Teeth and inflamed lymph nodes: what is the relationship? Symptoms of pathology, causes, treatment methods
When inflammation of the lymph nodes occurs after tooth extraction, not everyone is ready for such a turn of events. People who have not gone through the extraction procedure (removal) are even less likely to expect an inflammatory process in this important system for the body. However, this phenomenon is not uncommon. At the same time, doctors often find a connection in it with teeth. Let's look at the nuances of this difficult topic together.
Description of the disease
Not all dental surgeon patients know that inflammation may develop after removal, so they often ask the question: “Alveolitis - what is it, and why does it occur?” Other names for the disease: “dry socket”, “alveolar local osteitis”. The pathogenesis of the condition is based on a violation of the formation of a physiological clot or its loss from the socket after tooth extraction, which most often occurs due to a violation of the postoperative regimen or low human immunoresistance.
Inflammation of the alveoli is possible only due to removal of the segment. Alveolitis cannot develop after tooth treatment, since the hole is formed only as a result of extraction of the unit.
Why does the inflammatory process occur?
As you know, the lymphatic system is a very important component of our body. It prevents various pathogens from entering the blood and internal organs, but it itself is often the first to take the blow due to decreased immunity. Many people know that swollen lymph nodes are often the first signal that a person has some kind of disease in the body. They usually swell shortly before the first symptoms of the disease appear. Their increase may indicate a sore throat, HIV, syphilis, tonsillitis, lupus, measles, scarlet fever, arthritis and many other pathologies.
This is interesting! Scientists have found that in the human body there are more than 400 lymph nodes (they are located in small groups) and about 2 liters of lymph that passes through them. The greatest concentration is on the neck and head, under the jaw and chin, under the arms and in the groin. Each group is responsible for the well-being and protection of nearby organs.
However, not everyone knows that inflammation in this important system for the body often occurs due to dental pathologies. This means that the infection gets there from a nearby area, in this case, from the oral cavity, where a large number of different bacteria live. Naturally, staphylococci, streptococci and other harmful as well as beneficial bacteria are constantly present in the mouth, and this is normal. But the problem arises only if microbes multiply rapidly and pathogenic microflora begins to predominate. Why is this happening? Read on.
Why does swelling occur?
Edema is the excess accumulation of blood in the extracellular spaces of the body to speed up healing. If your cheek is swollen after wisdom tooth removal, there may be several physiological reasons:
- manifestation of an allergic reaction to the anesthetic;
- purulent focus of inflammation, usually eliminated before surgery;
- elongated roots of the tooth being removed,
- high pressure.
The listed factors are mainly individual for each organism. Most often, swelling of the cheek after wisdom tooth removal is a natural protective reaction to surgery. If no pathological factors are observed, and the dynamics of healing proceed as expected, then there is no need to worry.
If swelling occurs due to natural causes, this condition is considered normal.
How to determine natural origin?
- The tumor appears a day after the intervention.
- Pain and swelling gradually subside.
- Body temperature is normal or slightly elevated.
- Slight pain during swallowing or chewing processes.
Even if the tumor looks terrible, the first few days after surgery may be completely normal. You should be concerned if, after the allotted time, there is a tendency for pain and swelling to progress.
Main dental problems leading to pathology
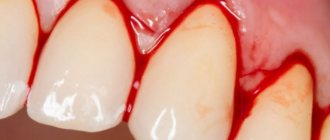
- abundant accumulation of bacterial plaque on and under the gums,
- gingivitis and periodontitis,
- advanced caries, pulpitis, periodontitis,
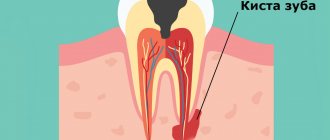
- purulent-inflammatory processes: flux, fistula, abscess, festering cyst and granuloma, osteomyelitis, phlegmon,
- damage to the oral mucosa by stomatitis, especially in acute and recurrent [1] varieties caused by the herpes virus or Candida fungus,
- glossitis of the tongue,
- poorly installed, old fillings and crowns under which inflammation has developed,
- long-term lack of sanitation of the oral cavity: during the sanitation process, the doctor applies a set of measures aimed at eliminating all dental pathologies.
