16.11.2019
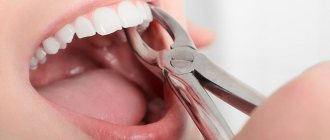
Such a complication as stomatitis after tooth extraction is well known in dental practice. Moreover, the source of inflammation can appear not only on the gum, where the tooth used to be, but also on other places on the mucous surface of the oral cavity. The cause of the disease may be the unscrupulous work of the dentist. The patient himself can influence the formation of ulcerative defects. In any case, it is necessary to carry out full treatment of the disease.
The connection between surgery and stomatitis
It would seem, what could be the connection between tooth extraction surgery and stomatitis - inflammation of the oral mucosa? The most direct one. Dentistry, which studies dental, jaw and other diseases of the oral cavity, has proven that all processes in the mouth are interconnected.
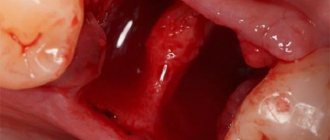
Accordingly, tooth extraction is quite capable of causing symptoms of stomatitis: painful ulcers, erosion, a specific white coating that hides bleeding wounds, and an unpleasant odor. Most often, defects appear on the gums or close to them: on the inside of the lips, palate, and floor of the mouth. The inner area of the cheek can also become inflamed if the disease occurs after the removal of a wisdom tooth. Without timely treatment, ulcers begin to spread throughout the mouth.
Of course, not every tooth extraction entails inflammation of certain areas of the oral mucosa. This requires additional conditions.
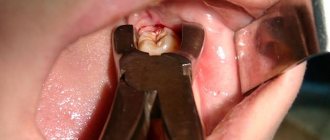
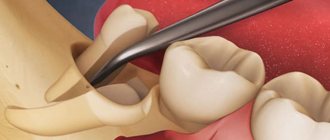
Indications for removal of eighth teeth
wisdom teeth
begin to grow much later than other permanent teeth, as a result of which they often do not have enough space in the jaw. Lack of space provokes all sorts of curvature of roots and crowns. Doctors advise removing such molars. Here is another list of problems that may require extraction:
- A pronounced tilt of the figure eight towards the seventh tooth or cheek.
- Hypercementosis (excessive deposition of secondary cement, in which the tooth root thickens and becomes deformed).
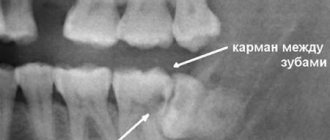
- Incomplete eruption of the tooth or its location in the bone (retention).
- Destruction of the crown or roots of the figure eight, as well as neighboring teeth (after injury or caries).
- Granuloma (granulation in the form of cystic sacs with pus located in the periodontium).
- Rotation of the tooth around its axis or horizontal position (dystopia).
- Deformation of the roots (they can bend in every possible way, even twist into a spiral or form an angle of 90°).
- The close location of the roots of the upper eights to the nasal maxillary sinuses.
- In the presence of pericoronitis (an acute inflammatory process in the area of the eruption of the figure eight, accompanied by pain and an increase in ESR in blood tests).
An incorrectly growing 8th tooth can compress the facial nerves and provoke neuritis, which is expressed by sharp pain radiating to the ears, neck, temple, and can lead to facial paralysis.
When the patient is to blame
Stomatitis can occur even if the dentist has followed safety precautions and completely removed the tooth. Sometimes the patient himself is to blame. This can happen due to neglect of postoperative care for the affected tooth socket. After pulling out a tooth, you should not pick at the wound with foreign objects or rinse your mouth vigorously. Otherwise, a blood clot will fall out of the tooth socket - protection against pathogens.
Stomatitis after tooth extraction can occur due to ignoring the rules of personal hygiene: poor oral care, eating unwashed foods, eating with dirty hands.
Other circumstances
Other circumstances may also influence the development of stomatitis after tooth extraction. For example, a patient has an allergic reaction to local or general anesthesia. In this case, an allergic form of the disease manifests itself.
Sometimes, after a tooth is pulled out, a blood clot does not appear in the tooth socket. Pathogenic microorganisms begin to penetrate into the tissue of the unprotected hole, causing inflammation.
Kissing an infected person can also lead to stomatitis at the site of an extracted tooth. Or using dirty common items in a cafe, canteen, or home.
There is a high probability of the disease occurring if the patient has a weak immune system, and there are several wounds and they take a long time to heal. Most often this happens after the removal of a wisdom tooth. Due to its inaccessibility, the dentist sometimes has to cut the gum and part of the cheek before surgery.
Symptoms
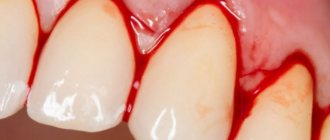
Depending on the form of the disease and its intensity, a variety of symptoms may appear. First of all, a person should be alert to the following points: the presence of foci of inflammation, ulcers, changes in the appearance of the mucous membrane, swelling and redness, burning, acute or aching pain, etc.
Bacterial stomatitis is characterized by the appearance of small round ulcers, a viral disease manifests itself in the form of multiple blisters over the entire surface of the mucous membrane, and fungal stomatitis can additionally be accompanied by a dense white coating.
The patient may also notice an increase in bad breath, bleeding at the slightest contact with the gums, an increase in body temperature and a deterioration in general condition. With the right approach, the disease can be treated quickly enough, within a few weeks. If you do not seek help in time, there is a high risk of serious complications, which will be much more difficult to cope with.
