminary examination and treatment using high-quality materials by an experienced dentist is necessary. If you experience severe pain after installing a filling, you should immediately contact your doctor.
Headache due to complications arising after dental intervention
Many patients experience headaches after visiting the dentist. Various factors can contribute to the appearance of pain symptoms:
- The appearance of complications that manifested themselves during dental treatment;
- Intolerance and allergic reactions to the use of drugs;
- Contraindications to tooth extraction;
- The appearance of a specific odor in the place of dental treatment;
- The presence of inflammation of the tissues of the oral cavity;
- The presence of swelling of the oral tissues;
Most often, pain occurs in several places. They begin in the jaw and gradually spread throughout the head. Painful sensations can be either sharp or aching. Complications after going to the dentist may depend on the presence of certain diseases in the patient:
- Very often, pain appears in patients suffering from diabetes. The headache may last for a long time;
- Ear disease, which can progress during dental treatment and cause headaches;
- Delay in contacting a specialist, which results in severe diseases of the teeth and gums, which are accompanied by painful symptoms of the head;
After symptoms of complications occur, you must go to the hospital to prescribe effective treatment. The occurrence of headaches may be due to the progression of certain dental diseases. Such as:
- Periodontitis – aching pain occurs in the temporal parts of the head;
- Alveolitis - severe pain occurs that begins in the jaw area;
Pain after root canal treatment
The need for root canal treatment worries the vast majority of patients in dental clinics. Many people are afraid of pain during and after the procedure. However, root canal treatment is primarily aimed at eliminating discomfort and pain in advanced stages of caries, when the nerve and pulp of the diseased tooth are involved in the pathological process.
To completely remove the affected tissue, the dentist opens, cleans, prepares and carefully fills the root canals of the tooth. This type of treatment is considered quite invasive and even after proper procedure, mild pain may bother the patient for 1-2 days. Unpleasant sensations do not affect general well-being or ability to work and are reduced by taking anti-inflammatory drugs (paracetamol, ibuprofen).
However, in some cases, severe pain indicates complications of root canal treatment:
- Exit of filling material beyond the root apex . A common complication of root canal treatment that occurs due to improper procedure technique. The patient may be bothered by aching pain that intensifies with load on the tooth. In combination with insufficient treatment of the canal, this can lead to severe periodontal inflammation, as well as intense pain after tooth treatment.
- Mechanical injury from tools . If, while cleaning the canals, the dentist does not fully comply with the accuracy and delicacy of the movements, then perforation (perforation) of the canal and damage to the periodontal tissues with the instrument are possible, followed by the development of inflammation and pain.
- Incomplete canal filling . In some cases, root canals have a complex structure and therefore are not completely filled with filling material. In unsealed areas, conditions are created for the development of an infectious process, which is accompanied by severe pain.
- Development of periodontitis . Advanced stages of caries and pulpitis can lead to inflammation of the periodontal tissues. At the initial stage of development of the disease, changes are not visible on an x-ray. Therefore, even after proper treatment of the tooth canals, the patient may complain of pain and an unpleasant feeling of fullness in the gums. As the disease progresses, granulation tissue or granuloma forms and must be removed surgically. In acute periodontitis, health worsens, the temperature rises, and general weakness is noted.
It is important to remember that during the first days after root canal treatment, slight pain (especially when putting stress on the tooth) is a physiological reaction. But if the pain is pronounced, interferes with meals, sleep and disrupts the usual daily routine, then it is necessary to be examined by a dentist and eliminate the complications that have developed as soon as possible. Treatment tactics in each case are selected individually, depending on the cause of the pain.
Complications of local anesthesia and endodontic treatment
Posted by Tara Renton
Translation: Gavryushina Anna
Possible mechanism of nerve damage during local anesthesia
Nerve injury due to local anesthesia is a complex problem. Nerve damage may be physical (needle, compression due to epineural or perineural hemorrhage) or chemical (bleeding or local anesthetic components). Thus, the resulting nerve injury may be a combination of peri-, epi-, and intraneural trauma causing subsequent hemorrhage, inflammation, and scarring leading to demyelination (loss of the nerve sheath). Administration of local anesthesia can cause nerve damage in a variety of ways. The location of the nerve injury may also be important, as well as the mechanism. Factors to consider are that only 1.3–8.6% of patients experience an "electric shock" type sensation when receiving mandibular anesthesia, and 57% of patients who suffer from long-term neuropathy did not experience discomfort during the injection , so this is not a specific sign.