This is interesting! The submandibular lymph nodes are responsible for the condition of the nose, throat, teeth and ears. If they are the ones that become inflamed, then you need to look for pathology in the listed organs, and to eliminate the problem, contact a dentist (in 60% of cases, dental pathologies are detected) or an ENT doctor.
How to treat alveolitis after tooth extraction
The main task of correction is aimed at eliminating the cause that caused the pathology and stopping the inflammatory process. The doctor decides how to treat alveolitis after tooth extraction. Treatment tactics depend on the stage of the pathological process. It may include revision (if necessary, curettage) of the hole, drug treatment, physical therapy (laser, magnet, fluctuarization, ultraviolet radiation). All manipulations are performed under local anesthesia.
Treatment program:
- Local anesthesia.
- Antiseptic treatment of the wound (removal of saliva, food debris, pus).
- Freeing the cavity from a disintegrated blood clot, foreign inclusions (tooth fragments, root remains, etc.), granular tissue.
- Repeated treatment with an antiseptic, application of a turunda soaked in an anesthetic drug.
- Applying a medicated antiseptic bandage.
When treating alveolitis, the doctor can use proteolytic enzymes (trypsin, chymotrypsin), which break down necrotic tissue, thereby helping to cleanse the socket. To reduce pain, a blockade is made with local anesthetics, which are injected into the soft tissue near the inflamed alveoli. To suppress the infectious process, a course of antibiotic therapy is prescribed.
Teething and enlarged lymph nodes
The problem is typical mainly for children whose first milk units are being cut. Babies have a weak immune system, and during this period it weakens even more, since the body is under a serious load. Often, teething itself is very difficult, accompanied by alarming symptoms (moodiness, cough, fever, runny nose) and even the addition of bacterial and viral infections.
This pathology does not always escape adults. For example, when a wisdom tooth is cut and the submandibular lymph node increases in size, this is a fairly common occurrence. The third molars pass through the jawbone, and this process takes a long time, plus it is often associated with disturbances. “Sages” can compress and touch the branches of the trigeminal nerve, rest against neighboring elements of the row and destroy them. Their eruption may be accompanied by a decrease in immunity and an increase in body temperature, to which all the defense systems of our body react very sensitively.
Sometimes growth pathologies of the “eights” lead to the development of a purulent-inflammatory process such as pericoronitis. The problem arises when a kind of hood forms between the gum and the not fully erupted “figure eight”, where bacteria and food debris get trapped.
On a note! If your wisdom tooth hurts and the lymph node is swollen, then the symptoms may indicate damage to the third molar by caries, pulpitis, or periodontitis. If the cheek is also swollen, then, most likely, gumboil has developed.
Causes of pain
The occurrence of pain after tooth extraction is associated with damage to nerve endings, vascular structures and soft tissues. The peak intensity of pain occurs in the first hours after the cessation of anesthesia. The symptom persists for about 12 hours.
In case of incisions in the gums or damage to the bone tissue, as well as after implantation after removal, toothache may persist for 2-3 days. Pain syndrome also occurs in the case of displacement of the dentition towards the formed void. Therefore, doctors recommend prosthetics as soon as possible after extraction.
Why does the problem occur after tooth extraction?
Let us list the main reasons why nodes become swollen after tooth extraction.
The body's response to surgery
It is not uncommon for a lymph node in the neck or under the jaw to slightly increase in size immediately after tooth extraction. Some experts believe that after surgery such a reaction is quite natural, because the body has activated all its forces in order to quickly cope with the physiological trauma inflicted on it.
If you have removed a wisdom tooth and then felt an enlarged lymph node in your neck, then you should not panic ahead of time. Procedures for extracting “eights” are always complex, large-scale and quite traumatic. Therefore, after them, a non-infectious inflammatory process almost always occurs, accompanied by a number of characteristic symptoms: increased body temperature, pain, limited jaw mobility and the inability to open the mouth wide, general weakness.
