Structure of the area under the tongue
Everything that is located under the tongue is called the floor of the mouth. This:
- nerve endings;
- hyoid bone;
- hypoglossal muscles;
- salivary gland;
- connecting folds called frenulums;
- vessels.
Each element of the floor of the mouth serves its own purpose and is irreplaceable. Only if all muscles, tissues, glands and nerves are healthy does the tongue function normally. If there is pain under the tongue, then we are talking about pathology.
Symptoms that indicate inflammation of the salivary gland:
- Inflammatory process in the tongue area;
- Pain that increases over time;
- The affected area has become bright red and shiny;
- Cloudy saliva accumulates under the tongue;
- The presence of purulent masses indicates an advanced condition that is dangerous to health;
- Increased body temperature to 39 degrees;
- Deterioration in health;
- It becomes painful to talk and eat.
This indicates prolonged absence of treatment and deterioration of the condition. It is important to choose the right comprehensive treatment, which will contain not only medications, but also nutritional correction. To stop the spread of the inflammatory process, it is enough to do good oral hygiene.
Saliva must be produced in the oral cavity constantly. If you notice that there is much less saliva, you need to consult a doctor to choose a remedy to activate its production. At home, cranberries, lemon and spices will help produce saliva.
Causes of pain under the tongue
- Allergic reactions cause tissue swelling and pain.
- Harmful microorganisms that appear in the mouth during a sore throat cause acute inflammation. Often, it affects the floor of the mouth.
- Mechanical injuries from a bruise or a fall damage blood vessels, nerves, and soft tissues. Vessels may rupture, which will lead to the accumulation of blood between the muscle fibers.
- Some untreated diseases lead to phlegmon, inflammation with pus inside. In most cases, phlegmon appears under the tongue.
- Ordinary caries, if left untreated, causes inflammation that reaches the sublingual area.
- There are many ducts in the salivary gland, and if an infection gets into it, then through these ducts it can easily enter the gland tissue.
- Injury to the frenulum of the tongue. In people with a congenital short frenulum, injuries occur more often. Even a normal conversation can cause a breakup. However, people with a normal frenulum size also suffer. Inflammatory diseases and allergic reactions often lead to injury, leading to swelling of the tongue and the appearance of ulcers. But also improper oral hygiene leads to damage to the frenulum - the so-called dangerous brushing.
Some people have asymmetry of the hyoid bone from birth, and sometimes this anomaly is formed due to injury. Asymmetry prevents the organs of the floor of the mouth from functioning properly.
What could be the cause of the problem?
- Damage to the frenulum. This is a common cause of the problem. The mucous membrane is very vulnerable. There is a very delicate structure here that can be damaged during hygiene procedures or eating. If you have a shortened frenulum, then it can be injured while talking or eating. In childhood, stomatitis often occurs, which is accompanied by erosion throughout the entire oral cavity. This can also cause swelling in the mouth;
- Acute sore throat can cause inflammation of the area under the tongue;
- Teeth with caries are a source of infections. As a result, the mucous membrane may be affected; the area under the tongue is no exception;
- Formation of phlegmon or abscess. Swelling under the tongue is associated with purulent inflammation. This is a very dangerous disease that requires immediate specialist intervention. Cellulitis develops due to untreated periodontitis or periostitis;
- Inflammatory process of the salivary gland;
- Anomalies in the development of the hyoid bone or mechanical trauma that made its shape asymmetrical;
- Allergic reaction to irritants;
- Mechanical injury to muscle fibers, nerve endings, and blood vessels located in the oral cavity.
During treatment, you cannot do without consulting a doctor, as self-medication can lead to unpleasant consequences. It is necessary to choose medications taking into account the cause of the problem. Otherwise, it will be possible to remove only the consequence, which means that after a while it will make itself felt again.
At the first manifestations of negative sensations, you can independently check the oral cavity for the presence of ulcers, plaque, abscesses, pus and rashes. This way you will roughly understand what the problem is and how to solve it.
How is the sublingual area treated?
Considering the above reasons, if you have the slightest pain in the sublingual space, you should immediately consult a doctor. The doctor will find out the source of the pain and determine a treatment regimen. In some cases, allergists and therapists provide treatment. But more often, pain in the floor of the mouth is treated by dentists.
In case of injury to the frenulum or the tissues of the area under the tongue, rinsing will be prescribed: with a solution of soda, romazulan, stomatophyte, hexoral, chlorophyllipt or iodinol. You should rinse your mouth according to the following schedule:
- morning and evening before bedtime;
- after meal.
The doctor also treats the area of injury with an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Inflammations caused by dental problems require immediate treatment - the specialists at Family Dentistry will get rid of caries, pulpitis or periodontitis and prescribe a course of anti-inflammatory drugs to cope with sublingual inflammation.
But one of the most dangerous diseases in the floor of the mouth is inflammation of the salivary glands. It is important to begin treatment before an abscess appears and complications develop. In this case, the doctor prescribes:
- antibacterial therapy - the doctor injects medicine into the gland and also prescribes a broader-spectrum antibiotic;
- drugs to activate saliva secretion - either a solution of potassium iodide or pilocarpine is used, sometimes regular lemon is used;
- hot dry compresses;
- physiotherapy course.
If the inflammation is advanced and pus appears or a stone has formed, the patient is sent to a surgeon, who cleans the gland cavity of pus and removes the stone.