Injuries during mandibular anesthesia
Neuropathy
Any damage to sensory nerve tissue can cause a combination of anesthesia (numbness), paresthesia (altered sensation that is not painful), dysesthesia (altered sensation that is unpleasant/painful), and neuropathic pain. Neuropathy in the orofacial region should be taken seriously and the cause should be determined as there are some serious conditions that need to be addressed if the cause is not obvious. It is often possible to determine its origin from the anamnesis. Lack of sensation must be noted on the face so that the increase or decrease in the insensitive area can be assessed. Any patient with an expanding area of paresthesia for which there is no known cause should be referred to a specialist. Among other things, paresthesia can result from trauma, nerve damage, surgery, infections and prolonged reactions to local anesthesia, viruses, malignancies, or serious illnesses. If a dental cause is suspected, patients require re-evaluation, careful documentation, and follow-up.
Unilateral paresthesia and facial paralysis can occur when conduction anesthesia is administered in the wrong direction when the local anesthetic solution is deposited in the parotid gland. This usually occurs when the depth of penetration of a long needle is approximately half its length. This most likely occurs when the mandibular ramus expands laterally, making it difficult for the operator to “feel the bone.” Unilateral facial paralysis is reversible. It goes away within a few hours. The patient should be reassured and his eyes protected until the blink reflex is restored, as the corneal reflex is often impaired.
Neurological damage from untreated periapical infections
In endodontic practice, we often encounter patients with apical periodontitis of endodontic origin, leading to impaired sensitivity of the inferior alveolar or mental nerve. It invariably resolves with a decrease in inflammation and local swelling. A number of authors have reviewed and documented clinical cases of a neurological disorder with paresthesia and hypoesthesia of the mental nerve arising as a consequence of apical periodontitis of the second premolar and second molar of the mandible.
Motor nerve palsy due to endodontic treatment
There are reports of shortages
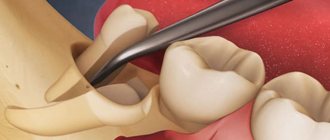
Pain after tooth extraction
In some cases, effective treatment of advanced diseases involves the removal of a diseased tooth followed by prosthetics. After tooth extraction, pain, swelling and redness of the gums are a normal reaction of the body to tissue injury. You should be concerned if:
- the intensity of the pain does not decrease over time and is poorly removed by painkillers;
- the hole does not overgrow for a long time;
- purulent discharge appears from the wound;
- severe swelling of the mucous membrane occurs;
- body temperature rises.
The above symptoms indicate the development of an infectious process in the gum tissue. This happens if the tooth extraction technique is not followed or if the patient does not follow the doctor’s recommendations for oral care.
Diagnostics
Pain when opening the mouth requires, first of all, diagnosis; only an experienced doctor can make a correct diagnosis. There may be several reasons for this pathology, and the doctor’s task is to correctly diagnose the disease, since the treatment method will depend on this. During the consultation, the doctor examines the patient and finds out, the patient’s posture is also assessed, and how difficult the functions of swallowing, chewing and breathing are.
During the examination, the doctor will also pay attention to the location of the pain, whether it manifests itself on one side or is bilateral. Based on the results, an additional examination will be prescribed: x-rays, manual functional analysis and other procedures.
An individual and comprehensive approach is the priority of the Orto-Artel clinic. Therefore, to establish the root cause of the problem and its further solution, consultations with specialists such as:
- osteopath;
- neurologist;
- kinesiologist;
- psychologist.
The joint efforts of dentists and general specialists will make it possible to make the correct diagnosis.
If your jaw hurts when chewing or opening your mouth, then in most cases, the pain is a sign of inflammation. Therefore, often, when ear pain or tinnitus is detected, it is associated with purely “ear” problems. And with pain localized in the area of the temporomandibular joint, doctors who do not have adequate experience in diagnosing and treating TMJ dysfunctions usually make a standard diagnosis - “arthritis of the temporomandibular joint.”
The diagnosis of arthritis in medicine means inflammation of the joint, but this formulation does not include information about the specific causes of such inflammation. Therefore, making such a diagnosis is a very general formulation. It's a very general diagnosis. Non-binding. Does not reflect the root cause of inflammation. In fact, it is only a statement of the fact of inflammation in the joint.