The procedure was carried out against the background of a purulent-inflammatory process
Typically, patients come for extraction (removal) if there are advanced dental diseases in the mouth that cannot be restored. Often the operation is performed urgently, against the background of an acute inflammatory process. Therefore, enlarged lymph nodes after tooth extraction with periodontitis, gumboil, fistula, cyst, granuloma are a common story. After all, the inflammatory process in this case had already been going on for some time. And it does not go away immediately after eliminating the problematic element; you still have to fight it by taking antibiotics and other medications, lotions, antiseptic rinses, and physiotherapy.
Extraction complications occurred
If several days have passed after tooth extraction, and you notice that the lymph node under the jaw hurts and is inflamed, this may indicate the development of the following complications of extraction:
- alveolitis: this is where it all begins. This is an inflammation of the socket that occurs due to a medical error or due to a violation of the postoperative regimen on the part of the patient. Actually, the complications that we will list below appear because the patient develops alveolitis, or tries to cure the disease on his own and does not seek medical help,
- flux, abscess, phlegmon, osteomyelitis.
The main reasons for the appearance of alveolitis after tooth extraction
Tooth extraction is a surgical procedure that is accompanied by the formation of a wound. A blood clot forms in it, protecting it from the penetration of microorganisms. Inflammation of the tooth socket after extraction occurs due to disruption of the process of formation or displacement of a blood clot. The most common causes of pathology:
- Difficult extraction. The more traumatic the operation, the more the tissue’s ability to regenerate decreases and the likelihood of infection increases.
- Wisdom tooth removal. The structure of the root system of third molars is complex, so their extraction is always traumatic. In addition, the bone in the figure eight area has increased density and is less vascularized compared to other areas, which also creates conditions for the formation of a dry socket.
- Concomitant somatic diseases of the patient (diabetes mellitus, immunodeficiency states).
- History of pericoronitis (inflammation of the soft tissues around the tooth).
- The presence of foci of infection in the mouth before surgery. Penetrating into the wound with saliva, pathogenic flora causes alveolitis.
- Inadequate sanitation of the alveoli. After removal, careful curettage of the wound is necessary to remove fragments of bone tissue, roots, pieces of filling, and granulations. Foreign fragments disrupt healing and lead to alveolitis.
- Exceeding the dose of anesthetic. Leads to a narrowing of the lumen of the capillaries, the development of local ischemia, which disrupts the filling of the hole with blood.
- Mechanical damage to the clot. Failure to follow the doctor’s recommendations during the postoperative period (rinsing the mouth, carelessly brushing teeth, etc.).
- Impaired hemostasis. Due to poor blood clotting, a clot does not form.
Alveolitis can be provoked by smoking, taking hormonal contraception, and insufficient oral hygiene. Age plays a certain role in the development of alveolitis after tooth extraction: the older the patient, the greater the likelihood of developing pathology. This is due to a slowdown in metabolic processes and a decrease in the regenerative ability of tissue cells.
Signs of pathology
If there is no pathology and the person is healthy, then the lymph nodes are quite difficult to palpate. But if there are problems in the body, their condition changes. At first, the inflamed areas only swell slightly and increase in size, which becomes noticeable upon palpation. The pathology is not accompanied by any other signs at the initial stages.
If, due to dental problems or after tooth extraction, the lymph node hurts, then it means that the person has started the underlying disease, against which he may have developed lymphadenitis. What is this? This is just inflammation of the lymph nodes. Let us list the symptoms of the pathology.
- Swelling and enlargement of the areas under the jaw, chin and neck. When you feel them, you can find lumps and even lumps. In rare cases, the lymph node behind the ear may also increase in size, for example, if there are eruption pathologies or complications arise after the removal of a wisdom tooth.
- Discomfort when opening the mouth, chewing and swallowing food, when swallowing saliva and drinking liquids (soups, drinks). Pain when pressing on inflamed and enlarged areas. In later stages of the disease, pain can spread to the neck, head, and radiate to the jaw and throat.
- Increased body temperature. The more the disease progresses, the higher the temperature. The thermometer can reach 40°C.
- The appearance of general malaise and weakness, chills, insomnia.
Alveolitis after wisdom tooth removal
Indications for the removal of eighth segments in a row can be different: deep caries, improper eruption, orthodontic correction of jaw bite, dystopia, etc. Extraction of third molars is always associated with trauma to nearby tissues, which increases the development of inflammation. The pathological process is observed in 45% of cases due to the removal of lower wisdom teeth.