Drug therapy
If any form of inflammation under the tongue appears, both mild and moderate, it is not recommended to take any therapeutic measures without first consulting a specialist. A swollen area in the sublingual area may hide the formation of a malignant tumor. Therefore, differential diagnosis is required.
As a rule, therapeutic tactics to combat symptoms of inflammation in the oral cavity begin with the use of rinsing solutions:
- antiseptic
- Miramistin, Furacilin, Chlorophyllipt; - anti-inflammatory
- Iodinol, Rotokan, Potassium permanganate, Chlorhexidine.
It is better to carry out procedures for rinsing the mouth 4-6 times a day to prevent further proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
If the tumor in the sublingual area is caused by damage to the salivary glands of bacterial etiology, the doctor will select antibacterial therapy. Injections directly into the swollen area have proven themselves to be excellent. Penicillin drugs are used in combination with novocaine. If the patient is intolerant to medications of the penicillin subgroup, inject streptomycin.
In severe cases of pathology, antibacterial drugs are recommended for parenteral administration - intramuscularly or intravenously. The total duration of therapy is determined by the doctor individually.
Symptomatic treatment:
- antipyretics – Paracetamol, Ibuprofen;
- analgesics - as needed;
- detoxification therapy for severe cases - intravenous drip administration of glucose solution, Ringer.
Prevention of inflammation of the floor of the mouth
To prevent diseases of the sublingual area, dentists give recommendations on proper oral care:
- take care of your gums;
- avoid the accumulation of bacterial plaque;
- visit the dentist 2 times a year;
- prevent the occurrence of caries;
- brush your teeth 2 times a day.
But if the patient has congenital or acquired anomalies in the development of the floor of the oral cavity, such as a shortened frenulum or structural asymmetry, then you will have to be more careful to prevent injury. Some abnormalities can be treated. Come to an appointment at Family Dentistry and experienced specialists will tell you how to get rid of defects, tumors and inflammations.
Symptoms and signs
The most common cause of sores and ulcers is sublingual stomatitis, which is characterized by the following symptoms:
- the appearance of a whitish or yellowish coating on the tongue;
- swelling;
- ulcers and abscesses in the sublingual area.
In especially severe cases, ulcerations heal poorly, fester, and subsequently leave a scar.
With herpetiform stomatitis, the ulcers are located at the bottom of the tongue. In appearance, they resemble herpes - small blisters filled with liquid.
With tuberculosis of the oral cavity, the sores initially look like small tubercles, the ulcers are round, their edges are undermined. Often the formations may bleed. Over time, they become very painful, the patient's condition worsens sharply, and pain occurs when eating and talking.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
With tongue cancer, the patient observes lumps. Mouth ulcers are a sign of metastatic disease. They can reach from 1 to 4 cm. The color of the affected area can vary from dark red to dark gray or yellow.
Tongue cyst is a rare disease. A small, painful white growth forms under the tongue. The patient has difficulty breathing and swallowing.
Tongue abscess: Causes
Most often, the problem occurs after a small wound on the tongue becomes infected with staphylococcal and streptococcal bacteria. Damage to the surface of the tongue can be caused by constantly rubbing dentures, sharp edges of unhealthy teeth, or a prick from a fish bone. Possible cross-infection of the tongue due to purulent inflammation of the gums on the inside of the teeth. This pathology can be a complication of glossitis (mild inflammation of the tongue), ulcerative stomatitis (inflammation of the mucous tissues of the oral cavity), and sometimes acute tonsillitis (inflammation of the tonsils). The nature of inflammation and its spread are determined by the peculiar structure of the tongue. Thus, damage to one lobe of the tongue never spreads to the opposite side. The most dangerous is the location of the purulent capsule at the root of the tongue (due to the proximity of the lymph nodes).
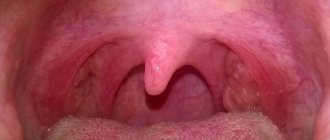
External manifestations (+photo)
Growths under the tongue in humans form in the form of warts, papillomas, and condylomas. All varieties are signs of the presence of VPI in the body. Their differences lie in the type of epithelium and external manifestation. Papillomas can be either protruding above the surface of the mucous membrane or flat with rough tissue. And condylomas always rise above the surface of the skin or mucous membrane with the help of a fairly high stalk.
Types of growths under the tongue:
Depending on the type and causes of formation, condylomas come in different colors:
- red;
- white;
- light with a yellow tint;
- pink;
- gray;
- from light to dark brown.
Growths in the oral cavity are most often localized in the following areas:
- on the mucous membrane under the tongue;
- on the bridle;
- on the gum under the tongue;
- on the inside of the tongue;
- along the rim of the tongue and other areas of the mucous membrane.
As a conclusion
You should not self-medicate if the situation gets out of control. At the slightest change in the condition of the tongue and mucous membranes, it is best to go to the hospital.
If the disease is chronic, such as a stomach ulcer, then to avoid complications you should take medications prescribed by your doctor and also follow a diet.
The tongue is an organ in the mouth that consists almost entirely of muscle tissue. Part of its surface contains taste buds, and it performs important functions in chewing, swallowing and speaking. Swelling of the tongue is a pathology in which its volume begins to exceed its standard dimensions.
If the swelling occurs instantly, it may be a sign of an acute anaphylactic reaction. Otherwise, there are a number of other factors, from illness to injury, that could cause a swollen tongue.