But the causes of this inflammation can be very different, and accordingly, treatment, depending on the causes of inflammation, will differ significantly in different patients, even those who have common symptoms - pain in the jaw joint when opening the mouth. Or ear pain. Inflammation is the body's normal response to injury. And injury can be caused by various factors.
Diagnostics is the first and key step in treating pain in the jaw when opening the mouth. Do you want to know why it’s impossible to do without diagnostics?
In the case of joints, most often the injury will be mechanical. It occurs when the bones that form a given joint (in particular the head of the mandibular condyle) exceed their normal range of mobility. And they overstretch the joint capsule, ligaments and muscles associated with this joint. Every person has encountered this at least once in their life. Because this process has a well-known name - joint dislocation.
The dislocation may be acute. This is when it happens sharply and suddenly. In the case of the temporomandibular joint - with sudden opening of the mouth (for example, when yawning). Or due to a blow to the lower jaw area.
The dislocation can be chronic. This is when the bones that form a joint regularly (constantly, for a long time) exceed the amount of their normal mobility. In the case of TMJ, this happens when the bite is incorrect. Then each closure of the teeth will direct the lower jaw into the “wrong” position. And it is chronic injury that is more dangerous. Because, unlike an acute injury, a gradual stretching of the capsule and ligaments of the joint occurs, which camouflages (hides) the painful manifestations of the problem. After all, pain will occur in the later stages, when the process has already gone quite far, which often leads to untimely (belated) seeking medical help. Chronic injury is the cause of 90% of all TMJ problems. And it refers to functional problems (dysfunctions). When the daily, seemingly normal functioning of this joint leads to its gradual wear and tear and, ultimately, destruction.
The generally accepted traditional allopathic approach to the treatment of TMJ pathology with a banal (simplified) diagnosis of arthritis, and the resulting treatment (all this anti-inflammatory therapy, using pills, physiotherapy and other “traditional” methods) is erroneous and ineffective, since it does not eliminate the root cause of the problem .
Treatment in installments
The Orto-Artel clinic offers installments for the entire process of treating any disease. Personal conditions are considered on an individual basis.
Find out more
or call 8 (495) 128-11-74
In addition, I would like to note that pain in the jaw when opening the mouth is not always associated with problems in the TMJ (just as pain in the ear or tinnitus is not always associated directly with “ear” problems). Therefore, to differentiate the cause of the problem, to determine the true source of pain, consultation and assistance from a qualified specialist who understands these subtleties is necessary.
How to cope with pain after dental treatment?
To feel comfortable after dental treatment, you must first take proper care of your oral cavity. The dentist must tell the patient in detail exactly how to carry out daily hygienic care of teeth and gums. After installing a filling or cleaning the canals, it is important not to put heavy stress on the treated tooth for some time. The following methods are also effective:
- Cold compress . Exposure to cold is good for eliminating swelling and dulling pain after invasive dental procedures. On the first day after treatment, you can apply cold compresses to the cheek in the area of pain. In order not to overcool the tissues, it is important to take a short break every 10-15 minutes.
- Baths with antiseptics or medicinal herbs . In some cases, it is recommended to take baths with antiseptic solutions several times a day to prevent infection and relieve pain.
- Taking medications . To improve your well-being in the first few days after dental treatment, you can take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that quickly and effectively relieve pain, swelling and other unpleasant symptoms. A safe remedy must be recommended by a doctor. Antibiotics after dental treatment are also prescribed exclusively by the attending physician.
If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations, the pain after tooth treatment will gradually decrease and completely disappear after a few days.
Treatment methods for headaches after dental surgery
If you have a headache for a long time, your dentist will prescribe treatment using the following medications:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs - help relieve inflammation;
- Analgesics – eliminate pain;
- Antispasmodics – relieve spasms that cause pain;
If the cause of pain is inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, then the presence of toxins, which are eliminated by the use of antibiotics, should initially be eliminated, and only then the prescribed medications should be used.
Taking such medications must be done under the supervision of a physician. The use of such drugs is contraindicated for patients suffering from stomach diseases.
When do you need to see a doctor urgently?
Acute, throbbing pain after dental treatment, deterioration in general health and an increase in body temperature are a signal for immediate medical attention. The appearance of purulent discharge, severe swelling of the gum mucosa, or various sensitivity disorders in the oral cavity require a thorough examination by a dentist. You should also consult with a specialist if mild, aching pain bothers you for a long time after treatment or occurs when exposed to any provoking factor.