Symptoms of alveolitis after wisdom tooth removal are similar to the general symptoms of the disease. However, with such localization of inflammation, a sore throat and impaired functionality of the temporomandibular joint on the affected side may occur (difficulty and painful opening of the mouth).
Dangerous consequences of pathology
If you do not promptly treat the underlying problem that caused the swelling and enlargement of the lymph node, then, as mentioned above, you will develop lymphadenitis.
Usually, the submandibular form of the disease occurs first, but in the absence of therapeutic measures, the infection descends lower, and then the cervical type of pathology develops. That is, the lymph nodes in the neck become inflamed, which poses a serious threat to life and health. For those who do not consult a doctor on time, the body may become severely intoxicated.
From the acute form, the disease passes into the chronic stage, and pus begins to accumulate in the tissues. When the pathology is neglected, there is a risk of developing phlegmon [2], thrombosis, the formation of malignant tumors, as well as a purulent abscess, the contents of which can at any time break into nearby organs, spread through the hematopoietic system, reach the bronchi and respiratory tract, and cause sepsis.
Professional diagnostic measures
When a lymph node becomes inflamed, you should not hesitate to see a doctor. It is better to start by visiting a dentist, who will examine the oral cavity and send you for an x-ray to obtain information about the presence or absence of hidden processes and dental pathologies.
Additionally, the patient may need the help of other specialists: an ENT doctor, a therapist, an infectious disease specialist. Be prepared that for a detailed diagnosis you may be referred for urine and blood tests (usually they reveal an increased number of leukocytes), bacterial culture, and ultrasound.
Measures to eliminate the problem
Dental treatment
In order for the lymph nodes to return to normal, it is first necessary to get rid of the main problem that caused their enlargement and inflammation. Depending on the pathology, the dentist can perform the following manipulations:
- cleaning teeth from plaque and tartar,
- treatment and filling of root canals,
- surgical opening and drainage of ulcers (with flux, abscess),
- cleaning the socket (for alveolitis),
- tooth-preserving operations: cystectomy and cystotomy, resection of the root apex for cysts and granulomas,
- replacement of unsuitable fillings and crowns.
After treatment of dental pathologies, the lymph nodes do not disappear immediately. Swelling may persist for the next 7-10 days. In order for the patient’s condition to normalize faster, he is additionally prescribed physiotherapy (for example, UHF therapy) and prescribed medicinal support.
“I once had a tooth removed with periodontitis on the lower jaw. A few days after this, I noticed that the lymph node was a little swollen and painful. I didn’t want to go to the dentist again, I hoped that it would go away on its own. Then the hole healed safely, but the swelling under the jaw sometimes appeared again. In general, I started this case, and when more frightening symptoms appeared, I ran to the doctors. I was told that there was pus inside the lymph nodes and it needed to be cut out. There was no choice, I had surgery, then took antibiotics. Now I regret that I didn’t go to the clinic right away...”
S. Tsareva, review from gidpozubam.ru
Drug therapy
The doctor will prescribe medications to take at home. In case of inflammation of the lymph nodes, as well as in advanced dental diseases, a course of antibiotic therapy is prescribed for 7-10 days. The patient is also recommended ointments for applying external lotions and applications to the affected areas. Additionally, immunostimulants and multivitamin preparations are prescribed, which must include vitamin C to boost immunity.
Symptomatic treatment is also prescribed. For fever, antipyretics are taken, and for pain, painkillers are taken.
Pain during difficult removal
The duration of pain after complex extraction (wisdom teeth, impacted or dystopic incisors) is associated with damage to a larger tissue area. Often such an operation involves making an incision in the gum, sawing out the roots, extracting tooth fragments, and draining an abscess, which increases the scope of the surgical intervention. If your ear hurts after wisdom tooth removal, this may indicate nerve damage.
In some cases, patients complain of persistent discomfort and pain for up to a week. Clinical manifestations such as swelling, swelling of the gums, enlarged submandibular lymph nodes, fever, and malaise are also common.