The consequences are dangerous
Without timely treatment, seemingly harmless stomatitis can bring many negative consequences. Pathogenic microorganisms begin to secrete toxins - poison of biological origin.
Once in the blood or stomach, toxins poison the body. Intoxication leads to deterioration of health. Headaches and joint pains appear, appetite disappears, lethargy, nausea are felt, diarrhea begins, and the temperature may rise.
Other pathologies may develop: from inflammation of the throat or respiratory tract to destruction of the jaw bone or general infection of the circulatory system.
Comprehensive treatment of stomatitis will help to avoid complications. But before you begin self-therapy, you need to contact your dentist again. Or visit a therapist for adults, or a pediatrician for children. Only a doctor can determine the type of disease and prescribe appropriate medications.
Professional care and disinfection
Treatment of stomatitis that occurs after tooth extraction begins with the elimination of concomitant diseases in the oral cavity and professional teeth cleaning. Then it is necessary to disinfect the surface of the mucous membrane using antiseptics:
- soda solution;
- brilliant greens;
- hydrogen peroxide;
- potassium permanganate solution;
- "Chlorhexidine";
- "Miramistina";
- "Furacilina".
This will minimize the number of pathogenic microorganisms, which will speed up recovery. Before treating stomatitis with any medication, you must obtain permission from your doctor.
What systemic diseases can manifest as aphthae?
- Reiter's syndrome
- Behçet's disease
- AIDS
- cyclic neutropenia
- PFAPA syndrome
The gastroenterologist is especially interested in the connection between recurrent ulcers and specialized systemic diseases.
Celiac disease is found in 5% , and for a long time canker sores may be the only manifestation of a reaction to gluten.
Let me remind you that the estimated prevalence of celiac disease in the general population is about 1%.
Enamel defects and aphthous stomatitis in celiac and healthy subjects: Systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled studies
Other important conditions that manifest as canker sores are inflammatory bowel diseases: Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
Extraintestinal Manifestations of Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Prevalence, Presentation, and Anti-TNF Treatment
Vitamins are the key to health
At the same time as using disinfectants, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system. This can be done with a diet rich in vitamins, macro and microelements. On the recommendation of a specialist, you can take a vitamin and mineral complex: “Alphabet”, Vitrum, “Multi Tabs”, “Centrum”.
Decoctions or extracts of echinacea, eleutherococcus, ginseng, and Schisandra chinensis will help. If necessary, the doctor prescribes drugs to enhance immunity: “Ribomunil”, “Imudon”, “Irs-19”, “Likopid”, “Derinat”, “Timaktide”.
If stomatitis occurs due to problems with the gastrointestinal tract, complex treatment should include drugs containing beneficial microorganisms - probiotics. They will help restore the microflora of the digestive tract. These include “Bifidumbacterin”, “Lactobacterin”, “Acilact”, “Bifilong”, “Narine”.
To speed up the healing of damaged mucosal surfaces, sea buckthorn or rosehip oil, vinylin, and propolis preparations are prescribed.
Features of treatment
The main goal of treating aphthous stomatitis is to completely get rid of the disease or at least reduce the frequency of relapses to a minimum. Therapy is aimed at relieving inflammation, relieving unpleasant symptoms, and accelerating the recovery processes of the mucous membrane.
For each specific case, the doctor will develop a set of measures. The main ones include local and systemic drug treatment.
Rinsing with antiseptics can be done using medications or mouth rinses that contain antibacterial components. An alternative to rinsing is to use a spray. Typically, the treatment regimen includes 2-3 sessions of 1-minute rinsing immediately after brushing your teeth.
Local treatment methods include the application of gels with anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.
Occlusive agents can reduce pain and speed up the healing of mucous membranes. They form an insoluble film on the ulcer, protecting the affected area from exposure to adverse factors.
Local glucocorticoid therapy is used against the background of immune diseases, as well as when standard measures are ineffective. They eliminate pain and quickly relieve inflammation, shortening the healing period. Such products are used only according to indications and are available with a prescription. In some cases, it is advisable to inject the drug under the base of the ulcer; this is done by a doctor.
Epithelialization drugs are used after acute inflammation has resolved. The specialist will prescribe a gel with an analgesic and healing effect, usually this occurs 5–6 days after the start of complex therapy.
Local laser therapy can relieve pain, speed up the healing process, and minimize the risk of relapse.
Systemic treatment of aphthous stomatitis in adults involves taking the following drugs:
- antihistamines (anti-allergic, anti-edematous effect);
- glucocorticoids (anti-inflammatory, analgesic effect);
- immunomodulators (to stimulate defenses and accelerate recovery).
And if antiallergic drugs can be recommended to any patient even in the absence of information about the exact causes of stomatitis, then other drugs are prescribed only according to indications: in case of acute severe course of the disease, frequent relapses, and the presence of severe systemic pathologies. An additional method of treatment is vitamin therapy - taking vitamins C, group B.
In addition to the main course of treatment, all patients without exception are recommended to adhere to a hypoallergenic diet, avoid taking too hot drinks and dishes, and spicy, irritating foods. It is better to give preference to toothpaste without sodium lauryl sulfate, this component can provoke the disease.
It is important to continue your oral hygiene, even if it is difficult. To make brushing your teeth easier, choose a soft toothbrush. If the disease recurs frequently, it is necessary to pay attention to the general state of health, promptly treat teeth and gums, replace fillings and dental structures.